Response and damage characteristics of composite laminates under high-energywide-area blunt impact
-
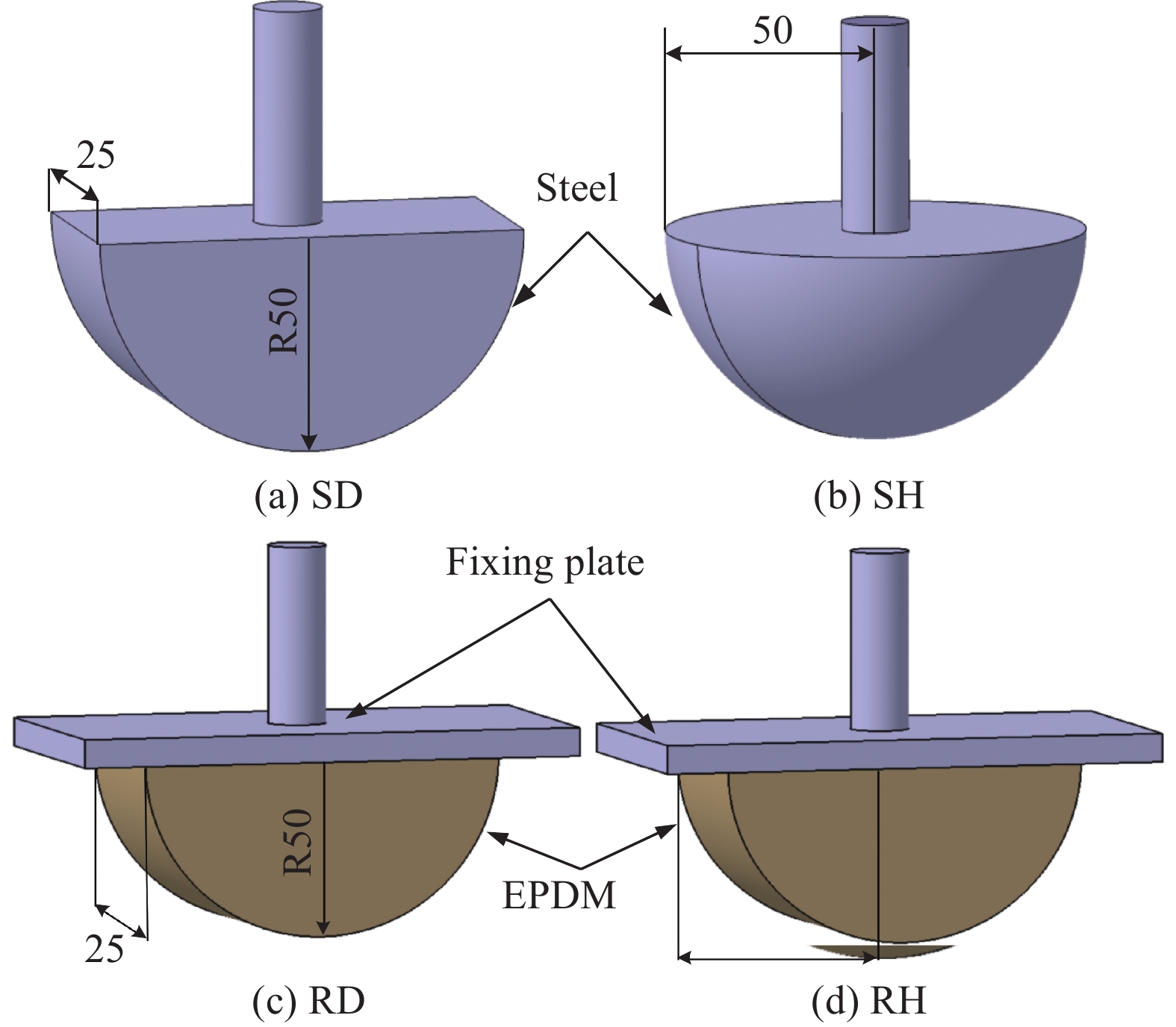
摘要: 高能量大面积钝物冲击(HEWABI)会导致复合材料飞机结构内部发生严重损伤,但在机身外部几乎目视不可见,从而会对飞机运营安全带来较大的威胁。采用不同形状的刚性冲头和橡胶冲头对层合板进行高能量准静态加载试验,随后建立了基于连续介质损伤力学(CDM)的仿真分析模型。结果表明:建立的仿真分析模型可有效预测在刚性和橡胶冲头下的响应和损伤情况。当载荷达到40 kN时,刚性冲头下的层合板会发生严重的分层损伤;而橡胶冲头在加载过程中发生大变形,降低了层合板的局部应力,直至90 kN时仍未对层合板产生任何损伤。层合板损伤情况受刚性冲头形状影响较大,橡胶冲头形状则几乎无影响。
-
关键词:
- 层合板 /
- 高能量大面积钝物冲击 /
- 橡胶冲击 /
- 冲击响应 /
- 损伤特性
Abstract: High-energy wide-area blunt impact (HEWABI) can lead to severe internal damage to the composite aircraft, which is barely visible from the outside of fuselage and cause a significant threat to flight safety. High energy quasi-static loading tests were carried out on the laminates with different shapes of rigid impactors and rubber impactors, then the finite element simulation models based on Continuum Damage Mechanics (CDM) were developed. The results show that the established simulation analysis models can effectively predict the response and damage of the laminated panels under rigid or rubber impactors. When the load reaches 40 kN, severe delamination damages will occur in the laminated panel for the rigid impactors. On the other hand, no damage can be observed at 90 kN for the rubber impactors, which can be attributed to the significant deformation of rubber impactors and the reduced local contact loads. The shape of rigid impactors has great effect on the damage to laminated panels, while the shape of the rubber impactors has almost no impact on the damages.-
Key words:
- laminate /
- high-energy wide-area blunt impact /
- rubber impact /
- impact response /
- damage characteristics
-
表 1 DE710-T700S单向板材料力学性能参数
Table 1. Mechanical property parameters of DE710-T700S unidirectional plate material
Parameter Value ρ/(g·cm−3) 1.53 E11/GPa 121 E22/GPa 8.6 E33/GPa 8.6 ν12 0.317 ν13 0.317 ν23 0.5 G12/GPa 3.7 G13/GPa 3.7 G23/GPa 3.7 Xt/MPa 2376 Xc/MPa 1068 Yt/MPa 69 Yc/MPa 208 Sl/MPa 110 St/MPa 110 Notes: Eii(i=1,2,3)—Elastic modulus in direction i; vij(i=1,2; j=2,3)—Poisson's ratio in different directions; Gij(i=1,2; j=2,3)—Shear modulus in different directions; Xt and Xc—Longitudinal tensile and compressive strengths; Yt and Yc—Transverse tensile and compressive strengths; Sl and St—Longitudinal and transverse shear strength. 表 2 DE710-T700S层合板层间性能参数
Table 2. Interface performance parameters of DE710-T700S laminate
Parameter Value E/GPa 8.6 $t_{\text{n}}^0$/MPa 26 $t_{\text{s}}^0$/MPa 62 $t_{\text{t}}^0$/MPa 62 GIC/(J·m−2) 771 GIIC/(J·m−2) 3152 GIIIC/(J·m−2) 3152 Notes: E—Elastic modulus of cohesive layer; $t_{\text{n}}^0$($t_{\text{s}}^0$,$t_{\text{t}}^0$)—Interfacial strengths in three main directions; GIC (GIIC, GIIIC)—Critical energy release rates for different types of cracking. 表 3 Ogden材料参数(N=2)
Table 3. Ogden material parameters (N=2)
i µi/MPa αi 1 0.459 3.564 2 3.409 −0.149 -
[1] ZHANG X W, MOHAMMED I K, ZHANG M Y, et al. Temperature effects on the low velocity impact response of laminated glass with different types of interlayer materials[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 124: 9-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.09.004 [2] CHAUPAL P, PRAKASH R. Damage identification in composite structure using machine learning techniques based on acoustic emission waveforms[J]. Recent Advances in Manufacturing Modelling and Optimization, 2022, 149-158. [3] NAM M. High energy wide area blunt impact damage to internal structural components of composite aircraft fuselage structures [D]. San Diego: University of California San Diego, 2021. [4] DEFRANCISCI G K. High energy wide area blunt impact on composite aircraft structures[D]. San Diego: University of California San Diego, 2013. [5] Federal Aviation Administration. High-energy wide-area blunt impact for composite structures: PS-ANM-25-20[S]. Washington DC: Federal Aviation Administration, 2016. [6] ZOU J C, LEI Z K, BAI R X, et al. Damage and failure analysis of composite stiffened panels under low-velocity impact and compression after impact[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 262: 113333. [7] 拓宏亮, 马晓平, 卢智先. 基于连续介质损伤力学的复合材料层合板低速冲击损伤模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7): 1878-1888. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180103.001TUO Hongliang, MA Xiaoping, LU Zhixian. A model for low velocity impact damage analysis of composite laminates based on continuum damage mechanics[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2018, 35(7): 1878-1888(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180103.001 [8] 马良颖. 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料的抗鸟撞性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.MA Liangying. Research on bird strike resistance of carbon fiber rein-forced resin matrix composites [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021( in Chinese). [9] CHEN Z M, KIM H, DEFRANCISCI G K. Experimental and modeling investigation of blunt impact to stringer-reinforced composite panels[C]// 28th Annual Technical Conference of the American Society for Composites 2013, ASC 2013. 2. 1848-1867. [10] HEIMBS S, VAN DE NBROUCKE B, DUPLESSIS KERGOMARD Y, et al. Rubber impact on 3D textile composites[J]. Applied Composite Materials, 2012, 19(3-4): 275-295. [11] MIKULIK Z, HAASE P. Composite damage metrics and inspection-blunt impact(CODAMEIN) [R]. Hambury: European Aviation Safety Agency, 2010. [12] DING Y Z, LIU J, HALL Z E C, et al. Damage and energy absorption behaviour of composite laminates under impact loading using different impactor geometries[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 321: 117259. [13] HABIBI M, ABBASSI F, LAPERRIÈRE L. Quasi-static indentation and acoustic emission to analyze failure and damage of bio-composites subjected to low-velocity impact[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 158: 106976. [14] BOZKURT M O, COKER D. In-situ investigation of dynamic failure in [05/903]s CFRP beams under quasi-static and low-velocity impact loadings[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2021, 217-218:134-154. [15] SUN X C, WISNOM M R, HALLETT S R. Interaction of inter- and intralaminar damage in scaled quasi-static indentation tests: Part 2–Numerical simulation[J]. Composite Structures, 2016, 136: 727-742. [16] HASHIN Z. Failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composites[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1980, 47(2): 329-334. doi: 10.1115/1.3153664 [17] 邹田春, 李龙辉, 巨乐章, 等. CFRP-铝合金板单、双搭接胶接接头刚度退化机理[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(19): 155-160.ZOU Tianchun, LI Longhui, JU Yuezhang, et al. Stiffness degradation mechanism of single and double lap bonded joints of CFRP-aluminum alloy plates[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(19): 155-160(in Chinese). [18] EBADI-RAJOLI J, AKHAVAN-SAFAR A, HOSSEINI-TOUDESHKYH, et al. Progressive damage modeling of composite materials subjected to mixed mode cyclic loading using cohesive zone model[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2020, 143: 103322. [19] JOHRI N, CHANDRA KANDPAL B, KUMAR N, et al. Effect of ply thickness and orientation on fatigue delamination of laminated composites using cohesive zone model[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 46(20): 11040-11045. [20] CAMANHO P P, DAVILA C G, DE MOURA M F. Numerical simulation of mixed-mode progressive delamination in composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2003, 37(16): 1415-1438. doi: 10.1177/0021998303034505 [21] KARNATI S R, SHIVAKUMAR K. Limited Input Benzeggagh and Kenane delamination failure criterion for mixed-mode loaded fiber reinforced composite laminates[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2020, 222(1-2): 221-230. doi: 10.1007/s10704-019-00418-1 [22] ZHOU J J, WEN P H, WANG S N. Numerical investigation on the repeated low-velocity impact behavior of composite laminates[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, 185: 107771 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107771 [23] 魏家威, 石霄鹏, 冯振宇. 应变率相关的橡胶本构模型研究[J]. 高压物理学报, 2022, 36(2): 107-117.WEI Jiawei, SHI Xiaopeng, FENG Zhenyu. Strain rate dependent constitutive model of rubber[J]. Chinese Journal of High Pressure Physics, 2022, 36(2): 107-117(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: