Effect of hygrothermal environment on vibration characteristic of composite honeycomb structure
-
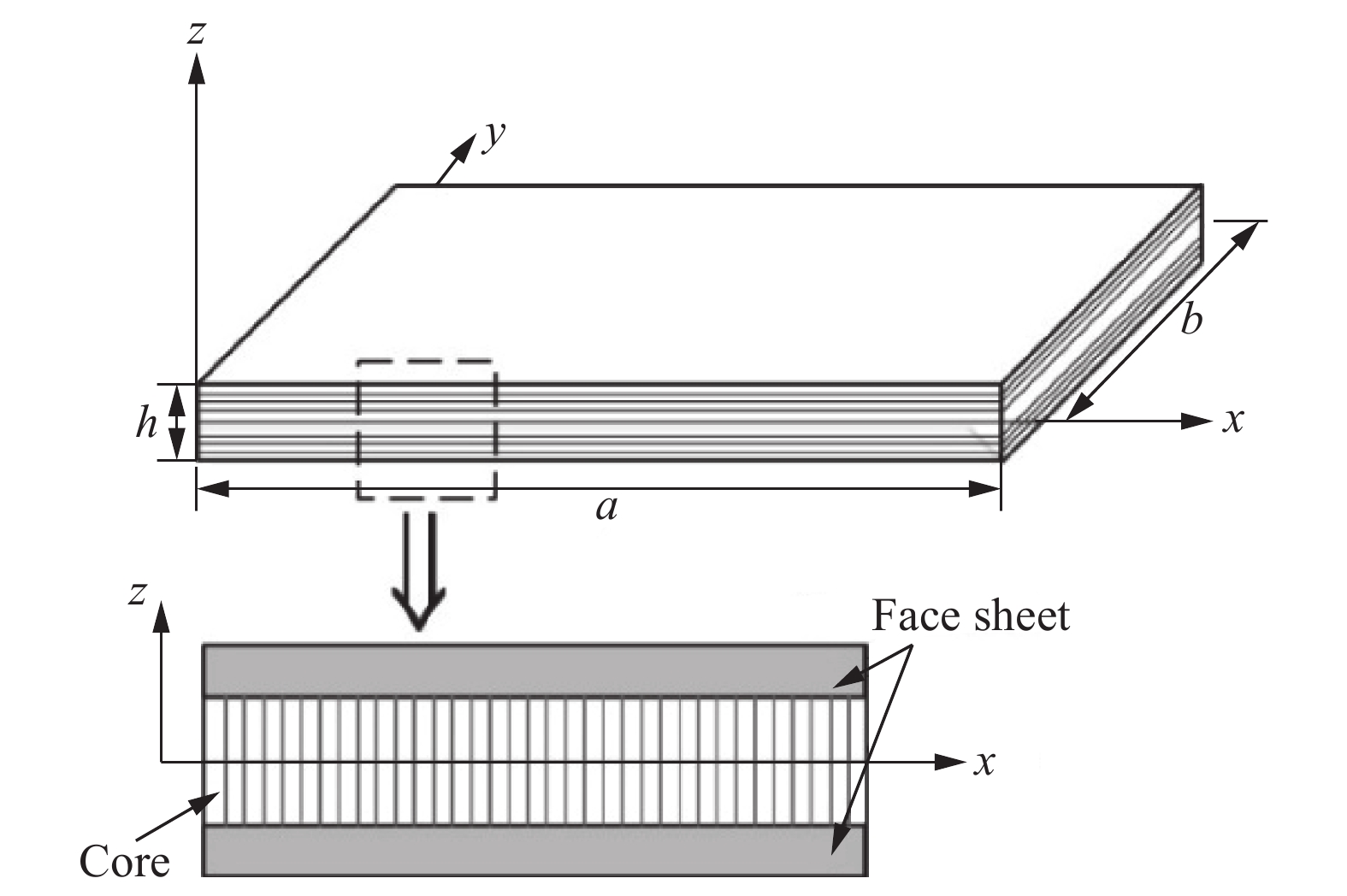
摘要: 为了研究复合材料蜂窝板在湿热环境下的振动特性,针对由碳纤维/双马来酰亚胺复合材料层合板和Nomex芯层复合而成的蜂窝板进行了不同温湿度下固有频率的数值分析。基于分段剪切变形理论,分别考虑复合材料蜂窝薄板和厚板两种情况,利用湿度与温度的等效性,求解了复合材料蜂窝板的振动特征方程。利用有限元软件ABAQUS,建立了四端固支的复合材料蜂窝板精细化模型。分别讨论了温度、湿度、温湿度联合作用对复合材料蜂窝薄板和厚板固有频率的影响。结果表明:相比于温度的升高,复合材料蜂窝板固有频率对吸湿量的增加更为敏感;相同的湿热环境下,复合材料蜂窝厚板结构的固有频率比薄板结构大,且阶次越高,固有频率上升的幅度越大;温湿度的联合作用比它们单独作用的叠加对复合材料蜂窝板固有频率的影响更大,且在复合材料蜂窝薄板中更加明显。Abstract: In order to study the vibration characteristic of composite honeycomb structure under hygrothermal condition, the natural frequencies of honeycomb structure composed by carbon fiber/bismaleimide composite laminate and Nomex core were numerically analyzed under different temperatures and humidities. Based on the piecewise shear deformation theory, considering the honeycomb thin plate and thick plate respectively, the eigenvibration equation of composite honeycomb structure was solved by finite element method using the equivalence of temperature and humidity. A detailed model of composite honeycomb structure with four-edge clamped support was established by using finite element software ABAQUS. The effects of temperature, humidity, and combined temperature and humidity on the vibration characteristic of composite honeycomb thin plate and thick plate were discussed respectively. The numerical results show that compared with the increase of temperature, the natural frequencies of honeycomb structure are more sensitive to the increase of moisture concentration. Under the same humid and thermal environment, the natural frequency of the thick plate structure is larger than that of the thin plate, and the higher order of natural frequency, the greater the increase of natural frequency. The coupling effect of temperature and humidity has a greater effect on the natural frequency of composite honeycomb structure than the superposition of temperature and humidity when they act alone, and this effect is more obvious for the composite honeycomb thin plate.
-
表 1 复合材料蜂窝板前三阶固有频率
Table 1. The first three natural frequencies of composite honeycomb plate
Modal Natural frequency/Hz Error/% Reference [19] FEM 1 313.92 324.64 3.4 2 1 107.33 1 072.60 3.1 3 1 367.39 1 329.30 2.8 Note: FEM—Numerical results of this work. 表 2 热环境下复合材料夹芯板前三阶固有频率(Hz)
Table 2. The first three natural frequencies of composite sandwich plate in thermal environment(Hz)
Modal T/K 273 298 323 348 1 Reference [15] 235.09 204.32 168.00 121.26 FEM 227.78 195.92 157.65 110.38 Error/% 3.1 4.1 6.2 8.9 2 Reference [15] 397.25 361.73 322.32 272.78 FEM 387.25 350.88 310.06 262.95 Error/% 2.5 3.0 3.8 3.6 3 Reference [15] 443.16 394.62 339.22 277.37 FEM 439.59 391.08 334.93 267.22 Error/% 0.8 0.9 1.3 3.7 Note: T—Kelvin temperature. 表 3 碳纤维/双马来酰亚胺树脂复合材料层合板的材料性能参数
Table 3. Material performance parameters of carbon fiber/bismaleimide resin composite laminate
E1/GPa E2/GPa E3/GPa μ12 μ13 μ23 G12/GPa G13/GPa G23/GPa ρ/(kg·m−3) 150 8.8 8.8 0.22 0.22 0.3 4.47 4.47 1.13 1 570 Notes: E1, E2, E3—Young's modulus; μ12, μ13, μ23—Poisson's ratio; G12,G13,G23—Shear modulus; ρ—Density. 表 4 碳纤维/双马来酰亚胺复合材料面板-Nomex芯层蜂窝板375 K下的前三阶固有频率值比300 K下的降低比率
Table 4. Decrease ratios of the first three natural frequencies of carbon fiber/bismaleimide composite plate-Nomex honeycomb plate under 375 K compared with 300 K
Modal Thin plate (λ=5.81) Thick plate (λ=3.21) 1 1.46% 0.81% 2 1.48% 0.82% 3 1.48% 0.81% 表 5 碳纤维/双马来酰亚胺复合材料面板-Nomex芯层蜂窝板0.75%吸湿量时的前三阶固有频率值比0%吸湿量时的降低比率
Table 5. Decrease ratios of the first three natural frequencies of carbon fiber/bismaleimide composite plate-Nomex honeycomb plate under 0.75% moisture content compared with 0% moisture content
Modal Thin plate(λ=5.81) Thick plate(λ=3.21) 1 1.58% 0.83% 2 1.61% 0.84% 3 1.62% 0.84% 表 6 湿热环境下碳纤维/双马来酰亚胺复合材料面板-Nomex芯层蜂窝薄/厚板前三阶固有频率
Table 6. The first three natural frequencies of carbon fiber/bismaleimide composite plate-Nomex honeycomb thin/thick plate under hygrothermal condition
Environment condition Thick plate (λ=3.21) Thin plate (λ=5.81) T/K C/% Thermal environment 300 0 7 866.3 5 796.8 8 460.9 6 209.4 9 391.5 6 878.5 325 0 7 848.1 5 771.0 8 441.4 6 181.4 9 370.1 6 847.4 350 0 7 825.1 5 742.5 8 416.4 6 150.6 9 342.2 6 813.5 375 0 7 802.2 5 712.0 8 391.8 6 117.6 9 315.0 6 776.8 Humid environment 300 0.25 7 844.5 5 766.2 8 437.0 6 175.8 9 364.6 6 840.8 300 0.5 7 823.6 5 735.9 8 414.5 6 142.8 9 339.7 6 804.0 300 0.75 7 801.2 5 705.4 8 390.2 6 109.6 9 312.6 6 766.9 Hygrothermal condition 325 0.25 7 789.6 5 692.8 8 377.8 6 096.2 9 298.8 6 752.5 350 0.5 7 738.2 5 621.9 8 322.3 6 019.4 9 237.3 6 667.1 375 0.75 7 687.0 5 549.5 8 267.0 5 941.0 9 176.0 6 580.0 Note: C —Moisture concentration. 表 7 碳纤维/双马来酰亚胺复合材料面板-Nomex芯层蜂窝板在375 K、C=0.75%下的前三阶固有频率较300 K、 C=0%时的下降比率
Table 7. Decrease ratios of the first three natural frequencies of carbon fiber/bismaleimide composite plate-Nomex honeycomb plate under 375 K, C=0.75% condition compared with 300 K, C=0% condition
Modal Thin plate (λ=5.81) Thick plate (λ=3.21) 1 4.27% 2.28% 2 4.32% 2.29% 3 4.34% 2.29% -
[1] 杜善义. 先进复合材料与航空航天[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(1):1-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001DU Shanyi. Advanced composite materials and aerospace engineering[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2007,24(1):1-12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001 [2] 马立敏, 张嘉振, 岳广全, 等. 复合材料在新一代大型民用飞机中的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(2):317-322.MA Limin, ZHANG Jiazhen, YUE Guangquan, et al. Application of composites in new generation of large civil aircraft[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(2):317-322(in Chinese). [3] 中国民用航空局. 运输类飞机适航标准: CCAR-25-R4[S]. 北京: 中国民航出版社, 2016.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Airworthiness standards for transport aircraft: CCAR-25-R4[S]. Beijing: China Civil Aviation Publishing House, 2016(in Chinese). [4] LIU Q L, ZHAO Y. Prediction of natural frequencies of a sandwich panel using thick plate theory[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2001,3(4):289-309. doi: 10.1106/86XW-ER9M-N0Q6-QWU1 [5] LIU Q L, ZHAO Y, ESLAMI H. Effect of soft honeycomb core on flexural vibration of sandwich panel[C]//46th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. Austin: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2005. [6] LIU Q L, ZHAO Y. Effect of soft honeycomb core on flexural vibration of sandwich panel using low order and high order shear deformation models[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures And Materials,2007,9(1):95-108. doi: 10.1177/1099636207070588 [7] TANIMOTO T, NISHIWAKI T, SHIOMI T, et al. A numerical modeling for eigenvibration analysis of honeycomb sandwich panels[J]. Composite Interfaces,2001,6(8):393-402. [8] ZHU K G, CHEN M J, LU Q H, et al. Debonding detection of honeycomb sandwich structures using frequency response functions[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,2014,333(21):5299-5311. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2014.05.023 [9] BURLAYENKO V N, SADOWSKI T. Influence of skin/core debonding on free vibration behavior of foam and honeycomb cored sandwich plates[J]. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics,2010,45(10):959-968. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnonlinmec.2009.07.002 [10] YEO E S Y, WANG J, MIRABELLA L, et al. Effect of humidity and thermal cycling on carbon-epoxy skin/aramid honeycomb structure[J]. Materials Science Forum,2010,654-656:2600-2603. [11] CHEN Z, YAN N, DENG J, et al. Influence of environmental humidity and temperature on the creep behavior of sandwich panel[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2017,134:216-223. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.10.013 [12] PADHI A, PANDIT M K. Bending and free vibration response of sandwich laminate under hygrothermal load using improved zigzag theory[J]. Journal of Strain Analysis,2017,52(5):288-297. doi: 10.1177/0309324717714710 [13] 李向阳, 蒋莉, 张志民. 湿热环境对损伤分层复合材料夹层板屈曲性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2000, 17(4):110-113. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.04.023LI Xiangyang, JIANG Li, ZHANG Zhimin. Hygrothermal effect on buckling of composite sandwich with delamination[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2000,17(4):110-113(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.04.023 [14] LI X Y, YU K P, HAN J Y, et al. A piecewise shear deformation theory for free vibration of composite and sandwich panels[J]. Composite Structures,2015,124:111-119. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.01.007 [15] LI X Y, YU K P. Vibration and acoustic responses of composite and sandwich panels under thermal environment[J]. Composite Structures,2015,131:1040-1049. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.06.037 [16] ZHAO R, YU K P, HULBERT G M, et al. Piecewise shear deformation theory and finite element formulation for vibration analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates in thermal environments[J]. Composite Structures,2017,160:1060-1083. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.10.103 [17] 胡建平, 蔡吉喆, 肇研, 等. 湿热环境对蜂窝夹层复合材料性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2010, 20(11):43-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2010.11.011HU Jianping, CAI Jizhe, ZHAO Yan, et al. Effects of hygrothermal environment on properties of nomex sandwich composite[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2010,20(11):43-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2010.11.011 [18] 白云鹤, 于开平, 赵锐, 等. 高温与脱粘对复合材料蜂窝板模态特性影响的试验[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(4):885-895.BAI Yunhe, YU Kaiping, ZHAO Rui, et al. Experimental investigation on the effects of the high temperature and debonding on the modal characteristics of the composite honeycomb structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(4):885-895(in Chinese). [19] 东巳宙. 高温环境下复合材料层合板与蜂窝板力学性能分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.DONG Sizhou. The analysis of mechanical proper-ties on composite laminated plate and honeycomb plate under the environment of high temperature[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [20] BAI Y H, YU K P, ZHAO J, et al. Experimental and simulation investigate on of temperature effects on modal characteristics of composite honeycomb structure[J]. Composite Structures,2018,201:816-827. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.06.106 [21] JIANG D, ZHANG D H, FEI Q G, et al. An approach on identification of equivalent properties of honeycomb core using experimental modal data[J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design,2014,90:84-92. doi: 10.1016/j.finel.2014.06.006 [22] 刘健, 周春燕. 长厚比对正六边形铝蜂窝夹层板等效板模型动力学计算精度的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(8):1838-1847.LIU Jian, ZHOU Chunyan. Influence of length-thickness ratio on dynamics calculation accuracy of equivalent plate model of hexagonal aluminum honeycomb sandwich plate[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(8):1838-1847(in Chinese). [23] 韩敬永, 于开平, 宋海洋, 等. 整流罩声振试验蜂窝夹层板建模方法[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2015, 35(5):65-68.HAN Jingyong, YU Kaiping, SONG Haiyang, et al. Study on the modeling methods of honeycomb sandwich panels based on fairing vibroacoustic experiments[J]. Noise and Vibration Control,2015,35(5):65-68(in Chinese). [24] 黄克智, 夏之熙, 薛明德, 等. 板壳理论[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1987.HUANG Kezhi, XIA Zhixi, XUE Mingde, et al. Theory of plate and shell[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1987(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: