Impact of wrinkle defects on failure behavior of L-shaped laminates: Experimental and numerical study
-
摘要: 通过实验和数值分析相结合的方法开展了褶皱缺陷对L型复合材料层合板承载能力和失效过程影响的研究。实验方面,通过“横条法”人为引入褶皱缺陷,制备了含两种缺陷大小的L型层合板,研究了其在弯曲载荷作用下的承载能力和损伤扩展形式,并与无缺陷L型层合板进行对比分析。数值分析方面,基于3D Hashin失效准则的渐进损伤失效模型, 研究其失效过程中应力分布特征和失效模式,探求褶皱缺陷对L型层合板失效行为的影响机制。实验结果表明,褶皱缺陷会显著降低曲梁的承载能力,并使分层损伤演化的空间扩展特征从无褶皱试样的逐层扩展转变为褶皱区域的聚集式扩展。数值预测与实验现象吻合,并共同表明褶皱处横向应力和面法线应力的集中是导致结构提前失效的主导因素,且褶皱区域的应力集中改变了损伤过程中应力逐层重分配的趋势,导致含褶皱试样呈现出聚集式扩展的破坏特征。该工作可扩展应用于含褶皱缺陷L型层合板的安全性能评估及损伤容限设计。Abstract: The mechanical responses and failure evolution process of L-shaped composite laminates with effect of wrinkle defects were investigated using experimental and numerical methods. In experimental study, L-shaped laminates containing different magnitudes of wrinkle defects were prepared with the aid of ‘transverse-strip’ method. The loading capability and damage propagation of L-shaped samples containing wrinkle defects were investigated within bending test and compared with ones of the intact samples. In numerical study, a progressive damage failure model was created based on 3D Hashin failure criterion. Afterwards, the numerical model was applied to predict the evaluation of stresses distribution and failure mode during failure process. The mechanism of wrinkle impact on the failure behavior of L-shaped laminates was explored further. Test result shows that wrinkle defects significantly reduce the loading capacity of L-shaped laminates and the spatial extension characteristic of delamination damage evolution is changed from the layer-by-layer extension to the aggregation extension of wrinkle area. The numerical predictions consist with the experimental observations. It is revealed that concentrations of transverse stress and out-of-plane stress at wrinkle area are the dominant factors response for the premature failure. In addition, the stress concentrations in wrinkle area destroy the tendency of layer-by-layer damage, leading to the wrinkled samples to exhibit agglomerated extended failure characteristics. The above-mentioned researches can provide a strategy to assess the structural integrity of L-shaped laminates containing wrinkle defects and determine their design of damage tolerance.
-
Key words:
- laminates /
- wrinkle defects /
- numerical analysis /
- delamination /
- progressive damage
-
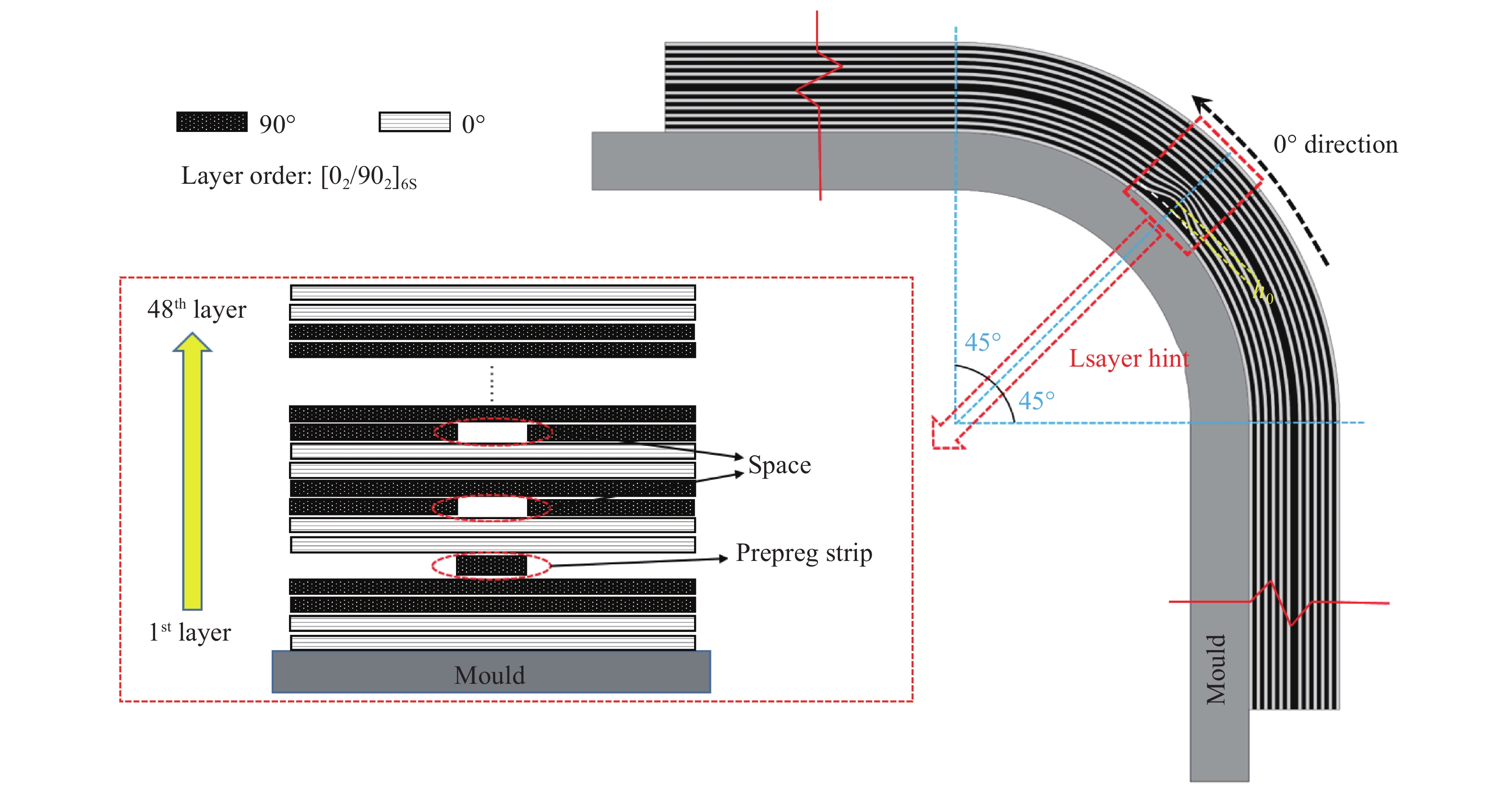
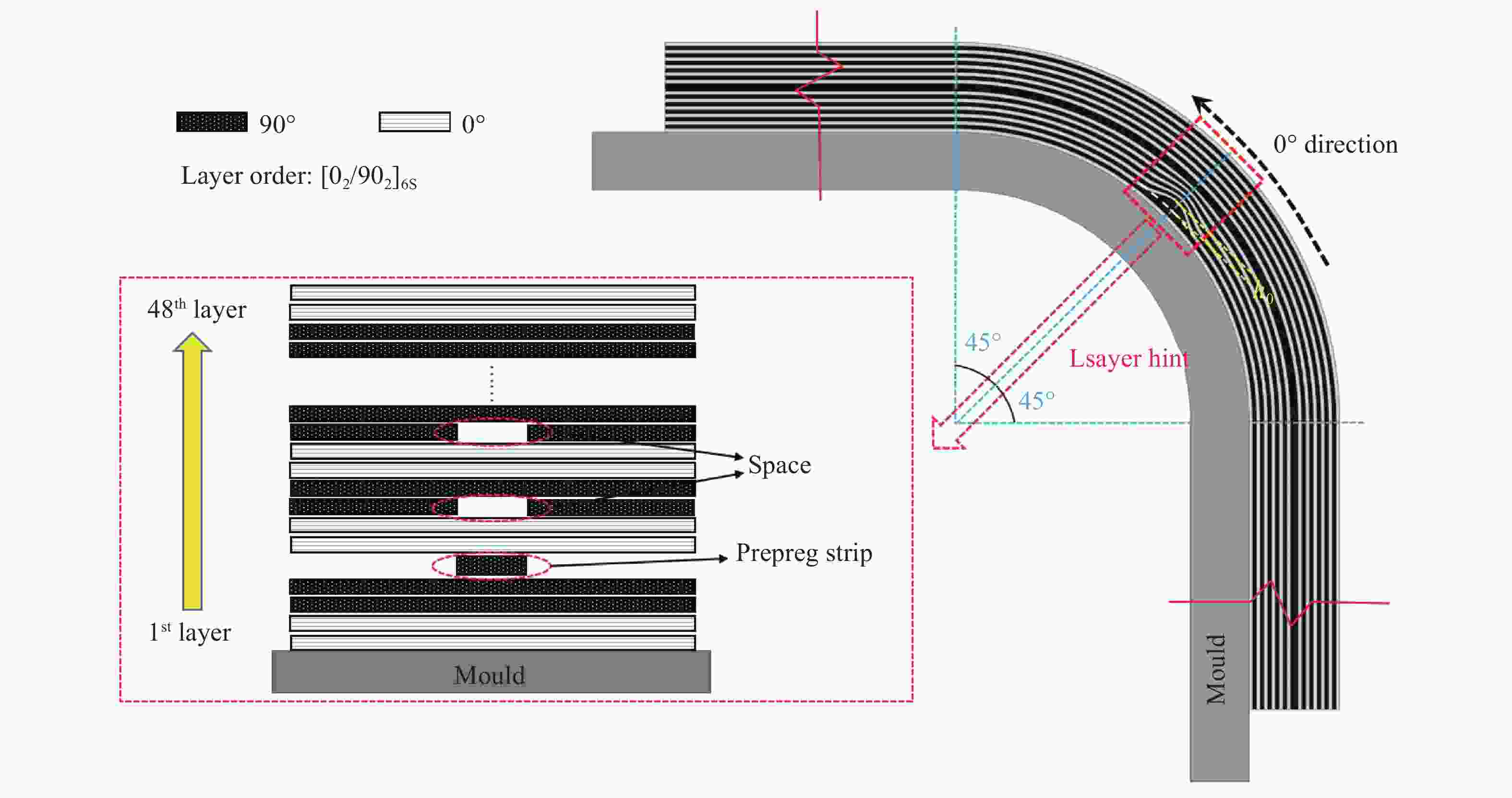
表 1 三组试样制备参数
Table 1. Parameters used for preparation of different samples
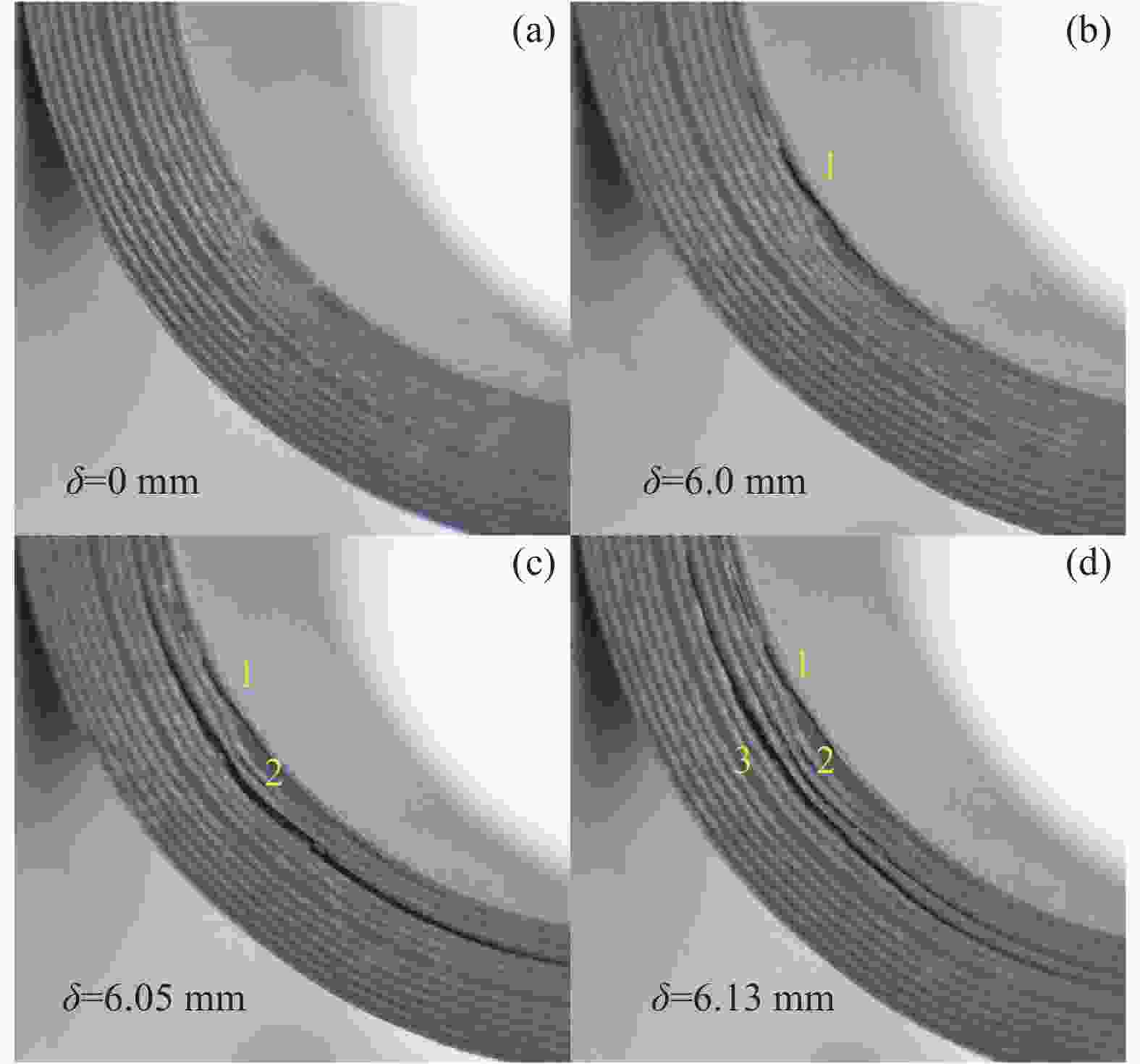
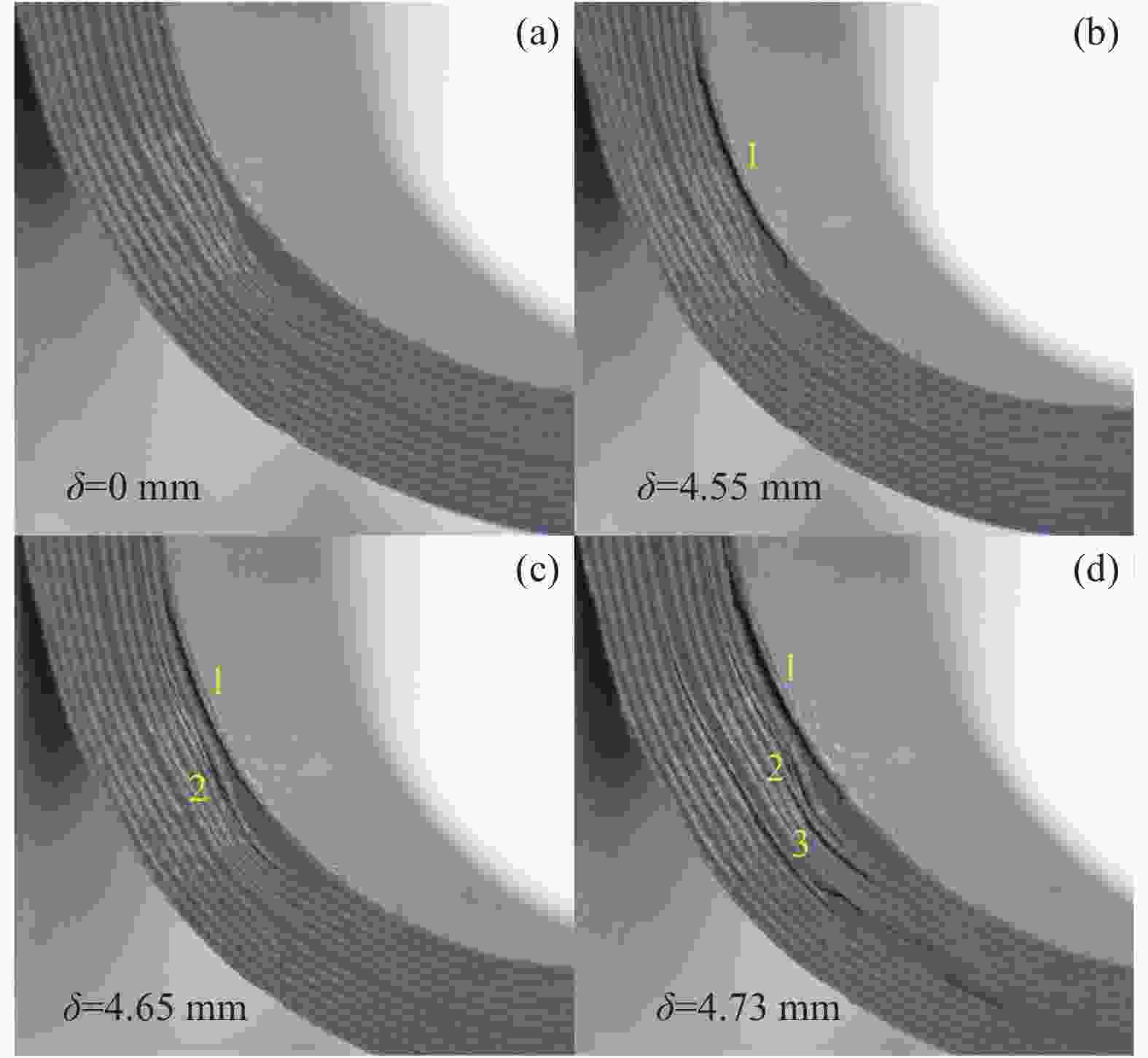
Set Quantity of stacked prepreg strips Quantity of space Location of spaces Height of wrinkle ${h_0}$/mm NW 0 0 No 0 SW 4 2 7,11 0.4 LW 8 4 7,11,15,19 0.8 表 2 HRC1单向层合板材料性能
Table 2. Material properties of HRC1 unidirectional laminate
$ {E}_{11} $/GPa $ {E}_{22} $/GPa $ {E}_{33} $/GPa ${\nu }_{12}$ ${\nu }_{13}$ ${\nu }_{23}$ $ {G}_{12} $/GPa $ {G}_{13} $/GPa $ {G}_{23} $/GPa 125 8.5 8.5 0.35 0.35 0.49 4.0 4.0 3.0 $ {X}_{\rm{T}} $/MPa $ {X}_{\rm{C}} $/MPa $ {Y}_{\rm{T}} $/MPa $ {Y}_{\rm{C}} $/MPa $ {Z}_{\rm{T}} $/MPa $ {Z}_{\rm{C}} $/MPa $ {S}_{12} $/MPa $ {S}_{13} $/MPa $ {S}_{23} $/MPa 1 700 1 000 45 180 40 160 75 75 70 Notes: E—Elastic modulus; ν—Poisson ratio; G—Shear modulus; X, Y, Z—Strength in different directions; T—Tensile; C—Compressive; S—Shear strength; 1—Direction of fiber; 2—Direction of matrix; 3——Thickness direction of layer. 表 3 含褶皱缺陷L型复合材料层合板弹性常数退化系数
Table 3. Degeneration coefficients of elastic constants of L-shaped composite laminates with wrinkle defects
Failure mode $ {E}_{11} $ $ {E}_{22} $ $ {E}_{33} $ ${\nu }_{12}$ ${\nu }_{13}$ ${\nu }_{23}$ $ {G}_{12} $ $ {G}_{13} $ $ {G}_{23} $ FV1 0.1 0.8 0.8 0.07 0.07 0.8 0.1 0.1 0.8 FV2 0.1 0.8 0.8 0.07 0.07 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 FV3 0.8 0.01 0.8 0.8 0.2 0.2 0.01 0.8 0.01 FV4 0.8 0.1 0.8 0.8 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.8 0.2 FV5 0.8 0.8 0.01 0.8 0.2 0.2 0.8 0.01 0.01 表 4 含褶皱缺陷L型复合材料层合板失效载荷、失效位移的模拟值与实验值对比
Table 4. Comparison of simulation and experimental failure load and failure displacement of L-shaped composite laminates with wrinkle defects
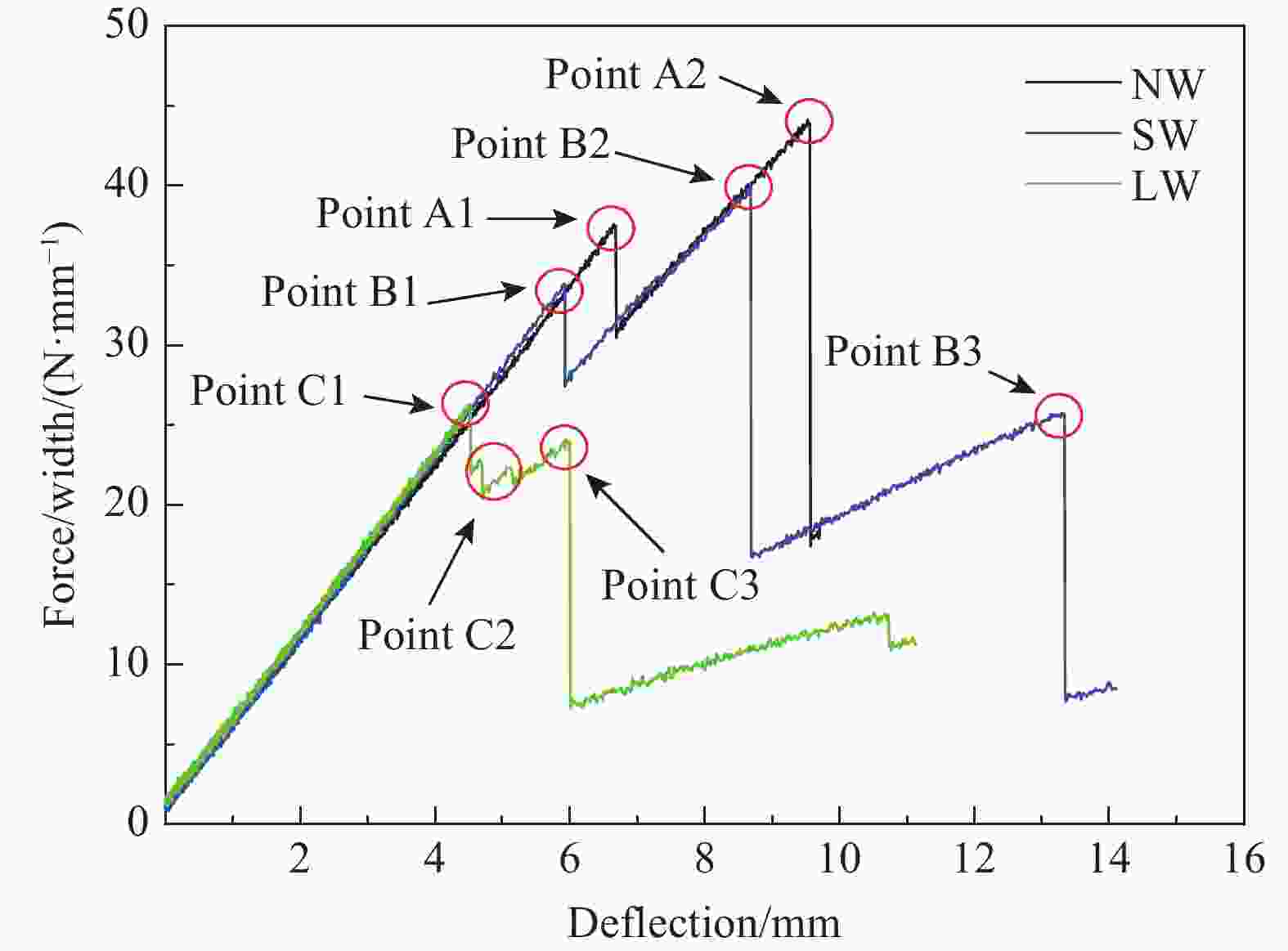
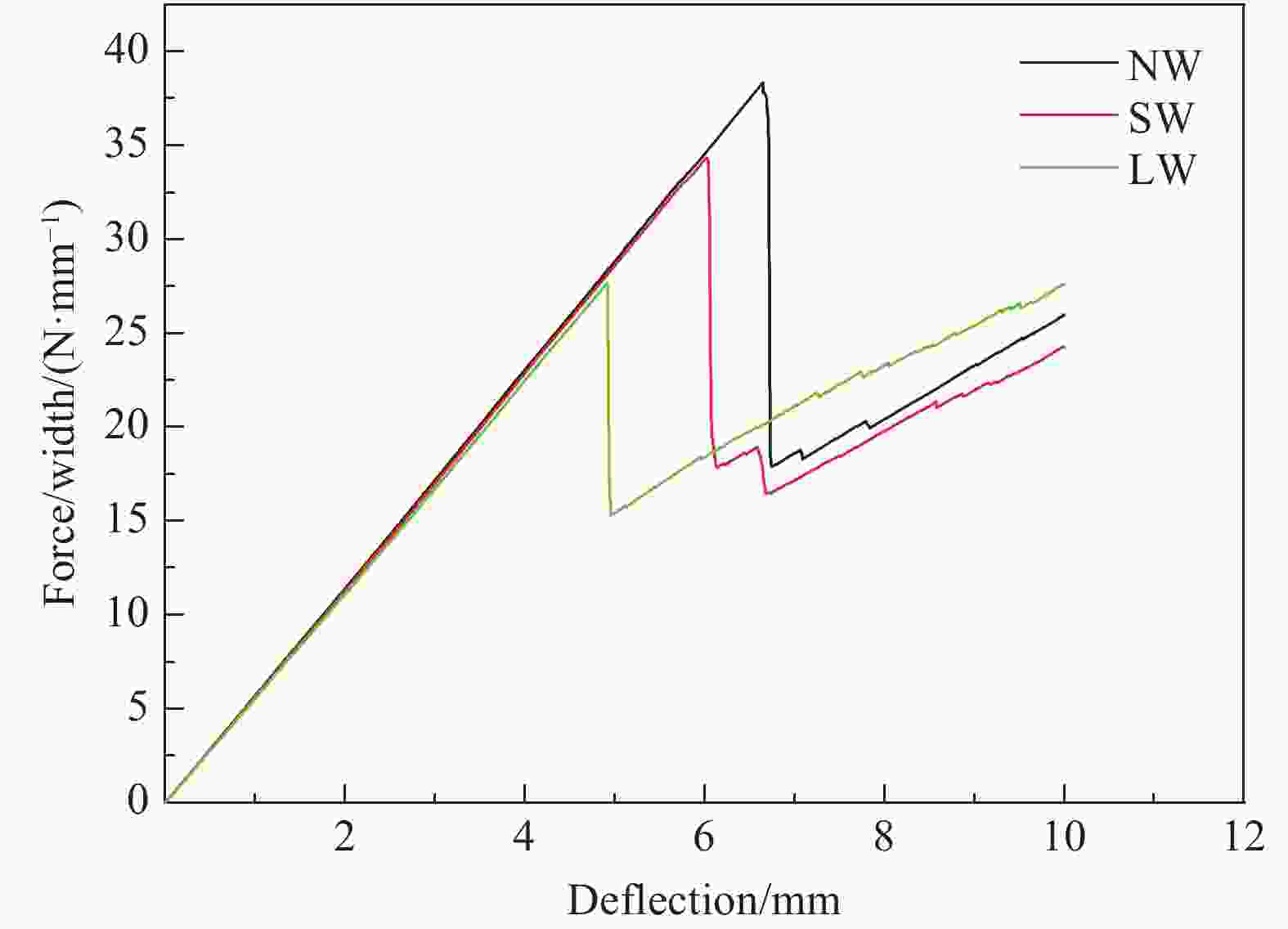
Index Failure load
(test data) /(N·m−1)Failure load
(FEA)/ (N·m−1)Error/
%Failure displacement
(test data)/mmFailure displacement
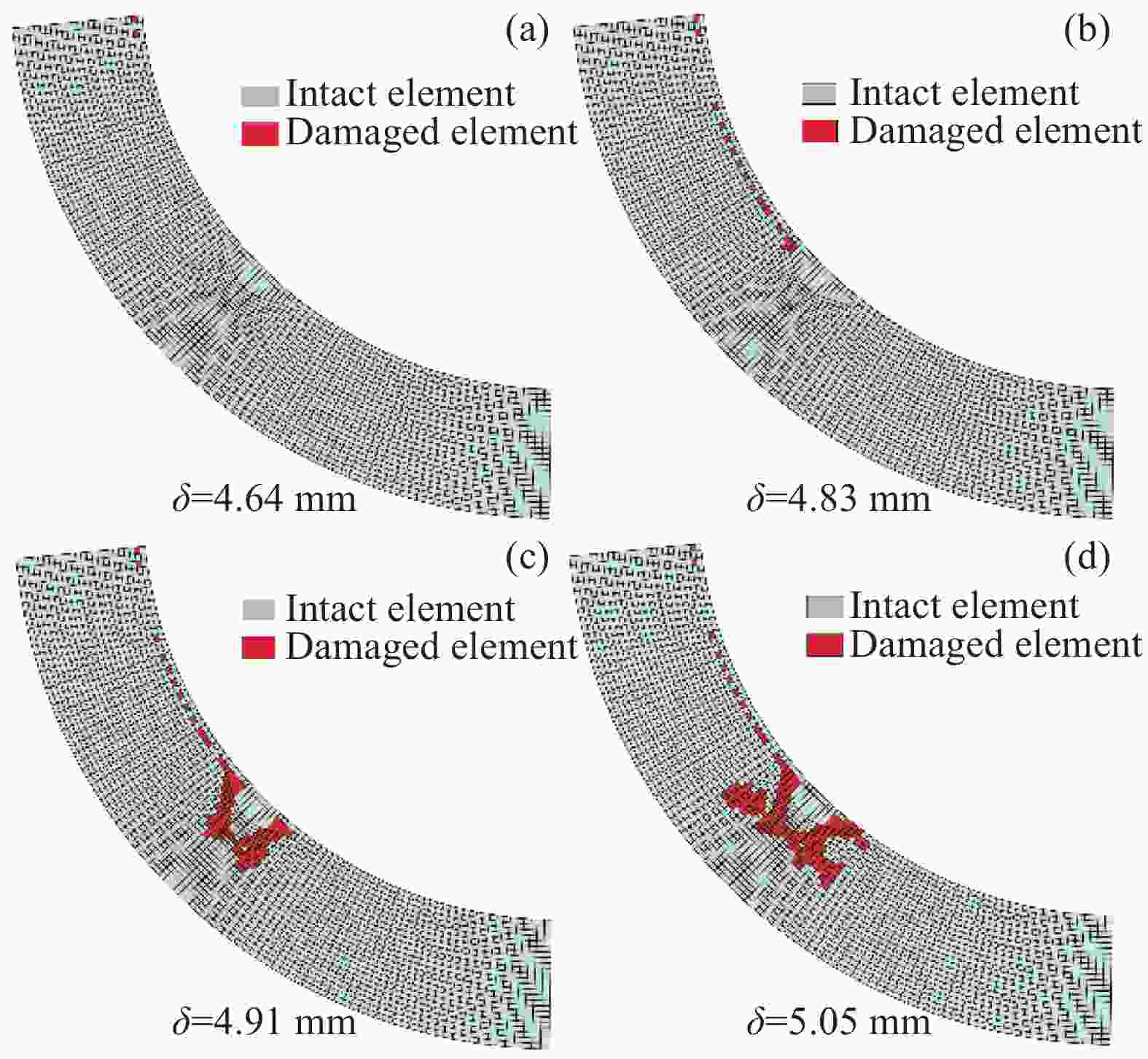
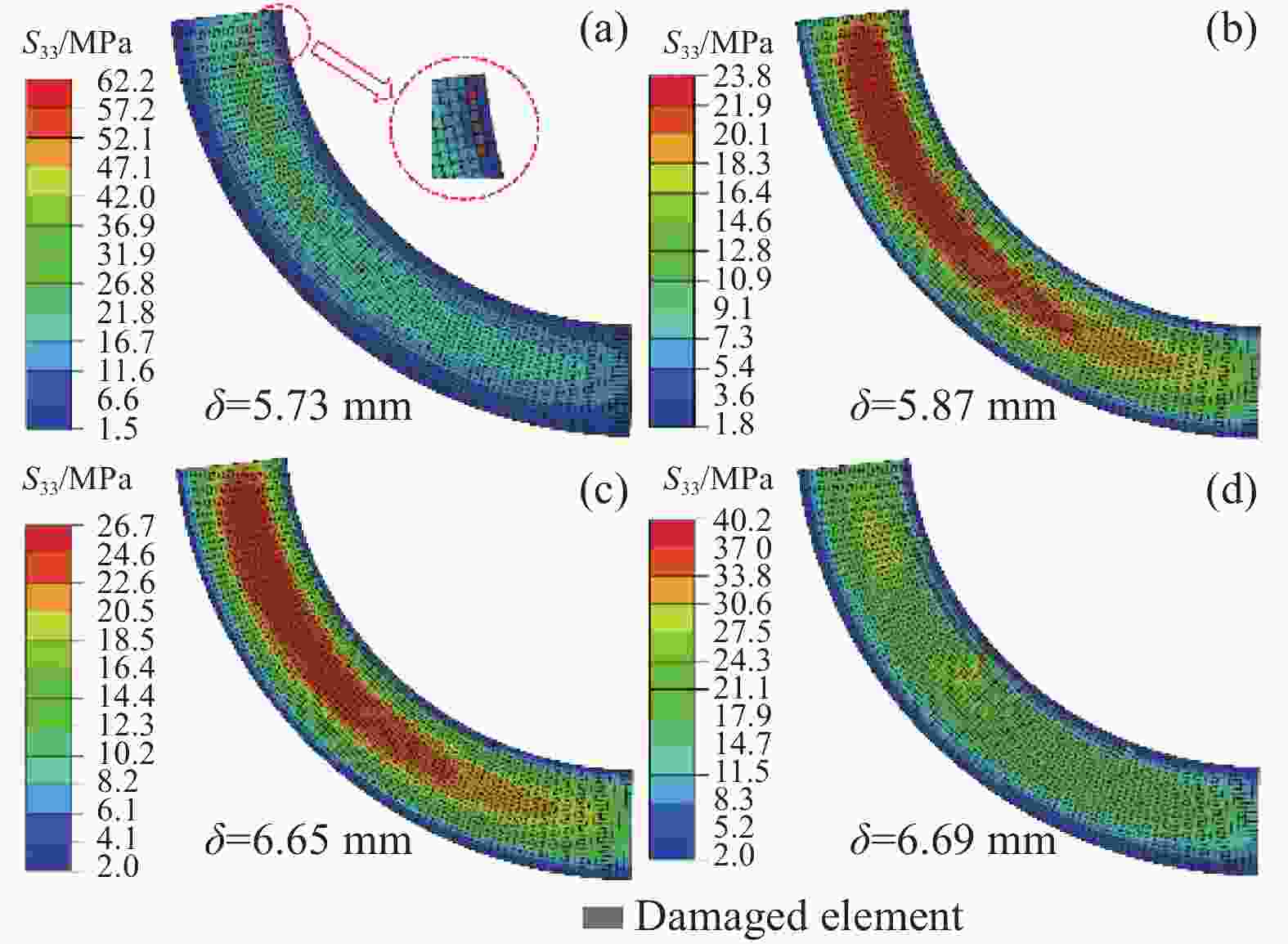
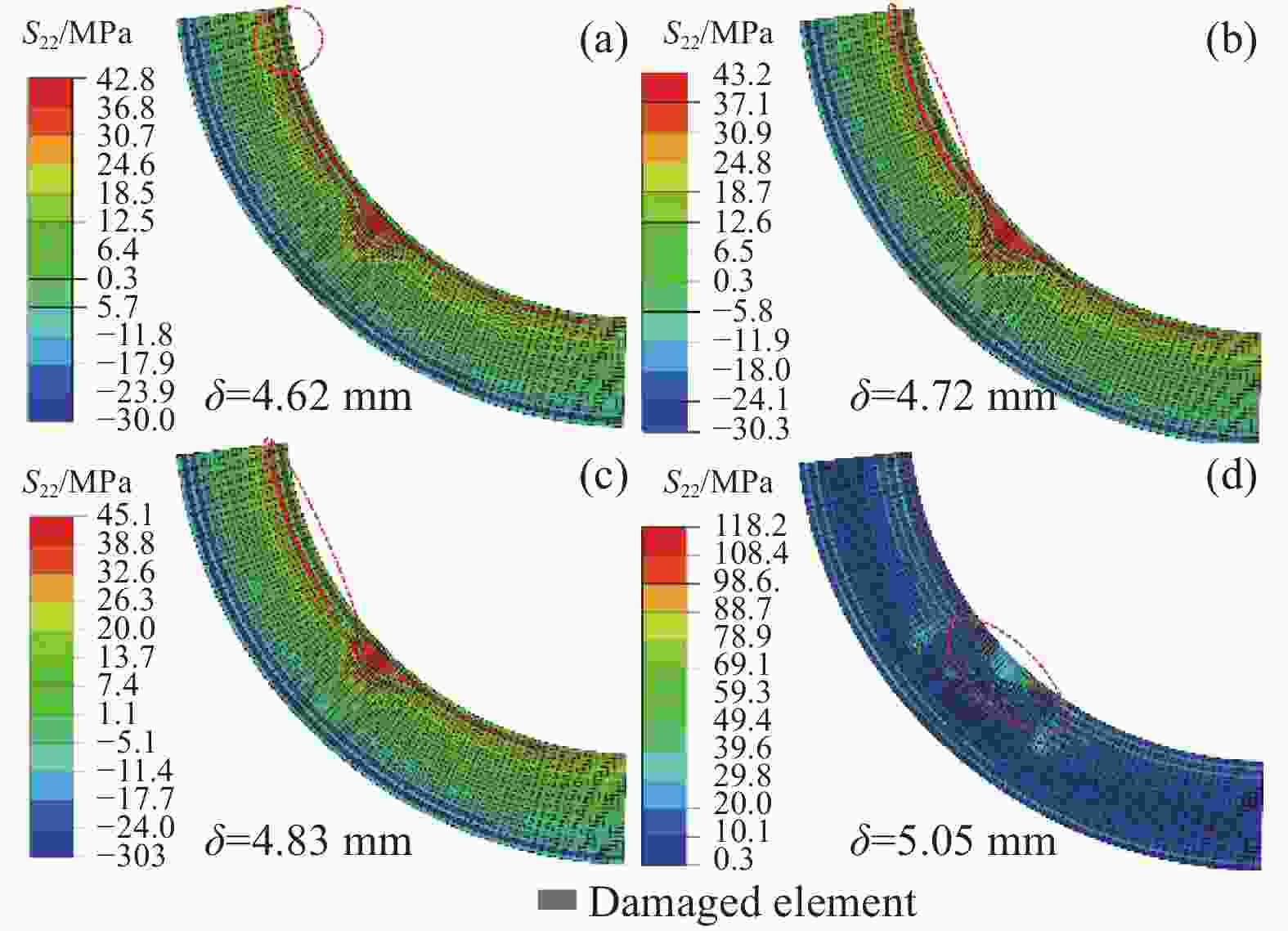
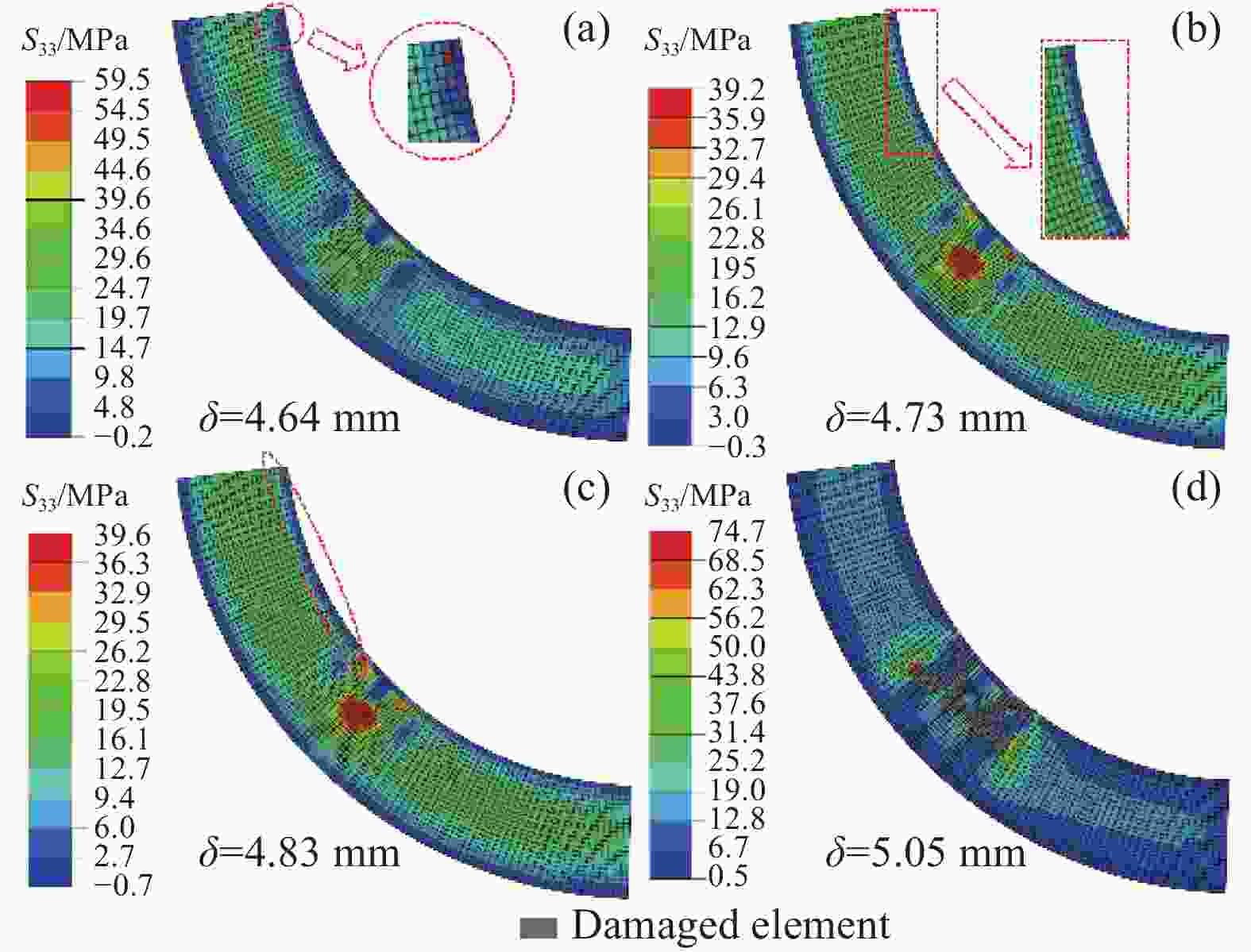
(FEA)/mmError/% NW 37.6 38.4 2.12 6.56 6.75 2.90 SW 33.8 34.4 1.78 5.95 6.13 3.03 LW 26.3 27.6 4.94 4.73 5.05 6.77 -
[1] KUGLER D, MOON T J. Identification of the most significant processing parameters on the development of fiber waviness in thin laminates[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2002,36(12):1451-1479. doi: 10.1177/0021998302036012575 [2] POTTER K D, CAMPBELL M, LANGER C, et al. The generation of geometrical deformations due to tool/part interaction in the manufacture of composite components[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2005,36(2):301-308. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(04)00150-2 [3] STECENKO T, PIGGOTT M. Fiber waviness and other mesostructures in filament wound materials[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,1997,16(18):1659-1674. doi: 10.1177/073168449701601803 [4] HYER M W, MAAS L C, FUCHS H P. The influence of layer waviness on the stress state in hydrostatically loaded cylinders[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,1988,7(8):601-613. [5] POTTER K, KHAN B, WISNOM M, et al. Variability, fibre waviness and misalignment in the determination of the properties of composite materials and structures[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2008,39(9):1343-1354. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.04.016 [6] ALTMANN A, GESELL P, DRECHSLER K. Strength prediction of ply waviness in composite materials considering matrix dominated effects[J]. Composite Structures,2015,127:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.02.024 [7] MIZUKAMI K, MIZUTANI Y, TODOROKI A, et al. Detection of in-plane and out-of-plane fiber waviness in unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced composites using eddy current testing[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2016,86:84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.09.041 [8] SUTCLIFFE M P F, LEMANSKI S L, SCOTT A E. Measurement of fibre waviness in industrial composite components[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2012,72(16):2016-2023. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.09.001 [9] LEONG M, OVERGAARD L C T, THOMSEN O T, et al. Investigation of failure mechanisms in GFRP sandwich structures with face sheet wrinkle defects used for wind turbine blades[J]. Composite Structures,2012,94(2):768-778. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.09.012 [10] WILHELMSSON D, GUTKIN R, EDGREN F, et al. An experimental study of fibre waviness and its effects on compressive properties of unidirectional NCF composites[J]. Compo-sites Part A: Applied Scienceand Manufacturing,2018,107:665-674. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.02.013 [11] 朱俊, 吴维清, 欧阳佳斯, 等. 面外波纹对复合材料层合板弹性性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(9):1981-1988.ZHU Jun, WU Weiqing, OUYANG Jiasi, et al. Influence of out-of-plane waviness on elastic properties of composite laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Composite Sinica,2016,33(9):1981-1988(in Chinese). [12] 曾文浩, 何鹏, 刘菲, 等. 含纤维波纹缺陷复合材料层合板的损伤分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(2):330-336.ZENG Wenhao, HE Peng, LIU Fei, et al. Damage analysis for composite laminate with fiber waviness[J]. Acta Materiae Composite Sinica,2019,36(2):330-336(in Chinese). [13] HAYMAN B, BERGGREEN C C, PETTERSSON R. The influence of face sheet wrinkle defects on the performance of FRP sandwich structures[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2005: 393-402. [14] MUKHOPADHYAY S, JONES M I, HALLETT S R. Compressive failure of laminates containing an embedded wrinkle: Experimental and numerical study[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,73:132-142. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.03.012 [15] EL-HAJJAR R F, PETERSEN D R. Gaussian function characterization of unnotched tension behavior in a carbon/epoxy composite containing localized fiber waviness[J]. Composite Structures,2011,93(9):2400-2408. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.03.029 [16] 何成智, 马小军, 李阳阳, 等. 褶皱对玻璃钢疲劳性能的影响[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2017(10):54-58.HE Chengzhi, MA Xiaojun, LI Yangyang, et al. Effect of wrinkles on fatigue properties of FRP[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites,2017(10):54-58(in Chinese). [17] BLOOM L D, WANG J, POTTER K D. Damage progression and defect sensitivity: An experimental study of representative wrinkles in tension[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2013,45(1):449-458. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.05.021 [18] WANG J, POTTER K, HAZRA K, et al. Experimental fabrication and characterization of out-of-plane fiber waviness in continuous fiber-reinforced composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2012,46(17):2041-2053. doi: 10.1177/0021998311429877 [19] DAVIDSON P, WAAS A M. The effects of defects on the compressive response of thick carbon composites: An experimental and computational study[J]. Composite Structures,2017,176:582-596. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.05.046 [20] LEMANSKI S L, WANG J, SUTCLIFFE M P F, et al. Modelling failure of composite specimens with defects under compression loading[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2013,48:26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.12.007 [21] XIE N, SMITH R A, MUKHOPADHYAY S, et al. A numerical study on the influence of composite wrinkle defect geometry on compressive strength[J]. Materials <italic>&</italic> Design,2018,140:7-20. [22] HALLANDER P, AKERMO M, MATTEI C, et al. An experimental study of mechanisms behind wrinkle development during forming of composite laminates[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2013,50:54-64. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.03.013 [23] DODWELL T J, BUTLER R, HUNT G W. Out-of-plane ply wrinkling defects during consolidation over an external radius[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2014,105:151-159. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.10.007 [24] LIGHTFOOT J S, WISNOM M R, POTTER K. A new mechanism for the formation of ply wrinkles due to shear between plies[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2013,49:139-147. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.03.002 [25] JOHNSON K J, BUTLER R, LOUKAIDES E G, et al. Stacking sequence selection for defect-free forming of unidirectional ply laminates[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,171:34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.11.048 [26] GUILLAUME S, YURI N, ANDREW M, et al. Mesh morphing methodology for strength predictions in composites[J]. Composite Structures,2016,140:612-620. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.12.021 [27] FEIH S, SHERCLIFF H R. Composite failure prediction of single-L joint structures under bending[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science <italic>& </italic>Manufacturing,2005,36(3):381-395. [28] CAO D, DUAN Q, HU H, et al. Computational investigation of both intra-laminar matrix cracking and inter-laminar delamination of curved composite components with cohesive elements[J]. Composite Structures,2018,192:300-309. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.072 [29] WIMMER G, KITZMÜLLER W, PINTER G, et al. Computational and experimental investigation of delamination in L-shaped laminated composite components[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,2009,76(18):2810-2820. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2009.06.007 [30] BURAK GÖZLÜKLÜ, COKER D. Modeling of the dynamic delamination of L-shaped unidirectional laminated composites[J]. Composite Structures,2012,94(4):1430-1442. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.11.015 [31] WISNOM M R. 3-D finite element analysis of curved beams in bending[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1996,30(11):1178-1190. doi: 10.1177/002199839603001101 [32] 王跃全, 童明波, 朱书华. 三维复合材料层合板渐进损伤非线性分析模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2009, 26(5):159-166. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2009.05.026WANG Yuequan, TONG Mingbo, ZHU Shuhua. 3D nonlinear progressive damage analysis model for composite laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Composite Sinica,2009,26(5):159-166(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2009.05.026 [33] ZHOU S, WANG Z, ZHOU J, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on bolted composite joint made by vacuum assisted resin injection[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2013,45(1):1620-1628. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.08.025 [34] 吴义韬, 姚卫星, 沈浩杰. 复合材料宏观强度准则预测能力分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(3):864-873.WU Yitao, YAO Weixing, SHEN Haojie. Prediction ability analysis of macroscopic strength criteria for composites[J]. Acta Materiae Composite Sinica,2015,32(3):864-873(in Chinese). [35] YU G C, WU L Z, MA L, et al. Low velocity impact of carbon fiber aluminum laminates[J]. Composite Structures,2015,119:757-766. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.09.054 [36] SU Z C, TAY T E, RIDHA M, et al. Progressive damage modeling of open-hole composite laminates under compression[J]. Composite Structures,2015,122:507-517. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.12.022 -





 下载:
下载: