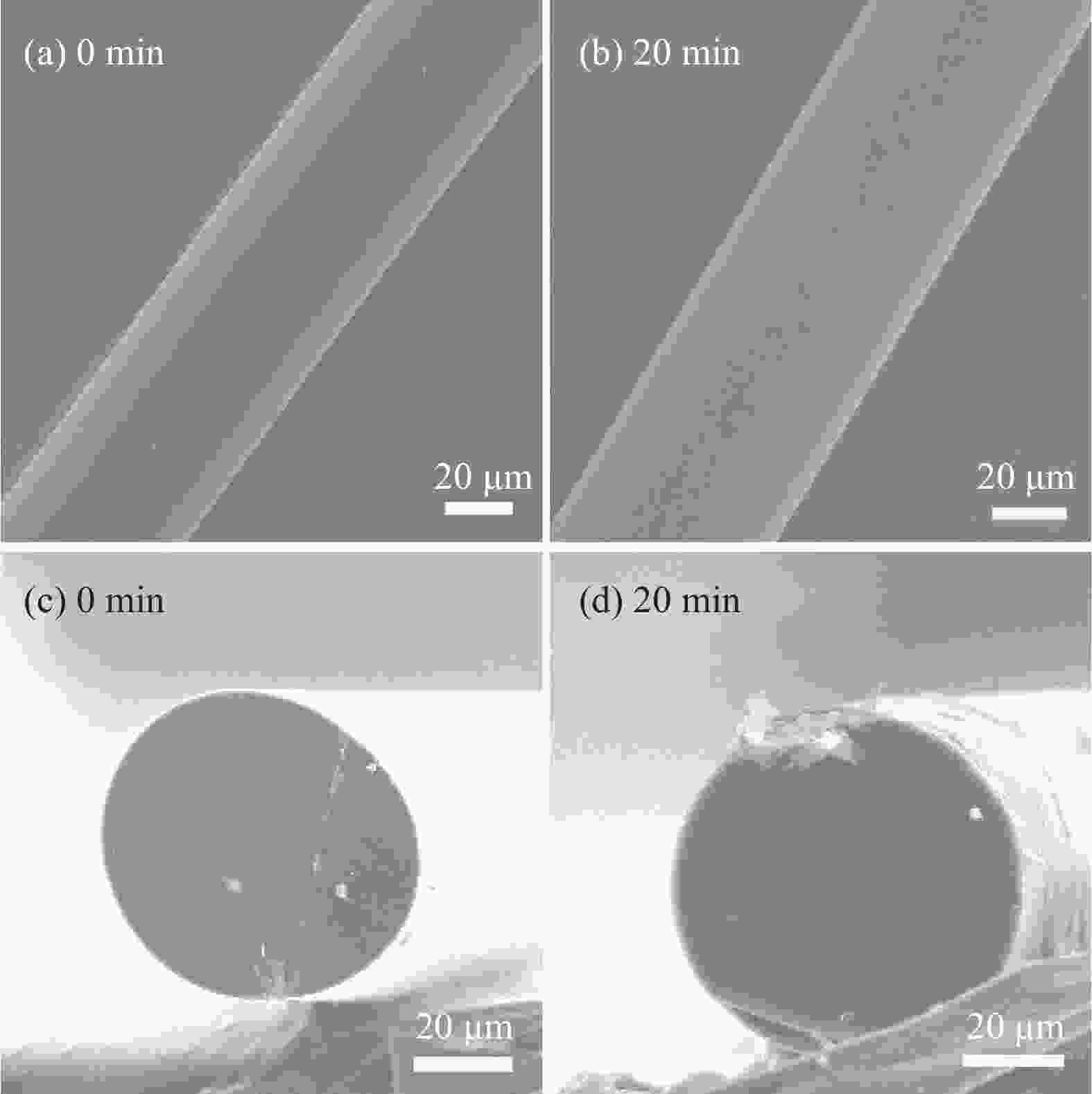
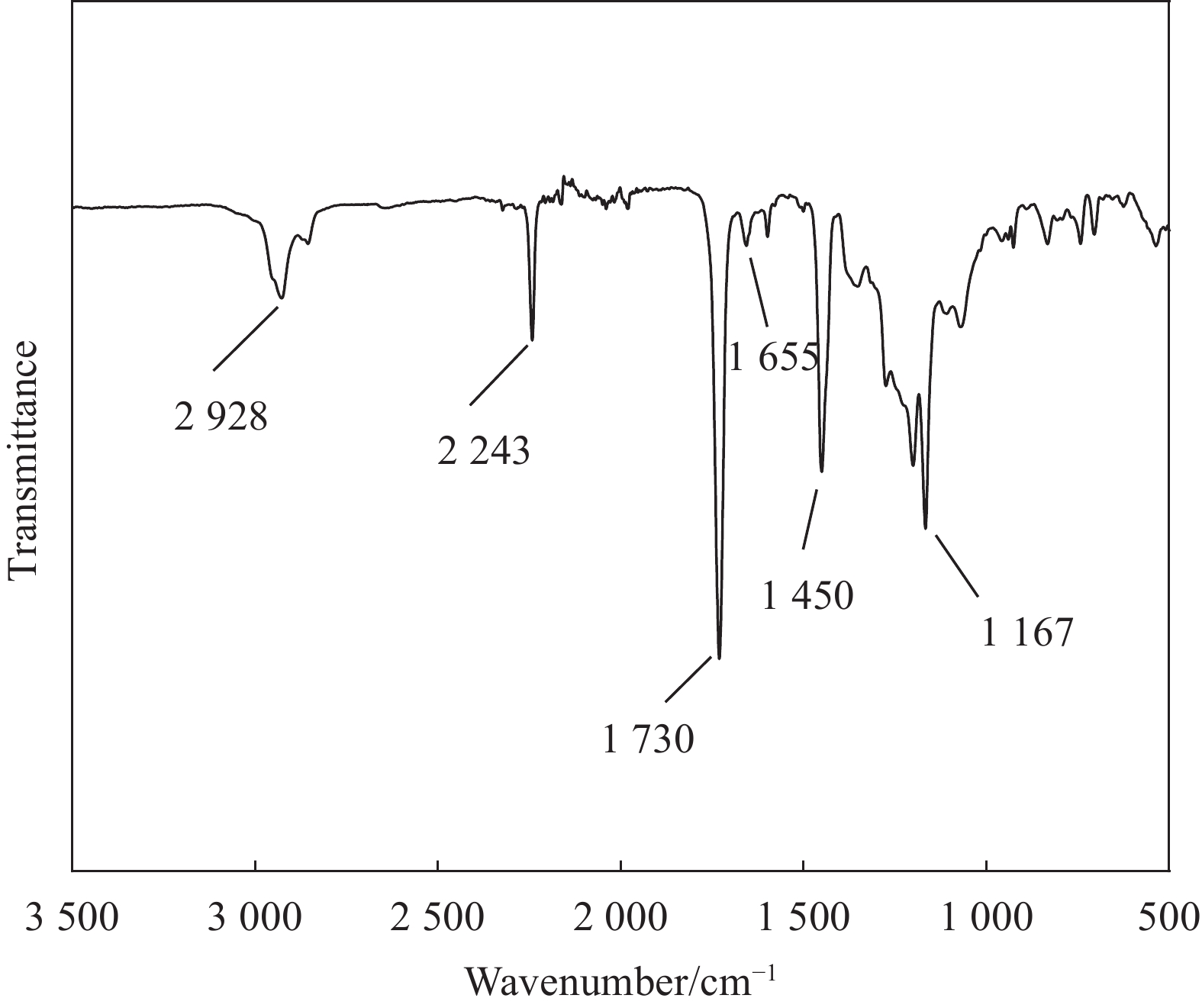
Preparation and properties of pitch plasticized melt spinning polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fibers precursor
-
摘要: 为了降低聚丙烯腈(PAN)的熔点和提升熔纺PAN纤维的性能,本文以各向同性萘沥青(INP)和煤焦油沥青(ICP)作为增塑剂,比较了二者对85∶14∶1 摩尔比的聚(丙烯腈-丙烯酸甲酯-4-丙烯酰氧基二苯甲酮)三元共聚物(P(AN-MA-ABP))的增塑效果。优选1wt%的INP与P(AN-MA-ABP)充分混合、熔融纺丝、牵伸制备了1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP)共聚物纤维,并研究了紫外(UV)辐照时间对1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP)共聚物纤维的影响。结果表明:相比于稠环结构的ICP,长链含硫杂环结构的INP具有良好的增塑效果。制备的1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP)共聚物纤维直径约52 μm,拉伸强度约250 MPa,表面光滑,结构致密。UV辐照时间从0 min增加到60 min,纤维表面氧含量由17.3%提高到26.0%。氮气条件下,环化起始温度由303.8℃降到292.4℃,环化峰值温度由318.0℃降到308.8℃。空气条件下,环化起始温度由299.9℃降到295.0℃,环化峰值温度由316.4℃降到312.6℃。UV辐照20 min,氮气条件下800℃时纤维的碳收率由41.0%提高到43.4%。UV辐照降低了1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP)共聚物纤维的环化起始温度、峰值温度、焓值,提高了碳收率,有利于后续热处理。Abstract: In order to reduce the melting point of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) and improve the properties of melt-spun PAN fibers, the effects of isotropic naphthalene pitch (INP) and coal tar pitch (ICP) as plasticizers on 85∶14∶1 mole percent poly(acrylonitrile-methyl acrylate-4-acryloxy dibenzophenone) terpolymer (P(AN-MA-ABP)) were investigated in detail. The 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers were prepared by mixing 1wt%INP with P(AN-MA-ABP), and then melting spinning and drawing. The effects of UV irradiation time on 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers were studied. The results show that the long-chain sulfur heterocyclic INP has a better plasticizing effect than the ICP with a thick ring structure. The diameter of the 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers is about 52 μm, and the tensile strength is about 250 MPa, which has a smooth surface and a dense structure. Delaying the UV irradiation from 0 min to 60 min, the oxygen content on the surface of 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers increases from 17.3% to 26.0%. Under nitrogen conditions, the initial cyclization temperature decreases from 303.8℃ to 292.4℃, and the cyclization peak temperature decreases from 318.0℃ to 308.8℃. Under air conditions, the initial cyclization temperature decrease from 299.9℃ to 295.0℃, and the cyclization peak temperature decreases from 316.4℃ to 312.6℃. After UV irradiation for 20 min, the carbon yield of 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers carbonized at 800℃ under nitrogen increases from 41.0% to 43.4%. UV irradiation decreases the initial cyclization temperature, peak temperature, and enthalpy value of 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers and increases the carbon yield, which are beneficial to the subsequent heat-treatment process.
-
Key words:
- pitch /
- plasticizer /
- melt spinning /
- polyacrylonitrile (PAN) /
- carbon fiber /
- precursor
-
表 1 样品的组成编号
Table 1. Composition number of the samples
Sample P(AN-MA-ABP)/wt% INP/
wt%ICP/
wt%0.5wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 99.5 0.5 – 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 99.0 1.0 – 3wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 97.0 3.0 – 5wt%ICP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 95.0 – 5.0 Notes: INP—Isotropic naphthalene pitch; ICP—Isotropic coal tar pitch; P(AN-MA-ABP)—Poly(acrylonitrile-methyl acrylate-4-acryloxy dibenzophenone) terpolymer. 表 2 P(AN-MA-ABP)三元共聚物的组成与性质
Table 2. Composition and properties of P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymers
Feed ratio
/mole percentComposition
/mole percentMn/(g·mol−1) Mw/(g·mol−1) Mw/Mn Melt processible 85∶14∶1 84.3∶14.3∶1.4 25000 52000 2.1 Yes 85∶14∶1 84.5∶14.2∶1.3 49000 74000 1.5 No 85∶14∶1 84.4∶14.3∶1.3 15000 30000 2.0 Yes 85∶14∶1 84.2∶14.4∶1.4 21000 42000 2.0 Yes Notes: Mn—Number average molecular weight; Mw—Weight average molecular weight. 表 3 同性萘沥青(INP)和煤焦油沥青(ICP)的元素组成(单位:wt%)
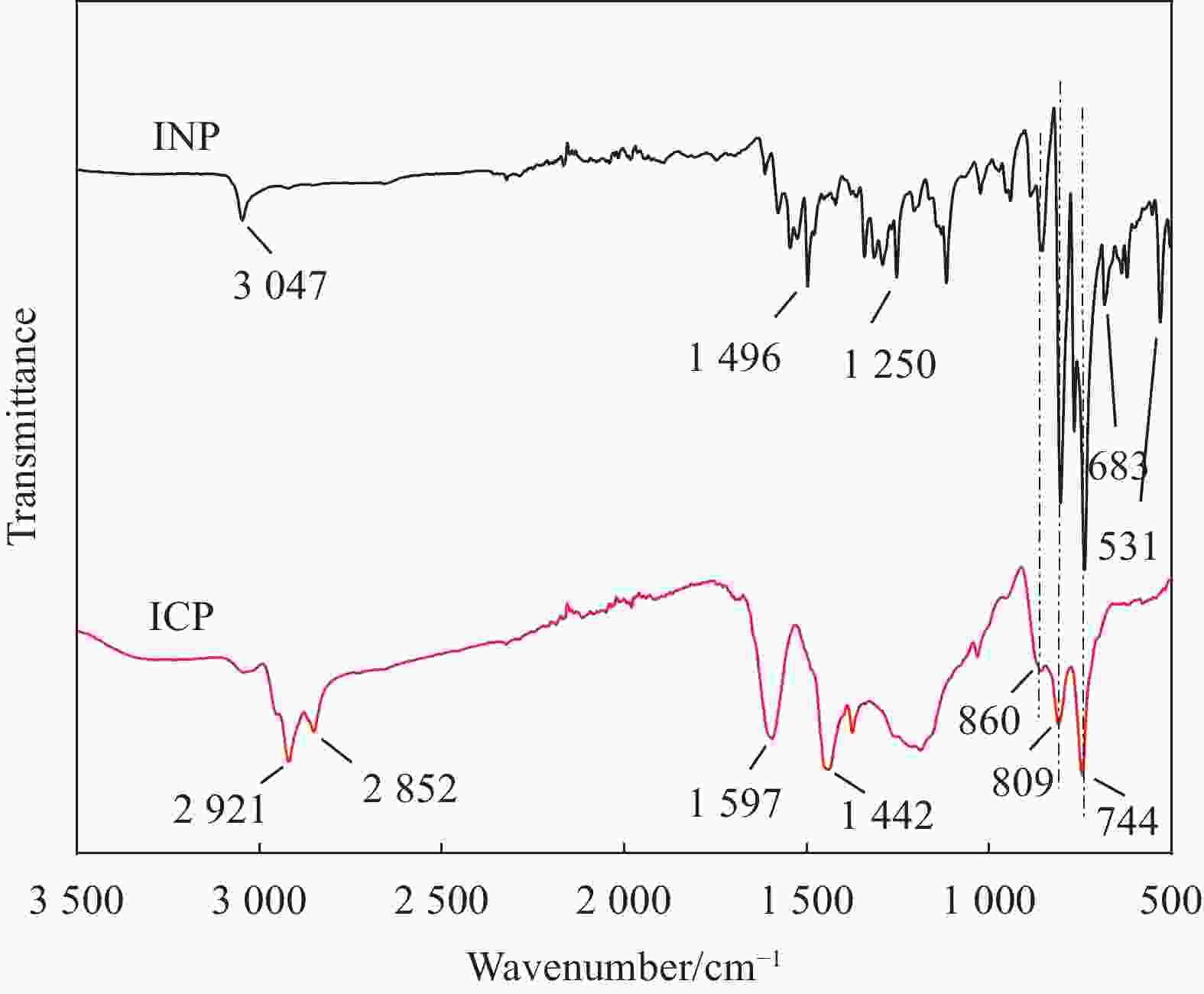
Table 3. Element composition of isotropic naphthalene pitch (INP) and coal tar pitch (ICP) (Unit: wt%)
Pitch C H N S O INP 67.6 2.1 0.2 27.1 1.2 ICP 84.7 5.1 1.2 0.4 5.5 表 4 熔纺聚丙烯腈(PAN)纤维的力学性能
Table 4. Mechanical properties of melt-spun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers
Sample Diameter/
μmTensile
strength/
MPaElongation/% P(AN-MA-ABP) 51±1.8 247.3±6.4 15.5±2.4 0.5wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 51±2.3 245.6±8.1 17.5±2.6 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 50±2.1 241.6±7.8 18.1±3.4 3wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 50±2.5 214.3±8.3 17.2±4.5 5wt%ICP/P(AN-MA-ABP) 52±1.7 175.9±7.9 23.2±5.1 表 5 UV辐照不同时间的1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP)三元共聚物纤维的原子浓度数据和原子比
Table 5. Atomic concentration data and atomic ratio of 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers irradiated by UV at different time
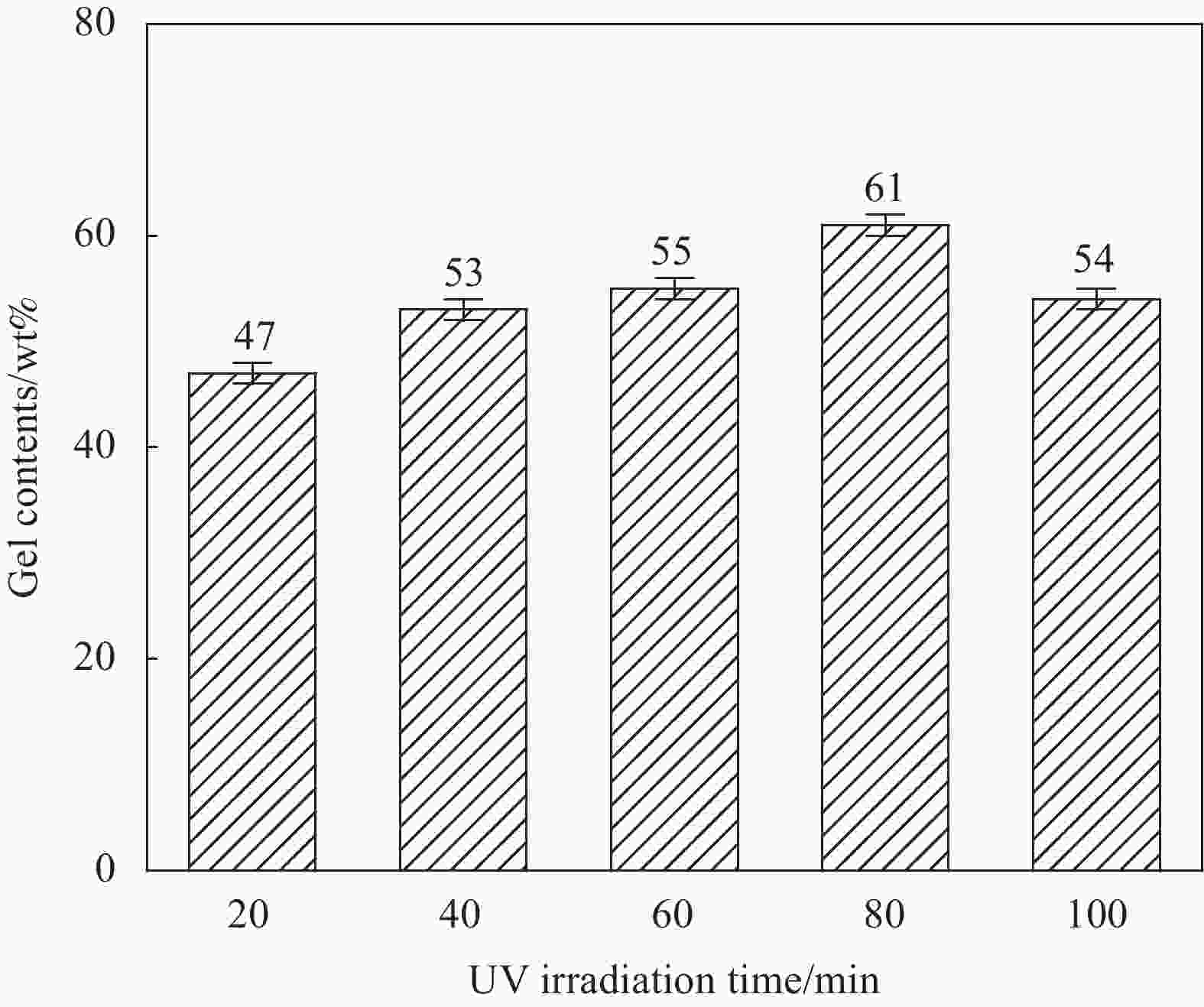
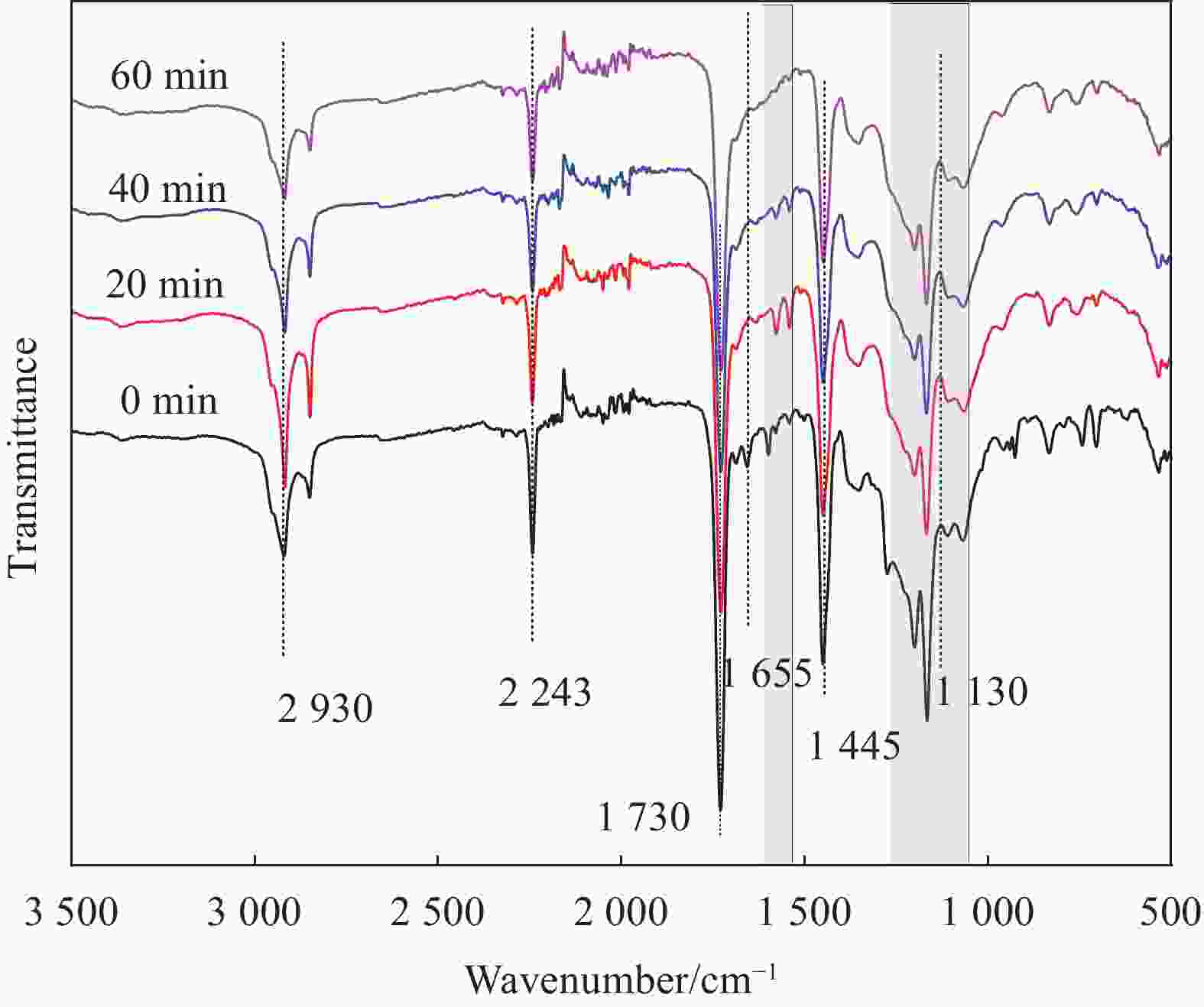
Element Atomic concentration/at% Non-irradiated UV 20 min UV 40 min UV 60 min C 74.6 72.0 69.9 67.0 O 17.3 21.3 22.3 26.0 N 8.1 6.7 7.8 7.0 O/C 0.2 0.3 0.3 0.4 N/C 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 表 6 UV辐照不同时间的1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP)三元共聚物纤维的DSC热力学数据
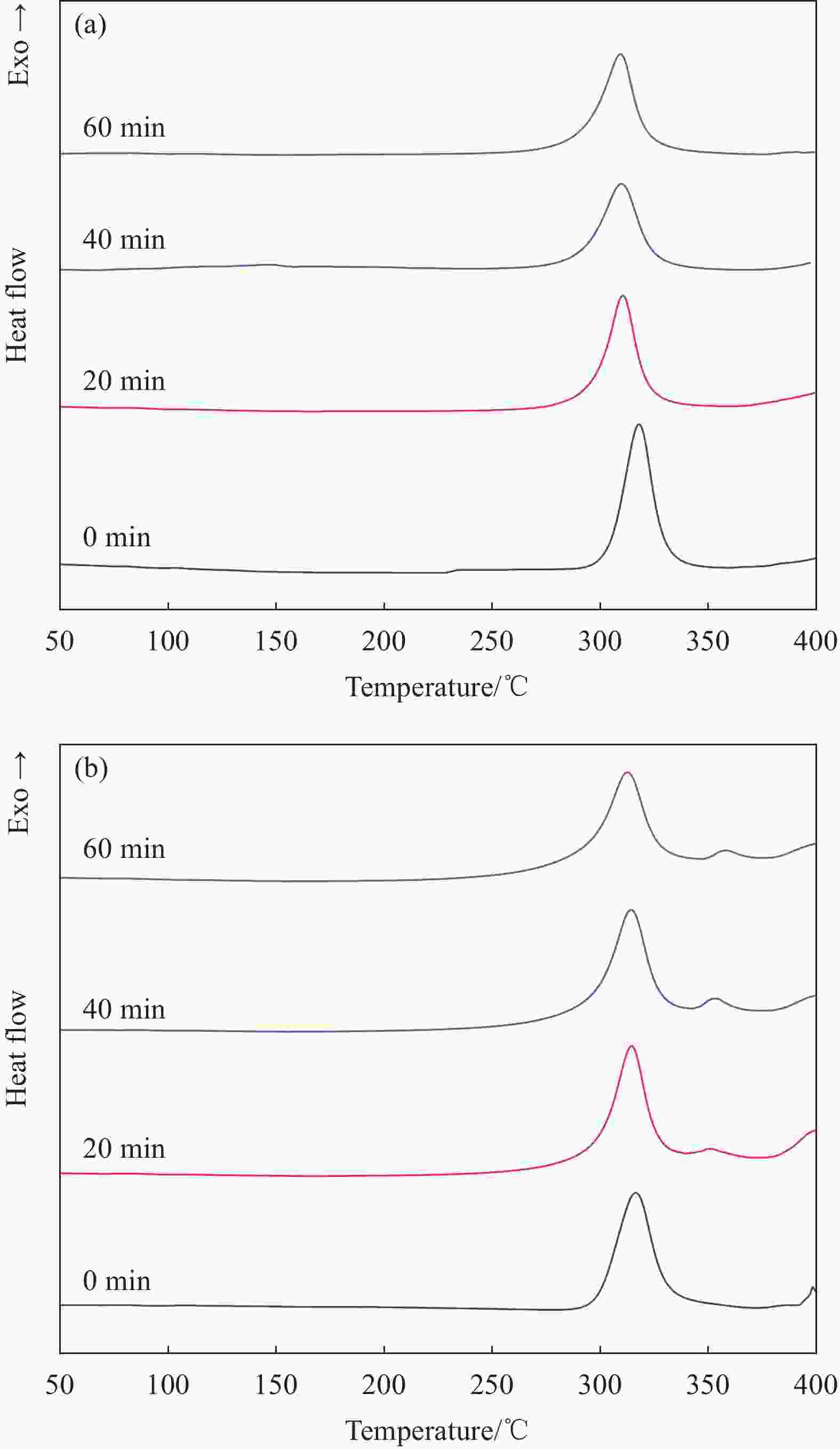
Table 6. DSC thermodynamic data of 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers irradiated by UV at different time
Atmosphere UV irradiation time/min Tonset
/℃TM
/℃△Hc
/(J·g−1)Nitrogen 0 303.8 318.0 537.8 20 296.4 310.6 474.8 40 294.0 309.1 443.7 60 292.4 308.8 442.1 Air 0 299.9 316.4 725.8 20 299.6 314.4 683.7 40 297.7 314.2 678.4 60 295.0 312.6 676.4 Notes: Tonset—Onset temperature of exothermic reaction (10℃/min); TM—Maximum temperature of exothermic reaction (10℃/min); ΔHc—Enthalpy of exothermic reaction (10℃/min). 表 7 UV辐照不同时间的1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP)三元共聚物纤维的力学性能
Table 7. Mechanical properties of 1wt%INP/P(AN-MA-ABP) terpolymer fibers irradiated by UV at different time
UV irradiation time/min Tensile strength/MPa Elongation/% 0 252.8±6.3 15.5±2.4 20 247.5±7.8 15.8±3.5 40 243.6±8.3 16.9±2.6 60 231.5±7.1 16.1±2.2 -
[1] NEWCOMB B A. Processing, structure, and properties of carbon fibers[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2016,91(Part 1):262-282. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.10.018 [2] CHOI D, KIL H S, LEE S. Fabrication of low-cost carbon fibers using economical precursors and advanced processing technologies[J]. Carbon,2019,142:610-649. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.10.028 [3] MIN B G, SON T W, JO W H, et al. Thermal stability of polyacrylonitrile in the melt formed by hydration[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,1992,46(10):1793-1796. doi: 10.1002/app.1992.070461010 [4] JIANG J X, SRINIVAS K, KIZILTAS A, et al. Rheology of polyacrylonitrile/lignin blends in ionic liquids under melt spinning conditions[J]. Molecules,2019,24(14):2650. doi: 10.3390/molecules24142650 [5] MARTIN H J, LUO H, CHEN H, et al. Effect of ionic liquid structure on the melt processability of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(7):8663-8673. [6] TIAN Y C, HAN K Q, ZHANG W H, et al. Influence of melt temperature on structure of polyacrylonitrile in ionic liquids during plasticized melt spinning process[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials,2012,(268-270):483-486. [7] KOENIG S, KREIS P, REINDERS L, et al. Melt spinning of propylene carbonate-plasticized poly(acrylonitrile)-co-poly(methyl acrylate)[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2020,31(8):1827-1835. doi: 10.1002/pat.4909 [8] MILLER G C, YU J, JOSEPH R M, et al. Melt-spinnable polyacrylonitrile copolymer precursors for carbon fibers[J]. Polymer,2017,126:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.08.023 [9] BAJAJ P, SREEKUMAR T V, SEN K. Thermal behaviour of acrylonitrile copolymers having methacrylic and itaconic acid comonomers[J]. Polymer,2001,42(4):1707-1718. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00583-8 [10] HAN N, ZHANG X X, WANG X C. Various comonomers in acrylonitrile based copolymers: Effects on thermal behavior[J]. Iranian Polymer Journal,2010,19(4):243-253. [11] HAN N, ZHANG X X, YU W Y, et al. Effects of copolymerization temperatures on structure and properties of melt-spinnable acrylonitrile-methyl acrylate copolymers and fibers[J]. Macromolecular Research,2010,18(11):1060-1069. doi: 10.1007/s13233-010-1115-7 [12] 韩娜, 张兴祥, 王学晨. 丙烯腈-丙烯酰胺共聚物的合成与性能研究[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2007, 25(1):71-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2812.2007.01.017HAN Na, ZHANG Xingxiang, WANG Xuechen. Synthesis and properties of acrylonitrile-acrylamide copolymer[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering,2007,25(1):71-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2812.2007.01.017 [13] BHANU V A, RANGARAJAN P, WILES K, et al. Synthesis and characterization of acrylonitrile methyl acrylate statistical copolymers as melt processable carbon fiber precursors[J]. Polymer,2002,43(18):4841-4850. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00330-0 [14] OUYANG Q, CHENG L, WANG H J, et al. Mechanism and kinetics of the stabilization reactions of itaconic acid-modified polyacrylonitrile[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2008,93(8):1415-1421. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2008.05.021 [15] DENG W J, LOBOVSKY A, IACONO S T, et al. Poly (acrylonitrile-co-1-vinylimidazole): A new melt processable carbon fiber precursor[J]. Polymer,2011,52(3):6221-6228. [16] LEE J H, JIN J U, PARK S, et al. Melt processable polyacrylonitrile copolymer precursors for carbon fibers: Rheological, thermal, and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2018,71:112-118. [17] RANGARAJAN P, YANG J, BHANU V, et al. Effect of comonomers on melt processability of polyacrylonitrile[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2002,85(1):69-83. doi: 10.1002/app.10655 [18] LI X, DANG X N. Effect of potassium permanganate modification on plasticized spinning polyacrylonitrile fibers with different diameters[J]. Polymers,2018,10(12):1330-1307. doi: 10.3390/polym10121330 [19] 赵雅娴, 武帅, 康宸, 等. H2O2改性对聚丙烯腈原丝化学结构的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(1):85-95.ZHAO Yaxian, WU Shuai, KANG Chen, et al. Effect of H2O2 modification on the chemical structure of polyacrylonitrile precursor[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae sinica,2019,36(1):85-95(in Chinese). [20] PARK S, KIL H S, CHOI D, et al. Rapid stabilization of polyacrylonitrile fibers achieved by plasma-assisted thermal treatment on electron-beam irradiated fibers[J]. Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry,2019,69:449-454. [21] SHIN H K, PARK M, KANG P H, et al. Preparation and characterization of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fibers produced by electron beam irradiation pretreatment[J]. Journal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry,2014,20(5):3789-3792. [22] MIAO P, WU D, ZENG K, et al. Influence of electron beam pre-irradiation on the thermal behaviors of polyacrylonitrile[J]. Polymer Degradation & Stability,2010,95(9):1665-1671. [23] LEE S W, LEE H Y, JANG S Y, et al. Tensile properties and morphology of carbon fibers stabilized by plasma treatment[J]. Carbon Letters,2011,12(1):16-20. doi: 10.5714/CL.2011.12.1.016 [24] ZHAO W, LU Y, ZHOU L, et al. Effects on the oriented structure and mechanical properties of carbon fibers by pre-irradiating polyacrylonitrile fibers with γ ray[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2016,51(15):7073-7084. doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-9875-x [25] PAIVA M C, KOTASTHANE P. UV stabilization route for melt-processible PAN-based carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2003,41(7):1399-1409. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00041-1 [26] SON S Y, JO A Y, JUNG G Y, et al. Accelerating the stabilization of polyacrylonitrile fibers by UV irradiation[J]. Jour-nal of Industrial & Engineering Chemistry,2019,73:47-51. [27] JO A Y, YOO S H, CHUNG Y S, et al. Effects of ultraviolet irradiation on stabilization of textile-grade polyacrylonitrile fibers without photo-initiator for preparing carbon fibers[J]. Carbon,2019,144:440-448. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.12.012 [28] NASKAR A K, WALKER R A, PROULX S, et al. UV assisted stabilization routes for carbon fiber precursors produced from melt-processible polyacrylonitrile terpolymer[J]. Carbon,2005,43(5):1065-1072. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.11.047 [29] MUKUNDAN T, BHANU V A, WILES K B, et al. A photocrosslinkable melt processible acrylonitrile terpolymer as carbon fiber precursor[J]. Polymer,2006,47(11):4163-4171. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2006.02.066 [30] 臧传起. 中间相沥青基碳纤维的结构调控与性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2019.ZANG Chuanqi. Study on structure regulation and properties of mesophase bituminous carbon fibers[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [31] 石奎. 乙烯焦油系沥青基炭纤维的制备与性能研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2019.SHI Kui. Study on preparation and properties of vinyl tar pitch-based carbon fibers[D]. Hunan: Hunan University, 2019(in Chinese). [32] 智林杰, 史景利, 宋进仁, 等. 交联萘沥青的组成与结构特征[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2000, 28(6):546-549. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2000.06.014ZHI Linjie, SHI Jingli, SONG Jinren, et al. Composition and structural characteristics of cross-linked naphthalene asphalt[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2000,28(6):546-549(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2409.2000.06.014 [33] 秦显营. 沥青基碳纤维的制备与性能研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2007.QIN Xianying. Preparation and properties of pitch carbon fibers[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2007(in Chinese). [34] 周良霄. PAN纤维稳定化过程中的交联结构[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2016.ZHOU Liangxiao. Cross-linked structure of PAN fibers during stabilization[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2016(in Chinese). [35] ZHANG W L, WANG M H, ZHANG W F, et al. Significantly reduced pre-oxidation period of PAN fibers by continuous electron beam irradiation: Optimization by monitoring radical variation[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2018,158:72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.10.027 [36] 刘伟华, 王谋华, 张文发, 等. γ射线辐照处理对聚丙烯腈纤维预氧化反应的影响[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2015, 31(5):51-55.LIU Weihua, WANG Mouhua, ZHANG Wenfa, et al. Effect of γ-ray irradiation on preoxidation of polyacrylonitrile fibers[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering,2015,31(5):51-55(in Chinese). [37] ZHANG W, WANG M, LIU W, et al. Higher dose rate effect of 500 keV EB irradiation favoring free radical annealing and pre-oxidation of polyacrylonitrile fibers[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2019,167:201-209. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.07.003 [38] 黄光林, 冯雨丁, 吴茂良. 高分子辐射化学基础[M]. 成都: 四川大学出版社, 1993.HUANG Guanglin, FENG Yuding, WU Maoliang. Fundamentals of polymer radiation chemistry[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan University Press, 1993(in Chinese). [39] LEI S, WU S, GAO A J, et al. The formation of conjugated structure and its transformation to pseudo-graphite structure during thermal treatment of polyacrylonitrile[J]. High Performance Polymers,2016,29(9):1097-1109. [40] ZHAO W Z, LV Y G, JIANG J Q, et al. The effect of γ-ray irradiation on the microstructure and thermal properties of polyacrylonitrile fibers[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(30):23508-23518. doi: 10.1039/C5RA01139F -





 下载:
下载: