Effect of polyethylene glycol on fluoride removal performance of hydroxyapatite
-
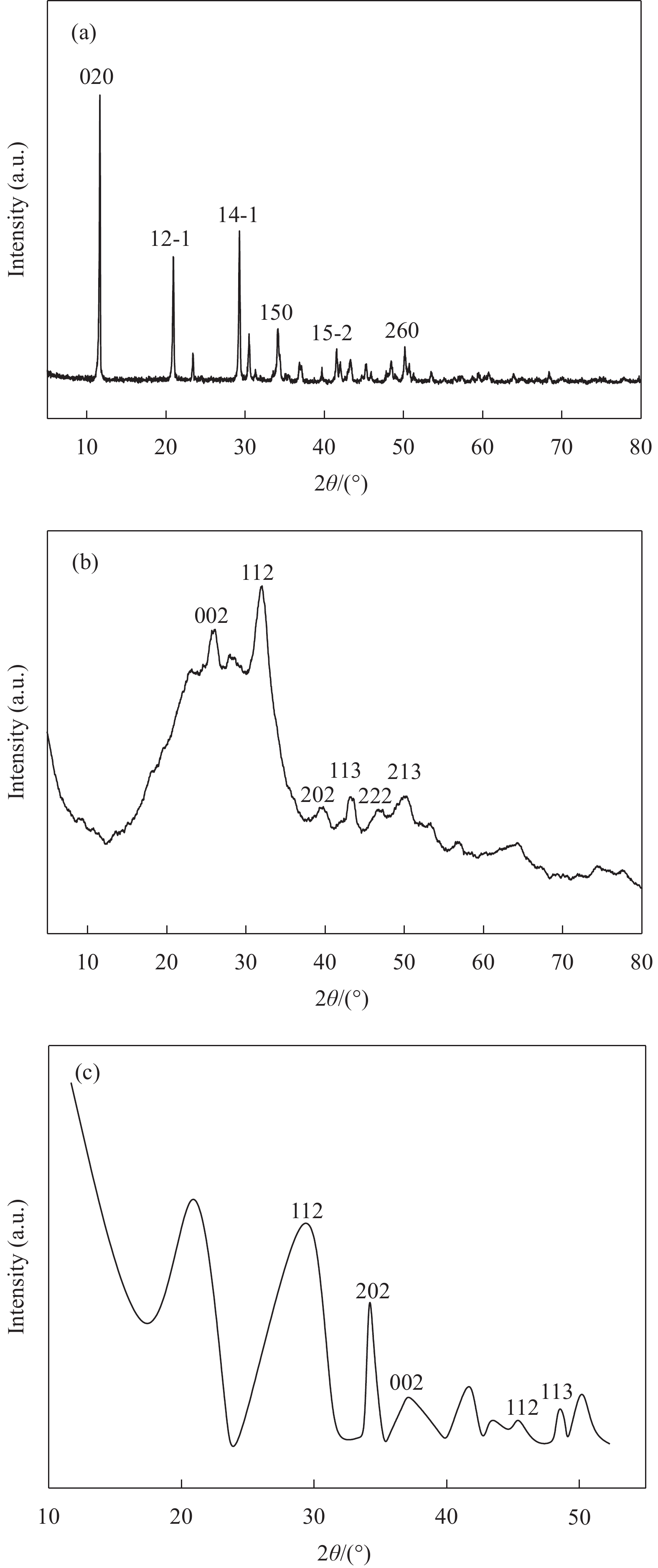
摘要: 为改善羟基磷灰石(HAP)合成过程易团聚导致其除氟效率不高的不足,本文应用清洁简便、绿色环保的电化学合成法,将亲水性强、分散性优异的非离子型表面活性剂聚乙二醇(PEG)加入到制备HAP的混合支持电解液中,在铜片作工作电极的表面制备出新型HAP复合材料(PEG/(HAP),并与纯HAP的晶体结构、孔径、比表面积、表面形貌、元素占比和官能团对比,以揭示PEG/HAP 除氟效率高于HAP的内在机制。结果发现,PEG/HAP与HAP有相同的晶面结构特征蜂、元素和化学键,但PEG/HAP的各元素含量占比、羟基和磷酸根离子官能团的吸收峰位和吸收强度与HAP 有一定差异;PEG使HAP从短棒状的表面形貌变成有利于交换和吸附氟离子的多孔和孔隙结构,其平均孔径由16.58 nm 减小到 11.93 nm,比表面积从24.29 m²/g 增加到29.83 m²/g;虽然PEG/ HAP与HAP的吸附类型均为IV型的H3滞后环,二者介孔分布范围一致,但PEG/ HAP的微孔和介孔数量明显高于HAP。尽管两种材料对氟离子的吸附反应均显示熵增、吸热和自发过程特征,吸附等温模型均符合Langmuir-Freundlich,但PEG/HAP的颗粒内扩散速率常数略大于HAP,PEG/HAP的吸附氟离子容量(9.56 mg/g)高于HAP( 8.36 mg/g);且去除氟离子的循环再生次数从HAP的4次增加到PEG/HAP的6次。此外,PEG的存在并没有影响制备条件参数如支持电解液pH值对HAP吸附氟离子容量的影响趋势,但却使HAP吸附氟离子容量增加。共存阴离子如Cl−、NO3 −、SO4 2−、CO3 2−均不干扰PEG/HAP和HAP对氟离子的吸附。Abstract: The removal efficiency of hydroxyapatite (HAP ) to fluoride was low due to its easy agglomeration during the synthesis process. Based on this, a clean,simple, green and environmentally fiendly electrochemcial synthesis method was applied to improve the fluoride removal efficiency. Polyethylene glycol (PEG), a non ionic surfactant with strong hydrophilicity and excellent dispersion,was added to the mixed support electrolyte for preparing HAP. A new type of HAP composite (PEG/(HAP) was prepared on the surface of copper sheet as the working electrode. By contrast to HAP, the crystal structure, pore size, specific surface area, surface morphology, elemental proportion, and functional groups of PEG/HAP were analyzed to reveal the instrinsic mechnism of the higher fluoride removal efficiency of PEG/HAP than HAP. The results showed that PEG/HAP and HAP had the same crystal plane structure characteristics, elements and chemical bonds, while the proportion of various elements as well as the absorption peaks and instensity of hydroxyl and phosphate ion functional groups in PEG/HAP had certain differences compared to HAP. PEG transformed HAP from a short rod-shaped surface morphology to a porous and porous structure that facilitated the exchange and adsorption of fluoride ions. Average pore size of PEG/HAP decreased from 16.58 nm of HAP to 11.93 nm, and its specific surface area increased from 24.29 m2/g OF HAP to 29.83 m2/g. Although the adsorption types of PEG/HAP and HAP were both IV type H3 hysteresis loop, and their mesoporous distribution ranges were consistent, the number of micropores and mesopores in PEG/HAP were significantly higher than those in HAP. Although the adsorption reactions of both materials for fluoride ions exhibited entropy increase, endothermic, and spontaneous process characteristics with the adsorption isotherm model conforming to Langmuir-Freundlich, the intra particle diffusion rate constant of PEG/HAP was slightly higher than HAP. Therefore, the maximum adsorption capacity of PEG/HAP for fluoride ions can reach 9.56 mg/g, which was higher than that of HAP of 8.36 mg/g. Compared with 4 times of recycle regeneration for removing fluoride ions of HAP, PEG/HAP can arrived at 6. In addition, the presence of PEG did not affect the change trend of preparation parameters such as electrolyte pH on the adsorption capacity of HAP for fluoride ions. However, PEG increased the adsorption capacity of HAP for fluoride ions. All coexisiting ions such as Cl−, NO3−, SO4 2−, and CO3 2− did not interfere with the adsorption of fluoride ions for PEG/HAP and HAP.
-
Key words:
- Polyethylene glycol /
- Hydroxyapatite /
- Electrochemical synthesis /
- Defluoridation /
- adsorptivity
-
表 1 HAP和PEG/HAP的孔结构参数
Table 1. Pore structure parameters of HAPand PEG/HAP
Material Parameters BET Surface Area/(m2·g−1) Average pore diameter/nm HAP 24.29 16.58 PEG/HAP 29.83 11.93 表 2 2种材料元素占比
Table 2. The atomic ratio of the two materials
Atomic/%
MaterialC O P Ca HAP 14.18 59.29 12.47 14.06 PEG/HAP 17.43 56.22 11.23 15.12 表 3 PEG/HAP和HAP吸附F−的热力学参数
Table 3. Thermodynamic parameters of PEG/HAP and HAP adsorption F−
F−initial concention mg/L T/K $\Delta {G}^{\ominus } $/(kJ·mol−1) $\Delta {S}^{\ominus } $/(J·K−1·mol−1) $\Delta {H}^{\ominus } $/(kJ·mol−1) PEG/HAP HAP PEG/HAP HAP PEG/HAP HAP 1.5 288.15 −20.6064 −20.8255 183.9473 108.6640 32.3980 10.4860 298.15 −22.4459 −21.9122 308.15 −24.2854 −22.9988 318.15 −26.1248 −24.0855 328.15 −27.9643 −25.1721 2 288.15 −20.6560 −20.8680 164.4675 112.0162 26.7353 11.4095 298.15 −22.3007 −21.9881 308.15 −23.9454 −23.1083 318.15 −25.5900 −24.2285 328.15 −27.2347 −25.3486 4 288.15 −18.1882 −17.3630 164.1350 169.6522 29.1073 31.5223 298.15 −19.8296 −19.0595 308.15 −21.4709 −20.7560 318.15 −23.1123 −22.4525 328.15 −24.7536 −24.1491 6 288.15 −16.6281 −15.7314 174.6855 167.8098 33.7075 32.6230 298.15 −18.3750 −17.4095 308.15 −20.1218 −19.0876 318.15 −21.8687 −20.7657 328.15 −23.6155 −22.4438 8 288.15 −15.8648 −14.9546 135.6928 151.0870 23.2351 28.5811 298.15 −17.2217 −16.4655 308.15 −18.5786 −17.9764 318.15 −19.9356 −19.4872 328.15 −21.2925 −20.9981 10 288.15 −15.2550 −14.6329 128.7755 129.4490 21.8517 22.6678 298.15 −16.5427 −15.9274 308.15 −17.8305 −17.2219 318.15 −19.1182 −18.5164 328.15 −20.4060 −19.8109 Notes:$\Delta {G}^{\ominus } $,$\Delta {S}^{\ominus } $ and $\Delta {H}^{\ominus } $ are standard Gibbs function change value, entropy change, and enthalpy change, respectively. 表 4 PEG/HAP与HAP的 Langmuir-Freundlich模型拟合参数
Table 4. Fitting parameters of Langmuir-Freundlich of PEG/HAP and HAP
Model T/K qm / (mg·g−1) b n R2 PEG/HAP HAP PEG/HAP HAP PEG/HAP HAP PEG/HAP HAP Langmuir-Freundlich 288.15 4.6058 3.4550 3.0896 3.0662 1.2522 3.8708 0.9701 0.9615 298.15 5.8948 4.3757 3.2896 27.3055 1.2079 2.8634 0.9858 0.9694 308.15 6.8707 5.6192 2.8382 4.3399 0.8620 1.3814 0.9914 0.9818 318.15 8.7941 7.2896 2.7633 3.3643 0.9144 1.4300 0.9757 0.9960 328.15 10.2706 8.9194 2.9674 2.7605 0.9658 1.3416 0.9822 0.9941 Notes: b in table 4 is the adsorption constant; n is the non-uniformity coefficient and R 2 is the correlation coefficient 表 5 PEG/HAP动力学方程拟合参数
Table 5. Fitting parameters of kinetics equation for PEG/HAP
Equation Parameters R2 Pseudo first-order model k1/min−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) 0.8953 0.0171 3.4672 Pseudo econd-order model k2 /(g·mg−1·min−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) 0.9854 0.0050 4.1203 Elovich A/(mg·g−1·min−1) B/(g·mg−1) 0.9663 0.2526 1.2902 Morrist intraparticle diffusion model k3/(g·g−1·min−0.5) C 0.9876 0.1774 0.6684 Notes:k1 is the adsorption rate constant of the quasi first order kinetic model; k2 is the adsorption rate constant of the quasi second order kinetic model; B is the desorption coefficient; A is the constant adsorption rate; k3 is the internal diffusion rate constant; C is for Boundary-layer thickness;Qe is the equilibrium adsorption capacity 表 6 HAP不同动力学模型的拟合参数
Table 6. Fitting parameters of kinetics equation for HAP
Equation Parameters R2 Pseudo first-order model k1/min−1 Qe/(mg·g−1) 0.9186 0.0136 3.1689 Pseudo econd-order model k2/(g·mg−1·min−1) Qe/(mg·g−1) 0.9770 0.0043 3.8226 Elovich A/(mg·g−1·min−1) B/(g·mg−1) 0.9595 0.1740 1.3443 Morrist intraparticle diffusion model k3/ (g·g−1·min−0.5) C 0.9915 0.1712 0.3834 Notes: k1 is the adsorption rate constant of the quasi first order kinetic model; k2 is the adsorption rate constant of the quasi second order kinetic model; B is the desorption coefficient; A is the constant adsorption rate; k3 is the internal diffusion rate constant; C is for Boundary-layer thickness;Qe is the equilibrium adsorption capacity 表 7 HAP和PEG/HAP吸附容量
Table 7. Adsorption capacity of HAP and PEG/HAP
q/(mg·g−1) Materials 1 st 2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th HAP 2.36 2.38 2.32 2.34 2.36 PEG/HAP 2.68 2.70 2.70 2.66 2.64 Notes: q is HAP or PEG/HAP adsorption capacity to F− in model waste water 表 8 两种材料氟离子去除率
Table 8. Defluoridation efficient of two materials
Defluoridationl efficient/% Materials 1 st 2 nd 3 rd 4 th 5 th HAP 59.0 59.5 58.0 58.5 59.0 PEG/HAP 67.0 67.5 67.5 66.5 66.0 表 9 HAP和PEG/HAP循环再生次数
Table 9. Recycling regeneration times of HAP and PEG/HAP
CF−/(mg·L−1) Materials First time Second time Third time Fourth time Fifth time Sixth time HAP 0.65 0.75 0.86 0.94 1.12 - PEG/HAP 0.42 0.51 0.64 0.73 0.86 0.94 Notes: CF− is the remain concentration of F− in model waste water -
[1] GEORGE S, MEHTA D, SAHARAN VK. Application of hydroxyapatite and its modified forms as adsorbents for water defluoridation: an insight into process synthesis[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2018, 36(3): 369-400. [2] GONG LY, FENG L. Preparation and defluorination mechanism of a novel copolymerized hydroxyapatite-aluminium chloride material[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(115): 95334-95343. doi: 10.1039/C5RA20372D [3] SAHU H, MOHANTY K. Al grafted natural hydroxyapatite for neem oil transesterification: Kinetic study at optimal point[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 280: 564-574. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.06.040 [4] MONDALl P, MEHTA D, GEORGE S. Defluoridation studies with synthesized magnesium-incorporated hydroxyapatite and parameter optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2016, 57(56): 27294-27313. doi: 10.1080/19443994.2016.1167628 [5] 赵瑨云, 胡家朋, 林皓等. Ag+改性羟基磷灰石制备及其除氟抑菌特性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(12): 3977-3984.ZHAO Jinyun, HU Jiapeng, LIN Hao, et al. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite-Modified Ag+ and its Property for defluorination andbacteriostasis activity[J]. Bulltin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(12): 3977-3984(in Chinese). [6] CHEN Z, LIU Y, MAO L, et al. Effect of cation doping on the structure of hydroxyapatite and the mechanism of defluoridation[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 44(6): 6002-6009. [7] GAO S, SUN R, WEI Z, et al. Size-dependent defluoridation properties of synthetic hydroxyapatite[J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2009, 130(6): 550-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2009.03.007 [8] 干成果, 冯莉. 负载羟基磷灰石活性炭的制备及除氟性能[J]. 功能材料, 2013, 44(22): 3243-3246.GAN Chengguo, FENG Li. Preparation of activated carbon supported hydroxyapatite and the removal performance of fluorine ion[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2013, 44(22): 3243-3246(in Chinese). [9] SANI T, GṌMEZ-HORTIGŰELA L, MAYORAL Á, et al. Controlled growth of nano-hydroxyapatite on stilbite: Defluoridation performance[J]. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2017, 254: 86-95. [10] GERGELY G, WéBER F, LUKáCS I, et al. Preparation and characterization of hydroxyapatite from eggshell[J]. Ceramics International, 2010, 36(2): 803-806. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.09.020 [11] WORKENEH K, ZEREFFA EA, SEGNE TA, et al. Eggshell-derived nanohydroxyapatite adsorbent for defluoridation of drinking water from bofo of ethiopia[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2019, 2: 1-12. [12] SAMANT A, NAYAK B, MISRA PK. Kinetics and mechanistic interpretation of fluoride removal by nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite derived from Limacine artica shells[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2017, 5: 5429-5438. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.09.058 [13] XU F, JIANG C, LI D. Defluoridation of wastewaters using HAP-coated-limestone[J]. Separation Science & Technology, 2018, 54(14): 2304-2313. [14] YU X, TONG S, GE M, et al. Removal of fluoride from drinking water by cellulose @hydroxyapatite nano-composites[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 92(1): 269-275. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.045 [15] 胡家朋. 羟基磷灰石复合改性材料的制备及其除氟性能研究[D]. 南昌, 南昌大学, 2016HU Jiapeng. Preparation and defluoridation properties of hydroxyapatite modified composites[D]. Nanchang, Nanchang Univercity, 2016 (in Chinese). [16] 赵瑨云, 刘瑞来, 徐婕, 等. 原位合成羟基磷灰石/壳聚 糖复合吸附剂及除氟特性研究[J]. 高分子通报, 2021, 2: 54-62.ZHAO Jinyun, LIU Ruilai, XU Jie, et al. In situ fabracation of hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite adsorbent and its property for defluorination[J]. Polymer . Bulletin, 2021, 2: 54-62(in Chinese ). [17] 叶建东, 肖锋, 王秀鹏, 等. 十二烷基硫酸钠在化学沉淀法合成羟基磷灰石粉体中的防团聚作用[J]. 功能材料, 2005, 10: 120-122.YE Jiandong, XIAO Feng, WANG Xiupeng, et al. Rol e of sodium dodecyl sulfate in de-agglomerati on of hydroxyapatite powder synthesi zed by chemical preci pitati on method[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2005, 10: 120-122(in Chinese). [18] MUKHERJEE S, KNDU B, CHANDA A, et al. Effect of functionalisation of CNT in the preparation of HAP-CNT biocomposites[J]. Ceramics International, 2015, 41(3): 3766-3774. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.11.052 [19] 章萍, 杨陈凯, 马若男, 等. 碳纳米管/羟基磷灰石复合材料对水体F−的去除研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(1): 179-187.ZHANG Ping, YANG Dongkai, MA Ruonan, et al. Effective Rem removal of fluoride by carbon nanotubes/hydroxyapatite Composite[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(1): 179 179-187(in Chinese). [20] PRABHU SM, ELANCHEZHIYAN SSD, LEE G, et al. Assembly of nano-sized hydroxyapatite onto graphene oxide sheets via in-situ fabrication method and its prospective application for defluoridation studies[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 300: 334-342. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.111 [21] 贾晓林, 钟香崇. 聚乙二醇在MgAl2O4前驱体表面的吸附及改性作用[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2004, 5: 12-15.JIA Xiaolin, ZHONG Xiangchong. Effect of PEG on absorption state and surface modification of MgAlO4 precursor[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2004, 5: 12-15 (in Chinese ). [22] 逯英英, 陈肖平, 马枭, 等. 聚乙二醇改性酚醛树脂基球形炭吸附脱硫脱氮性能研究[J]. 石油与天然气化工, 2017, 46(4): 6-10.LU Yingying, CHEN Xiaoping, MA Xiao, et al. Performance study on adsorption removal of sulfur and nitrogen compounds of carbon spheres derived from phenolic res-in with polyethylene glycol[J]. Chemical Engineering of Oil & Gas, 2017, 46(4): 6-10 (in Chinese ). [23] 李金鑫, 龚巧迪, 杨金燕. 改性羟基磷灰石对水体中五价钒的吸附[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(4): 1355-1362+1386.LI Jinxin, GONG Qiao di, YANG Jinyan. Adsorption of vanavandium(V) in aqueous solution by modified hydroxyapatite[J]. Bulltin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018: 37(4: 1355-1362+1386 (in Chinese ). [24] 朱丹琛, 刘秀秀, 陈彰旭等. 羟基磷灰石微球的仿生合成及除氟性能[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2019, 31(3): 570-575.ZHU Danchen, LIU Xiuxiu, CHEN Zhangxu, et al. Biomimetic synthesis of hydroxyapatite microspheres and its defluoridation properties[J]. Chemical research and application, 2019, 31(3): 570-575 (in Chinese ). [25] RIVERA E M, ARAIZA M, BROSTOW W, et al. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite from eggshells[J]. Materials Letters, 1999, 41(3): 128-134. doi: 10.1016/S0167-577X(99)00118-4 [26] JIE W, Li Y. Tissue engineering scaffold material of nano-apatite crystals and polyamide composite[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2004, 40(3): 509-515. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2003.10.028 [27] 周婷婷. 磁性导电聚合物材料的合成及其对水中 Cr(Ⅵ)的吸附研究[D]. 广州, 华南理工大学, 2020.ZHOU Tingting. Preparation of magnetic conductive polymers materials and their performance in removing Cr(Ⅵ) in water[J]. Guangzhou, South China University of Technology, 2020(in Chinese). [28] BAUTISTA LF, PINILLA J, ARACIL J, et al. Adsorption isotherms of aspartame on commercial and chemically modified divinylbenzene styrene resins at different temperatures[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, 2002, 47(3): 620-627. doi: 10.1021/je010325a [29] GAUTHAM PJ, PRABHAKAR TC. A modified Langmuir-Freundlich isotherm model for simulating pH-dependent adsorption effects[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2012, 129-130: 46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2011.12.001 [30] LI H, XIAO DL, HE H, et al. Adsorption behavior and adsorption mechanism of Cu(II) ions on amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(9): 2657-2665. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62782-X [31] TOFIGHY MA, MOHAMMADI T. Adsorption of divalent heavy metal ions from water using carbon nanotube sheets[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 185(1): 140-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.008 [32] 周亚平, 周理. 超临界氢在活性炭上的吸附等温线研究[J]. 物理化学学报, 1997, 13(2): 119-127. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB19970205ZHOU Yaping, ZHOU Li. Study on the adsorption isotherms of supercritical hydrogen on activated carbon[J]. Acta Physical Chemisry, 1997, 13(2): 119-127(in Chinese ). doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB19970205 [33] GREGORIO M. BET adsorption reaction model based on the pseudo steady-state hypothesis for describing the kinetics of adsorption in liquid phase[J]. Journal of Colloid And Interface Science, 2016, 467: 170-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.01.016 [34] 蔡金水, 康得军, 杨天学等. 铁改性杭锦土吸附剂对水中砷的去除研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(2): 346-355.CHAI Jinshui, KANG Dejun, YANG Tian xue, et al. Removal of Arsenic from Water by Iron Modified Hangjin Clay Adsorbent[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(2): 346-355(in Chinese). [35] HOSLETT J, GHAZAL H, KATSOU E, et al. The removal of tetracycline from water using biochar produced from agricultural discarded material[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 751: 141755. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141755 [36] ZHANG CJ, HU M, KE QF, et al. Nacre-inspired hydroxyapatite/chitosan layered composites effectively remove lead ions in continuous-flow wastewater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 386: 121999. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121999 [37] TIAN Y, LI JB, TODD WW, et al. Application of oily sludge-derived char for lead and cadmium removal from aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 384: 123386. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123386 [38] KIM YS, KIM JH. Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the adsorption of paclitaxel onto sylopute[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2019, 130: 104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.jct.2018.10.005 [39] CRINI G, PEINDY N, GIMBERT F. Removal of C. I. basic green 4 (Malachite Green) from aqueous solutions by absorption using cyclodextrinbased adsorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies[J]. Separation Purification Technology, 2007, 53: 97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2006.06.018 [40] 赵佳昕, 李文博 , 王吉坤. 柠檬酸优化水热合成羟基磷灰石及矿井水除氟性能[J]. 洁 净 煤 技 术, 2022, 28(2): 175-185.ZHAO Jiaxin, LI Wenbo, WANG Jikun. Optimization of hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite with citric acid and its fluorine removal[J]. Clean coal technology , 2022, 28(2): 175-185 (in Chinese). [41] 张强英, 陶金帅, 李 伟, 等. 废弃茶叶吸附剂去除水中的氟离子[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4): 1303-1311.ZHANG Qiangying, TAO Jinshuai, LI Wei, et al. Removal of fluoride ions from water using discarded tea adsorbent[J]. Environmental chemistry, 2022, 41(4): 1303-1311(in Chinese) . [42] 刘瑞来. 聚乳酸 /羟基磷灰石复合纤维膜制备及其对水中氟离子的吸附[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(31): 50-57.LIU Ruilai. Preparation of polylactic acid /hydroxyapatite composite fiber membrane and its adsorption of fluoride ions[J]. Science and Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(31): 50-57(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: