Preparation and properties of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2(Me=V, W) high entropy boride ceramics
-
摘要: 为了制备性能优异的高熵硼化物陶瓷,通过硼热/碳热还原法与放电等离子烧结技术 (SPS) 结合制备(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2(Me=V, W) 高熵硼化物陶瓷,研究V和W对高熵硼化物陶瓷物相组成、形貌和力学性能的影响。结果表明,在1600℃合成的(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2(Me=V, W)高熵硼化物粉末均未形成单相固溶体,经2000℃烧结后(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2V0.2Ti0.2)B2形成了完全固溶体,但是(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2样品中还检测到WB相。(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2V0.2Ti0.2)B2样品致密度(93.1%)低于(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2(96.7%),但其晶粒尺寸显著小于(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2。(Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2具有较高的硬度(24.0 GPa),但断裂韧性低于 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2V0.2Ti0.2)B2(3.32 MPa·m1/2)。Abstract: In order to prepare high entropy boride ceramics with excellent performance, (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2(Me=V, W) high entropy boride ceramics were fabricated though boro/carbothermal reduction method combined with spark plasma sintering (SPS) in this paper. The effects of V and W on phase composition, morphology and mechanical properties of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2(Me=V, W) high entropy boride ceramics were investigated. Results show that (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2(Me=V, W) high entropy boride powders are failed formed single-phase solid solution in 1600℃, but (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2V0.2Ti0.2)B2 is formed a complete solid solution after 2 000℃ sintering. However, WB phase is still detected in (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2 sample. The density of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2V0.2Ti0.2)B2(93.1%) is lower than that of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2(96.7%), but its grain size is smaller. The hardness of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2(24.0 GPa) is higher, but the fracture toughness is lower than that of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2V0.2Ti0.2)B2 (3.32 MPa·m1/2).
-
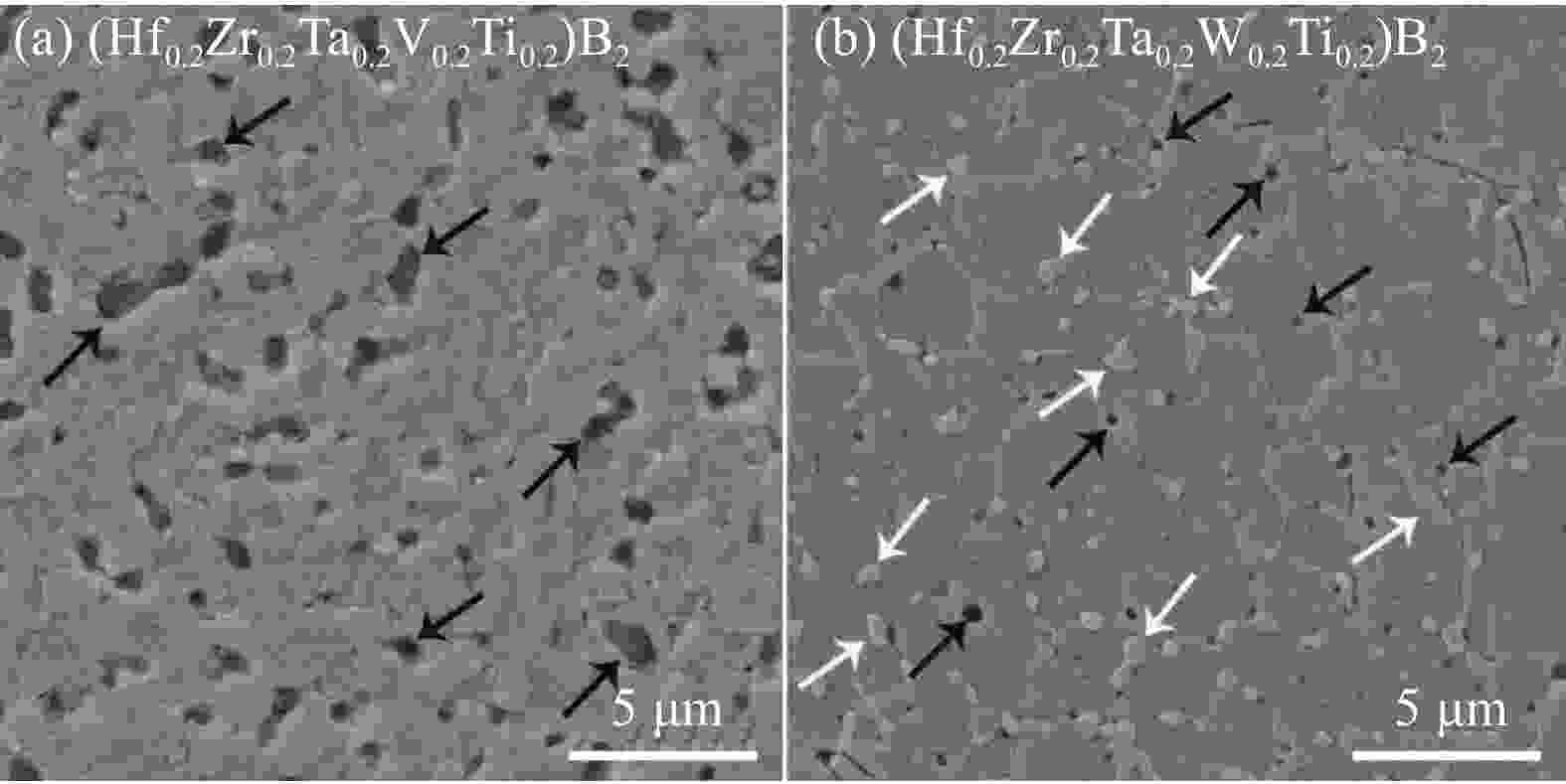
表 1 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2 (Me=V, W)高熵陶瓷(HEB)粉末的成分、粒径、晶粒尺寸和致密度
Table 1. Composition, particle, grain size and relative density of (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2Ti0.2Me0.2)B2 (Me=V, W) high-entropy boride (HEB) powders
Composition Particle size of HEB powders/μm Grain size of HEB ceramics/μm Relative density/% (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2V0.2Ti0.2)B2 0.24±0.06 1.07±0.29 93.1±0.6 (Hf0.2Zr0.2Ta0.2W0.2Ti0.2)B2 0.22±0.06 1.83±0.39 96.7±0.9 -
[1] ROST C M, SACHET E, BORMAN T, et al. Entropy-stabi-lized oxides[J]. Nature Communacation, 2015, 6: 84-85. [2] TSAI M H, YEH J W. High-entropy alloys: A critical review[J]. Materials Research Letter,2014,2:107-123. doi: 10.1080/21663831.2014.912690 [3] GAO M C, MIRACLE D B, MAURICE D, et al. High-entropy functional materials[J]. Journal of Materials Research,2018,33:3138-3155. doi: 10.1557/jmr.2018.323 [4] CHEN J, ZHOU J, WANG W, et al. A review on fundamental of high-entropy alloys with promising high-temperature properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Componds,2018,760:15-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.067 [5] GILD J, SAMIEE M, BRAUN J L, et al. High-entropy fluorite oxides[J]. Journal of European Ceramic Society,2018,38:3578-3584. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2018.04.010 [6] BÉ RARDAN D, FRANGER S, DRAGOE D, et al. Colossal dielectric constant in high entropy oxides[J]. Physica Status Solidi RRL,2016,10:328-333. doi: 10.1002/pssr.201600043 [7] JIN T, SANG X, UNOCIC R R, et al. Mechanochemical-assisted synthesis of high-entropy metal nitride via a soft urea strategy[J]. Advanced Material,2018,30:1707512. doi: 10.1002/adma.201707512 [8] ZHANG R Z, GUCCI F, ZHU H Y, et al. Data-driven design of ecofriendly thermoelectric high-entropy sulfides[J]. Inorganic Chemistry,2018,57:13027-13033. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.8b02379 [9] FENG L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, et al. Syn-thesis of single-phase high entropy carbide powders[J]. Scripta Materialia,2019,162:90-93. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.10.049 [10] CASTLE E, CSANÁ DI T, GRASSO S, et al. Processing and properties of high-entropy ultra-high temperature carbides[J]. Science Repprt,2018,8:8609. [11] ZHANG Y, GUO W M, JIANG Z B, et al. Dense high-entropy boride ceramics with ultra-high hardness[J]. Scripta Materialia,2019,164:135-139. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2019.01.021 [12] QIN Y, LIU J X, LI F, et al. A high entropy silicide by reac-tive spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of Advanced Ceramic,2019,8:148-152. doi: 10.1007/s40145-019-0319-3 [13] 任会兰, 龙波, 宁建国, 等. ZrO2增韧Al2O3陶瓷的力学性能和增韧机制 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(3):776-781.REN Huilan, LONG Bo, NING Jianguo, et al. Mechanical properties and toughening mechanisms of toughened ceramics[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(3):776-781(in Chinese). [14] GILD J, ZHANG Y, HARRINGTON T, et al. High-entropy metal diborides: A new class of high-entropy materials and a new type of ultrahigh temperature ceramics[J]. Science Report,2016,6:37946. doi: 10.1038/srep37946 [15] GILD J, WRIGHT A, QUIAMBAO-TOMKO K, et al. Thermal conductivity and hardness of three single-phase high-entropy metal diborides fabricated by boro/carbothermal reduction and spark plasma sintering[J]. Ceramic International,2020,46(5):6906-6913. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.186 [16] GU J F, ZOU J, SUN S K, et al. Dense and pure high-entropy metal diboride ceramics sintered from self-synthesized powders via boro/carbothermal reduction approach[J]. Science China Materials,2019,62(12):1898-1909. doi: 10.1007/s40843-019-9469-4 [17] ZHANG Y, SUN S K, ZHANG W, et al. Improved densification and hardness of high-entropy diboride ceramics from fine powders synthesized via borothermal reduction process[J]. Ceramic International,2020,46(9):14299-14303. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.214 [18] QIN M, GILD J, WANG H, et al. Dissolving and stabilizing soft WB2 and MoB2 phases into high-entropy borides via boron-metals reactive sintering to attain higher hardness[J]. Journal of European Ceramic Society,2020,40(12):4348-4353. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2020.03.063 [19] MAYRHOFER P H, KIRNBAUER A, ERTELTHALER P, et al. High-entropy ceramic thin films: A case study on transi-tion metal diborides[J]. Scripta Materialia,2018,149:93-97. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.02.008 [20] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 精细陶瓷 室温硬度试验方法: GB/T 16534—2009[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.Standardization Administration of China. Fine ceramics (advanced ceramics, advanced technical ceramics)-Test method for hardness of monolithic ceramics at room temperature: GB/T 16534—2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009. [21] TELLE R, MOMOZAWA A, MUSIC D, et al. Boride-based nano-laminates with MAX-phase-like behavior[J]. Jour-nal of Solid State Chemistry,2006,179(9):2850-2857. doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2006.01.028 [22] OTANI S, OHASHI H, ISHIZAWA Y. Lattice constants and nonstoichiometry of WB2-x[J]. Journal of Alloys and Componds,1995,221(1/2):8-10. doi: 10.1016/0925-8388(94)01486-8 [23] GROMILOV S A, KINELOVSKII S A, ALEKSEEV A V, et al. Investigation of WzB and 3-WB high-temperature phases in coatings produced by a shaped charge explosion[J]. Jour-nal of Structural Chemistry,2010,51(6):1126-1131. doi: 10.1007/s10947-010-0171-3 [24] GUO W M, ZHANG G J. Reaction processes and characteri-zation of ZrB2 powder prepared by boro/carbothermal reduction of ZrO2 in vacuum[J]. Journal of American Ceramic Society,2009,92:264-267. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02836.x [25] NI D W, ZHANG Y, ZHANG G J, et al. Synthesis of mono-dispersed fine hafnium diboride powders using carbo/borothermal reduction of hafnium dioxide[J]. Journal of American Ceramic Society,2008,91:2709-2712. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2008.02466.x [26] ZHANG W, ZHANG Y, GUO W M, et al. Powder synthesis, densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of Hf-based ternary boride ceramics[J]. Journal of European Ceramic Society,2021,41:3922-3928. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.02.045 [27] NI D W, ZHANG G J, KAN Y M, et al. Hot pressed HfB2 and HfB2-20vol%SiC ceramics based on HfB2 powder synthe-sized by borothermal reduction of HfO2[J]. International Journal of Appllied Ceramic Technology,2010,7:830-836. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7402.2009.02404.x [28] CHAMBERLAIN A L, FAHRENHOLTZ W G, HILMAS G E, et al. High-strength zirconium diboride-based ceramics[J]. Journal of American Ceramic Society,2004,87:1170-1172. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2004.01170.x [29] SHEN X Q, LIU J X, LI F, et al. Preparation and characterization of diboride-based high entropy (Ti0.2Zr0.2Hf0.2Nb0.2Ta0.2)B2-SiC particulate composites[J]. Ceramics International,2019,45:24508-24514. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.08.178 [30] LIU J X, SHEN X Q, WU Y, et al. Mechanical properties of hot-pressed high-entropy diboride-based ceramics[J]. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2020, 9(3): 503-510. [31] TAYA M, HAYASHI S, KOBAYASHI A S, et al. Toughening of a particulate-reinforced ceramic-matrix composite by thermal residual stress[J]. Journal of American Ceramic Society,1990,73:1382-1391. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1990.tb05209.x [32] RITCHIE R O. The conflicts between strength and toughness[J]. Nature Materials,2011,10:817-822. doi: 10.1038/nmat3115 -






 下载:
下载: