Influence mechanism of curing temperature on the characteristics of dredged ultrafine mortar from Yangtze River
-
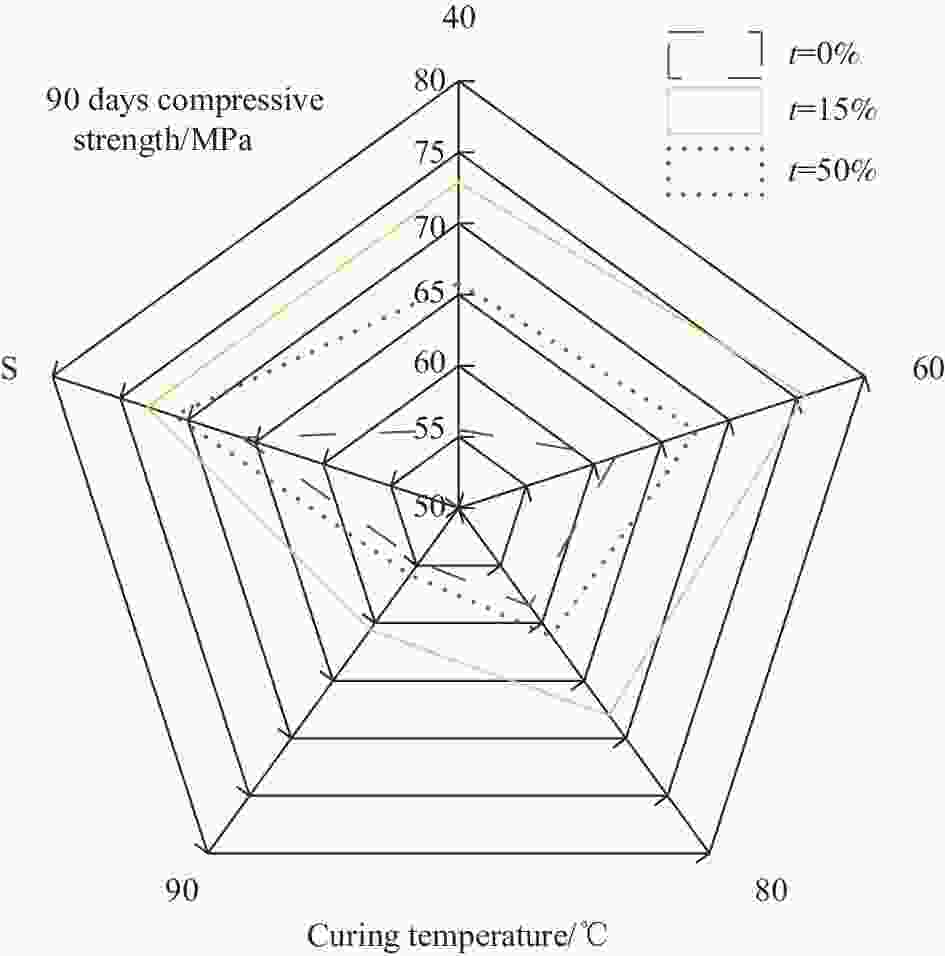
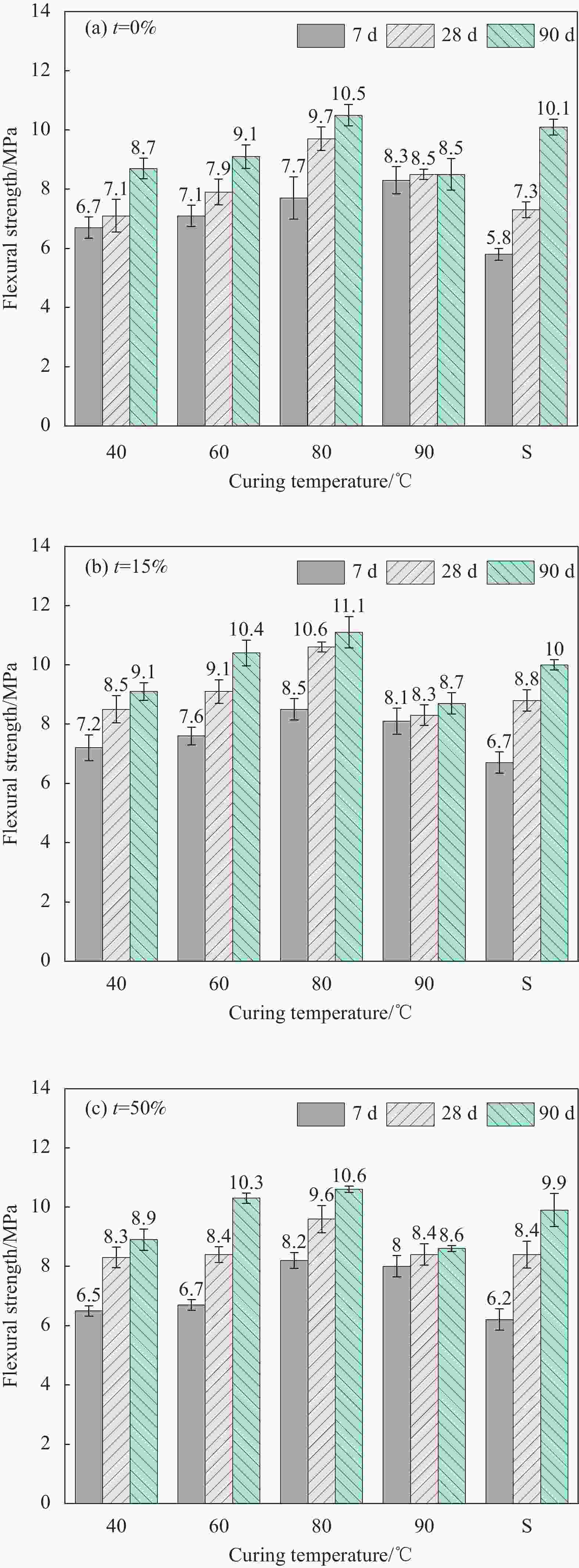
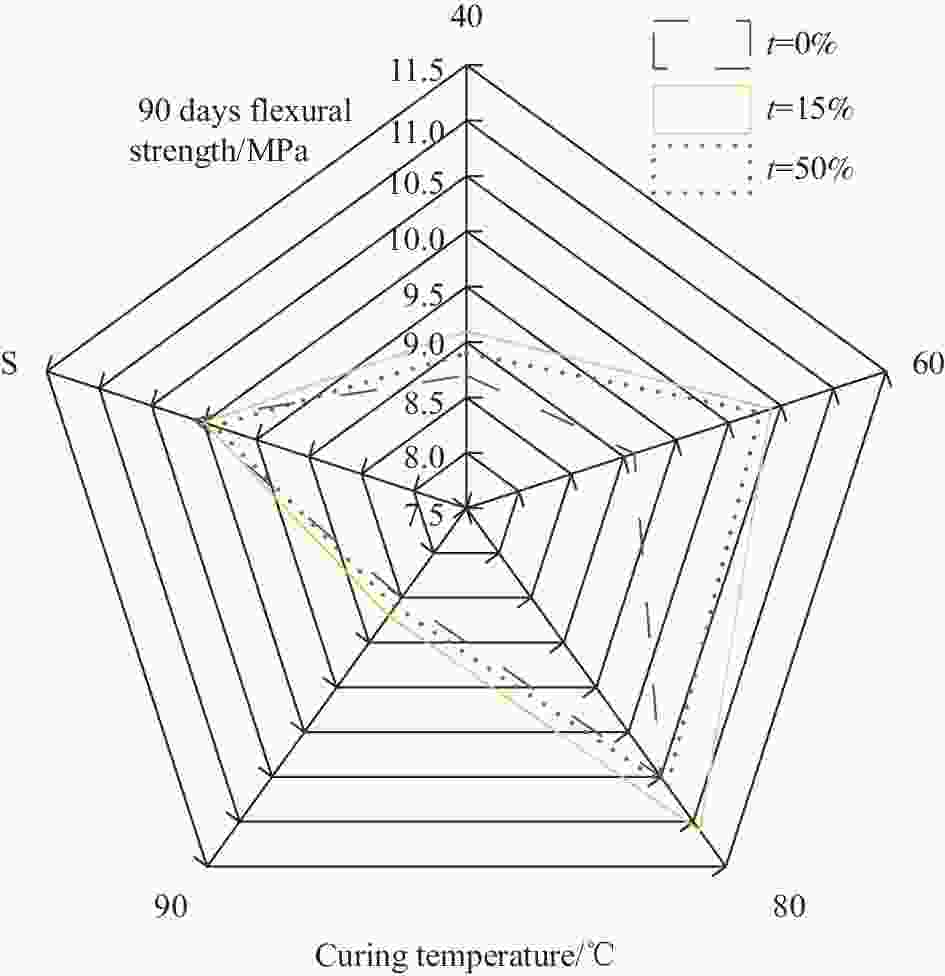
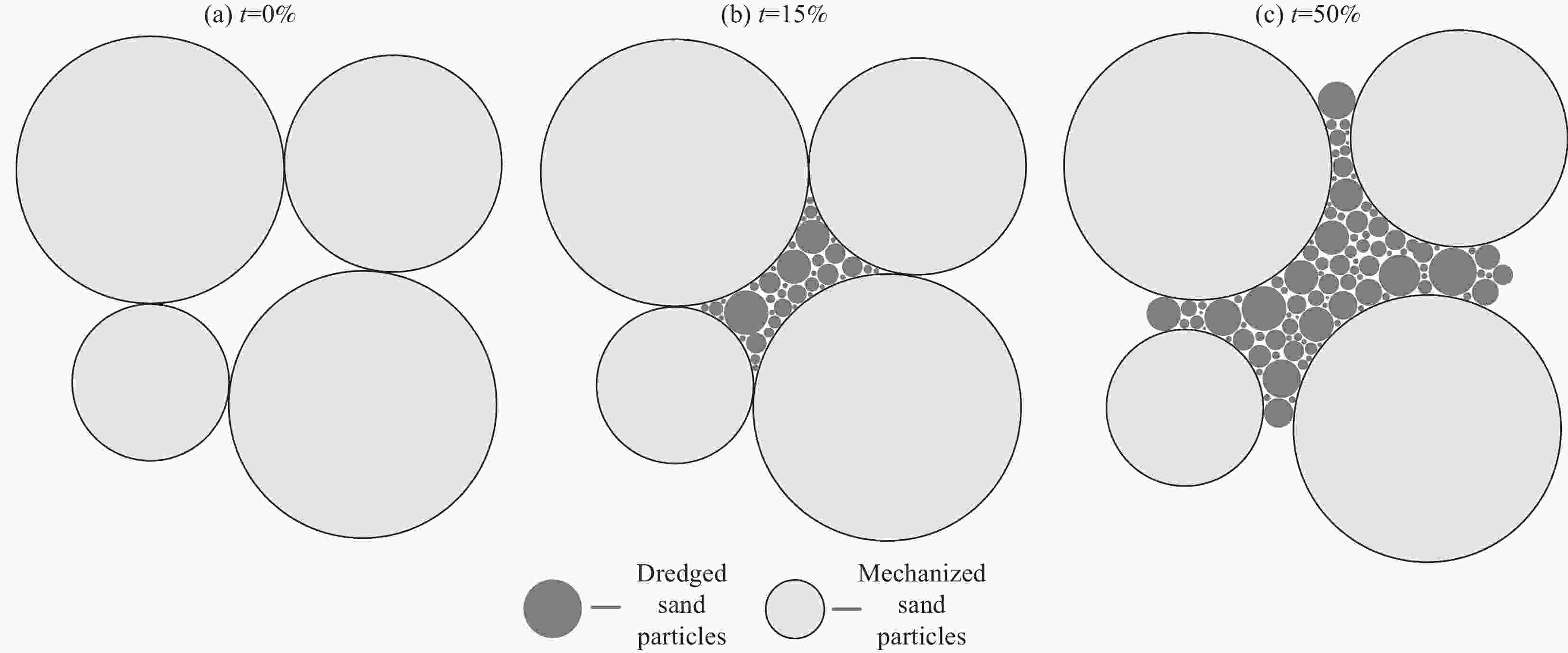
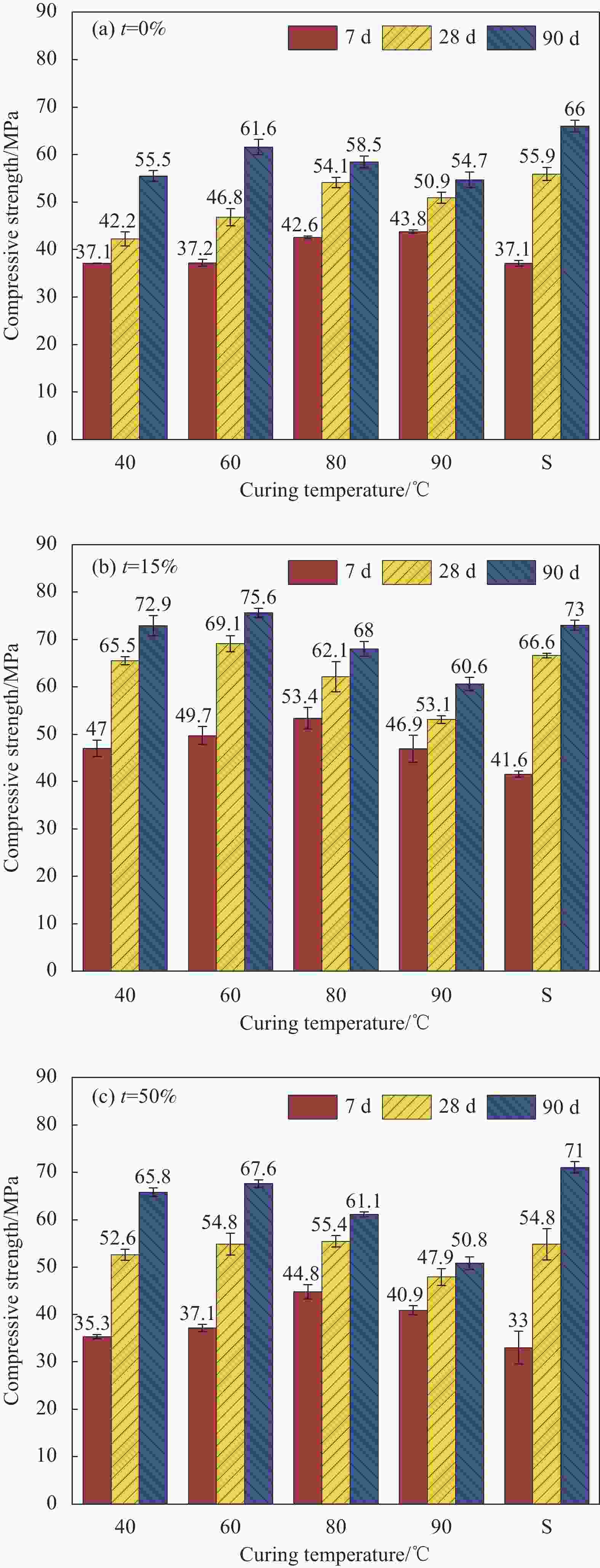
摘要: 为了实现长江下游疏浚砂的综合利用,拓展细骨料来源,研究不同养护温度对不同疏浚砂掺量砂浆特性的影响。以疏浚砂为原料,设计了3种不同疏浚砂掺量的砂浆配合比,研究了40、60、80、90℃ 4种养护温度对不同龄期抗压、抗折强度的影响,并结合X射线衍射、热重-差示扫描量热、扫描电镜、压汞测试,分析了不同养护温度及不同疏浚砂掺量砂浆的微观结构。研究结果表明:随着养护温度升高,砂浆内部水化产物分布不均匀,阻碍了后续的水化反应,砂浆的抗压、抗折强度总体上先增大后减小,养护温度越高,蒸养损伤越大;疏浚砂颗粒粒径极小,具有良好的填充效果,适量掺入疏浚砂能提高体系的密实度,同时还能减少有害孔和多害孔的数量,进而提高砂浆的力学性能;蒸养条件下,砂浆孔结构缺陷增多,疏浚砂的优化作用被放大,一定程度上可以抵消蒸养带来的部分不利影响,随养护温度的升高,疏浚砂对抗压强度的提升率逐渐降低,最大能提升31.35%,对抗折强度的提升率先增大后减小,最大能提升14.29%。Abstract: In order to realize the comprehensive utilization of dredged sand in the lower Yangtze River and expand the source of fine aggregate, the effects of different maintenance temperatures on different dredged sand admixtures mortar characteristics were investigated. Using dredged sand as raw material, three mortar mix ratios with different dredged sand admixtures were designed, and the effects of four curing temperatures of 40, 60, 80 and 90℃ on the compressive and flexural strengths at different ages were investigated, The microstructures of specimens with different curing temperatures and different dredged sand admixtures were analyzed by combining X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric-differential scanning calorimetry, scanning electron microscopy and mercury injection test. The results show that with the increase of curing temperature, the distribution of hydration products in mortar is uneven, which hinder the subsequent hydration reaction. The compressive and flexural strengths of mortar increase first and then decrease. The higher the curing temperature is, the greater the steam curing damage is. The particle size of dredged sand is very small, and it has good filling effect. Appropriate incorporation of dredged sand can improve the compactness of the system, and reduce the number of harmful holes and multiple harmful holes, thereby improving the mechanical properties of mortar. Under the condition of steam curing, the pore structure defects of mortar increase, and the optimization effect of dredged sand is amplified, which can offset some adverse effects of steam curing to a certain extent. The enhancement rate of the dredged sand on the compressive strength gradually decreases with the increase of the curing temperature, and the maximum could enhance 31.35%. The enhancement of the flexural strength increases first and then decreases, and the maximum could enhance 14.29%.
-
表 1 粉煤灰化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of fly ash
Ingredients CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO TiO2 P2O5 MnO K2O Fe2O3 Mass fraction/wt% 1.47 55.78 34.69 0.25 1.74 1.17 0.02 1.32 3.56 表 2 矿粉化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of mineral powder
Ingredients CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO TiO2 SO3 MnO K2O Fe2O3 Mass fraction/wt% 39.19 26.31 16.17 9.99 2.18 3.71 1.04 0.38 1.03 表 3 疏浚砂与机制砂物理性能参数
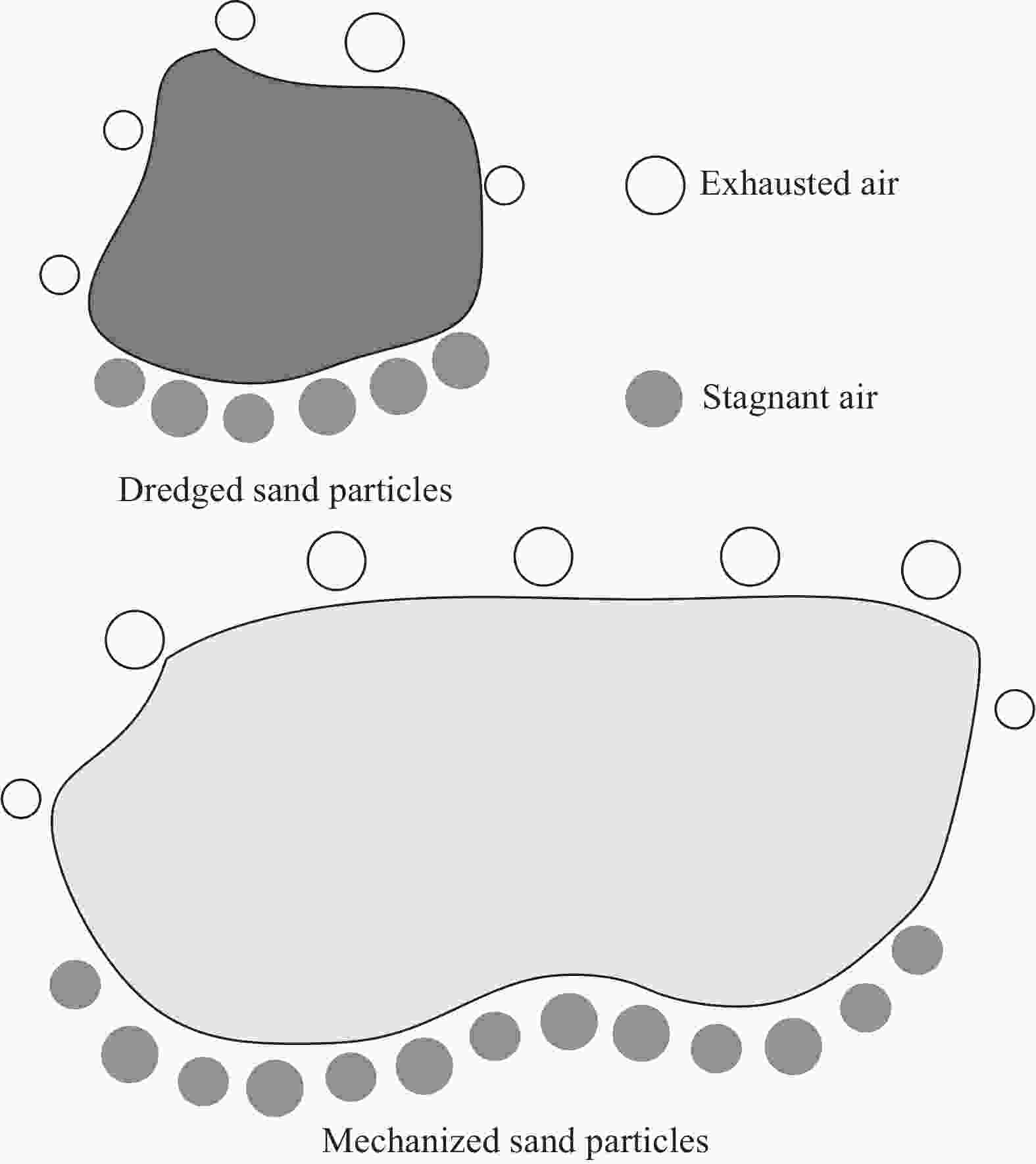
Table 3. Physical property parameters of dredged sand and mechanism sand
Sand Apparent density/(kg·m−3) Stacking density/(kg·m−3) Porosity/% Mud content/% Water content/% Fineness modulus Dredged sand 2690 1365 12.3 1.9% 13.5 0.5 Mechanism sand 2591 1484 43 — — 3.2 表 4 砂浆配合比
Table 4. Mortar mix ratio
kg·m−3 Dredged sand content t/% Cement Fly ash Mineral powder Dredged sand Mechanized sand Water Additives 0 322 264.7 150 0.00 1035.00 279.3 3.3 15 322 264.7 150 155.25 879.75 279.3 3.3 50 322 264.7 150 517.50 517.50 279.3 3.3 表 5 试件编号
Table 5. Specimen number
Specimen
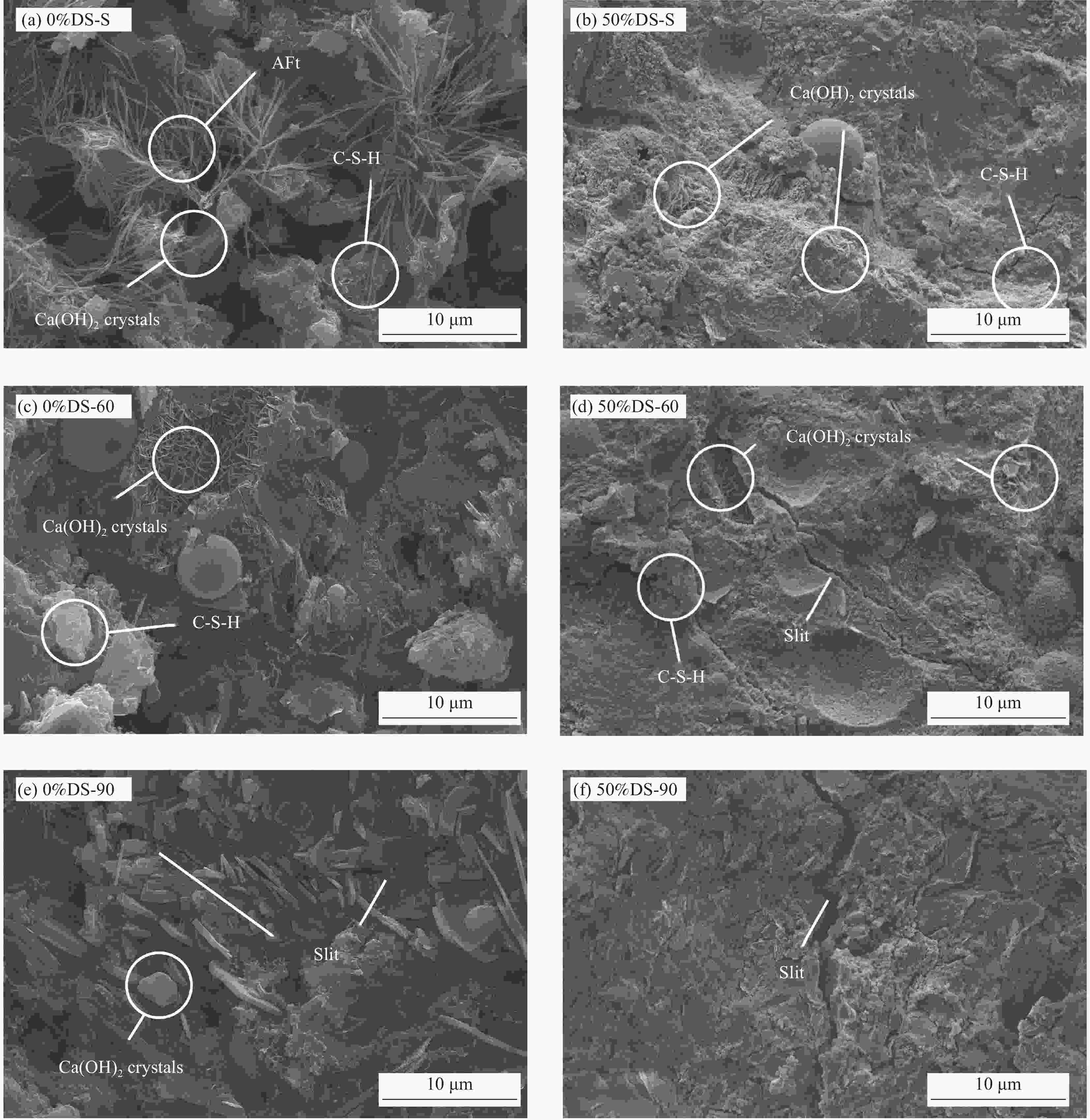
numberDredged sand content t/% Curing temperature/℃ 0%DS-S 0 S 15%DS-40 15 40 50%DS-60 50 60 0%DS-80 0 80 15%DS-90 15 90 Notes: S—Standard curing; Taking 15%DS-40 as an example, 15%DS represents the dredged sand admixture is 15%, 40 represents the curing method is 40°C steam curing. 表 6 疏浚砂砂浆质量损失率及Ca(OH)2含量
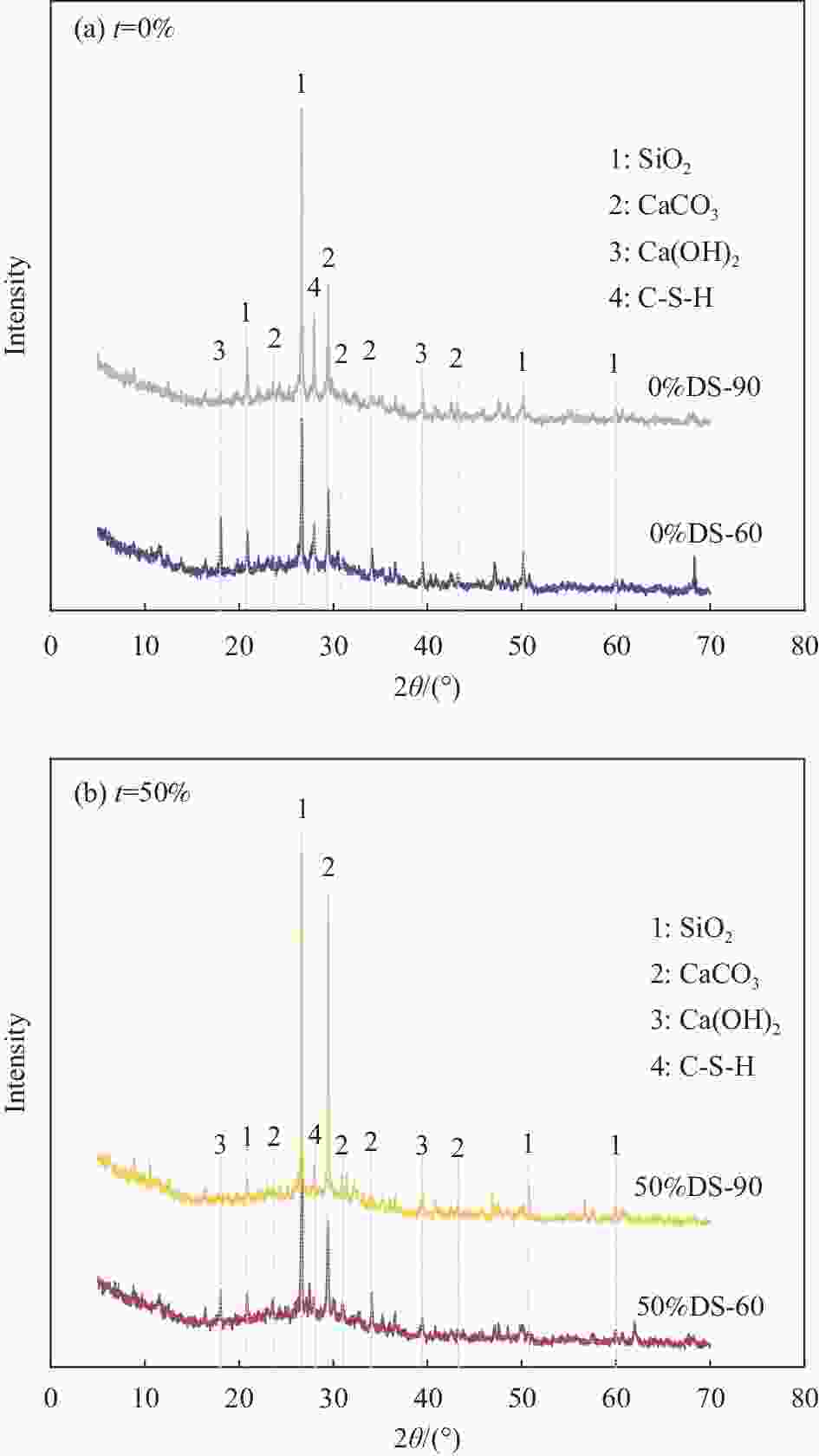
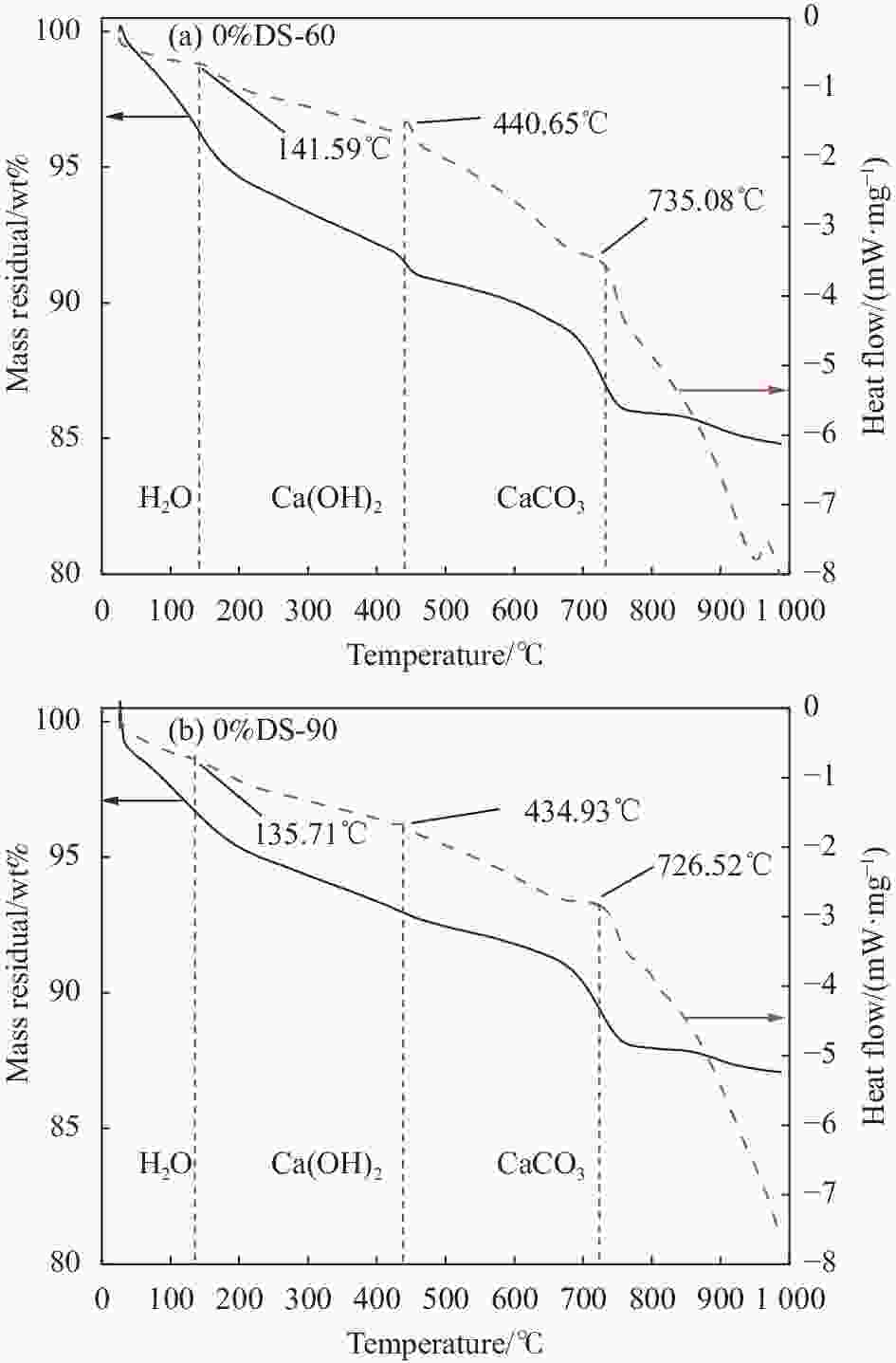
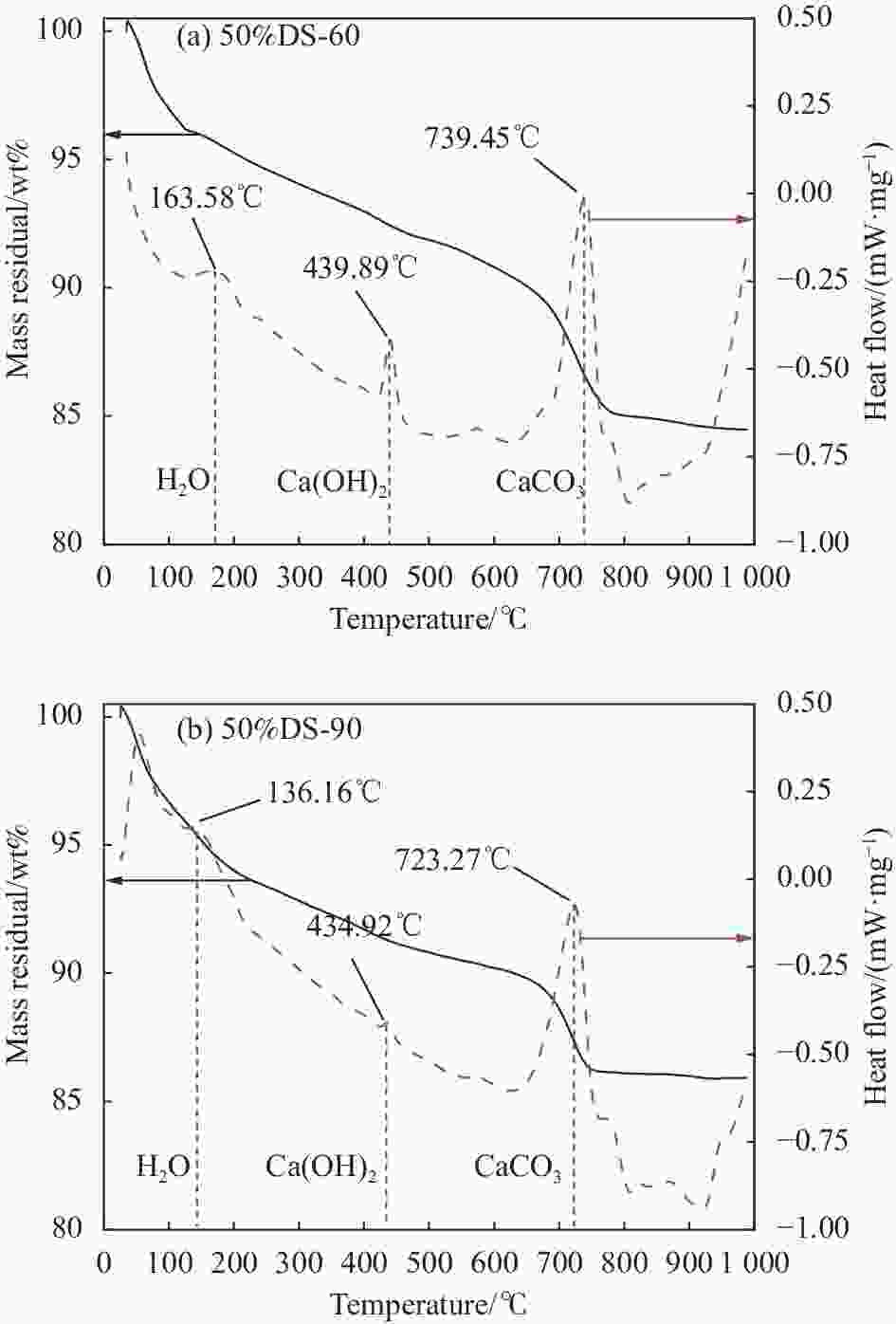
Table 6. Mass loss rate and Ca(OH)2 content of dredged sand mortar
Specimen number Mass loss rate/% Ca(OH)2 content/wt% 0%DS-60 15.20 5.85 0%DS-90 12.93 3.78 50%DS-60 15.53 4.56 50%DS-90 14.08 3.69 表 7 疏浚砂砂浆平均孔径与孔径分布
Table 7. Average pore size and pore size distribution of dredged sand mortar
Specimen number Average pore size/nm Pore size distribution/% <20 nm 20-50 nm 50-200 nm >200 nm 0%DS-40 11.19 36.97 13.76 13.08 36.19 0%DS-60 11.86 54.39 15.46 5.09 25.06 0%DS-80 16.36 53.27 8.34 1.63 36.76 0%DS-90 16.98 51.01 8.07 2.51 38.41 0%DS-S 13.71 50.97 17.40 7.97 23.66 50%DS-40 10.60 62.95 6.71 4.87 25.47 50%DS-60 10.77 71.35 9.06 3.67 15.92 50%DS-80 11.66 57.20 11.53 6.89 24.38 50%DS-90 11.95 60.68 9.79 4.73 24.80 50%DS-S 10.93 66.28 12.08 0.84 20.80 -
[1] 李青云. 推进长江航道疏浚砂综合利用[N]. 中国水运报, 2020-04-01(001).LI Qingyun. Promote the comprehensive utilization of dredged sand in the Yangtze River waterway[N]. China Water Transport News, 2020-04-01(001)(in Chinese). [2] ZHANG G, SONG J, YANG J, et al. Performance of mortar and concrete made with a fine aggregate of desert sand[J]. Building and Environment,2006,41(11):1478-1481. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2005.05.033 [3] QIAO H, NDAHIRWA D, LI Y, et al. The feasibility of basalt rock powder and superfine sand as partial replacement materials for portland cement and artificial sand in cement mortar[J]. Research and Application of Materials Science,2019,1(1):1-6. [4] HASSOUNE M, CHRAIBI G, FATMAOUI H, et al. Stability of quay wall made on concrete blocks with a formulation based on dredging sand[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2021,36:47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.163 [5] HASSOUNE M, FATMAOUI H, CHAOUFI J. Use of concrete formulations based on dredging sand in the fabrication of tetrapods for protection of harbour dykes[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2022,52:60-63. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.10.281 [6] 李升涛, 陈徐东, 张伟, 等. 基于长江下游超细疏浚砂的碱激发矿渣混凝土力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):335-343.LI Shengtao, CHEN Xudong, ZHANG Wei, et al. Mechanical properties of alkali activated slag concrete with ultra fine dredged sand from Yangtze River[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):335-343(in Chinese). [7] ZHANG Q, LIU H, LIU Q, et al. Study the fire resistance of desert sand concrete (DSC) with interface phase through uniaxial compression tests and analyses[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2021,2021:8863136. doi: 10.1155/2021/8863136 [8] LIU H, MA Y, MA J, et al. Frost resistance of desert sand concrete[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2021,2021:6620058. doi: 10.1155/2021/6620058 [9] PENG X, ZHOU Y, JIA R, et al. Preparation of non-sintered lightweight aggregates from dredged sediments and modification of their properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,132:9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.088 [10] 刘霞, 李峰, 佘殷鹏. 玄武岩纤维增强聚合物筋增强珊瑚礁砂混凝土柱轴压试验[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(10):2428-2438.LIU Xia, LI Feng, SHE Yinpeng. Axial compression test of basalt fiber reinforced polymer reinforced coral reef and sand aggregate concrete column[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(10):2428-2438(in Chinese). [11] 秦拥军, 张亮亮, 渠长伟, 等. 钢纤维沙漠砂混凝土梁受弯力学性能试验[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 39(11):5599-5610.QIN Yongjun, ZHANG Liangliang, QU Changwei, et al. Testing of flexural mechanical properties of steel fiber desert sand concrete beams[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,39(11):5599-5610(in Chinese). [12] 梅军帅, 吴静, 王罗新, 等. 珊瑚砂浆的力学性能与微观结构特征[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(2):263-270.MEI Junshuai, WU Jing, WANG Luoxin, et al. Mechanical properties and microstructural characteristics of coral mortar[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2020,23(2):263-270(in Chinese). [13] HUANG X, LI G, PAN X, et al. Kinetic characteristics of lightweight aggregates obtained from dredged sediment[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,2016,126(3):1201-1209. doi: 10.1007/s10973-016-5610-8 [14] ZEYAD A M, JOHARI M A M, ALHARBI Y R, et al. Influence of steam curing regimes on the properties of ultrafine POFA-based high-strength green concrete[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2021,38:102204. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102204 [15] MO Z, GAO X, SU A. Mechanical performances and microstructures of metakaolin contained UHPC matrix under steam curing conditions[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,268:121112. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121112 [16] YANG J, HU H, HE X, et al. Effect of steam curing on compressive strength and microstructure of high volume ultrafine fly ash cement mortar[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,266:120894. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120894 [17] 黄安, 李北星, 杨建波, 等. 蒸养制度对预制桥面板混凝土强度与抗渗性的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2021, 40(4):1170-1177.HUANG An, LI Beixing, YANG Jianbo, et al. Effect of steam curing system on strength and impermeability of precast bridge deck concrete[J]. Bulletin of Silicate,2021,40(4):1170-1177(in Chinese). [18] QIAN X, JIANG L, SONG Z, et al. Impact of elevated curing temperature on mechanical properties and microstructure of MgO-based expansive additive cement mortars[J]. Structural Concrete,2020,21(3):1082-1092. doi: 10.1002/suco.201900127 [19] DE LARRARD F. Concrete mixture proportioning: A scientific approach[M]. Florida: CRC Press Inc., 1999. [20] 李玉根, 张慧梅, 刘光秀, 等. 风积砂混凝土基本力学性能及影响机理[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(5):1212-1221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.05.030LI Yugen, ZHANG Huimei, LIU Guangxiu, et al. Basic mechanical properties and influence mechanism of aeolian sand concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2020,23(5):1212-1221(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.05.030 [21] 桑国臣, 曹艳洲, 樊敏, 等. 硫铝酸盐水泥基复合相变储能砂浆的制备及其性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(8):2124-2131.SANG Guochen, CAO Yanzhou, FAN Min, et al. Preparation and properties of sulfoaluminate cement-based composite phase change energy storage mortar[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(8):2124-2131(in Chinese). [22] YANG S, WANG J, CUI S, et al. Impact of four kinds of alkanolamines on hydration of steel slag-blended cementitious materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,131:655-666. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.09.060 [23] 朱红光, 霍青杰, 倪亚东, 等. 煤矸石细集料-矿渣混凝土抗压强度与抗冻性能研究[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(22):22085-22091. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20080019ZHU Hongguang, HUO Qingjie, NI Yadong, et al. Research on compressive strength and frost resistance of coal gangue fine aggregate-slag concrete[J]. Materials Reports,2021,35(22):22085-22091(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.20080019 [24] 张高展, 葛竞成, 张春晓, 等. 养护制度对混凝土微结构形成机理的影响进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(15):15125-15133. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20060297ZHANG Gaozhan, GE Jingcheng, ZHANG Chunxiao, et al. Advances in the effect of curing system on the formation mechanism of concrete microstructure[J]. Materials Reports,2021,35(15):15125-15133(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.20060297 [25] 黄时玉, 霍彬彬, 陈春, 等. 蒸养条件下偏高岭土对钢渣水泥基复合体系水化的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(5):73-78.HUANG Shiyu, HUO Binbin, CHEN Chun, et al. The influence of metakaolin on the hydration of steam-cured steel slag blended cement[J]. Materials Reports,2022,36(5):73-78(in Chinese). [26] BAHAFID S, GHABEZLOO S, DUC M, et al. Effect of the hydration temperature on the microstructure of Class G cement: CSH composition and density[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2017,95:270-281. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2017.02.008 -





 下载:
下载: