Removal of Cr(VI) from water by modified attapulgite adsorbent
-
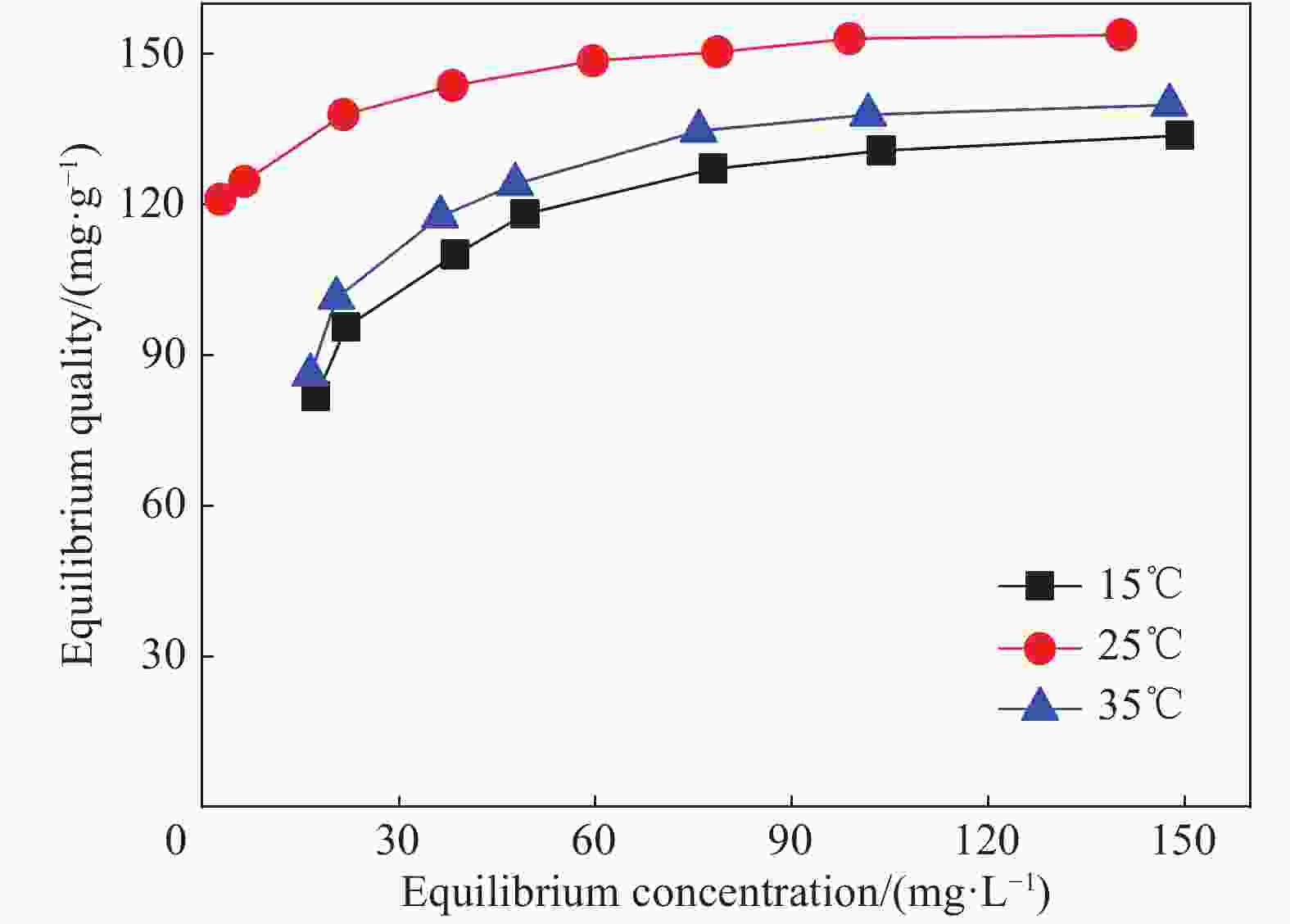
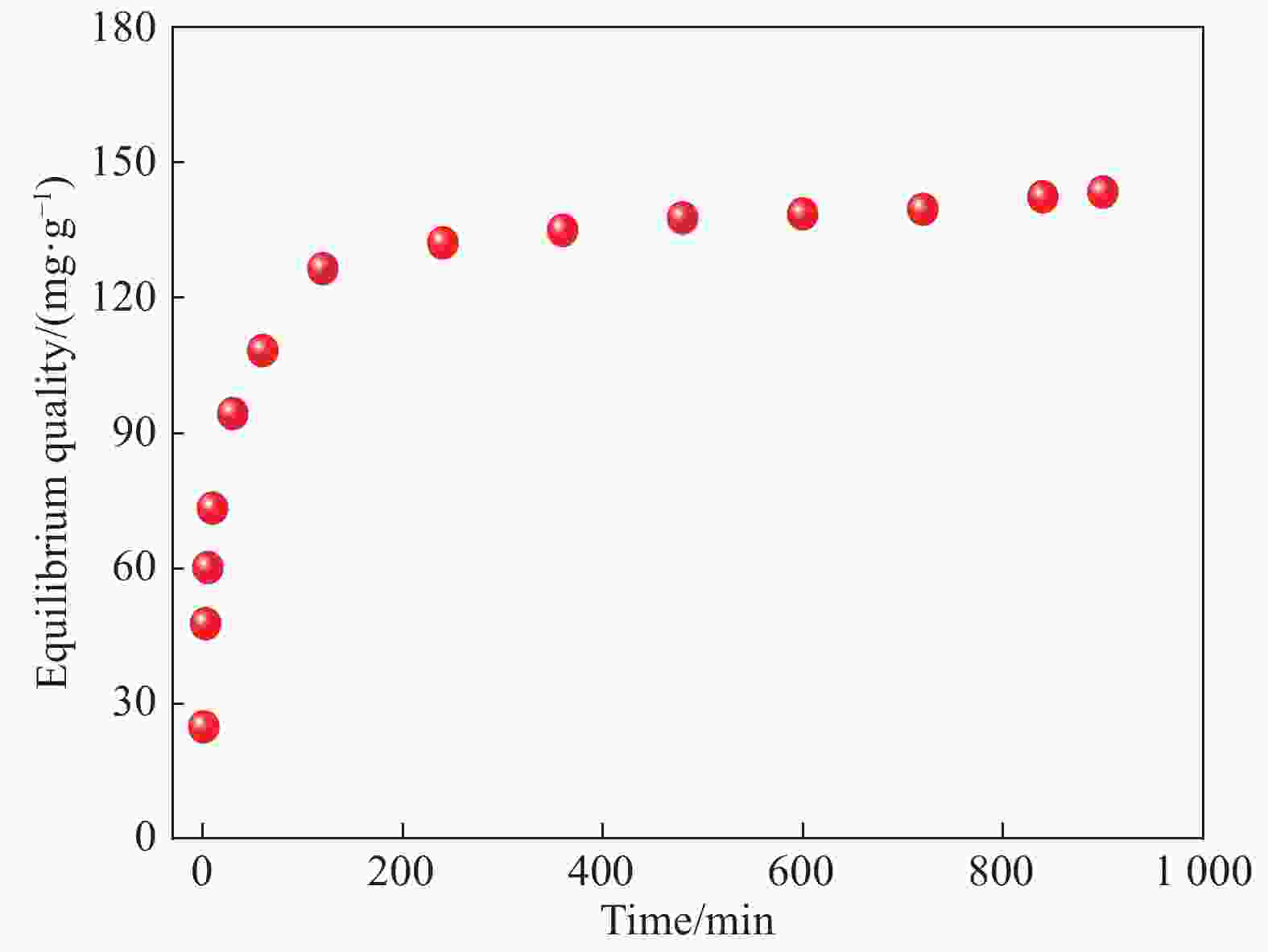
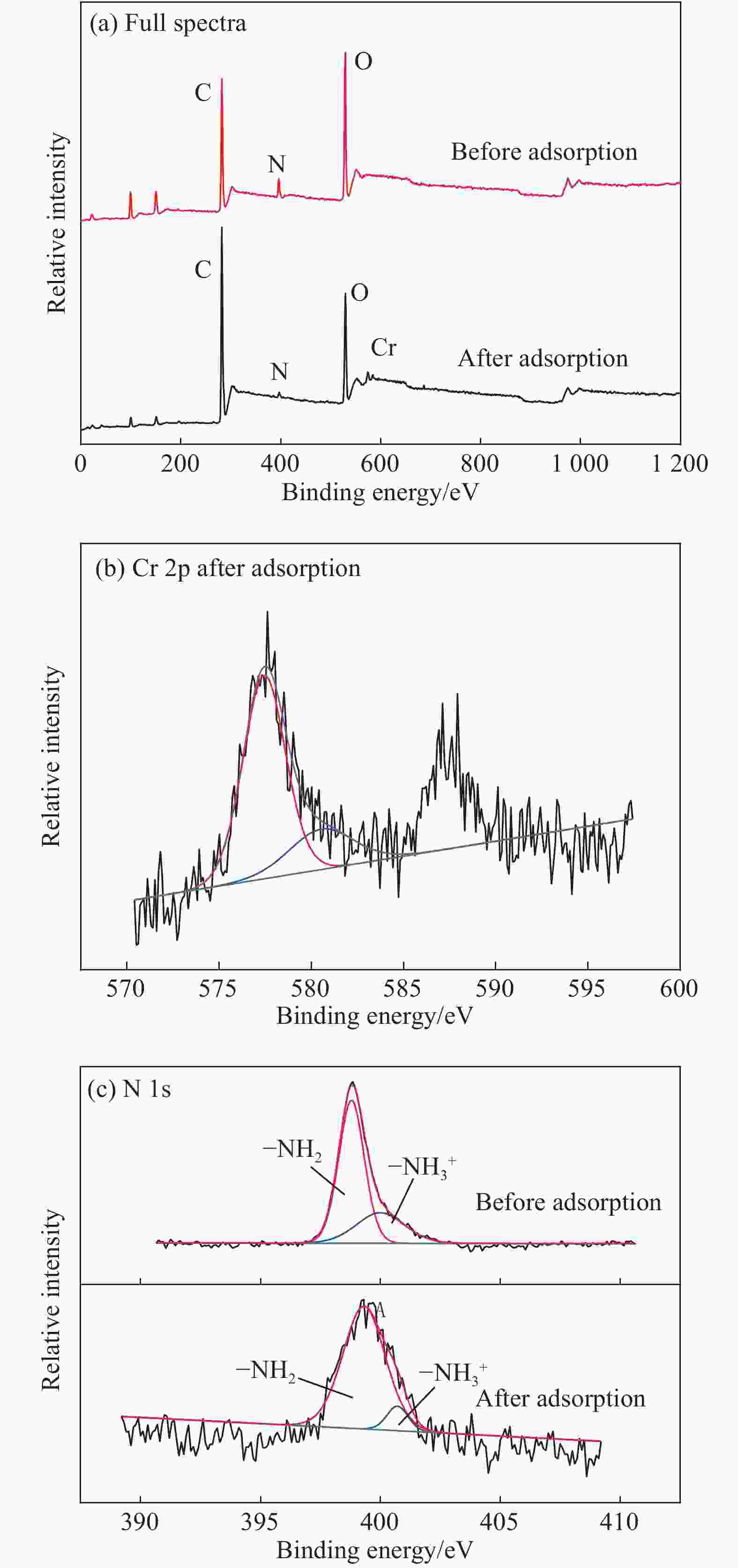
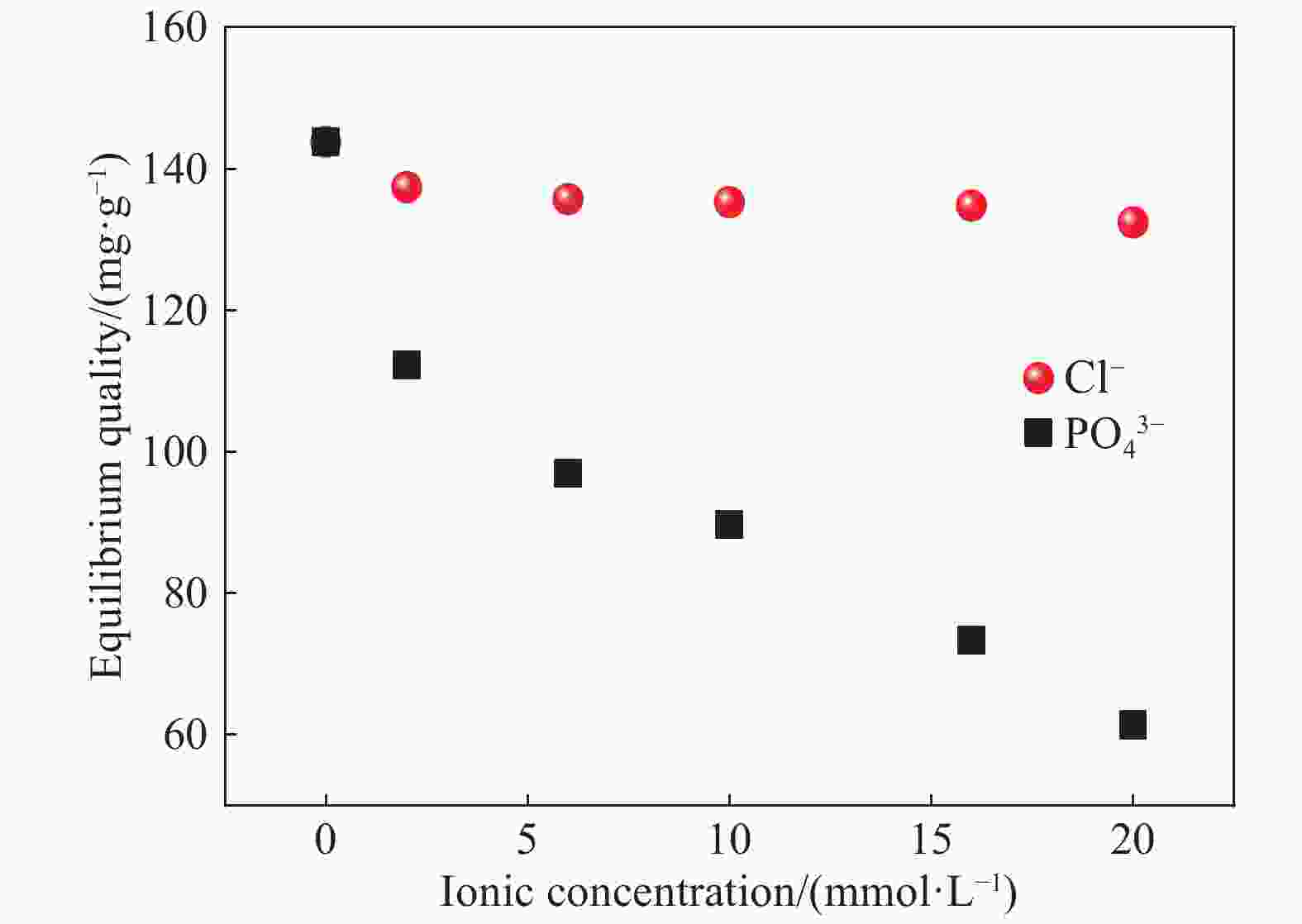
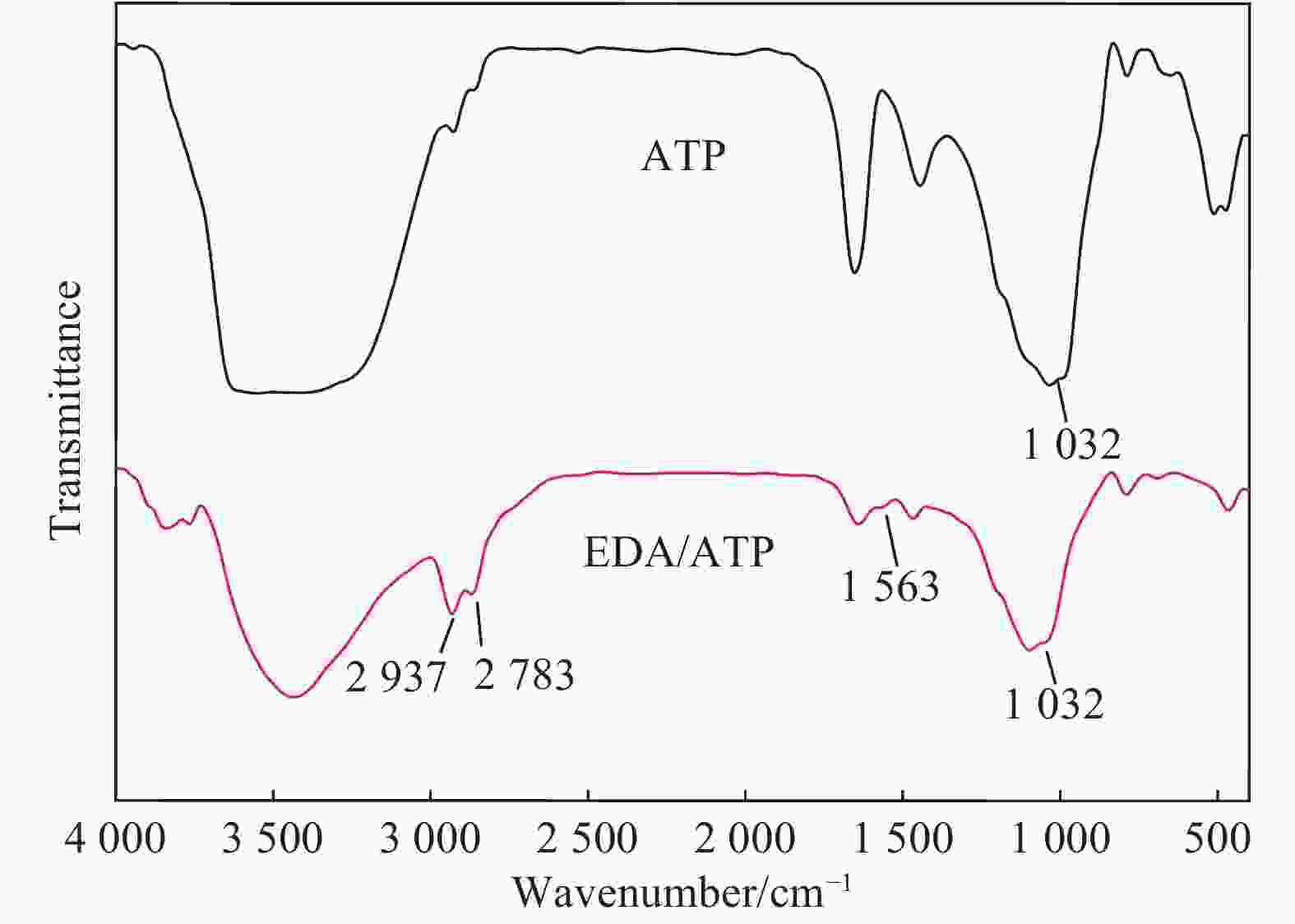
摘要: 以凹凸棒土为载体,合成了乙二胺(EDA)改性凹凸棒土(ATP)吸附剂EDA/ATP复合材料。采用FTIR、TGA对吸附剂进行表征,同时将其应用于对水中Cr(VI)的吸附,研究了溶液初始浓度、吸附时间、溶液pH、Cl−与PO43−阴离子浓度对吸附的影响。FTIR和TGA结果表明乙二胺已成功接枝到凹凸棒土表面。吸附实验表明,25℃时EDA/ATP复合材料对Cr(VI)的最大吸附容量为153.78 mg·g−1,吸附在800~900 min内达到平衡,吸附符合Freundlich吸附等温模型和拟二级动力学模型;在初始溶液pH为2~10条件下,随着pH的增加,吸附量先增加再降低,pH为3时,吸附量最大;Cl−对吸附影响较小,PO43−对吸附的影响较大,当PO43−浓度达到20 mmol·L−1时,Cr(VI)最大吸附量下降了83 mg·g−1;实验表明EDA/ATP可作为一种潜在处理水中Cr(VI)的吸附剂。Abstract: Ethylenediamine modified attapulgite(EDA/ATP) adsorbent was synthesized by using clay-based adsorbent ATP as carrier. The EDA/ATP composite adsorbent was characterized by FTIR and TGA. The adsorbent was applied to the adsorption of Cr(VI) in aqueous. The effects of initial concentration of Cr(VI) solution, adsorption time, solution pH and the anion concentration Cl− and PO43− on the adsorption of Cr(VI) were studied. The FTIR and TGA results show that EDA has been successfully grafted onto the surface of ATP. The adsorption experimental results show that at 25℃ the maximum adsorption capacity of EDA/ATP composite for Cr(VI) is 153.78 mg·g−1, and the adsorption reaches equilibrium within 800~900 min. The adsorption experimental data conform to Freundlich adsorption isotherm model and the pseudo-second-order kinetics. The initial pH of solution is ranging from 2 to 10. With the increase of pH, the adsorption capacity first increases and then decreases. When the pH is 3, the adsorption capacity reaches the maximum adsorption amount. PO43− has greater effect on the adsorption than Cl−, and the maximum adsorption capacity decreases by 83 mg·g−1 when the concentration of PO43− is 20 mmol·L−1. The experimental results show that EDA/ATP composite can be used as a potential adsorbent for Cr(VI) in water treatment.
-
Key words:
- attapulgite /
- ethylenediamine /
- modification /
- adsorption /
- Cr(VI) /
- water treatment
-
表 1 EDA/ATP复合材料吸附剂对Cr(VI)的吸附等温线拟合参数
Table 1. Adsorption isotherm fitting parameters of Cr(VI) by EDA/ATP composite adsorbent
Temperature/℃ Equation parameters of Langmuir Equation parameters of Freundlich qm/(mg·L−1) b/(L·mg−1) R2 n Kf R2 15 130.55 0.87 0.866 17.17 100.27 0.990 25 149.25 0.76 0.818 14.81 111.84 0.989 35 136.05 1.06 0.825 30.21 104.40 0.993 Notes:qm—Theoretical maximum adsorption capacity;b—Affinity coefficient;R2—Determination coefficient;n—Adsorption intensity;Kf—Freundlich constants related to adsorption capacity. 表 2 EDA/ATP复合材料吸附剂对Cr(VI)的拟一级、拟二级动力学参数
Table 2. Simulated parameters of Cr(VI) adsorption by EDA/ATP composite using pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetics
Adsorbent qe/(mg·g−1) Pseudo-first-order kinetics equation Pseudo-second-order kinetics equation k1/ [g· (mg·min)−1] qcal/ (mg·g−1) R2 k2/[g· (mg·min)−1] qcal/ (mg·g−1) R2 EDA/ATP 127.85 1.38×10−3 105.12 0.837 2.26×10−4 147.06 0.998 Notes: qe—Equilibrium adsorption capacity;qcal—Maximum theoretical adsorption capacity calculated by the corresponding kinetic equation;k1, k2—Pseudo-first-order kinetic and pseudo-second-order kinetic equation constants, respectively. -
[1] EGODAWATTE S, DATT A, BURNS E, et al. Chemical insight into the adsorption of chromium(Ⅲ) on iron oxide/mesoporous silica nanocomposites[J]. Langmuir,2015,31(27):7553-7562. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01483 [2] GUAN X., CHEN Y, FAN H. Stepwise deprotonation of magnetite-supported gallic acid modulates oxidation state and adsorption-assisted translocation of hexavalent chromium[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(18):15525-15532. [3] KUMAR A, PAUL P, SANNA K N. Bio-nanomaterial scaffolds for effective removal of fluoride, chromium and dye[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2016,5(1):895-903. [4] GOPALAKANNAN V, VISWANATHAN N. Development of nano-hydroxyapatite embedded gelatin biocomposite for effective Cr(VI) removal[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2015,54(50):12561-12569. [5] 林国庆, 李文娟. 海蒿子和三价铁溶液绿色制备纳米铁及其去除六价铬的实验研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 48(S2):127-133.LIN G Q, LI W J. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using sargassum pallidum with ferric iron solution and its experimental study on hexavalent chromium removal[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China,2018,48(S2):127-133(in Chinese). [6] QIU B, XU C, SUN D, et al. Polyaniline coated ethyl cellulose with improved hexavalent chromium removal[J]. Acs Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2014,2(8):2070-2080. [7] 任阳民, 梁宏, 邱阳, 等. 脉冲电解技术处理含铬废水实验研究[J]. 四川理工学院学报(自然科学版), 2017, 30(3):1-5.REN Y M, LIANG H, QIU Y, et al. Study on treatment of chromium-containing waste water by pulse-electrolysis technique[J]. Journal of Sichuan University of Science & Engineering (Natural Science Edition),2017,30(3):1-5(in Chinese). [8] LIU S, MISHRA S B, ZHANG Y, et al. Uptake of hexavalent chromium in electroplating wastewater by hydrothermally treated and functionalized sand and its sustainable reutilization for glass production[J]. Acs Sustainable Chemistry,2017,5(2):1509-1516. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02185 [9] ABUBAKR A H, GURMAN S J, MURPHY L M, et al. Remediation of chromium(VI) by a methane-oxidizing bacterium[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2010,44(1):400-405. [10] WANG T, CHEN Y, MA J, et al. Attapulgite nanoparticles-modified monolithic column for hydrophilic in-tube solid-phase microextraction of cyromazine and melamine[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2016,88(3):1535-1541. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b03478 [11] 陈浩, 赵杰. 凹凸棒与酸化凹凸棒对Pb(Ⅱ)和Zn(Ⅱ)的选择吸附性差异[J]. 材料工程, 2008(10):154-157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2008.10.039CHEN H, ZHAO J. The difference of selective adsorption between palygorskite and acid-activated palygorskite for Pb(Ⅱ) and Zn(Ⅱ)[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2008(10):154-157(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2008.10.039 [12] 陈泳, 郝蓉蓉, 王洁琼. 酸改性聚吡咯/凹凸棒复合材料对胭脂红染料的吸附[J]. 化工新型材料, 2018, 46(4):148-151.CHEN Y, HAO R R, WANG J Q. Adsorption of carmine onto acid modified polypyrrole/attapulgite composite[J]. New Chemical Materials,2018,46(4):148-151(in Chinese). [13] YI X, SHAO D, LU X, et al. Spectroscopic investigation of enhanced adsorption of U(VI) and Eu(Ⅲ) on magnetic attapulgite in binary system[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(22):7533-7543. [14] WANG Y, FENG Y, ZHANG X F, et al. Alginate-based attapulgite foams as efficient and recyclable adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2018,514:190-198. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.12.035 [15] CHEN L F, LIANG H W, LU Y, et al. Synthesis of an attapulgite clay@carbon nanocomposite adsorbent by a hydrothermal carbonization process and their application in the removal of toxic metal ions from water[J]. Langmuir,2011,27(14):8998-9004. doi: 10.1021/la2017165 [16] LI B, LI W, ZHANG Q, et al. Attapulgite as natural catalyst for glucose isomerization to fructose in water[J]. Catalysis Communications,2017,99:20-24. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2017.05.011 [17] ZANG Z, HU Z, LI Z, et al. Synthesis, characterization and application of ethylenediamine-modified multiwalled carbon nano tubes for selective solid-phase extraction and preconcentration of metal ions[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,172(2):958-963. [18] WANG S, WANG J, ZHANG W, et al. Ethylenediamine modified graphene and its chemically responsive supramolecular hydrogels[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2014,53(33):13205-13209. [19] 黄京晶, 陈宏, 刘江, 等. 改性水葫芦粉对水体中Hg2+的吸附[J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(2):798-804. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509164HUANG J J, CHEN H, LIU J. Adsorption of Hg2+ from aqueous solution by modified eichhornia crassipes powder[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2017,11(2):798-804(in Chinese). doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201509164 [20] XING Y, CHEN X, WANG D, et al. Electrically regenerated ion exchange for removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(4):1439-1443. [21] 赵永纲. 氨基功能化纳米Fe3O4磁性高分子复合材料的合成、表征及其对废水中Cr(VI)的吸附研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2010.ZHAO Y G. Synthesis and characterization of amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymer composites and their ad sorption of Cr(VI) in wastewater[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010(in Chinese). [22] 鲁秀国, 黄燕梅, 曹禹楠. 氨基改性核桃壳对废水中Cr(VI)的静态吸附研究[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2014, 30(6):491-498.LU X G, HUANG Y M, CAO Y N. Static adsorption of Cr(VI) in simulated wastewater by amino modified walnut shells[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption,2014,30(6):491-498(in Chinese). [23] JUN W, ZHANG H, HE P, et al. Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution by dried activated sludge biomass[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,176(1):697-703. [24] BAE S, SIHN Y, KYUNG D, et al. Molecular identification of Cr(VI) removal mechanism on vivianite surface[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2018,52(18):10647-10650. -





 下载:
下载: