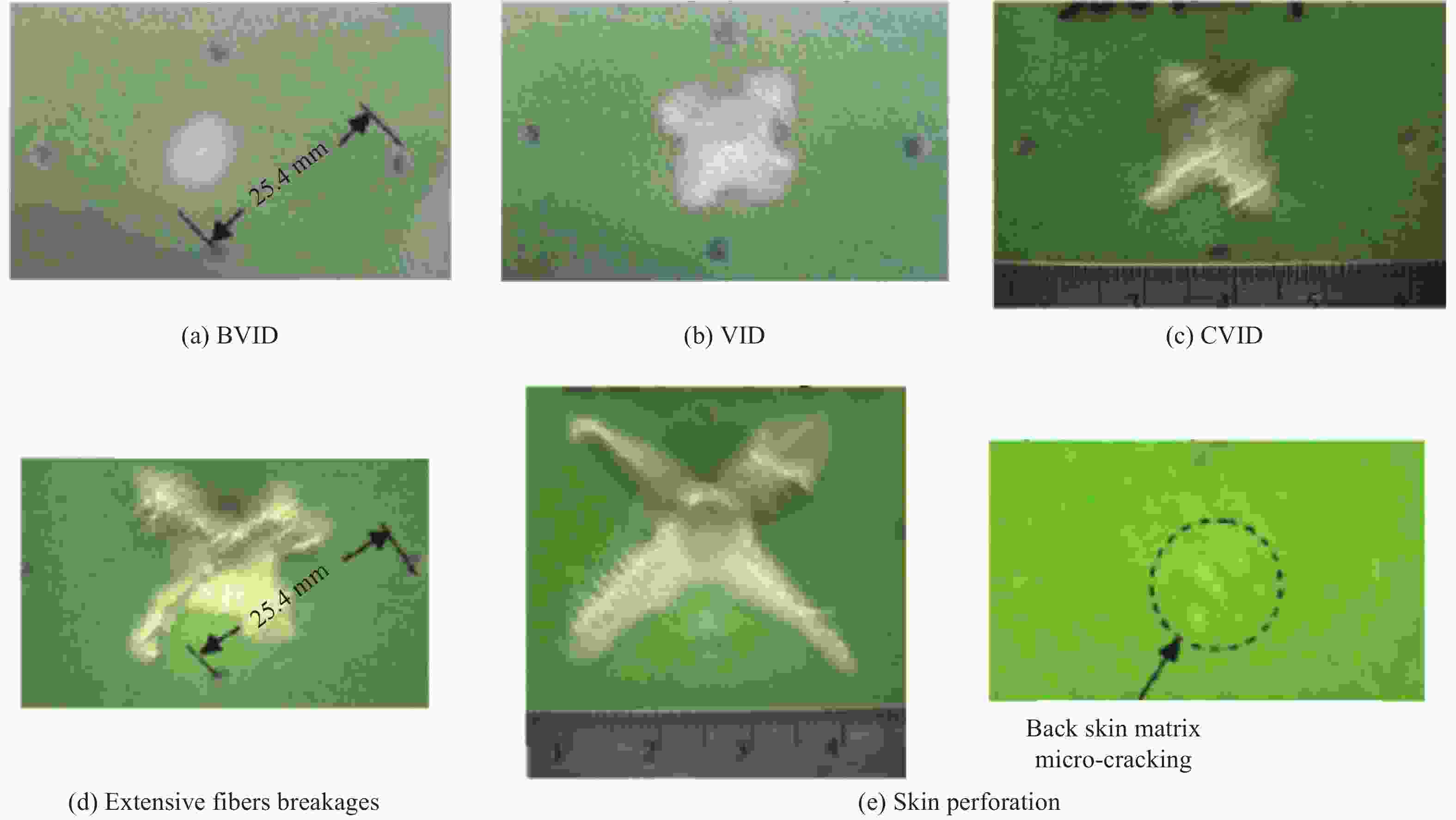
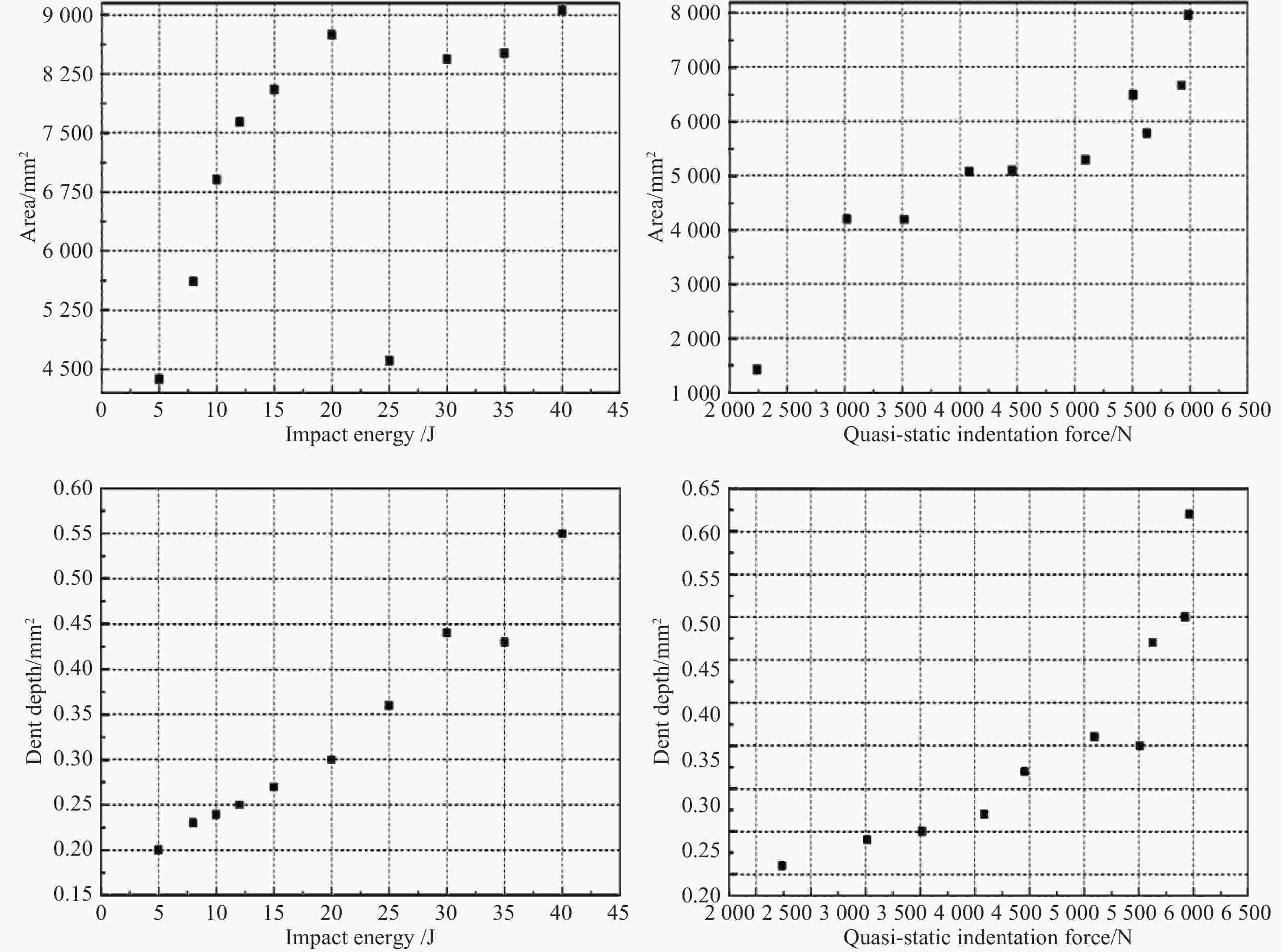
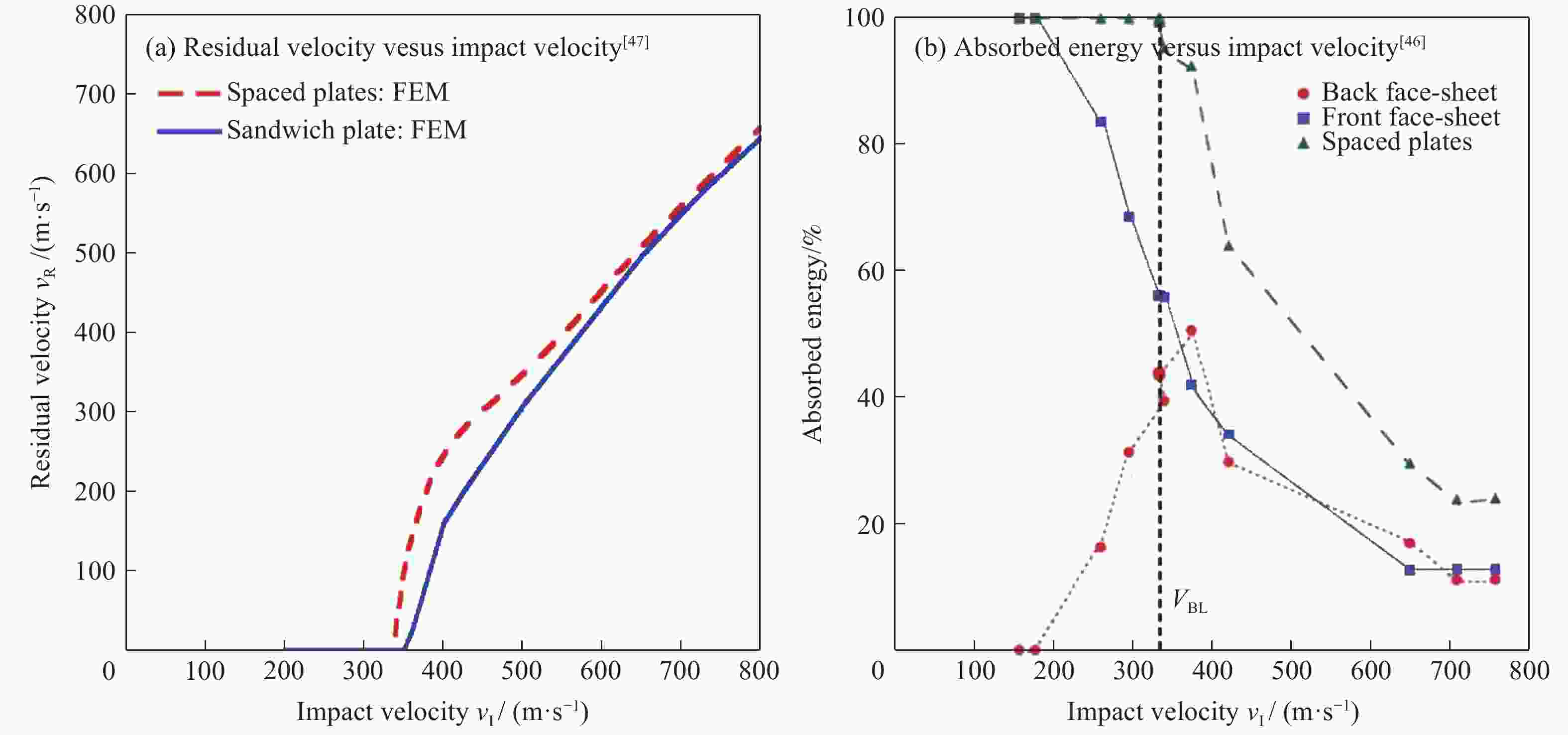
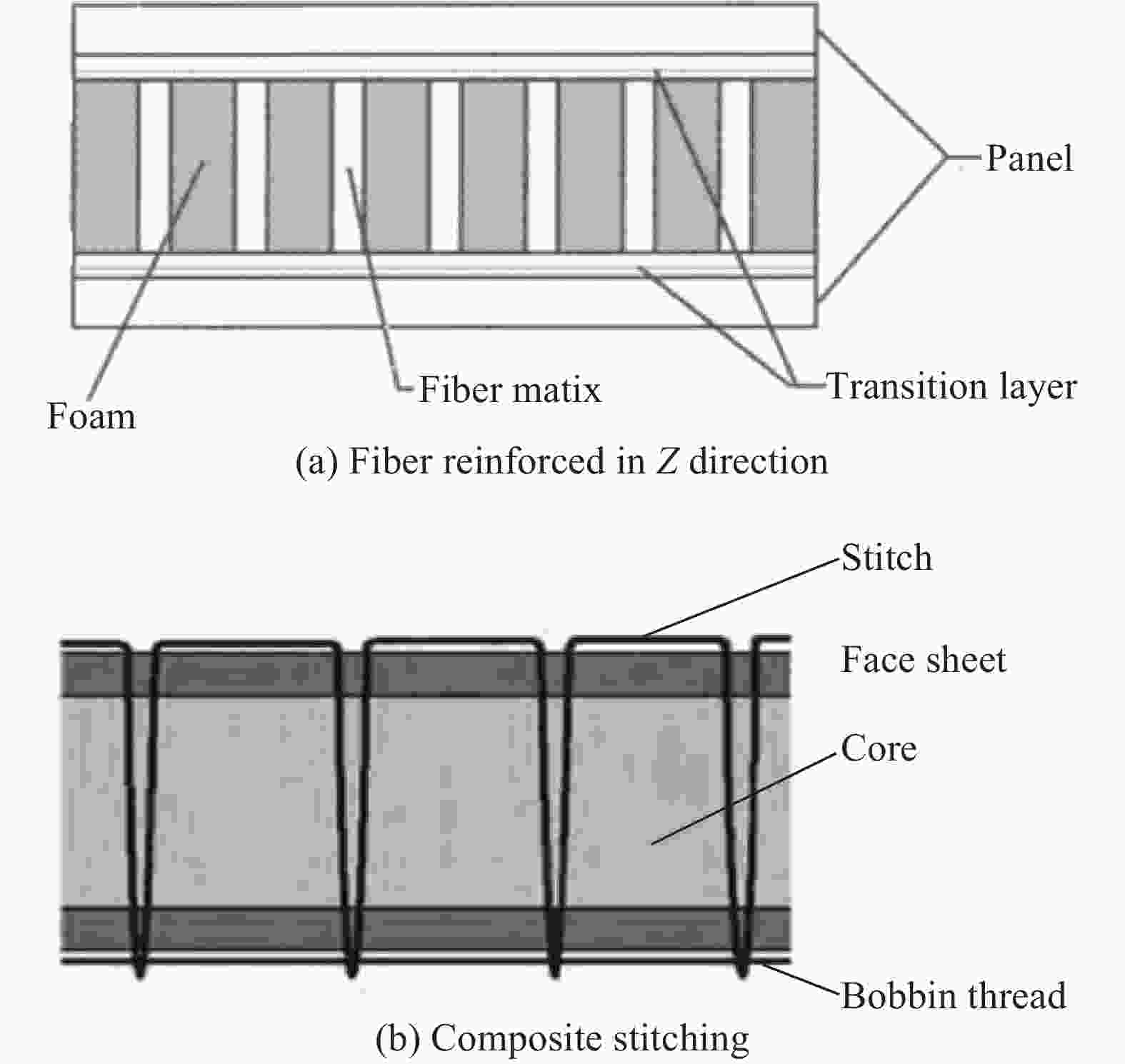
Progress on study of key technologies for polymethacrylimide foam core sandwich lifecycle
-
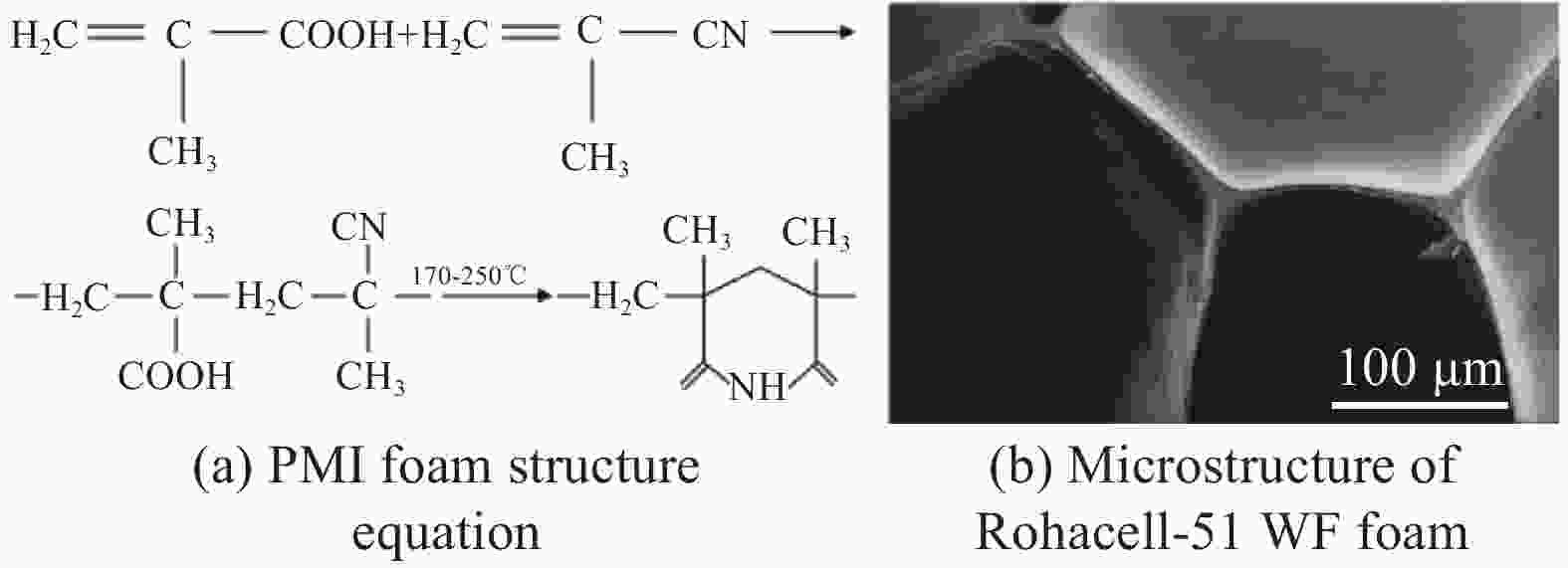
摘要: 聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺(Polymethylimide,PMI)泡沫夹层结构特有的性能优势使其广泛应用于航空航天领域。为推动PMI泡沫夹层结构的稳定化、系列化和高性能化,本文系统地综述了面向全生命周期的PMI泡沫夹层结构设计与制造技术的研究现状与发展趋势。首先,总结了PMI泡沫及其夹层结构的性能和应用现状,分析了PMI泡沫夹层结构的市场需求。然后,概述了面向全生命周期的PMI泡沫夹层结构关键技术现状,包括PMI泡沫研发、结构设计与分析、结构固化成型、维修及维护。最后,展望了PMI泡沫夹层结构的发展趋势,以期为该领域后续的研究工作提供参考。Abstract: Polymethylimide (PMI) foam core sandwich has unique performance advantages, which leads to a wide application in aerospace structures. In order to promote the stabilization, serialization and high performance for PMI foam core sandwich, the present research situation and development trend of PMI foam core sandwich design and manufacturing technology for lifecycle were systematically reviewed. Firstly, the performance and application situation of PMI foam and its core sandwich were summarized, and the market demand of PMI foam core sandwich was analyzed. Then, the key technologies situations of PMI foam core sandwich lifecycle were curtly described, including the research of PMI foam, structure design and analysis, structure curing and forming, repair and maintenance, etc. Finally, the development trend of PMI foam core sandwich was prospected, so that to provide reference for further research.
-
Key words:
- polymethacrylimide /
- sandwich /
- composites /
- design /
- manufacture /
- maintenance
-
表 1 聚甲基丙烯酰亚胺(PMI)泡沫夹层结构的应用现状[1, 7-10]
Table 1. Application status of polymethylimide (PMI) foam core sandwich[1, 7-10]
Field Structure Proportion Application example Legend demonstration Fixed wingaircraft Fuselage, wing, tail and floor 80% MD11, Airbus A320/A340/A380, C-17, ATR 72, Dornier 728,Embraer 145, ARJ21, C919 
Helicopter Paddle, floor, fairing, hatch, water drip, side vertical tail, engine hood "Dolphin", "SM", "King of the sea", EC135, NH90, "Tiger" helicopter, LE100 
Rocket Cowling, cryogenic tank Delta carrier rocket, Hll-a carrier rocket, Long 3A series carrier rocket 
Traffic Locomotive, ship superstructure, upper deck and bulkhead 15% E4 Shinkansen, New generation maglev train of CRRC Zhuzhou Electric Locomotive Co. Ltd., Ships manufactured by Kvarner mandal 
Sports, medical treatment, power generation, communication Bicycle frame, CT scanning bed plate, wind turbine blade, car body 5% Medical X-ray full body CT scanners of general motors, Siemens, et al, Wind turbine blades of Vestas, Ferrari formula one body structure, New generation bicycles 
表 2 PMI泡沫力学性能指标和测试方法
Table 2. Mechanical properties and test methods of PMI foam
Foam mechanical property Evaluation index Test method Tensile strength and modulus X3、X4、X7 ASTM D638[24] Compressive strength and modulus X3、X5、X8 ASTM D1621[25] Bending strength and modulus X2、X3 ASTM D790[26] Shear strength and modulus X1-X7 ASTM C273[27] Fatigue strength X4、X6、X7 ASTM C394[28] Thermal deformation temperature X8 ASTM D648[29] Moisture absorption X9、X10 ASTM C272[30] Aging X11 ASTM C481[31] 表 3 PMI泡沫蜂窝夹芯结构的弯曲试验数据[33]
Table 3. Bending test data of sandwich structures between PMI foam and honeycomb cores[33]
Failure detail Honeycomb core Rohacell 71 foam core Failure load/N 2 541+2 541 3 947+3 947 Deformation/mm 58.34 17.33 Failure type Permanent set (8 mm) Failure at bond and core shear Sandwich Impact energy/J Maximum load/KN Initial damage load/KN Initial damage energy/J PMI 19.90 1.78 1.78 7.64 PVC 19.70 1.53 1.51 8.70 NOMEX 19.47 1.52 1.49 5.43 Note: PVC—Polyvinyl chloride. 表 5 复合材料泡沫夹层结构固化方法对比
Table 5. Comparison of curing method of composite foam core sandwich structure
Method Process characteristic Autoclave molding Uniform distribution of pressure and temperature, low internal void ratio, simple mold, suitable for complex parts, high technical requirements for process personnel, high cost of autoclave Resin transfer molding Good surface quality, low porosity, high fiber density, overall integrity, suitable for medium batch production, complex mold manufacturing Resin film infusion Short process flow, fiber easy to be soaked, high fiber content, low porosity, excellent mechanical properties, good product reproducibility Vacuum assisted resin infusion Single side mold, low degree of mechanization and automation, long production cycle, low production cost, high resin requirements, low molding and curing pressure, suitable for large parts Compression molding High dimensional accuracy, high efficiency, high mold requirements, strict process control 表 6 PMI泡沫夹层结构的维修方法对比
Table 6. Comparison of maintenance methods for PMI foam core sandwich structure
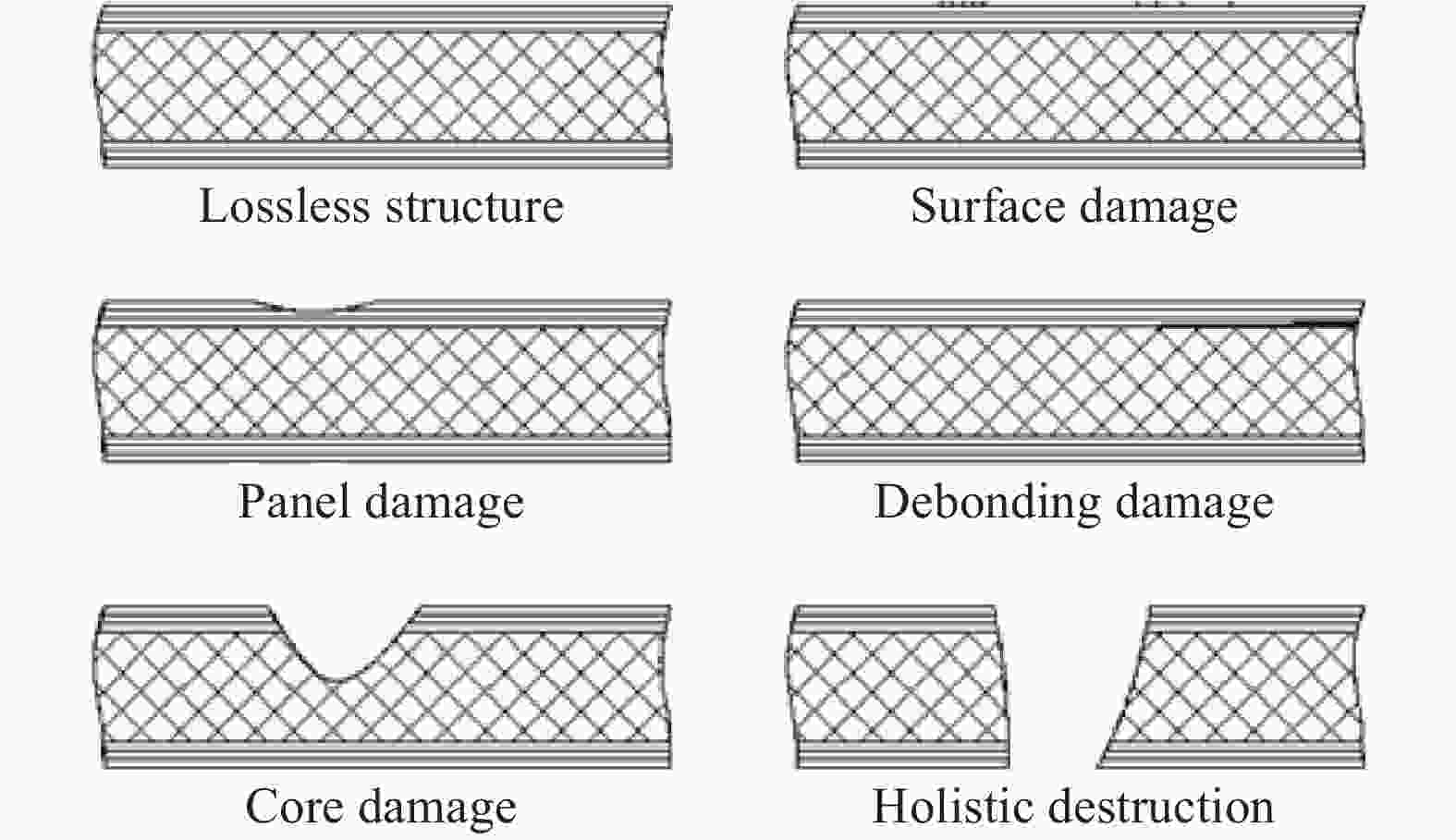
Method Process Failure mode Filling method First remove the surface damage, then carry out layer repair, and finally cure Surface damage Perfusion method First drill the glue injection hole and overflow hole, prepare the glue, then inject the glue until the glue overflows from the overflow holes around Debonding damage Inlay method Including inclined excavation repair and ladder repair. The laying parameters of patch are consistent with those of mother board. Add 1-2 layers of patches to the final surface Panel damage,Core damage Flush repair Same as inlay. The difference is that the backing plate should be placed under the panel Holistic destruction,Core damage -
[1] SEIBERT H F. Applications for PMI foams in aerospace sandwich structures[J]. Reinforced Plastics,2006,50(1):44-48. doi: 10.1016/S0034-3617(06)70873-6 [2] SEIBERT H F. PMI foam cores find further applications[J]. Reinforced Plastics,2000,44(1):36-38. doi: 10.1016/S0034-3617(00)86485-1 [3] MICHAELA N, MICHAELA T, PETER P, et al. Analysis of the macroscopic behaviour of PMI foam[J]. Key Engineering Materials,2019,48(3):285-290. [4] TANG H Y, CHEN Q Z, RAO X B. Study on foaming of PMI foam materials[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials,2014,16(5):624-628. [5] CHOI I, KIM J G, SEO I S, et al. Radar absorbing sandwich construction composed of CNT, PMI foam and carbon/epoxy composite[J]. Composite Structures,2012,94(9):3002-3008. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.04.009 [6] WANG C, ZHANG X M, TANG C Y. Manufacturing process of large scale sandwich structure with variable thickness of PMI foam core[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2011,299-300:816-819. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.299-300.816 [7] 李照谦, 南博华, 何腾锋, 等. 新一代运载火箭贮箱大温差泡沫夹层共底研制[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2016, 46(4):68-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2016.04.017LI Z Q, NAN B H, HE T F, et al. Development of large temperature difference foam sandwich co-bulkhead of cryogenic tank for new-generation launch vehicle[J]. Aerospace Materials <italic>&</italic> Technology,2016,46(4):68-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2016.04.017 [8] WENNBERG D, STICHEL S. Multi-functional design of a composite high-speed train body structure[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization,2014,50(3):475-488. doi: 10.1007/s00158-014-1056-4 [9] BAI X, LI N. The application of carbon fiber composite material for sports equipment[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2012,496:480-483. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.496.480 [10] MALYSHEVA A Y, BELETSKII B I, VLASOVA E B. Structure and properties of composite materials for medical application[J]. Glass <italic>&</italic> Ceramics,2001,58(1):66-69. [11] 高丽红, 杨利. 某型飞机用PMI泡沫夹层复合材料的设计[J]. 航空工程进展, 2010, 1(4):68-72.GAO L H, YANG L. Design of PMI foam plastic sandwich composite for the airplane[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering,2010,1(4):68-72(in Chinese). [12] 罗辑, 何凯, 郭纯武. 磁浮车辆车头及其夹层结构的制造方法: 中国, 200510021883.5[P]. 2006-03-22.LUO J, HE K, GUO C W. Manufacturing method of maglev vehicle head and its sandwich structure: China, 200510021883.5[P]. 2006-03-22(in Chinese). [13] TANG H Y, CHEN L. Preparation and characterization of polymethacrylimide foam[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2010,160-162:1309-1313. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.160-162.1309 [14] LI Q M, MINES R A W, BIRCH R S. The crush behaviour of Rohacell-51WF structural foam[J]. International Journal of Solids <italic>&</italic> Structures,2000,37(43):6321-6341. [15] 姚正军, 钱逸, 周金堂, 等. 一种高密度超厚吸波型PMI泡沫复合材料的制备方法: 中国, 201810250508.5[P]. 2018-09-07.YAO Z J, QIAN Y, ZHOU J T, et al. A high-density ultra thick absorbing PMI foam composite material preparation method: China, 201810250508.5[P]. 2018-09-07(in Chinese). [16] 郑乐, 马晓雄, 陈泽强, 等. 一种高性能PMI泡沫及其制备方法: 中国, 201610678069.9[P]. 2017-01-04.ZHENG L, MA X X, CHEN Z Q, et al. A high performance PMI foam and its preparation method: China, 201610678069.9[P]. 2017-01-04(in Chinese). [17] 胡培. 为树脂转移注射工艺开发的新型PMI泡沫[J]. 航空制造技术, 2008, 15:99-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2008.15.024HU P. New type PMI foam for resin transter technique[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2008,15:99-101(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2008.15.024 [18] YUAN C X, OTTO B, SOTIRIS K, et al. Optimization of sandwich composites fuselages under flight loads[J]. Applied Composite Materials,2012,19(1):47-64. doi: 10.1007/s10443-010-9180-9 [19] SHAFIQ B, QUISPITUPA A. Fatigue characteristics of foam core sandwich composites[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2006,28(2):96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2005.05.002 [20] 赵锐霞, 尹亮, 潘玲英, 等. PMI泡沫夹层结构性能研究[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2011, 42(5):34-37.ZHAO R X, YIN L, PAN L Y, et al. Properties of PMI foam sandwich structure[J]. Aerospace Materials <italic>&</italic> Technology,2011,42(5):34-37(in Chinese). [21] RAJU K S, SMITH B L, TOMBLIN J S, et al. Impact damage resistance and tolerance of honeycomb core sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2008,42(4):385-412. doi: 10.1177/0021998307088596 [22] SIIVOLA J T, MINAKUCHI S, TAKEDA N. Effect of temperature and humidity conditions on polymethacrylimide(PMI) foam core material and indentation response of its sandwich structures[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures and Materials,2015,17(4):335-358. doi: 10.1177/1099636215570831 [23] ABRATE S. Impact on laminated composite materials[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 1991, 44(4): 155-189. [24] ASTM International. Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics: ASTM D 638[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2014. [25] ASTM International. Standard test method for compressive properties of rigid cellular plastics: ASTM D 1621[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2016. [26] ASTM International. Standard test methods for flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics and electrical insulating materials: ASTM D 790[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2017. [27] ASTM International. Standard test method for shear properties of sandwich core materials: ASTM C 273[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2020. [28] ASTM International. Standard test method for shear fatigue of sandwich core materials: ASTM C 394[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2016. [29] ASTM International. Standard test method for deflection temperature of plastics under flexural load in the edgewise position: ASTM D 648[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2018. [30] ASTM International. Standard test method for water absorption of core materials for sandwich constructions: ASTM C 272[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2018. [31] ASTM International. Standard test method for laboratory aging of sandwich constructions: ASTM C 481[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2016. [32] HERRANEN H, PABUT O, EERME M, et al. Design and testing of sandwich structures with different core materials[J]. Materials Science, 2012, 18(1): 45-50. [33] RUCHA L, MALHAR G, ASHISH M. Flexural behavior of sandwich structures with Rohacell 71-hero foam and ox-honeycomb cores[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2020,21(2):1116-1122. [34] 张广成, 何祯, 刘良威, 等. 夹层结构复合材料低速冲击试验与分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(4):176-183.ZHANG G C, HE Z, LIU L W, et al. Low-velocity impact experiment and analysis of sandwich structure compo-sites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2012,29(4):176-183(in Chinese). [35] MILTZ J, RAMON O, MIZRAHI S. Mechanical behavior of closed cell plastic foams used as cushioning materials[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,1989,38:281-290. doi: 10.1002/app.1989.070380209 [36] GRACE I, PILIPCHUK V, IBRAHIM R, et al. Temperature effect on non-stationary compressive loading response of polymethacrylimide solid foam[J]. Composite Structures,2012,94(10):3052-3063. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2012.04.022 [37] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids (structure and properties)[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997: 175-234. [38] MILLS N J, ZHU H X. The high strain compression of closed-cell polymer foams[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,1999,47(3):669-695. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5096(98)00007-6 [39] COQUARD R, LORETZ M, BAILLIS D. Conductive heat transfer in metallic/ceramic open-cell foams[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,2008,10(4):323-337. doi: 10.1002/adem.200700331 [40] BECKMANN C, HOHE J. A probabilistic constitutive model for closed-cell foams[J]. Mechanics of Materials,2016,96:96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2016.01.016 [41] CHAI G B, ZHU S. A review of low velocity impact on sandwich structures[J]. Journal of Materials and Applications,2011,225(4):207-230. [42] GORDON S, BOUKHILI R, MERAH N. Impact behavior and finite element prediction of the compression after impact strength of foam/vinylester-glass composite sandwiches[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures <italic>&</italic> Materials,2014,16(5):551-574. [43] GONG S W, LAM K Y. Effects of structural damping and stiffness on impact response of layered structure[J]. AIAA Journal,2000,38(9):1730-1735. doi: 10.2514/2.1161 [44] KHALILI M R, MALEKZADEH K, MITTAL R K. Effect of physical and geometrical parameters on transverse low-velocity impact response of sandwich panels with a transversely flexible core[J]. Composite Structures,2007,77(4):430-443. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.07.016 [45] ABRATE S. Localized impact on sandwich structures with laminated facings[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews,1997,50(2):69-82. doi: 10.1115/1.3101689 [46] 蔡建丽. 泡沫夹层结构复合材料低速冲击损伤阻抗特性[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2011.CAI J L. Damage resistance of low velocity impacted on foam-core sandwich structure composites[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2011(in Chinese). [47] CAIRNS D S, LAGACE P A. Transient response of graphite/epoxy and kevlar/epoxy laminates subjected to impact[J]. AIAA Journal,1989,27(11):1590-1596. doi: 10.2514/3.10306 [48] KASSAPOGLOU C. Buckling, post-buckling and failure of elliptical delaminations in laminates under compression[J]. Composite Structures,1988,9(2):139-159. doi: 10.1016/0263-8223(88)90004-9 [49] MINGUET P. A model for predicting the behavior of impact-damaged minimum gage sandwich panels under compression[C]//32rd Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. Baltimore, Maryland: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Inc, 1991: 1112-1122. [50] BAI R X, GUO J J, LEI Z K, et al. Compression after impact behavior of composite foam-core sandwich panels[J]. Composite Structures,2019,225:1-10. [51] 李亚智, 黄其青, 傅祥炯, 等. 含裂纹结构剩余强度的一种估算方法[J]. 机械强度, 2003, 25(1):71-75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2003.01.019LI Y Z, HUANG Q Q, FU X J, et al. Methodology for residual strength evaluation of cracked structures[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength,2003,25(1):71-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9669.2003.01.019 [52] SHIPSHA A, ZENKERT D. Compression after impact strength of sandwich panels with core crushing damage[J]. Applied Composite Materials,2005,12(3):149-164. [53] ABRATE S. Impact on composite structures[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998: 240-257. [54] GARCÍA-CASTILLO S K, BUITRAGO B L, BARBERO E. Behavior of sandwich structures and spaced plates subjected to high-velocity impacts[J]. Polymer Composites,2011,32(2):290-296. doi: 10.1002/pc.21047 [55] IVANEZ I, SANTIUSTE C, BARBERO E, et al. Numerical modelling of foam-cored sandwich plates under high-velocity impact[J]. Composite Structures,2011,93(9):2392-2399. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.03.028 [56] PORA J. Composite materials in the Airbus A380 from history to future[C]//13rd International Conference on Composite Materials. Beijing: ICCM 13 Proceedings, 2001: 28-37. [57] RESEWSKI C, BUCHGRABER W. Properties of new polyimide foams and polyimide foam filled honeycomb composites[J]. Materialwissenschaft Und Werkstofftechnik,2003,34(4):365-369. doi: 10.1002/mawe.200390076 [58] 罗小敏, 易洪林, 赵晓东, 等. 一种PMI泡沫夹层结构的飞机雷达罩及其设计方法和制造方法: 中国, 201810946546.4[P]. 2019-01-04.LUO X M, YI H L, ZHAO X D, et al. A PMI foam sandwich structure aircraft radome and its design method and manufacturing method: China,, 201810946546.4[P]. 2019-01-04(in Chinese). [59] CARTIÉ D D, FlECK N A. The effect of pin reinforcement upon the through-thickness compressive strength of foam-cored sandwich panels[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2003,63(16):2401-2409. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(03)00273-2 [60] HAO J J, ZHANG Z G, LI M, et al. The influence of preparing method on novel x-truss/foam sandwich structure[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2009,28(13):1553-1565. doi: 10.1177/0731684408089534 [61] ALMULA T A D M S, SHARIFI S, SHARIFISHOURA-BI G, et al. Static analysis of stitched sandwich beams with functionally graded foam core[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials,2013,393:381-386. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.393.381 [62] LASCOUP B, ABOURA Z, KHELLIL K, et al. On the mechanical effect of stitch addition in sandwich panel[J]. Compo-sites Science and Technology,2005,66(10):1385-1398. [63] 刘振东, 郑锡涛, 冯雁, 等. 无人机全复合材料机翼结构设计与试验验证[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(5):108-116.LIU Z D, ZHENG X T, FENG Y, et al. Structural design and test verification of all-composite wing for unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(5):108-116(in Chinese). [64] LEE C S, LEE D G. Manufacturing of composite sandwich robot structures using the co-cure bonding method[J]. Composite Structures,2004,65(3-4):307-318. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2003.11.011 [65] TRAUTH A, BONDY M, WEIDENMANN K A, et al. Mechanical properties and damage evolution of a structural sheet molding compound based on a novel two step curing resin system[J]. Materials <italic>&</italic> Design,2018,143:224-237. [66] 张钟, 李勇, 肖军, 等. 泡沫夹层结构复合材料热膨胀模压法工艺研究[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2007, 39(5):670-675. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2007.05.024ZHANG Z, LI Y, XIAO J, et al. Processing of foam core sandwich structures by thermal expansion molding[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics <italic>&</italic> Astronautics,2007,39(5):670-675(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2007.05.024 [67] FERNLUND G, COURDJI R, POURSARTIP A, et al. Process induced deformations of the Boeing 777 aft strut trailing edge fairing[C]//33rd International SAMPE Technical Conference. Seattle: SAMPE, 2001: 347-355. [68] 刘小龙, 顾轶卓, 李敏, 等. 采用薄膜传感器的树脂基复合材料热压罐工艺密实压力测试方法[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(5):73-79.LIU X L, GU Y Z, LI M, et al. Compacting pressure measuring method in autoclave processing of polymer compo-sites using film sensor[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(5):73-79(in Chinese). [69] 成艳娜, 刘向阳. 某型飞机PMI泡沫夹层结构翼梢小翼成型技术研究[J]. 粘接, 2018, 39(4):55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5922.2018.04.009CHENG Y N, LIU X Y. Forming technology of PMI foam sandwich structure winglets for a specific aircraft[J]. Adhesion,2018,39(4):55-58(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5922.2018.04.009 [70] 杨纪来. PMI泡沫材料固定装置L 中国, 201520569993.4[P]. 2015-12-02.YANG J L. PMI foam fixtures. China: 201520569993.4[P]. 2015-12-02(in Chinese). [71] 龚文, 马军, 鄢和庚, 等. 一种硬质泡沫芯材热成型方法. 中国: 201611079984.2[P]. 2017-05-31.GONG W, MA J, YAN H G, et al. A hot forming method for rigid foam core material: China, 201611079984.2[P]. 2017-05-31(in Chinese). [72] 高申煣. PMI泡沫夹层结构动态力学性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2018.GAO S R. Research on dynamic mechanical properties of PMI foam sandwich plate[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2018(in Chinese). [73] HOPKINSON B. A method of measuring the pressure produced in the detonation of high explosives or by the impact of bullets[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London,1914,213:437-456. [74] QU J, JU D W, GAO S R, et al. Research on the dynamic mechanical properties of polymethacrylimide foam sandwich structure[J]. Composite Structures,2018,204:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.07.078 [75] ASTM International. Standard test method for compressive residual strength properties of damaged polymer matrix composite plates: ASTM D 7137[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2017. [76] BURMAN M, ZENKERT D. Fatigue of foam core sandwich beams-1: Undamaged specimens[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,1997,19(7):551-561. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(97)00069-8 [77] BURMAN M, ZENKERT D. Fatigue of foam core sandwich beams-2: Effect of initial damage[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,1997,19(7):563-578. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(97)00068-6 [78] 王璐. 复合材料夹层结构理论、设计与应用[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019: 58-59.WANG L. Theory, design and application of composite sandwich structure[M]. Beijing: China Architecture Publishing & Media CO. LTD., 2019: 58-59(in Chinese). [79] ZENKERT D, BURMAN M. Failure mode shifts during constant amplitude fatigue loading of GFRP/foam core sandwich beams[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 33(2): 217-222. [80] AREZOO S, TAGARIELLI V L, SIVIOUR C R, et al. Compressive deformation of Rohacell foams: Effects of strain rate and temperature[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2013,51:50-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2012.07.010 [81] YIN W L, WANG J T S. The energy-release rate in the growth of a one-dimensional delamination[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1984,51(4):939. doi: 10.1115/1.3167752 [82] CARLSON L A, KARDOMATEAS G A. Structural and failure mechanics of sandwich composites[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2011: 191-192. [83] AVILÉS F, CARLSSON L A. Analysis of the sandwich DCB specimen for debond characterization[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2008, 75(2): 153-168. [84] 王灿, 陈浩然. 泡沫夹芯复合材料梁界面裂纹曲折扩展实验与数值模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(1):129-135.WANG C, CHEN H R. Experimental investigation and numerical simulation of interfacial crack kinking in foam core composite sandwich beams[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2012,29(1):129-135(in Chinese). [85] QUISPITUPA A, BERGGREEN C, CARLSSON L A. Face/core interface fracture characterization of mixed mode bending sandwich specimens[J]. Fatigue <italic>&</italic> Fracture of Engineering Materials <italic>&</italic> Structures,2011,34(11):839-853. [86] ZHOU G. Static behaviour and damage of thick composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures,1996,36(1-2):13-22. [87] CUCINOTTA F, GUGLIELMINO E, RISITANO G, et al. Assessment of damage evolution in sandwich composite material subjected to repeated impacts by means optical measurements[J]. Procedia Structural Integrity,2016,2:3660-3667. doi: 10.1016/j.prostr.2016.06.455 [88] SIKDAR S, MIRGAL P, BANERJEE S. Damage induced acoustic emission source monitoring in a honeycomb sandwich composite structure[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,158:179-188. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.09.071 [89] FALZON B G. Impact damage and repair of composite structures[J]. Aeronautical Journal,2009,113(1145):431-445. doi: 10.1017/S0001924000003109 [90] 刘畅, 岳珠峰, 耿小亮, 等. PMI复合材料泡沫夹层结构小能量冲击后回弹规律研究[J]. 实验力学, 2015, 30(6):757-767.LIU C, YUE Z F, GENG X L, et al. On the rebound regularity of PMI foam core composite structure subjected to low energy impact[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics,2015,30(6):757-767(in Chinese). [91] 邵俊欣, 鲁礼菊, 李仁鹏, 等. 一种飞机复合材料泡沫夹层结构的修理方法: 中国, 201611153931.0[P]. 2017-05-10.SHAO J X, LU L J, LI R P, et al. A repair method for aircraft composite foam sandwich structure: China, 201611153931.0[P]. 2017-05-10(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: