Comparison of methods for fabricating superhydrophobic surface
-
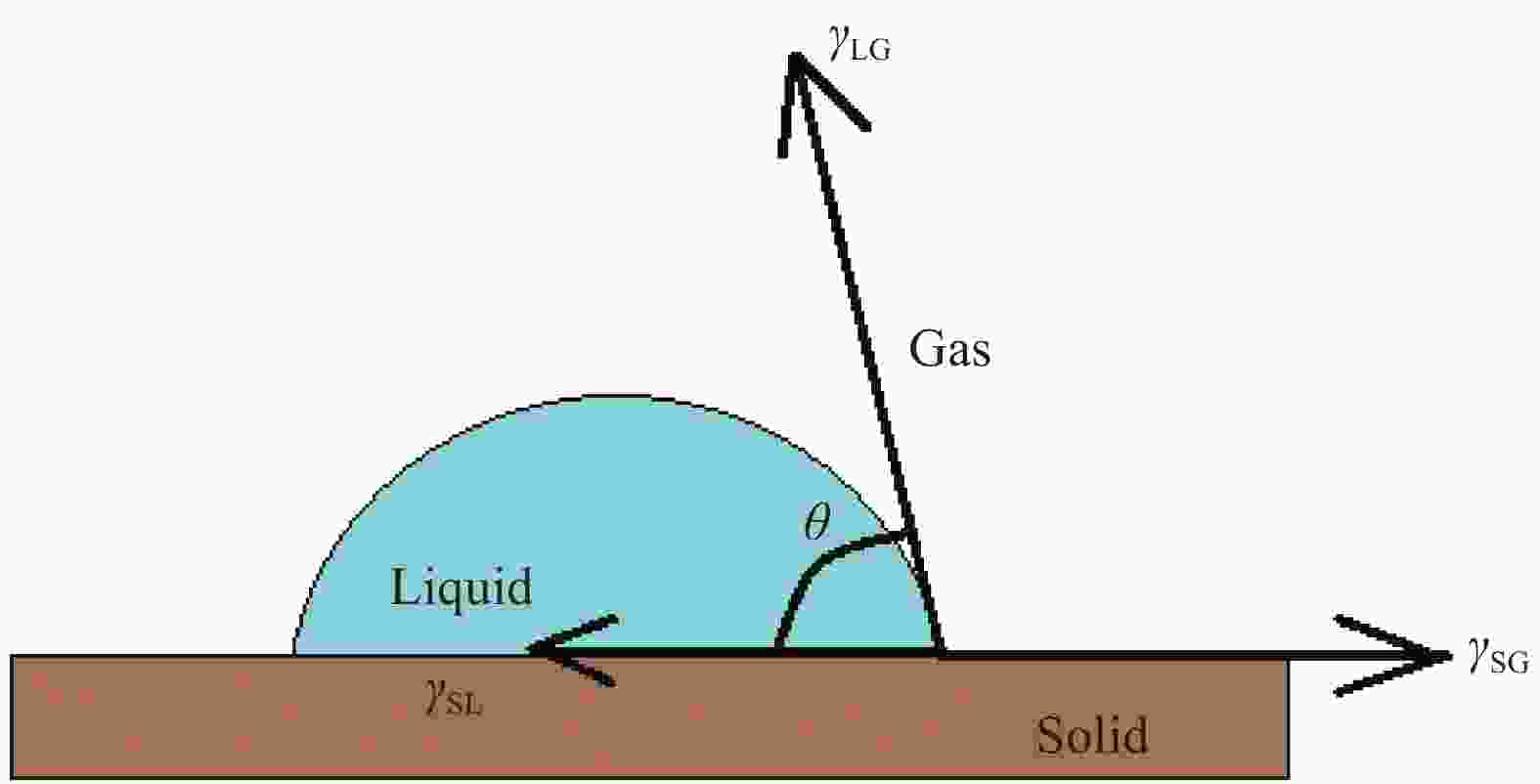
摘要: 超疏水性是一种特殊的润湿性,它是指水滴与表面的静态接触角大于150°或者滑动角小于10°,其最初来源于“荷叶效应”。本文对近几年关于超疏水理论和自然界中超疏水现象研究进行介绍,并对超疏水表面的制备方法及其应用进行综述。分别总结了基于模板法、涂覆法、刻蚀法的超疏水表面制备方案的优缺点及其改进措施,重点阐述超疏水表面在金属表面抗腐蚀方面的应用。最后对具有特殊功能的超疏水表面的制备进行了介绍,如自愈性超疏水表面、润湿转变型超疏水表面。在制备方法中,模板法和涂覆法制备时间短、成本低,但稳定性和耐磨性较差;刻蚀法易于控制,但实用性受限。Abstract: Superhydrophobic, a kind of special wetting ability, primarily originated from the "Lotus effect". It is defined as a special surface with a static contact angle of water droplets greater than 150° or a sliding angle less than 10°. This review introduces the research on superhydrophobic theory and phenomena in nature and summarizes methods of superhydrophobic surface preparation and applications in recent years. The advantages and disadvantages of the templating method, the coating method and the etching method are compared, and improvement measures of these methods are proposed. Besides, one of the most important applications of superhydrophobic surface to the metal corrosion resistance is emphasized. At last, the fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces with special abilities is introduced, such as self-healing superhydrophobic surfaces, wetting reversal superhydrophobic surfaces. In these fabrication methods, the templating method and the etching method have advantages of time saving and low costing, but are usually accompanied by poor stability and abrasion resistance. The etching method is easier to control surface parameters, but limited in usefulness.
-
Key words:
- superhydrophobic /
- templating method /
- coating method /
- etching method /
- self-healing
-
表 1 超疏水表面三类制备方法总结
Table 1. Summarize of three type methods for fabricating superhydrophobic surface
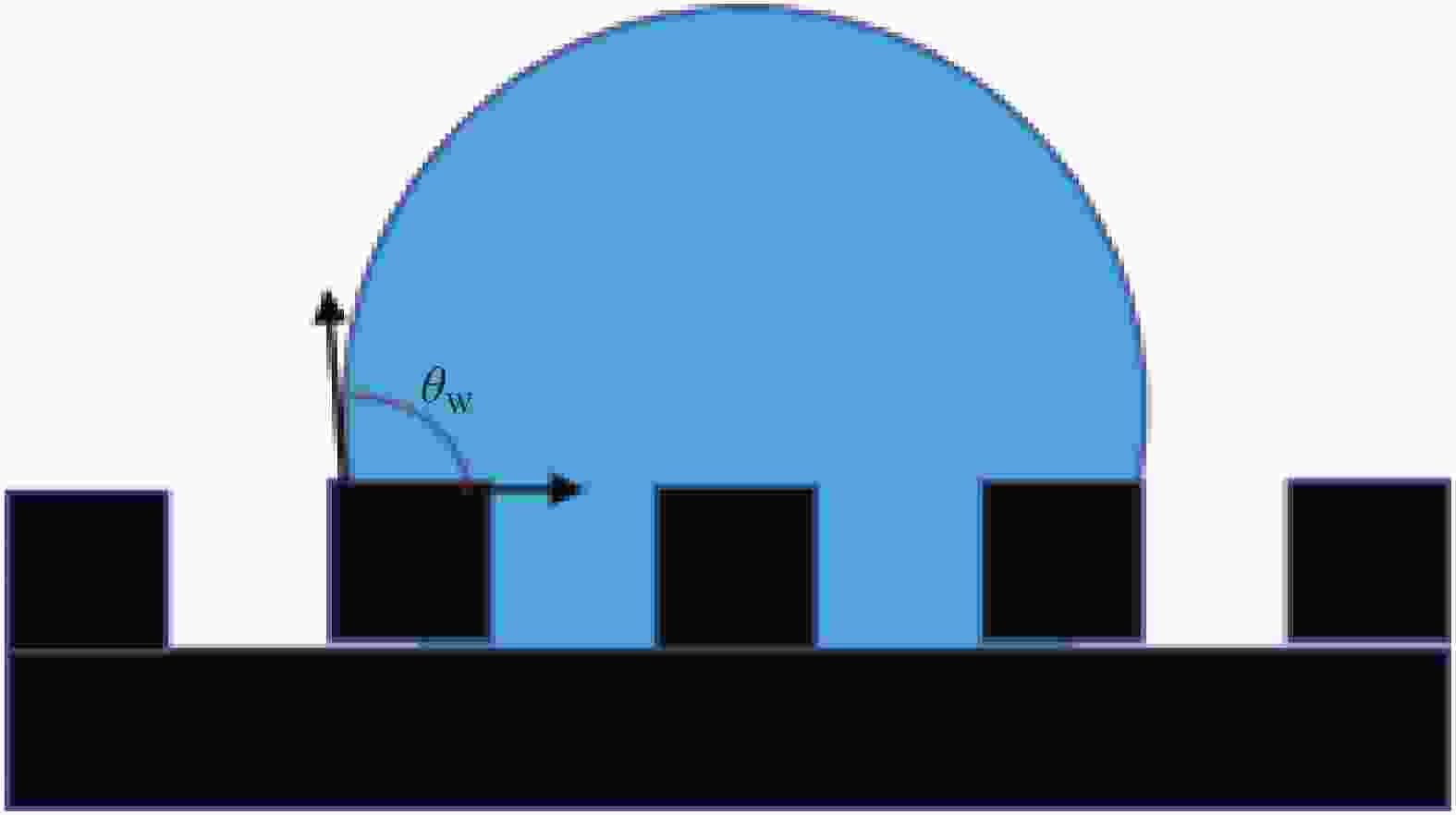
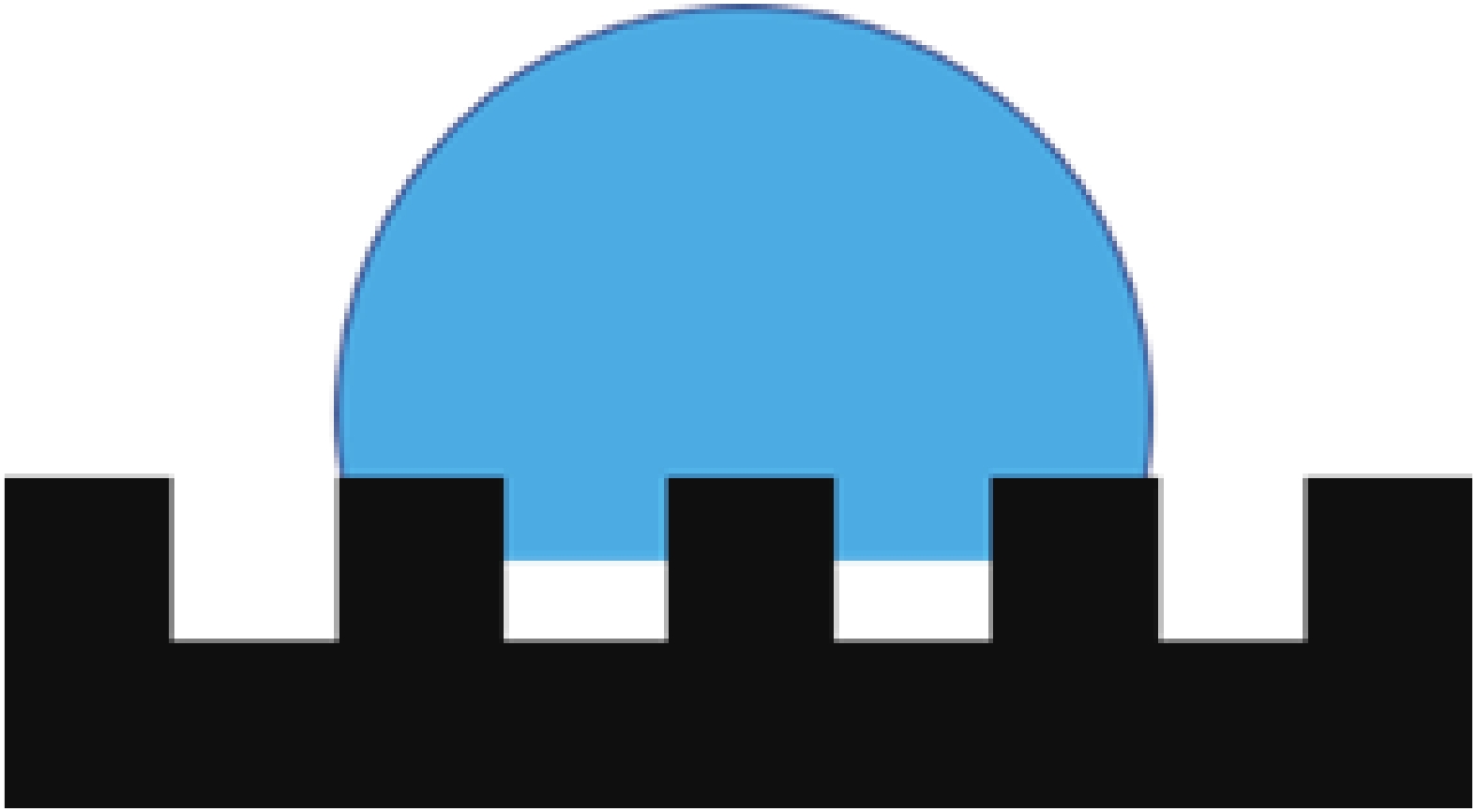
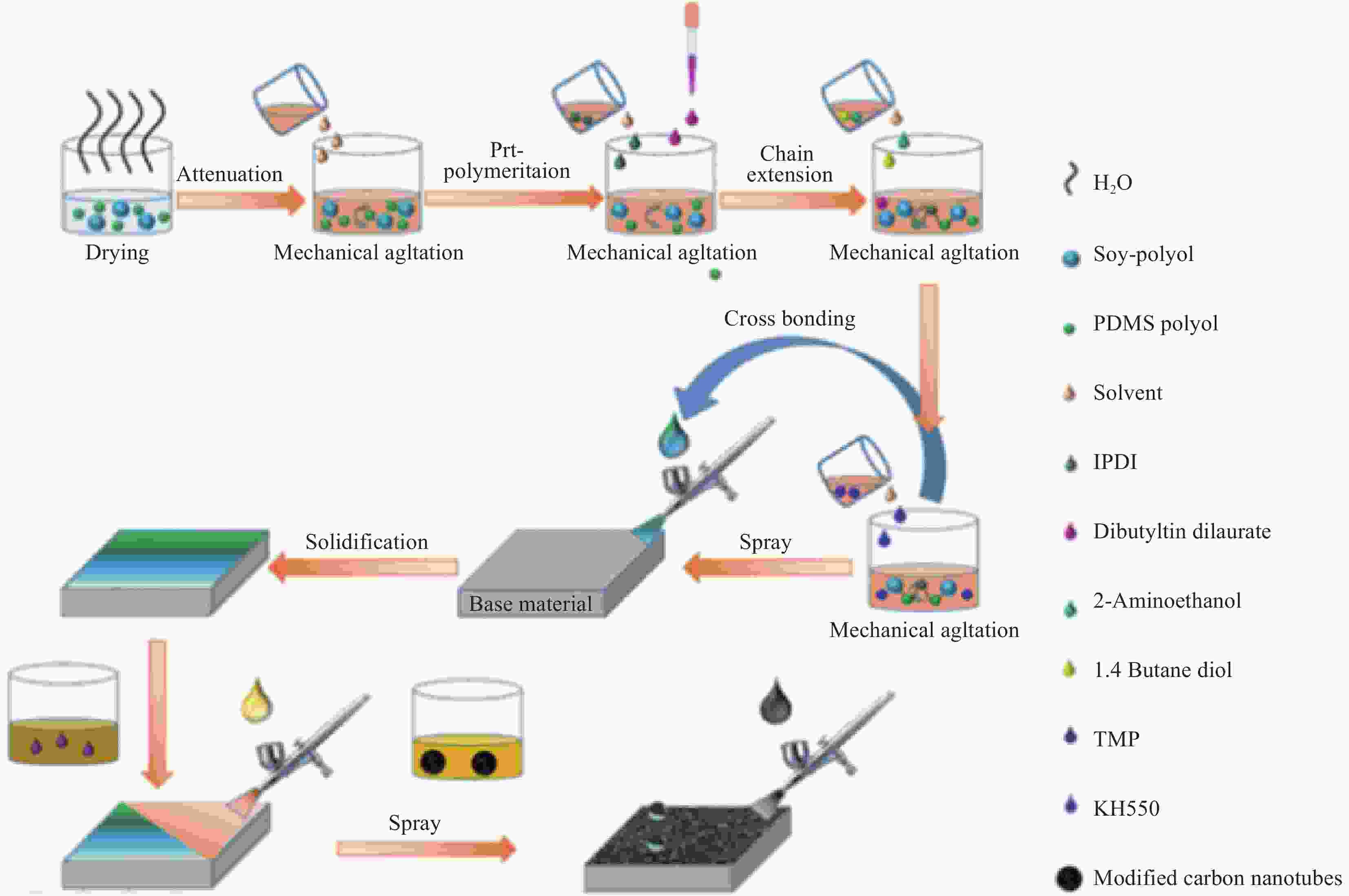
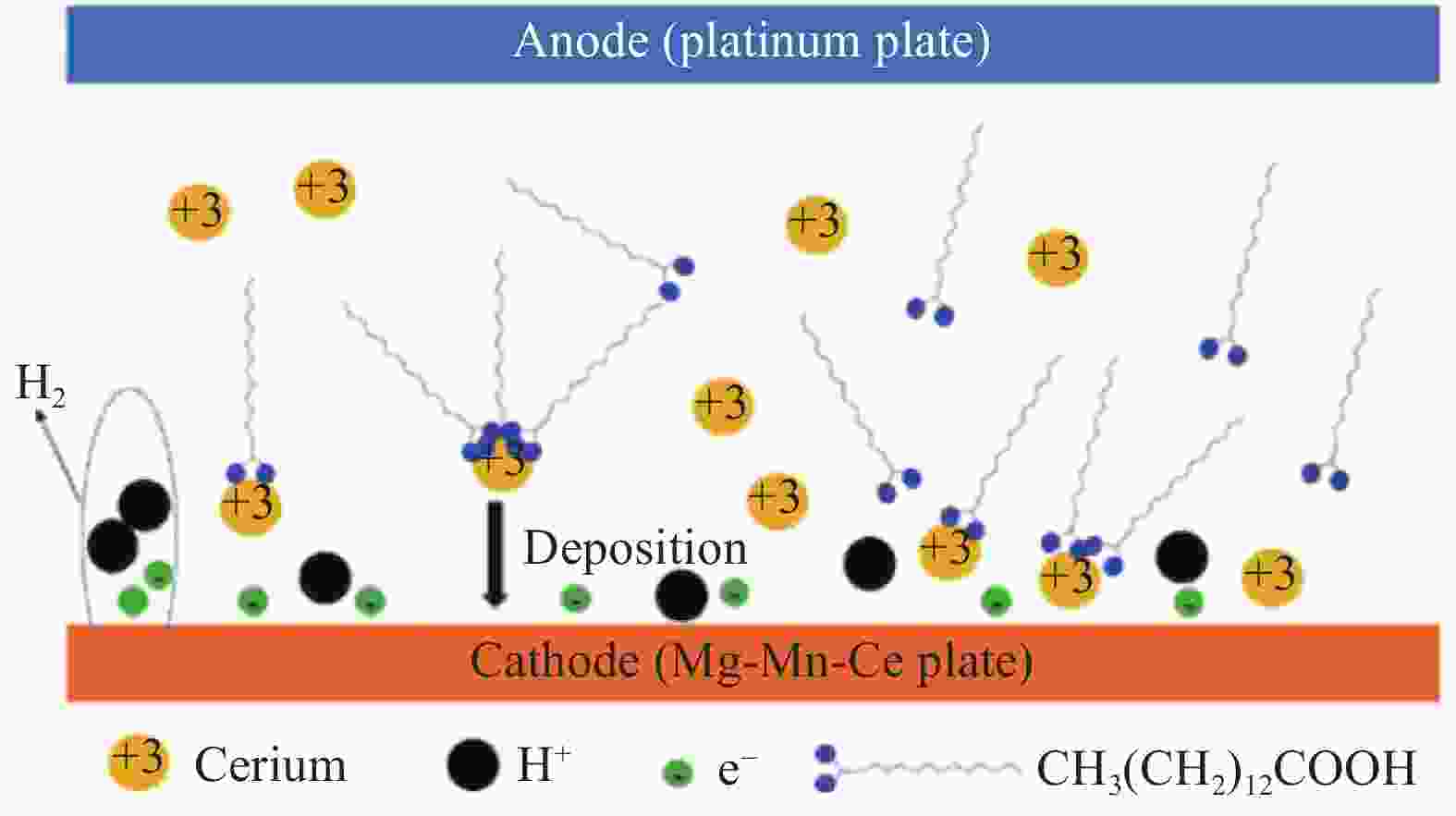
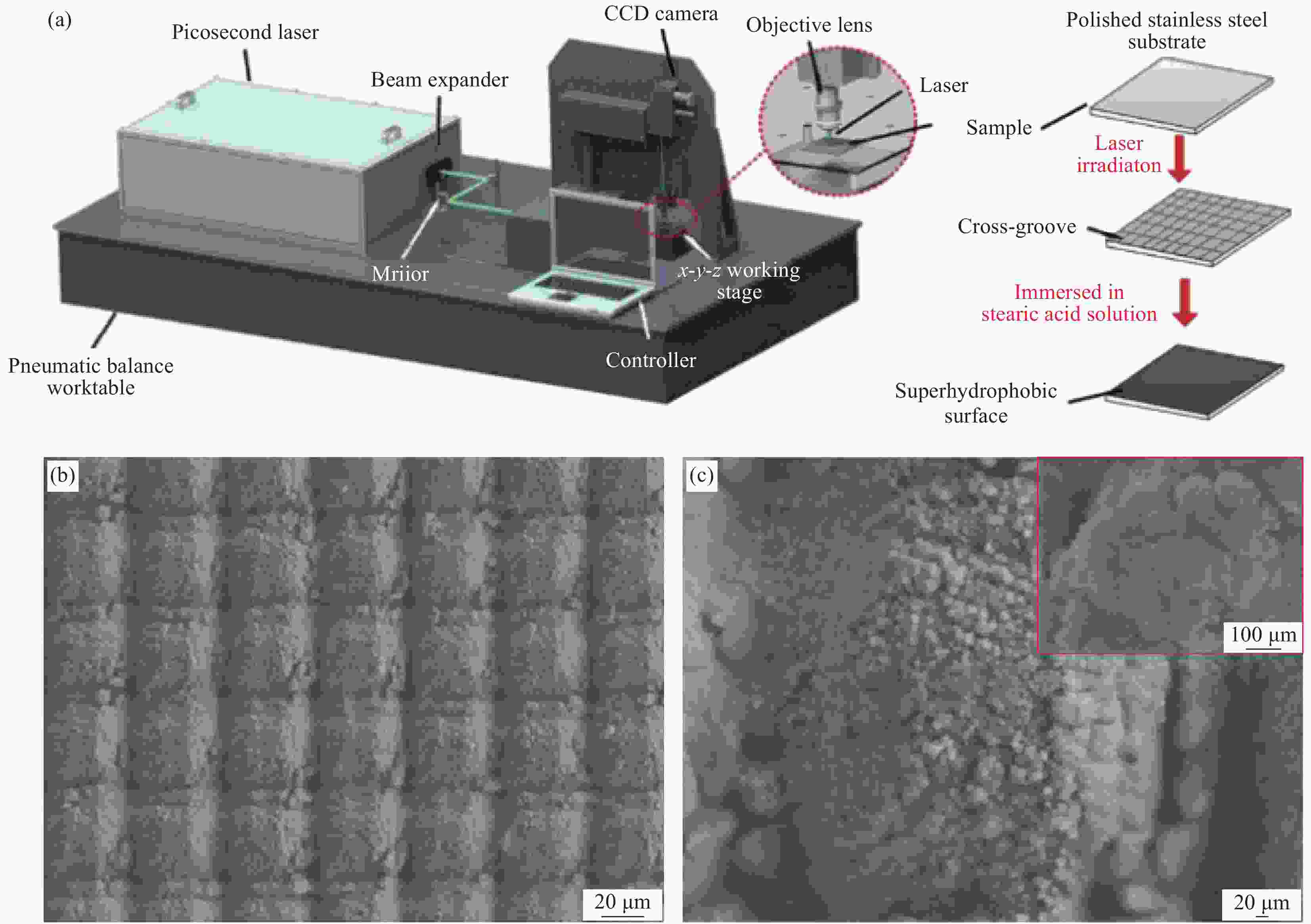
Method Process Advantages Disadvantages Substrates Templating method Replicate rough microstructures on low surface energy template surfaces Time saving, low costing, well reproducibility, wide application range, mass production Hard to endure, poor abrasion resistance, small area. Polymer glass Powder coating Spray solid superhydrophobic coating on the surface of easily corrosive substrate Wide application range, convenient and fast, easy to manipulate Unstable interface, uneven coating surface, poor abrasion resistance Glass polymer metal wood Chemical deposition A coating or film is formed by a reaction between the substrate and a solution or gas containing a metal element Time saving, low costing, well reproducibility Air pollution, difficult to control, poor adhesion strength and abrasion resistance Glass polymer metal wood Electro-chemical deposition External electric field, a redox reaction occurs in the plating layer and is formed on an electrode Time saving, low costing, mass production, easy to control Air pollution, poor adhesion strength and abrasion resistance, waste of materials Conductor(metal) Laser etching Ablation on the surface by laser to change the surface rough structure Corrosion resistance, well stability, uniform surface, easy to control and manipulate High cost, long processing time, difficult to be widely used Metal glass silicon Chemical etching Roughness caused by immersion of target surface in chemical mixture or gas discharge produces roughness Low costing, easy to control, corrosion resistance Limited in application, air pollution, poor strength Metal glass -
[1] SUN T, FENG L, GAO X, et al. Bioinspired surfaces with special wettability[J]. ChemInform,2005,38(8):644-652. doi: 10.1021/ar040224c [2] NISHIMOTO S, BHUSHAN B. Bioinspired self-cleaning surfaces with superhydrophobicity, superoleophobicity, and superhydrophilicity[J]. RSC Advances,2012,3:671-690. [3] GUO Z, LIU W. Biomimic from the superhydrophobic plant leaves in nature: Binary structure and unitary structure[J]. Plant Science,2007,172(6):1103-1112. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.03.005 [4] CHANG F M, HONG S J, SHENG Y J, et al. High contact angle hysteresis of superhydrophobic surfaces: Hydrophobic defects[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2009,95(6):064102. [5] YU S, WANG X, WANG W, et al. A new method for preparing bionic multi scale superhydrophobic functional surface on X70 pipeline steel[J]. Applied Surface Science,2013,271:149-155. [6] LIU T, CHEN S, CHENG S, et al. Corrosion behavior of super-hydrophobic surface on copper in seawater[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2007,52(28):8003-8007. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2007.06.072 [7] XIANG Y, LI X, DU A, et al. Timing of polyethylene glycol addition for the control of SiO2 sol structure and sol-gel coating properties[J]. Journal of Coatings Technology and Research,2017,14(2):447-454. doi: 10.1007/s11998-016-9864-7 [8] HUANG X, LEE J, LEE J, et al. A one-step route to a perfectly ordered wafer-scale microbowl array for size-dependent superhydrophobicity[J]. Small,2008,4(2):211-216. doi: 10.1002/smll.200700881 [9] MORTAZAVI V, KHONSARI M, et al. On the degradation of superhydrophobic surfaces: A review[J]. Wear,2017,372:145-157. [10] ROWELL R L. Physical chemistry of surfaces, 6th ed[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science,1998,208(2):582. [11] POMPE T, FERY A, HERMINGHAUS S. Measurement of contact line tension by analysis of the three-phase boundary with nanometer resolution[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology,1999,13(10):1155-1164. doi: 10.1163/156856199X00848 [12] MARMUR A. Line tension and the intrinsic contact angle in solid–liquid–fluid Systems[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,1997,186(2):462-466. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1996.4666 [13] VOGLER E A. Structure and reactivity of water at biomaterial surfaces[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,1998,74:69-117. doi: 10.1016/S0001-8686(97)00040-7 [14] YAMINSKY V. Molecular mechanisms of hydrophobic transitions[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology,2000,14(2):187-233. doi: 10.1163/156856100742537 [15] TADMOR R, BAHADUR P, LEH A, et al. Measurement of lateral adhesion forces at the interface between a liquid drop and a substrate[J]. Physical Review Letters,2009,103(26):266101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.103.266101 [16] BORMASHENKO E. Progress in understanding wetting transitions on rough surfaces[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2014,222:92-103. [17] ARJMANDI-TASH O, KOVALCHUK N M, TRYBALA A, et al. Kinetics of wetting and spreading of droplets over various substrates[J]. Langmuir,2017,33(18):4367-4385. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b04094 [18] 秦亮. 亲/疏水表面上液滴接触角滞后的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2012.QIN Liang. Investigation on contact angle hysteresis of droplets on hydrophilic and hydrophobic surface[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [19] LIU Q, YU J, WANG H. The role of the substrate roughness in contact angle hysteresis and dynamic deviation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 148: 118985. [20] GIACOMELLO A, SCHIMMELE L, DIETRICH S. Wetting hysteresis induced by nanodefects[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2016,113(3):E262-E271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1513942113 [21] WENZEL, ROBERT N. resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1936,28(8):988-994. [22] GUO C, WANG S, et al. Wettability alteration of polymer surfaces produced by scraping[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology,2008,22(3-4):395-402. doi: 10.1163/156856108X304832 [23] CASSIE A, BAXTER S. Wettability of porous surfaces[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1944,40:546-551. doi: 10.1039/tf9444000546 [24] 李小磊, 张磊, 马晓雯, 等. 疏水/超疏水硅表面的制备及液滴的运动特性[J]. 功能材料, 2016, 47(11):11201-11209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2016.11.040LI Xiaolei, ZHANG Lei, MA Xiaowen, et al. Preparation of hydrophobic/superhydrophobic Si surfaces and dynamic characteristics of drop moving on these surface[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2016,47(11):11201-11209(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2016.11.040 [25] NOSONOVSKY M, BHUSHAN B. Superhydrophobic surfaces and emerging applications: Non-adhesion, energy, green engineering[J]. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science,2009,14(4):270-280. [26] MARMUR A. Wetting on hydrophobic rough surfaces: To be heterogeneous or not to be[J]. Langmuir,2003,19(20):8343-8348. doi: 10.1021/la0344682 [27] ISHINO C, OKUMURA K. Wetting transitions on textured hydrophilic surfaces[J]. The European Physical Journal E,2008,25(4):415-424. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2007-10308-y [28] JOSÉ B, THIELE U, QUÉRÉ D. Wetting of textured surfaces[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2002,206(1-3):41-46. [29] EXTRAND C W. Contact angles and hysteresis on surfaces with chemically heterogeneous islands[J]. Langmuir,2003,19(9):3793-3796. doi: 10.1021/la0268350 [30] PATANKAR N A. Transition between superhydrophobic states on rough surfaces[J]. Langmuir the Acs Journal of Surfaces & Colloids,2004,20(17):7097-7102. [31] QUÉRÉ D. Non-sticking drops[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics,2005,68(11):2495. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/68/11/R01 [32] MCHALE G, AQIL S, SHIRTCLIFFE N, et al. Analysis of droplet evaporation on a superhydrophobic surface[J]. Langmuir,2005,21(1):1053-1060. [33] JUNG Y C, BHUSHAN B. Dynamic effects of bouncing water droplets on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Langmuir,2008,24(12):6262-6269. doi: 10.1021/la8003504 [34] YEONG Y H, BURTON J, LOTH E, et al. Drop impact and rebound dynamics on an inclined superhydrophobic surface[J]. Langmuir,2014,30(40):12027-12038. doi: 10.1021/la502500z [35] SONG J, GAO M, ZHAO C, et al. Large-area fabrication of droplet pancake bouncing surface and control of bouncing state[J]. ACS Nano,2017,11(9):9259-9267. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b04494 [36] WU L, ZHANG J, LI B, et al. Facile preparation of super durable superhydrophobic materials[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science,2014,432:31-42. [37] CHEN J, SHEN C, YANG S, et al. Acid and temperature dual-responsive cotton fabrics with polymer coating[J]. Composites Communications,2017,4:10-15. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2017.03.003 [38] ZHANG Q, JIN B, WANG B, et al. Fabrication of a highly stable superhydrophobic surface with dual-scale structure and its antifrosting properties[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2017,56(10):2754-2763. [39] TRAN T, LEE B, NGO. C. Durable superhydrophobic cotton filter prepared at low temperature for highly efficient hexane and water separation[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2017, 71: 527-536. [40] XUE C, LI M, GUO X, et al. Fabrication of superhydrophobic textiles with high water pressure resistance[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2017,310(Complete):134-142. [41] SUN M, LUO C, XU L, et al. Artificial lotus leaf by nanocasting[J]. Langmuir,2005,21(19):8978-8981. doi: 10.1021/la050316q [42] HONG S, WANG J, LEE H. Replication of cicada wing’s nano-patterns by hot embossing and UV nanoimprinting[J]. Nanotechnology,2009,20(38):385303. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/20/38/385303 [43] 黄明达. 模板法制备聚合物超疏水表面[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2012.HUANG Mingda. Fabrication of super hydrophobic polymer surfaces by using PDMS and metal templates[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [44] TOOSI S, MORADI S, EBRAHIMI M, et al. Microfabrication of polymeric surfaces with extreme wettability using hot embossing[J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,378:426-434. [45] YAN Z, LIANG X, SHEN H, et al. Preparation and basic properties of superhydrophobic silicone rubber with micro-nano hierarchical structures formed by picosecond laser-ablated template[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2017,24(3):1743-1750. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2017.005924 [46] MAGHSOUDI K, MOMEN G, JAFARI R, et al. Direct replication of micro-nanostructures in the fabrication of superhydrophobic silicone rubber surfaces by compression molding[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,458:619-628. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.07.099 [47] 王志一. 空气中水滴与超疏水表面接触过程测量方法研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018.WANG Zhiyi. Study on the measurement method of the interaction between water droplets and hydrophobic surface in the air[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018(in Chinese). [48] WANG J, WU Y, ZHANG D, et al. Preparation of superhydrophobic flexible tubes with water and blood repellency based on template method[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020,587:124331. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124331 [49] LI J, WU R N, JING Z J, et al. One-step spray-coating process for the fabrication of colorful superhydrophobic coatings with excellent corrosion resistance[J]. Langmuir,2015,31:10702-10707. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b02734 [50] WANG H, ZHOU H, GESTOS A, et al. Robust, superamphiphobic fabric with multiple self-healing ability against both physical and chemical damages[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2013,5(20):10221-10226. doi: 10.1021/am4029679 [51] ZHU Y, SUN F, QIAN H, et al. A biomimetic spherical cactus superhydrophobic coating with durable and multiple anti-corrosion effects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,338:670-679. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.082 [52] JORDAN E H, JIANG C, GELL M G. The solution precursor plasma spray (SPPS) process: A review with energy considerations[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology,2015,24(7):1153-1165. doi: 10.1007/s11666-015-0272-9 [53] CAI Y, COYLE T, AZIMI G, et al. Superhydrophobic ceramic coatings by solution precursor plasma spray[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6:24670. doi: 10.1038/srep24670 [54] SHEN Y, WU Z, TAO J, et al. Spraying preparation of eco-friendly super-hydrophobic coatings with ultralow water adhesion for effective anticorrosion and antipollution[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(22):25484-25493. [55] SU F, YAO K. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic sur-face with excellent mechanical abrasion and corrosion resistance on copper substrate by a novel method[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces,2014,6(11):8762-8770. [56] ISHIZAKI T, HIEDA J, SAITO N, et al. Corrosion resistance and chemical stability of super-hydrophobic film deposited on magnesium alloy AZ31 by microwave plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2010,55(23):7094-7101. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2010.06.064 [57] ZHANG J, GU C, TONG Y, et al. A smart superhydrophobic coating on AZ31B magnesium alloy with self-healing effect[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces,2016,3(14):1500694. [58] YU S Q, LING Y H, WANG R G, et al. Constructing superhydrophobic WO3@TiO2 nanoflake surface beyond amorphous alloy against electrochemical corrosion on iron steel[J]. Applied Surface Science,2017,436:527-535. [59] 张凯, 文邦伟, 谭勇. 超疏水膜层防腐蚀机理及气相法制备技术研究进展[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2018, 30(4):107-114.ZHANG Kai, WEN Bangwei, TAN Yong. Current status of research on anticorrosion mechanism and vapor phase preparation technique of uperhydrophobic film on metallic materials[J]. Corrosion Science And Protection Technology,2018,30(4):107-114(in Chinese). [60] BARTHWAL S, LIM S. Rapid fabrication of a dual-scale micro-nanostructured superhydrophobic aluminum surface with delayed condensation and ice formation properties[J]. Soft Matter,2019,15(39):7945. [61] GUO X, XUE C, SATHASIVAM S, et al. Fabrication of robust superhydrophobic surfaces via aerosol-assisted CVD and thermo-triggered healing of superhydrophobicity by recovery of roughness structures[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2019,7(29):17604-17612. [62] FENG S, LUO W, WANG, L, et al. Preparation and property of extremely stable superhydrophobic carbon fibers with core-shell structure[J]. Carbon,2019,150:284-291. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.05.021 [63] LIU Y, LI S, ZHANG J, et al. Corrosion inhibition of biomimetic super-hydrophobic electrodeposition coatings on copper substrate[J]. Corrosion Science,2015,94:190-196. [64] ZOU Y, WANG Y, XU S, et al. Superhydrophobic double-layer coating for efficient heat dissipation and corrosion protection[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,362:638-649. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.086 [65] LIU Q, CHEN D, KANG Z. One-step electrodeposition process to fabricate corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic surface on magnesium alloy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(3):1859-1867. [66] ZHENG T, HU Y, PAN F, et al. Fabrication of corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic coating on magnesium alloy by one-step electrodeposition method[J]. Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 2019, 7(2):193-202. [67] YANG Z, LIU X, TIAN Y. Fabrication of super-hydrophobic nickel film on copper substrate with improved corrosion inhibition by electrodeposition process[J]. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects,2019,560:205-212. [68] TA D V, DUNN A, WASLEY T J, et. al. Nanosecond laser ablated superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications[J]. Applied Surface Science,2015,357:248-254. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.027 [69] LONG J, ZHONG M, ZHANG H, et al. Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of picosecond laser micro-structured aluminum in ambient air[J]. Journal of Colloid Interface Science,2015,441:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2014.11.015 [70] JAGDHEESH R, GARCíA-BALLESTEROS J J, OCANA J L. One-step fabrication of near superhydrophobic aluminum surface by nanosecond laser ablation[J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,374:2-11. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.06.104 [71] PAN Q, CAO Y, XUE W, et al. Picosecond laser-textured stainless steel superhydrophobic surface with an antibacterial adhesion property[J]. Langmuir,2019,35(35):11414-11421. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01333 [72] LIN Y, HAN J, CAI M, et al. Durable and robust transparent superhydrophobic glass surfaces fabricated by a femtosecond laser with exceptional water repellency and thermostability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(19): 9049-9056. [73] YANG Z, LIU X, TIAN Y. Hybrid laser ablation and chemical modification for fast fabrication of bio-inspired super-hydrophobic surface with excellent self-cleaning, stability and corrosion resistance[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering,2019,16(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s42235-019-0002-y [74] YANG Z, TIAN Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Study on the fabrication of super-hydrophobic surface on inconel alloy via nanosecond laser ablation[J]. Materials,2019,12(2):278. doi: 10.3390/ma12020278 [75] SHEN P, UESAWA N, INASAWA S, et al. Characterization of flowerlike silicon particles obtained from chemical etching: visible fluorescence and superhydrophobicity[J]. Langmuir,2010,26(16):13522-13527. doi: 10.1021/la102516g [76] XIANG T, LV Z, WEI F, et al. Superhydrophobic civil engineering materials: A review from recent developments[J]. Coatings,2019,9:753. doi: 10.3390/coatings9110753 [77] JIE H, XU Q, WEI L, et al. Etching and heating treatment combined approach for superhydrophobic surface on brass substrates and the consequent corrosion resistance[J]. Corrosion Science,2016,102:251-258. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2015.10.013 [78] ZHANG X, ZHAO J, MO J, et al. Fabrication of superhydrophobic aluminum surface by droplet etching and chemical modification[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 567: 205-212. [79] YANG T, WANG M, WANG X, et al. Fabrication of a waterborne, superhydrophobic, self-cleaning, highly transparent and stable surface[J]. Soft Matter,2020,16:3678-3685. doi: 10.1039/C9SM02473E [80] ZHU J, TIAN Y, LIU X. Rapid fabrication of super-hydrophobic surfaces of silicon wafers with excellent anisotropic wetting[J]. Microsystem Technologies,2018,25:237-243. [81] LI Y, LI L, SUN J. Bioinspired self-healing superhydrophobic coatings[J]. Angewandte Chemie,2010,49(35):6129-6133. doi: 10.1002/anie.201001258 [82] CHEN K L, ZHOU S X, WU L M. Fabrication of all-water-based self-repairing superhydrophobic coatings based on UV-responsive microcapsules[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2015,25:1035-1041. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201403496 [83] LI B C, ZHANG J P. Polysiloxane/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites and their applications as ultrastable, healable and superhydrophobic coatings[J]. Carbon,2015,93:648-658. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.05.103 [84] BAI N, LI Q, DONG H Z, et al. A versatile approach for preparing self-recovering superhydrophobic coatings[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2016,293:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.023 [85] ZHANG X, SI Y, MO J, et al. Robust micro-nanoscale flowerlike ZnO/epoxy resin superhydrophobic coating with rapid healing ability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,313:1152-1159. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.014 [86] ZANG D, ZHU R, ZHANG W, et al. Corrosion-resistant superhydrophobic coatings on Mg alloy surfaces inspired by lotus seedpod[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2017,27:1605446. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201605446 [87] HE G, LU S, XU W, et al. Stable superhydrophobic Zn/ZnO surfaces fabricated via electrodeposition on tin substrate for self-cleaning behavior and switchable wettability[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,747:772-782. [88] ELMIRA V, REZA N, Fabrication of fluorine-free ZnO/CuO nanocomposite superantiwetting surfaces with reversible wettability tuning[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019, 367: 252-261. -





 下载:
下载: