Effect of discontinuous interfacial phase Al4C3 on interface bonding of SiC/Al composites: A first-principle and experiment
-
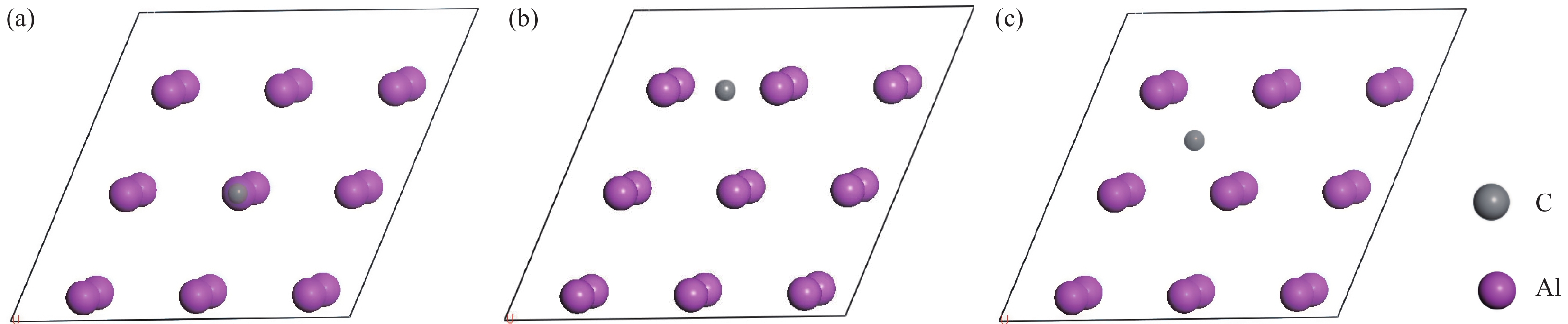
摘要: 采用密度泛函理论的第一性原理及实验相结合的方法,探讨了不连续界面相Al4C3对SiC/Al复合材料界面结合的影响,并与无界面新相生成时进行对比。研究表明,当Al(111)表面吸附C原子时,在Bridge位置上吸附C原子最为稳定;随着C覆盖率的增加,C原子吸附能逐渐减小;当界面相呈不连续分布时,界面由原来的SiC/Al转变为(SiC+Al4C3)/Al,界面黏着功由原来的0.851 J/m2增加至1.231 J/m2,这主要由于当C原子在Al表面吸附时,C原子和Al原子间形成共价键和离子键,且与界面处的Si原子也形成共价键,从而促进界面结合。利用第一性原理计算的SiC/Al和(SiC+Al4C3)/Al体系黏着功与实验值较为接近,且变化规律相同,具有较高的参考价值。
-
关键词:
- SiC/Al界面 /
- 不连续界面相Al4C3 /
- 界面结合 /
- 第一性原理 /
- 黏着功
Abstract: The effect of discontinuous interfacial phase Al4C3 on the interface bonding of SiC/Al composites was discussed by using the first-principle approach based on density functional theory and experimental method, in comparison, the interface without new phase was also investigated. The results show that the C atom adsorbed on the surface of Al(111) is the most stable at the bridge position, and the adsorption energy of C atoms decreases gradually with the increase of C coverage. The formation of a discontinuous Al4C3 product leads to the interface changing from SiC/Al to (SiC+Al4C3)/Al, and their corresponding work of interfacial adhesion increases from 0.851 J/m2 to 1.231 J/m2, which is attributed to the fact that covalent bonds or ionic bonds are formed between C atoms with Al atoms when C atoms are adsorbed on the surface of Al, and covalent bonds between C atoms with Si atoms. In addition, the calculated adhesions of SiC/Al, (SiC+Al4C3)/Al system by first-principles are in good agreement with these of experiment, which has high reference value. -
表 1 不同覆盖率下C原子在Al(111)表面的吸附能
Table 1. Adsorption energies of C atom on Al (111) surface with different coverages
eV/atom Coverage Top Bridge Hollow 0.25 5.97 7.04 6.89 0.50 5.13 6.37 5.32 1.00 4.57 5.67 5.01 表 2 SiC/Al和(SiC+Al4C3)/Al界面间距d0和界面黏着功Wad
Table 2. Ideal interface spacings d0 and works of interfacial adhesion Wad of SiC/Al and (SiC+Al4C3)/Al interface
Model d0 (Before optimization)/nm d0 (After optimization)/nm Wad/
(J·m−2)SiC/Al 0.2 0.190 0.851 (SiC+Al4C3)/Al 0.2 0.183 1.231 -
[1] TENG F, YU K, LUO J, et al. Microstructures and properties of Al-50% SiC composites for electronic packaging applications[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2016,26(10):2647-2652. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(16)64358-3 [2] 许小静, 张绪虎, 王亮, 等. 中低体积分数SiCP/Al在航空航天领域的应用与发展[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2011, 41(3):5-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2011.03.002XU Xiaojing, ZHANG Xuhu, WANG Liang, et al. Development and application of medium/low volume-fraction SiCP/Al composites in aerospace field[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2011,41(3):5-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2011.03.002 [3] HUNT M. Electronic packaging[J]. Materials Engineering,1991,108(1):24-25. [4] LEE H S, JEON K Y, KIM H Y, et al. Fabrication process and thermal properties of SiCP/Al metal matrix composites for electronic packaging applications[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2000,35(24):6231-6236. doi: 10.1023/A:1026749831726 [5] WANG K K, KANG Y L, SONG P G, et al. Preparation of SiCP/A356 electronic packaging materials and its thixo-forging[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2010,20(3):988-992. [6] LI S, XIONG D G, LIU M, et al. Thermophysical properties of SiC/Al composites with three dimensional interpenetrating network structure[J]. Ceramics International,2014,40(5):7539-7544. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.12.105 [7] 刘俊友, 刘英才, 刘国权, 等. SiC颗粒氧化行为及SiCP/铝基复合材料界面特征[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2002, 12(5):961-966. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2002.05.021LIU Junyou, LIU Yingcai, LIU Guoquan, et al. Oxidation behavior of silicon carbide particales and their interfacial characterization in aluminum matrix composites[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2002,12(5):961-966(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2002.05.021 [8] REN S B, HE X B, QU X H, et al. Effect of Mg and Si in the aluminum on the thermo-mechanical properties of pressureless infiltrated SiCP/Al composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2007,67(10):2103-2113. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.11.006 [9] AGUILAR-MARTÍNEZ J A, PECH-CANUT M I, RODRIGUEZ-REYES M, et al. Effect of processing parameters on the degree of infiltration of SiCP preforms by Al-Si-Mg alloys[J]. Materials Letters,2003,57(26-27):4332-4335. doi: 10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00323-9 [10] MOLINA J M, SARAVANAN R A, ARPÓN R, et al. Pressure infiltration of liquid aluminium into packed SiC particulate with a bimodal size distribution[J]. Acta Materialia,2002,50(2):247-257. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00348-2 [11] AKSSAY L A, HOGE C E, PASK J A. Wetting under chemical equilibrium and nonequilibrium conditions[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry,1974,78(12):1178-1183. doi: 10.1021/j100605a009 [12] LAURENT V, CHATAIN D, EUSTATHOPOULOS N. Wettability of SiC by aluminium and Al-Si alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science,1987,22(1):244-250. doi: 10.1007/BF01160579 [13] LIU X H, LI J J, LIU E Z, et al. Effectively reinforced load transfer and fracture elongation by forming Al4C3 for in-situ synthesizing carbon nanotube reinforced Al matrix composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2018,718:182-189. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.01.065 [14] LIU X Q, LI C J, ECKERT J, et al. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes reinforced Al matrix composites[J]. Materials Characterization,2017,133:122-132. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.09.036 [15] YAN L P, TAN Z Q, JI G, et al. A quantitative method to characterize the Al4C3-formed interfacial reaction: The case study of MWCNT/Al composites[J]. Materials Characterization,2016,112:213-218. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2015.12.031 [16] LI D S, YE Y, LIAO X J, et al. A novel method for preparing and characterizing graphene nanoplatelets/aluminum nanocomposites[J]. Nano Research,2018,11(3):1642-1650. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1779-9 [17] WANG C C, CHEN G Q, WANG X, et al. Effect of Mg content on the thermodynamics of interface reaction in Cf/Al composite[J]. Metallurgical and Materlals Transactions A,2012,43(7):2514-2519. doi: 10.1007/s11661-012-1090-z [18] KAWAI C. Effect of interfacial reaction on the thermal conductivity of Al-SiC composites with SiC dispersions[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2001,84(4):896-898. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.2001.tb00764.x [19] JONES R O, GUNNARSSON O. The density functional formalism, its applications and prospects[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics,1989,61(3):689-746. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.61.689 [20] HONG T, SIMTH J R, SROLVVITZ D J. Theory of meta-ceramic adhesion[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia,1995,43(7):2721-2730. doi: 10.1016/0956-7151(94)00457-S [21] 邹爱华, 周贤良, 康志兵, 等. 基体合金元素对SiC/Al界面结合影响的第一性原理及实验研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1167-1174.ZOU Aihua, ZHOU Xianliang, KANG Zhibing, et al. Effect of alloy elements on SiC/Al interface: A first-principle and experimental study[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(11): 1167-1174(in Chinese). [22] 陈建, 顾明元, 潘复生. 活性金属/陶瓷粘着功[J]. 复合材料学报, 2003, 20(3): 85-88.CHEN Jian, GU Mingyuan, PAN Fusheng. Work of adhesion for reactive metal/ceramic systems[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2003, 20(3): 85-88(in Chinese). [23] CONG X S, SHEN P, WANG Y, et al. Wetting of polycrystalline SiC by molten Al and Al-Si alloys[J]. Applied Surface Science,2014,317:140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.055 [24] FANG X, FAN T X, ZHANG D. Work of Adhesion in Al/SiC composites with alloying element addition[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,2013,44(1):5192-5201. [25] FERRO A C, DERBY B. Wetting behavior in the Al-Si/SiC system: Interface reactions and solubility effects[J]. Acta Materialia,1995,43(8):3061-3073. -






 下载:
下载: