Effect of different enzyme modification on properties of wheat straw fiber/high density polyethylene composites
-
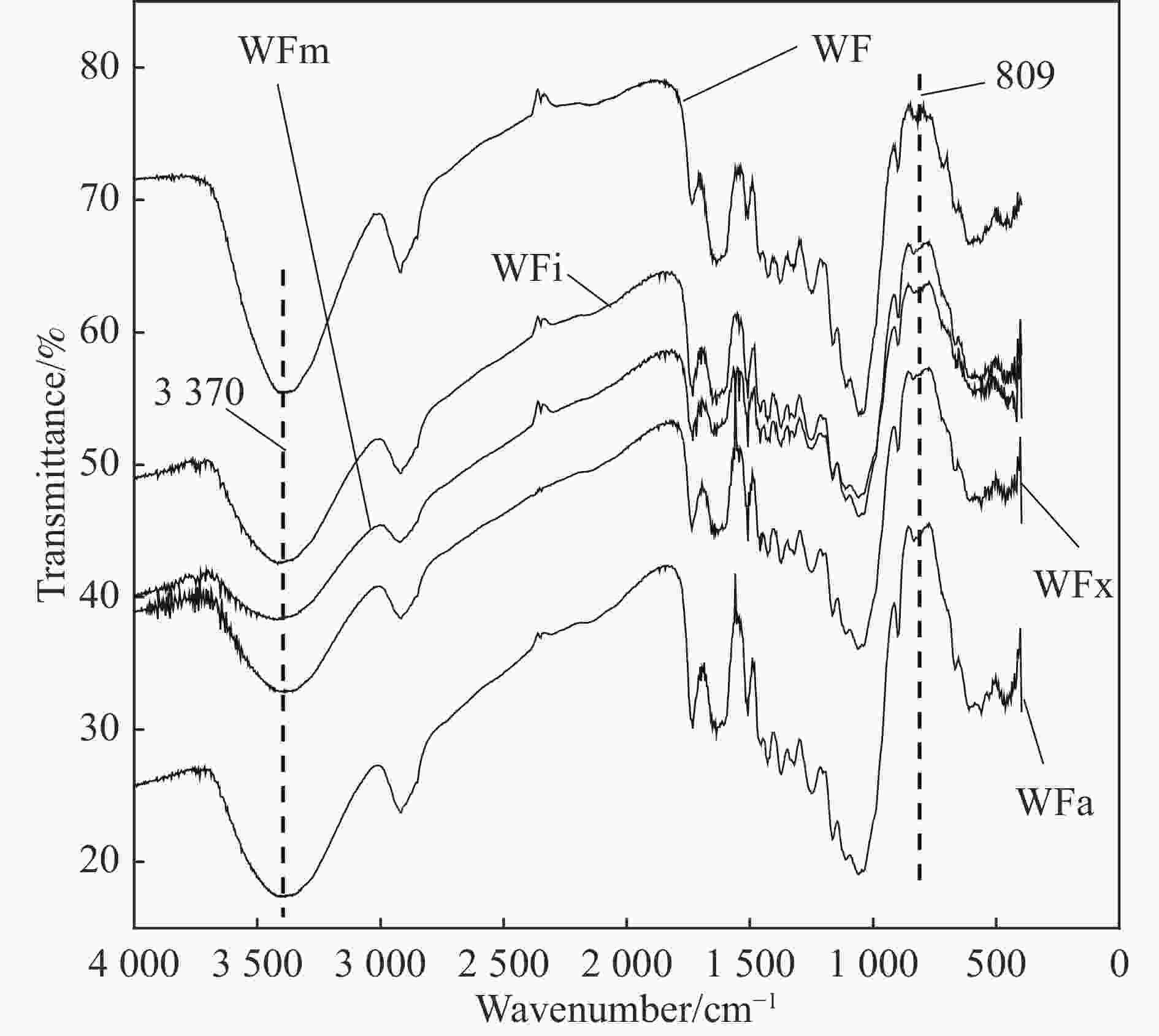
摘要: 以麦秸秆纤维(WF)和高密度聚乙烯(HDPE)为原料,利用混炼和注塑成型的方法制备WF/HDPE复合材料。考察了木聚糖酶、漆酶、脂肪酶、木聚糖酶与脂肪酶复合处理对WF/HDPE复合材料力学性能、热稳定性、吸水率的影响,通过FTIR分析了酶处理前后的WF化学官能团变化,利用SEM观察了酶处理前后的WF表面形貌和WF/HDPE复合材料拉伸断裂面。结果表明:当WF/HDPE复合材料经木聚糖酶与脂肪酶复合处理后,吸水率最低且WF/HDPE复合材料的力学性能最好,其拉伸强度、弯曲强度、弯曲模量分别达到23.4 MPa、34.0 MPa、1 944.6 MPa;TG结果表明WF/HDPE的热分解过程分两个部分:WF的分解过程和HDPE的分解过程,酶能有效提高WF/HDPE的热稳定性;FTIR显示经酶处理后,WF的羟基振动峰微弱减小,在1 706~1 290 cm−1处光谱上出现部分小峰,SiO2的振动峰变得平缓;SEM显示经酶处理后,WF表面变粗糙,WF与HDPE结合紧密,其中经木聚糖酶和脂肪酶共同处理后两者界面结合性能最好。Abstract: WF/HDPE composites were prepared from wheat straw fiber (WF) and high density polyethylene (HDPE) by mixing and injection moulding. The effects of xylanase, laccase, lipase, xylanase and lipase on the mechanical properties, thermal stability and water absorption of WF/HDPE composites were investigated. The changes of chemical functional groups of WF before and after enzyme treatment were analyzed by FTIR. The surface morphologies of WF and the tensile fracture surface of WF/HDPE composites before and after enzymatic treatment were observed by SEM. The results show that WF/HDPE composites treated with xylanase and lipase have the lowest water absorption and the best mechanical properties. The tensile strength, flexural strength and flexural modulus of WF/HDPE composites reach 23.4 MPa, 34.0 MPa and 1 944.6 MPa, respectively. TG results show that the thermal decomposition process of WF/HDPE is divided into two parts: WF decomposition process and HDPE decomposition process, and the thermal stability of WF/HDPE composites can be effectively improved by enzyme. After treatment, the hydroxyl vibration peak of WF decreases, and some small peaks appeare in the spectrum at 1 706-1 290 cm−1, and the vibration peak of SiO2 becomes gentle. SEM shows that the surface of WF becomes rough after enzyme treatment, and WF and HDPE are closely bound, among which the interface bonding performance of WF and HDPE treated by xylanase and lipase is the best.
-
表 1 不同生物酶处理的麦秸秆纤维/高密度聚乙烯(WF/HDPE)复合材料原材料配方分组
Table 1. Prescription of wheat straw fiber/high density polyethylene(WF/HDPE) composition treated with different enzymes
No. Enzyme quantity/g Enhancer content/wt% Matrix content/wt% Xylanase Lipase Laccase WF HDPE WF/HDPE − − − 30 70 WFx/HDPE 0.35 − − 30 70 WFi/HDPE − 0.7 − 30 70 WFa/HDPE − − 0.35 30 70 WFm/HDPE 0.35 0.7 − 30 70 Notes: WF—Untreated WF; WFx—Treated by xylanase; WFi—Treated by lipase; WFa—Treated by laccase; WFm—Treated by xylanase and lipase. 表 2 处理、未处理WF/HDPE复合材料及HDPE样品的热稳定性
Table 2. Thermal stabilities of modified, unmodified WF/HDPE composites and HDPE samples
Sample T5/℃ TP/℃ Char at TP1 TP2 600℃/% HDPE 437 − 495 2.1 WF/HDPE 276 350 490 11.5 WFx/HDPE 315 360 490 10.1 WFm/HDPE 322 370 500 10.8 WFa/HDPE 326 360 490 10.4 WFi/HDPE 311 350 490 10.5 Notes: T5—Temperature of heat loss of 5%; TP1—Fastest thermal decomposition temperature in the first stage; TP2—Fastest thermal decomposition temperature in the second stage; Char at 600℃—Solid residue at 600℃. -
[1] 杨雪慧, 汤丽娟, 章蓉, 等. 农作物秸秆表面改性处理的研究进展[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 37(3):157-162.YANG Xuehui, TANG Lijuan, ZHANG Rong, et al. Research progress on surface modification of crop straw[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition),2013,37(3):157-162(in Chinese). [2] 陈政豪, 李锦琦, 田兰馨, 等. 秸塑复合材料界面改性研究现状与展望[J]. 木材加工机械, 2017, 28(3):41-48.CHEN Zhenghao, LI Jinqi, TIAN Lanxin, et al. Research status and prospect of interface modification of straw-plastic composites[J]. Wood Processing Machinery,2017,28(3):41-48(in Chinese). [3] 丛龙康, 张效林. 秸秆纤维增强热塑性树脂基复合材料界面改性研究新进展[J]. 化工进展, 2015, 34(11):3970-3974.CONG Longkang, ZHANG Xiaolin. Recent progress in research on interface modification of straw fiber reinforced thermoplastic resin matrix composites[J]. Chemical Progress,2015,34(11):3970-3974(in Chinese). [4] 聂孙建, 张效林, 丛龙康, 等. 界面改性对麦秸秆纤维/聚乙烯复合材料性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7):1783-1790.NIE Sunjian, ZHANG Xiaolin, CONG Longkang, et al. Effect of interface modification on properties of wheat straw fiber/polyethylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(7):1783-1790(in Chinese). [5] MAMUN A A. Micro fibre reinforced PLA and PP composites: Enzyme modification, mechanical and thermal properties[J]. Composites Science & Technology,2013,78(2):10-17. [6] 陈云, 张喜燕, 雷亚芳, 等. 麦秸的微观构造及化学成分分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(2):179-183, 190.CHEN Yun, ZHANG Xiyan, LEI Yafang, et al. Microstructure and chemical composition analysis of wheat straw[J]. Journal of Northwest University of Agriculture and Forestry Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2015,43(2):179-183, 190(in Chinese). [7] 伍波, 张求慧, 王永波. 木塑复合材料界面化学改性研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2010, 38(5):28-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2010.05.009WU Bo, ZHANG Qiuhui, WANG Yongbo. Research progress on interfacial chemical modification of wood-plastic composites[J]. New Chemical Materials,2010,38(5):28-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2010.05.009 [8] JAUHARI N, MISHRA R, THAKUR H. Natural fibre reinforced composite laminates : A review[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2015,2(4-5):2868-2877. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2015.07.304 [9] ZHOU Y, FAN M, CHEN L. Interface and bonding mechanisms of plant fibre composites: An overview[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2016,101:31-45. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.06.055 [10] 余贞梅. 木粉、玉米秸秆改性聚烯烃基木塑复合3D打印材料研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2017.YU Zhenmei. Study on 3D printing materials of wood flour and corn straw modified polyolefin-based wood-plastic composites[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2017(in Chinese). [11] 严婷婷, 史凯欣, 易鹏, 等. 秸秆/合成橡胶复合材料的界面改性及性能研究[J]. 森林工程, 2017, 33(3):48-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2017.03.011YAN Tingting, SHI Kaixin, YI Peng, et al. Interface modification and properties of straw/synthetic rubber composites[J]. Forest Engineering,2017,33(3):48-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2017.03.011 [12] 江华, 张洋, 王雪飞. 脂肪酶对麦秸亲脂类抽提物的影响[J]. 南京林业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 34(3):25-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2010.03.006JIANG Hua, ZHANG Yang, WANG Xuefei. Effects of lipase on lipophilic extracts from wheat straw[J]. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University (Natural Science Edition),2010,34(3):25-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2006.2010.03.006 [13] ZOU Y, HUDA S, YANG Y. Lightweight composites from long wheat straw and polypropylene web[J]. Bioresource Technology,2010,101(6):2026-2033. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.10.042 [14] LU Fang, LIANG Chang, GUO Wenjing, et al. Influence of silane surface modification of veneer on interfacial adhesion of wood–plastic plywood[J]. Applied Surface Science,2014,288:682-689. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.098 [15] YANG S, BAI S, WANG Q. Sustainable packaging biocomposites from Polylactic acid and wheat straw: Enhanced physical performance by solid state shear milling process[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,158:34-42. [16] KELLERSZTEIN I, SHANI U, ZILBER I, et al. Sustainable composites from agricultural waste: The use of steam explosion and surface modification to potentialize the use of wheat straw fibers for wood plastic composite industry[J]. Polymer Composites,2017,40(S1):E53-E61. [17] 安红玉, 杨建忠, 郭昌盛. 纤维素的改性技术研究进展[J]. 成都纺织高等专科学校学报, 2016, 33(3):160-163.AN Hongyu, YANG Jianzhong, GUO Changsheng. Progress in cellulose modification technology[J]. Journal of Chengdu Textile College,2016,33(3):160-163(in Chinese). [18] 周亚巍, 宁莉萍, 王燕高, 等. 木聚糖酶处理对西南桦木/HDPE复合材料性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(2):338-344.ZHOU Yawei, NING Liping, WANG Yangao, et al. Effects of xylanase treatment on properties of southwestern birch/HDPE composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2014,31(2):338-344(in Chinese). [19] 张亚卓. 漆酶预处理制备麦秸无胶纤维板工艺研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2012.ZHANG Yazhuo. Study on the technology of preparing wheat straw glue-free fiberboard by laccase pretreatment[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2012(in Chinese). [20] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 纤维增强塑料拉伸性能试验方法: GB/T 1447—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005.China National Standardization Administration Committee. Test method for tensile properties of fiber reinforced plastics: GB/T 1447—2005[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2005(in Chinese). [21] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 纤维增强塑料弯曲性能试验方法: GB/T 1449—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005.China National Standardization Administration Committee. Test method for flexural properties of fiber reinforced plastics: GB/T 1449—2005[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2005(in Chinese). [22] 国家质量技术监督局.人造板及饰面人造板理化性能试验方法: GB/T 17657—1999[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 1999.State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Test methods for physical and chemical properties of wood-based panels and veneered panels: GB/T 17657—1999[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 1999(in Chinese). [23] KALIA S, THAKUR K, KUMAR A, et al. Laccase-assisted surface functionalization of lignocellulosics[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic,2014,102:48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2014.01.014 [24] DWIVEDI U N, SINGH P, PANDEY V P, et al. Structure–function relationship among bacterial, fungal and plant laccases[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B Enzymatic,2011,68(02):117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2010.11.002 [25] 杨少杰, 高海有, 李晞, 等. 甘露聚糖酶和木聚糖酶在纸浆漂白中的应用[J]. 造纸科学与技术, 2016, 35(4):71-76.YANG Shaojie, GAO Haiyou, LI Xi, et al. Application of mannanase and xylanase in pulp bleaching[J]. Paper Science and Technology,2016,35(4):71-76(in Chinese). [26] KALIA S, THAKUR K, CELLI A, et al. Surface modification of plant fibers using environment friendly methods for their application in polymer composites, textile industry and antimicrobial activities: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2013,1(3):97-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2013.04.009 [27] DEREWENDA Z S. Structure and function of lipases[J]. Advances in Protein Chemistry,1994,45(1):1-52. -






 下载:
下载: