Construction of microstructured composite coatings based on polyetheramine ED900-tannic acid and cytocompatibility study
-
摘要: 为改善医用材料的生物相容性并赋予材料表面一定的生物学功能,本文以单宁酸(TA)和聚醚胺ED900为组装单元,通过层层自组装的方法制备了复合涂层。采用纳米粒度仪、Zeta电位分析仪、紫外分光光度计、红外光谱、石英晶体微天平(QCM-D) 、扫描电子显微镜等仪器对ED900-TA复合溶液行为及复合涂层的理化性质进行表征。通过细胞实验考察了涂层对细胞行为的影响。利用1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)法和总抗氧化能力检测试剂盒(FRAP)法评价了涂层的抗氧化性。最后,分别通过琼脂糖插入实验和细胞培养液浸泡研究涂层的稳定性。结果表明:ED900-TA涂层具有良好的细胞相容性和抗氧化性,表面的微结构呈现调控亲/憎细胞的能力。此外,涂层在模拟植入的过程未出现脱落。并在细胞培养条件下,涂层形貌在21天的评价周期内无显著变化。该复合涂层为生物材料表面多功能化提供了新思路。Abstract: To improve biocompatibility of biomaterials and endow the surface with biological functions, a new type of composite coatings was developed using the natural biomacromolecule tannic acid (TA) and polyetheramine ED900 through a layer-by-layer self-assembly method. The behavior of ED900-TA complexation in water and the physical/chemical properties of the ED900-TA coatings were characterized using nanoparticle sizer, Zeta potential analyzer, UV-vis spectrophotometer, FTIR spectrometer, quartz crystal microbalance (QCM-D), and SEM. The effect of coatings on cell behavior was investigated in vitro. The anti-oxidative property was measured by 1,1-diphenyl-2-trinitrophenylhydrazine (DPPH) and total antioxidant capacity assay kit (FRAP) assays. Finally, coating stability was evaluated by agarose insertion and incubation in cell culture medium. The results show the coatings being biocompatible and anti-oxidative. Depending on the surface microstructures, the coatings can be cytophilic or cytophobic. Besides, the coatings can withstand the shear force of insertion and the morphology is maintained up to 21 days in culture medium. This composite coating provides a new option for surface functionalization of biomaterials.
-
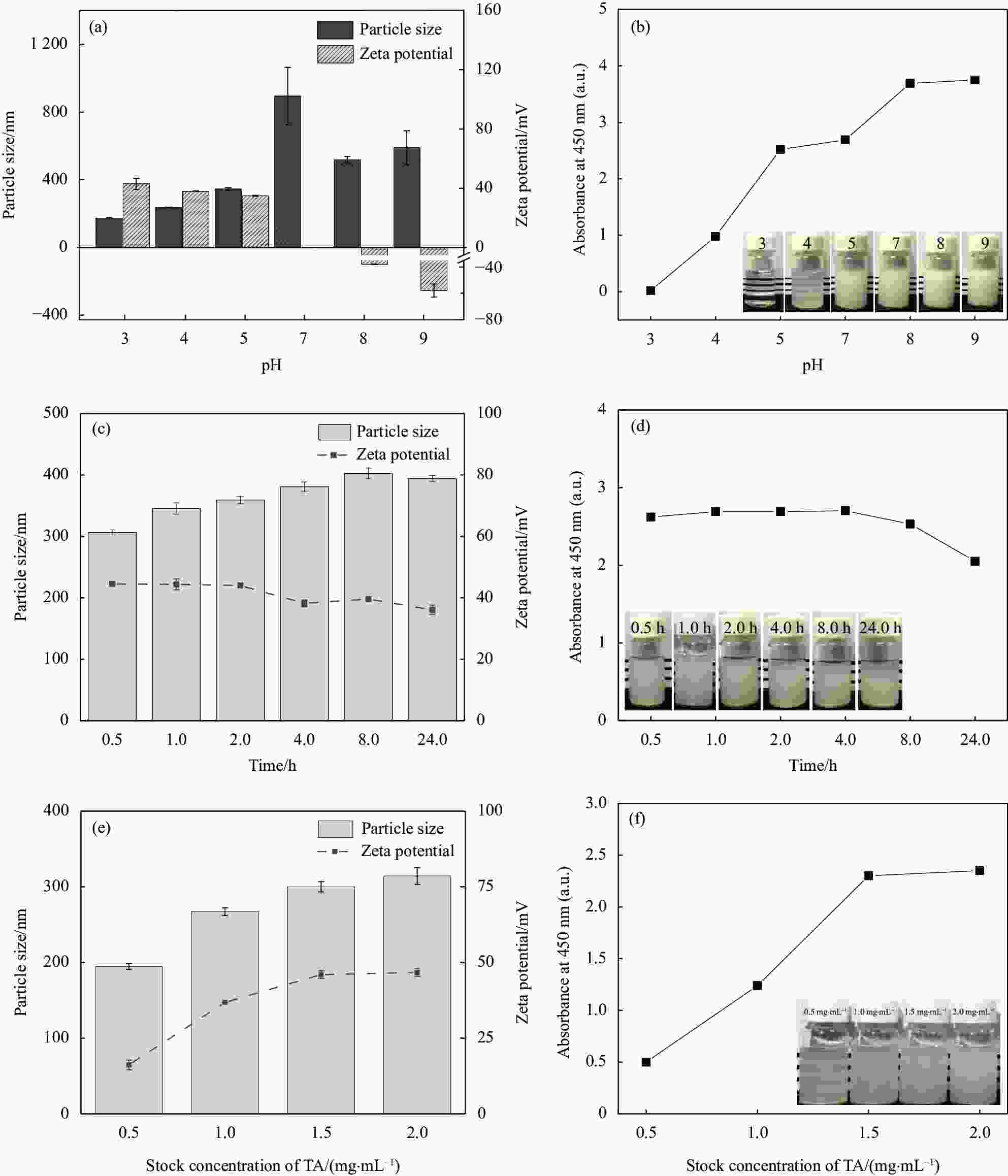
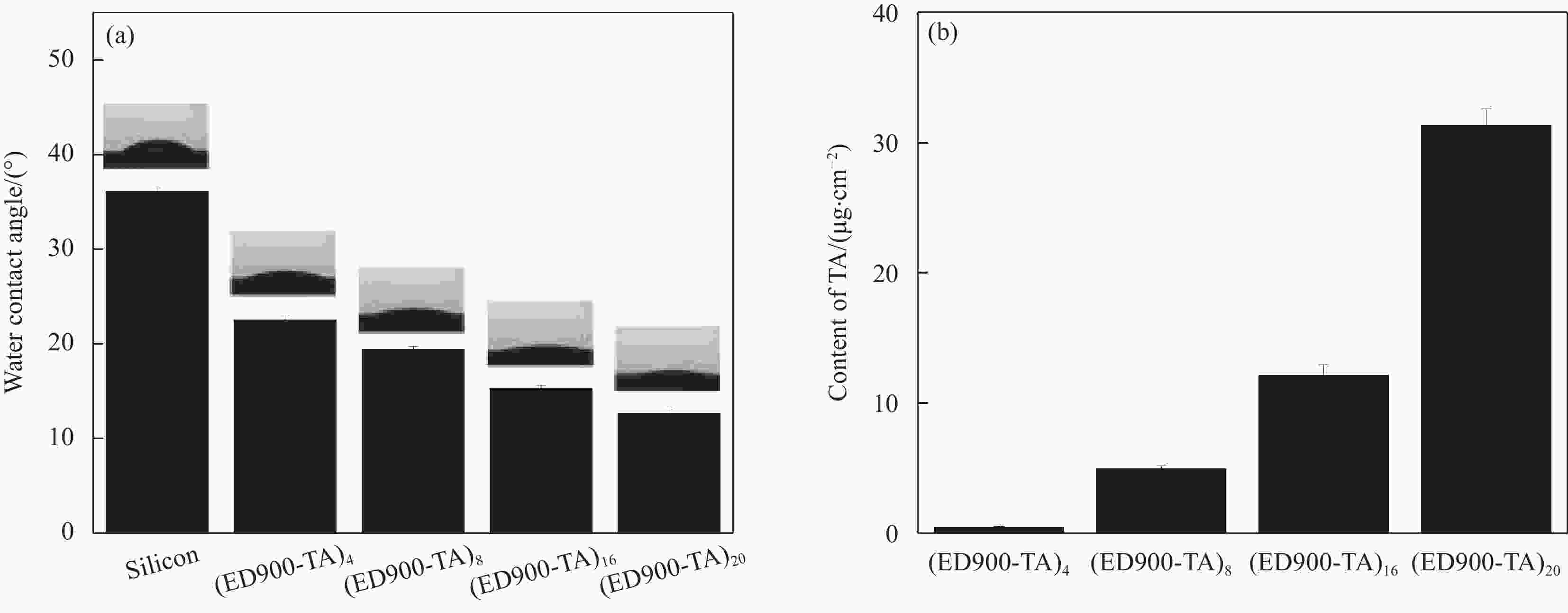
图 2 ED900-TA水溶液复合(2 mg/mL ED900 与2 mg/mL TA等体积混合)对混合物粒径、Zeta电位及浊度的影响:((a)、(b)) pH 值;((c)、(d)) 时间(ED900 (pH 7)、TA (pH 5));((e)、(f)) TA溶液浓度
Figure 2. Effect of ED900-TA solution on particle size, Zeta potential and turbidity of mixtures (Equal volume of 2 mg/mL ED900 with 2 mg/mL TA): ((a), (b)) pH; ((c), (d)) Time (ED900 (pH 7) and TA (pH 5)); ((e), (f)) TA concentration
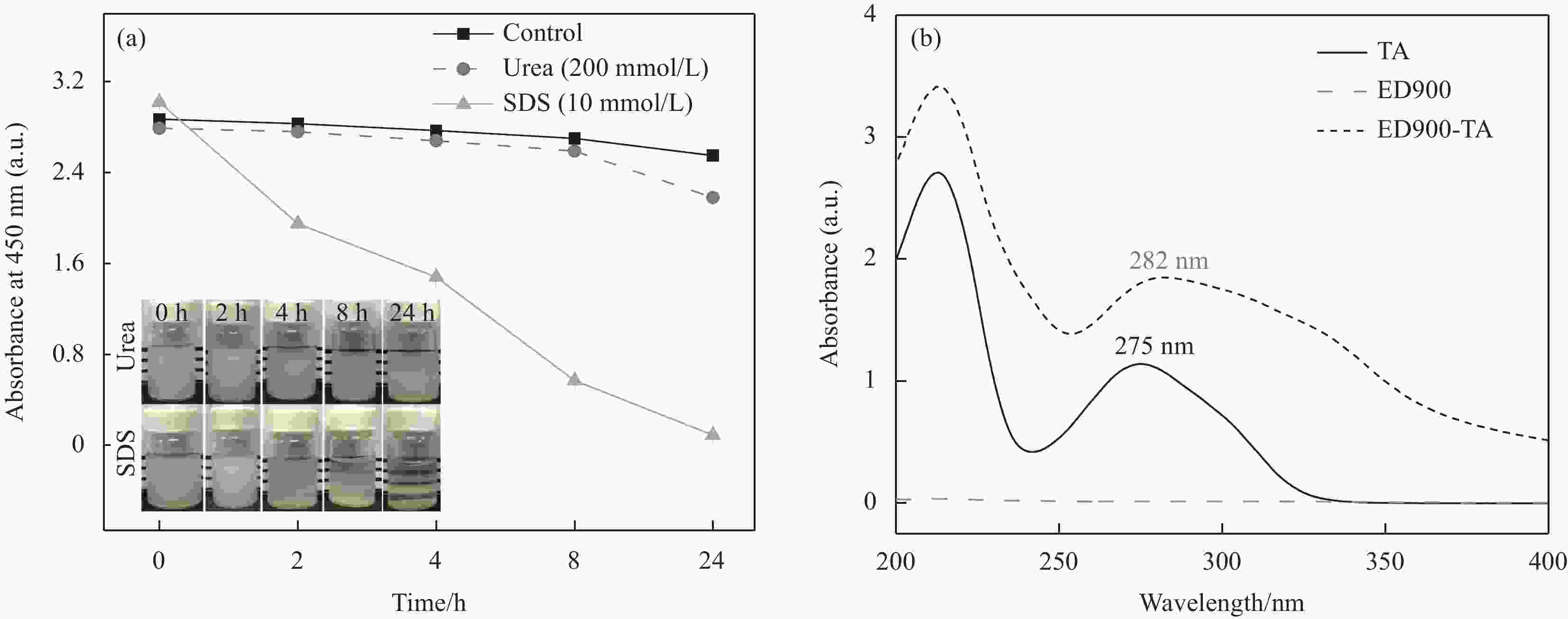
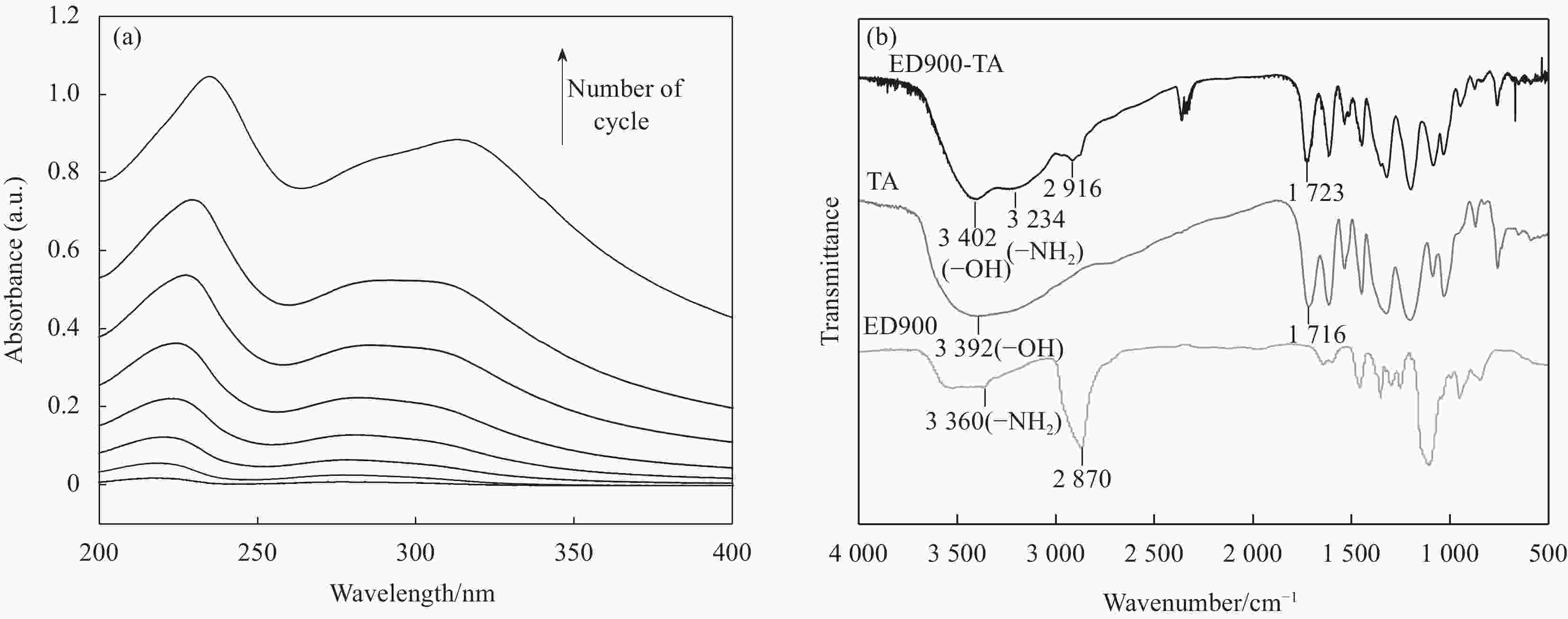
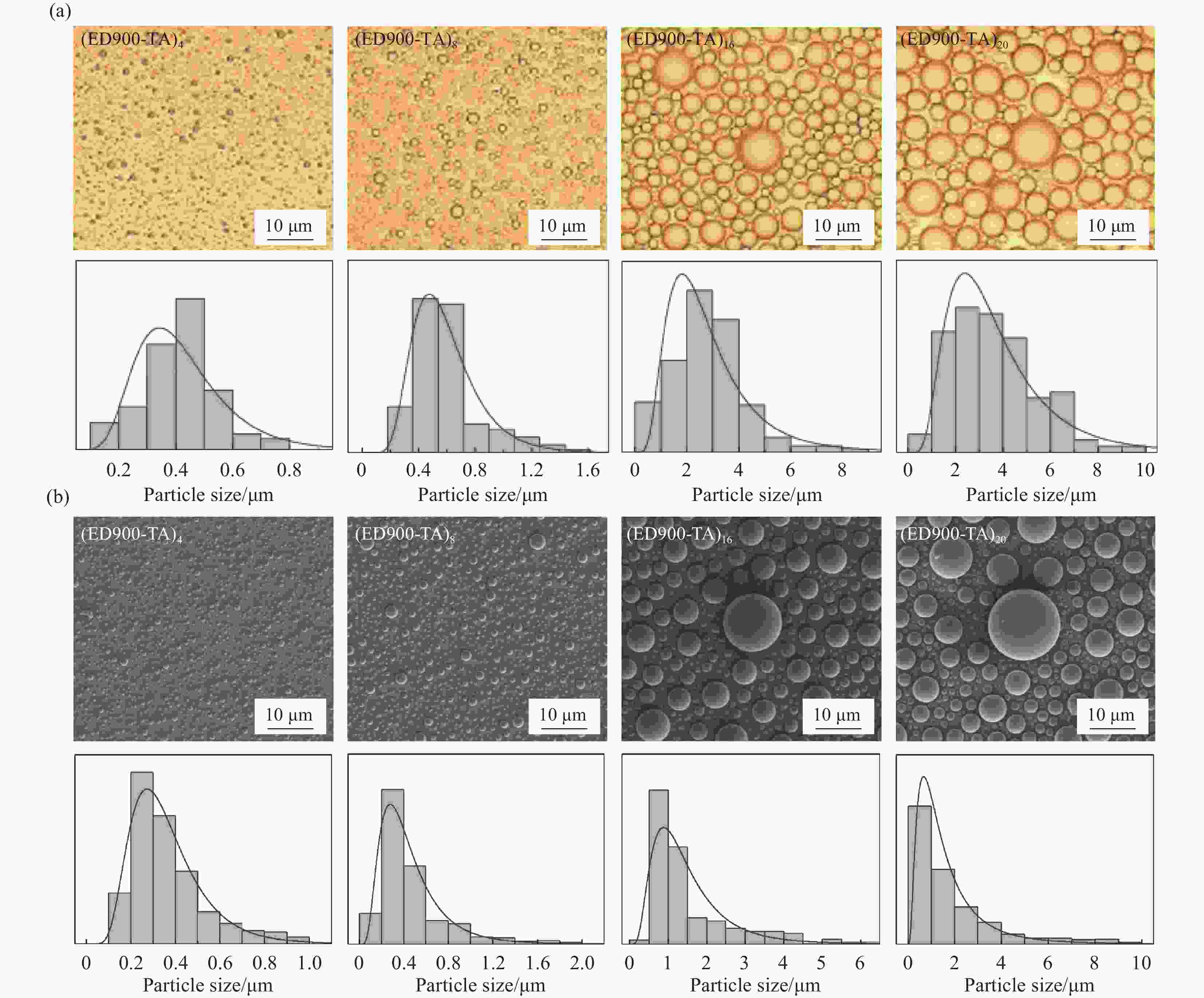
图 5 石英晶体微天平 (QCM-D) 研究ED900-TA组装过程中频率及耗散随时间的变化(竖直箭头为冲洗步骤) (插图为净频率随循环周期的变化)
Figure 5. Quartz crystal microbalance (QCM-D) study frequency and dissipation changes as a function of time during assembly of ED900-TA (Vertical arrows indicate rinsing steps) (Inset: Net change in frequency as a function of assembly cycles)
ΔF—Frequency change; ΔD—Dissipation change
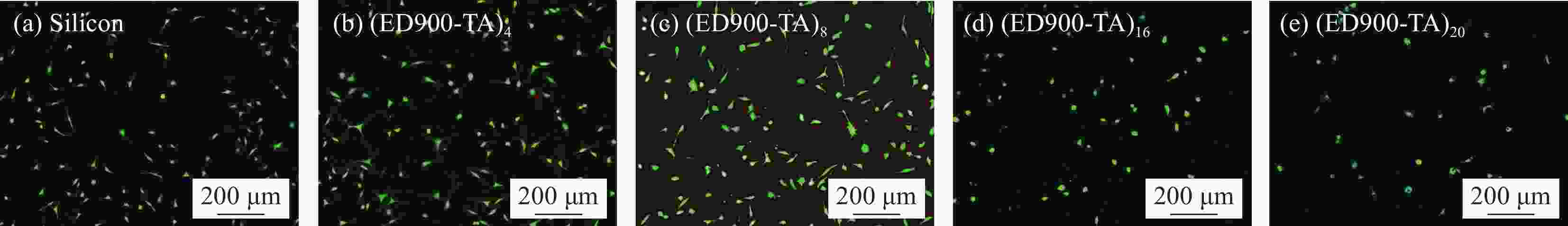
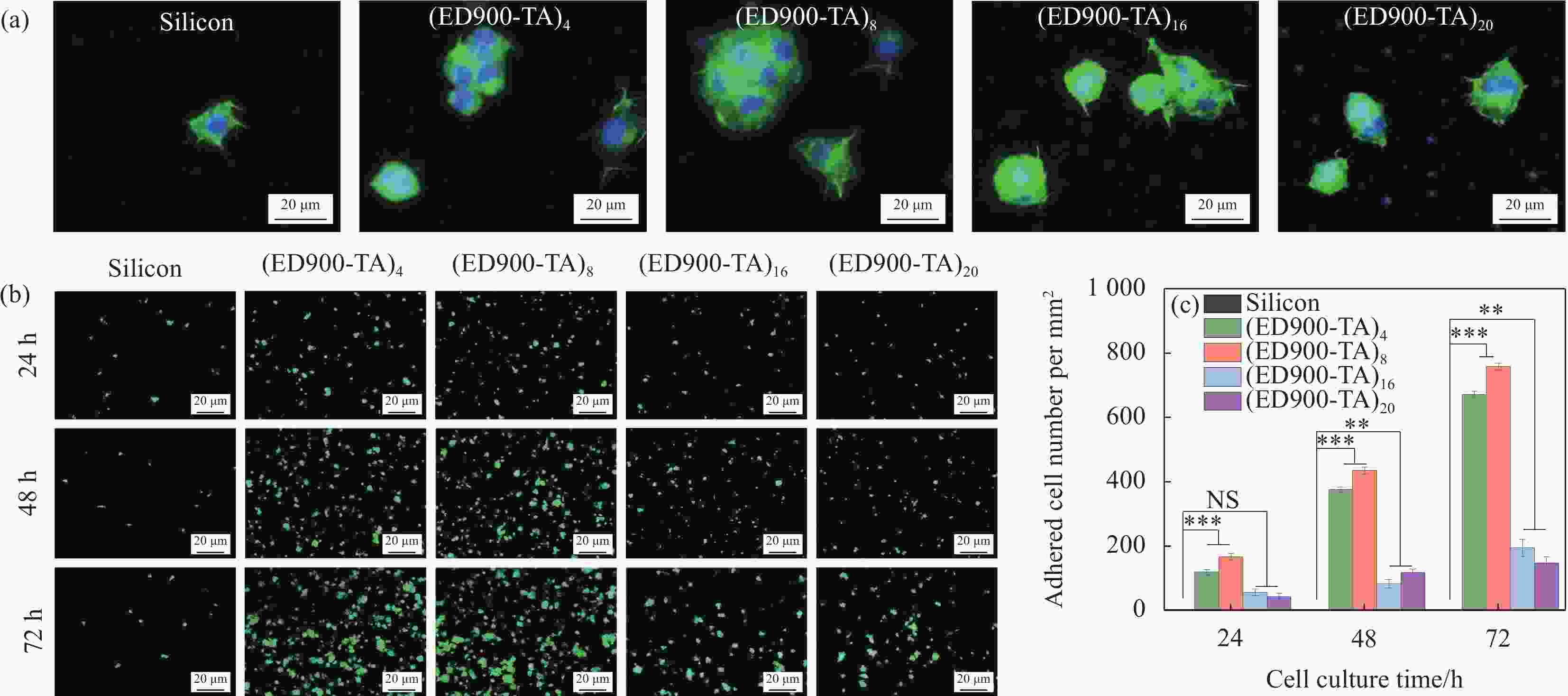
图 9 L929细胞在ED900-TA涂层的响应:(a) 24 h时细胞SEM图像和荧光图像;((b)、(c)) 各个样品表面细胞在不同培养时间点的荧光图像和细胞数量化统计图 (平均值±std (标准差),样本数n=4,*代表概率p < 0.05,**代表p < 0.01)
Figure 9. L929 cell response of ED900-TA coating: (a) SEM and fluorescent images of cells cultured for 24 h; ((b), (c)) Fluorescent images and cell number quantification at various time points (Average ± std (Standard deviation), number of samples n = 4, * indicates probability p < 0.05, ** indicates p < 0.01)
NS—Not significant
图 10 PC12细胞在ED900-TA涂层的响应:(a) 24 h时的细胞SEM图像和荧光图像;((b)、(c)) 各个样品表面细胞在不同培养时间点的荧光图像和细胞数量化统计图(平均值 ± std,n=4,**代表p < 0.01,***代表p < 0.001)
Figure 10. PC12 cell response of ED900-TA coating: (a) SEM images and fluorescent images of cells cultured for 24 h; ((b), (c)) Fluorescent images and cell number quantification at various time points (Average ± std, n=4, ** indicates p < 0.01, *** indicates p < 0.001)
图 11 (a) 1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)溶液分别与硅片和ED900-TA涂层作用后的紫外光谱;(b) ED900-TA涂层总抗氧化性
Figure 11. (a) UV-vis spectra of the 1,1-diphenyl-2-trinitrophenylhydrazine (DPPH) solution after incubation with silicon substrates with or without various repeats of ED900-TA assembly; (b) Total antioxidant activity of silicon substrates with various modifications
-
[1] 赵鸣岐, 黄威嫔, 胡米, 等. 生物医用材料表面高分子基涂层的功能化构筑[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(1):27-39. doi: 10.11896/cldb.201901003ZHAO Mingqi, HUANG Weibin, HU Mi, et al. Functional-polymer-based coatings for biomedical materials' surface[J]. Materials Reports,2019,33(1):27-39(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.201901003 [2] 郭志君, 邹琴, 王立军, 等. 钛表面聚氨酯涂层的生物矿化及其细胞生物学响应[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(6):1612-1617.GUO Zhijun, ZOU Qin, WANG Lijun, et al. Biomineralization of polyurethane-coated titanium surface and cell behavior[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2014,31(6):1612-1617(in Chinese). [3] WANG H P, GONG X C, MIAO Y L, et al. Preparation and characterization of multilayer films composed of chitosan, sodium alginate and carboxymethyl chitosan-ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,283:397-403. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.022 [4] 朱继翔, 李树祎, 阳范文, 等. 负载淫羊藿苷的丝蛋白/β-磷酸三钙复合骨修复材料制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(11):2580-2585. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170228.002ZHU Jixiang, LI Shuyi, YANG Fanwen, et al. Preparation and properties of icariin loaded silk fibroin/β-tricalcium phosphate bone repair composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(11):2580-2585(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170228.002 [5] CHUNG K T, WONG T Y, WEI C I, et al. Tannins and human health: A review[J]. Critical Review in Food Science and Nutrition,1998,38(6):421-464. doi: 10.1080/10408699891274273 [6] WANG J, TIAN L L, CHEN N, et al. The cellular response of nerve cells on poly-L-lysine coated PLGA-MWCNTs aligned nanofibers under electrical stimulation[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2018,91(1):715-726. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.06.025 [7] VANCHA A R, GOVINDARAJU S, PARSA K V L, et al. Use of polyethyleneimine polymer in cell culture as attachment factor and lipofection enhancer[J]. BMC Biotechnology,2004,4(1):23-34. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-4-23 [8] SU J M, SUN Y, LI Z S, et al. Effect of tannic acid on lysozyme activity through intermolecular noncovalent binding[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research,2019,1:100004. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2019.100004 [9] SAGLE L B, ZHANG Y J, LITOSH V A, et al. Investigating the hydrogen-bonding model of urea denaturation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2009,131(26):9304-9310. doi: 10.1021/ja9016057 [10] DUARTE A, JONG E, KOEHORST R, et al. Conformational studies of peptides representing a segment of TM7 from H+-VO-ATPase in SDS micelles[J]. Biophysics of Structure and Mechanism,2010,39(4):639-646. doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0522-1 [11] EREL I, SUKHISHVILI S A. Hydrogen-bonded multilayers of a neutral polymer and a polyphenol[J]. Macromolecules,2008,41(11):3962-3970. doi: 10.1021/ma800186q [12] FEI L, KOZLOVSKAYA V, ZAVGORODNYA O, et al. Encapsulation of anticancer drug by hydrogen-bonded multilayers of tannic acid[J]. Soft Matter,2014,10(46):9237-9247. doi: 10.1039/C4SM01813C [13] HOOK F, RODAHL M, KASEMO B, et al. Structural changes in hemoglobin during adsorption to solid surfaces: Effects of pH, ionic strength, and ligand binding[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,1998,95(21):12271-12276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.21.12271 [14] PENG L H, CHENG F, ZHENG Y N, et al. Multilayer assembly of tannic acid and an amphiphilic copolymer Poloxamer 188 on planar substrates toward multifunctional surfaces with discrete microdome-shaped features[J]. Langmuir,2018,34(36):10748-10756. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01982 [15] HAN J M, XIA Y X, CHENG F, et al. Mechanistic understanding of the discrete morphology formed by multi-cycle assembly of tannic acid with Poloxamer 188 on silicon using QMC-D[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2021,628:127302. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.127302 [16] LAMPIN M, WAROCQUIER-CLEROUT R, LEGRIS C, et al. Correlation between substratum roughness and wettability, cell adhesion, and cell migration[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research,1997,36(1):99-108. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(199707)36:1<99::AID-JBM12>3.0.CO;2-E [17] BACAKOVA L, FILOVA E, PARIZEK M, et al. Modulation of cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation on materials designed for body implants[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2011,29(6):739-767. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.06.004 [18] ZHAO L Z, MEI S L, CHU P K, et al. The influence of hierarchical hybrid micro/nano-textured titanium surface with titania nanotubes on osteoblast functions[J]. Biomaterials,2010,31(19):5072-5082. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.014 [19] NGUYEN A T, SATHE S R, YIM E K F. From nano to micro: Topographical scale and its impact on cell adhesion, morphology and contact guidance[J]. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter,2016,28(18):183001. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/28/18/183001 [20] LI J G, ZHANG K, YANG P, et al. Human vascular endothelial cell morphology and functional cytokine secretion influenced by different size of HA micro-pattern on titanium substrate[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2013,110:199-207. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.04.048 [21] DALBY M J, RIEHLE M O, JOHNSTONE H, et al. Investigating the limits of filopodial sensing: A brief report using SEM to image the interaction between 10 nm high nano-topography and fibroblast filopodia[J]. Cell Biololgy International,2004,28(3):229-236. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2003.12.004 [22] KANG K, CHOI S E, JANG H S, et al. In vitro developmental acceleration of hippocampal neurons on nanostructures of self-assembled silica beads in filopodium-size ranges[J]. Angewandte Chemie,2012,124(12):2839. doi: 10.1002/ange.201108840 -





 下载:
下载: