Preparation and properties of regenerated polyester hollow fiber wikis for sound absorption
-
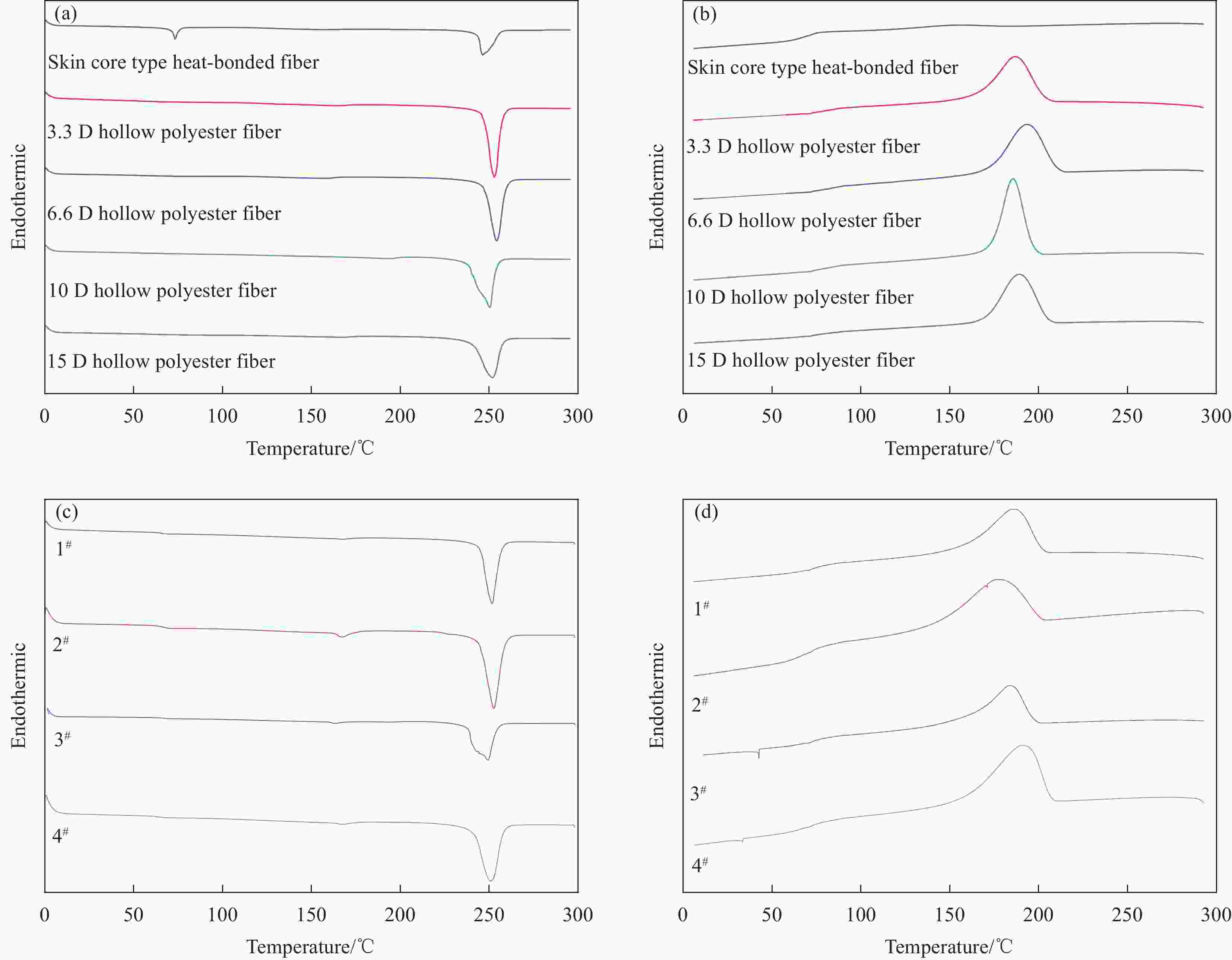
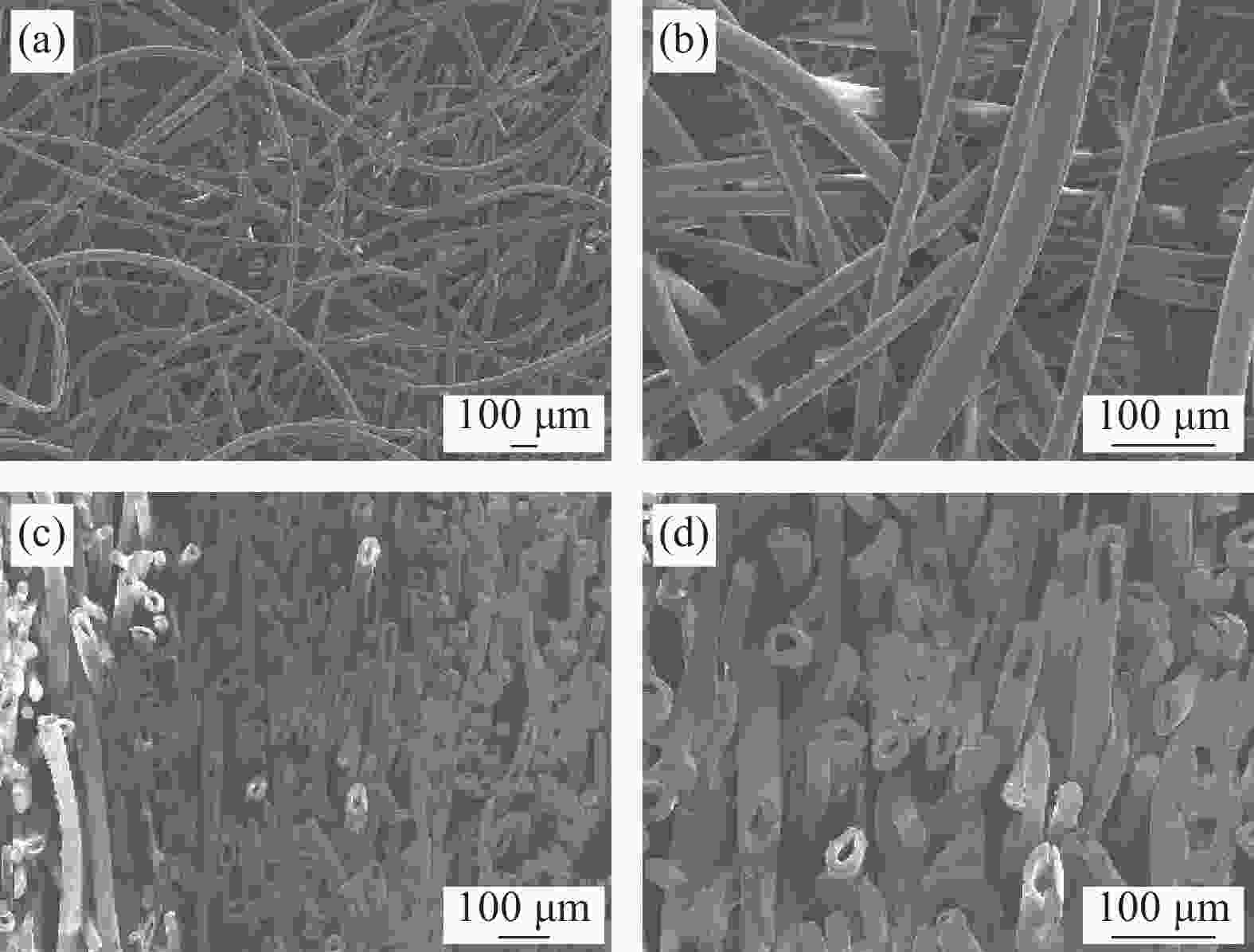
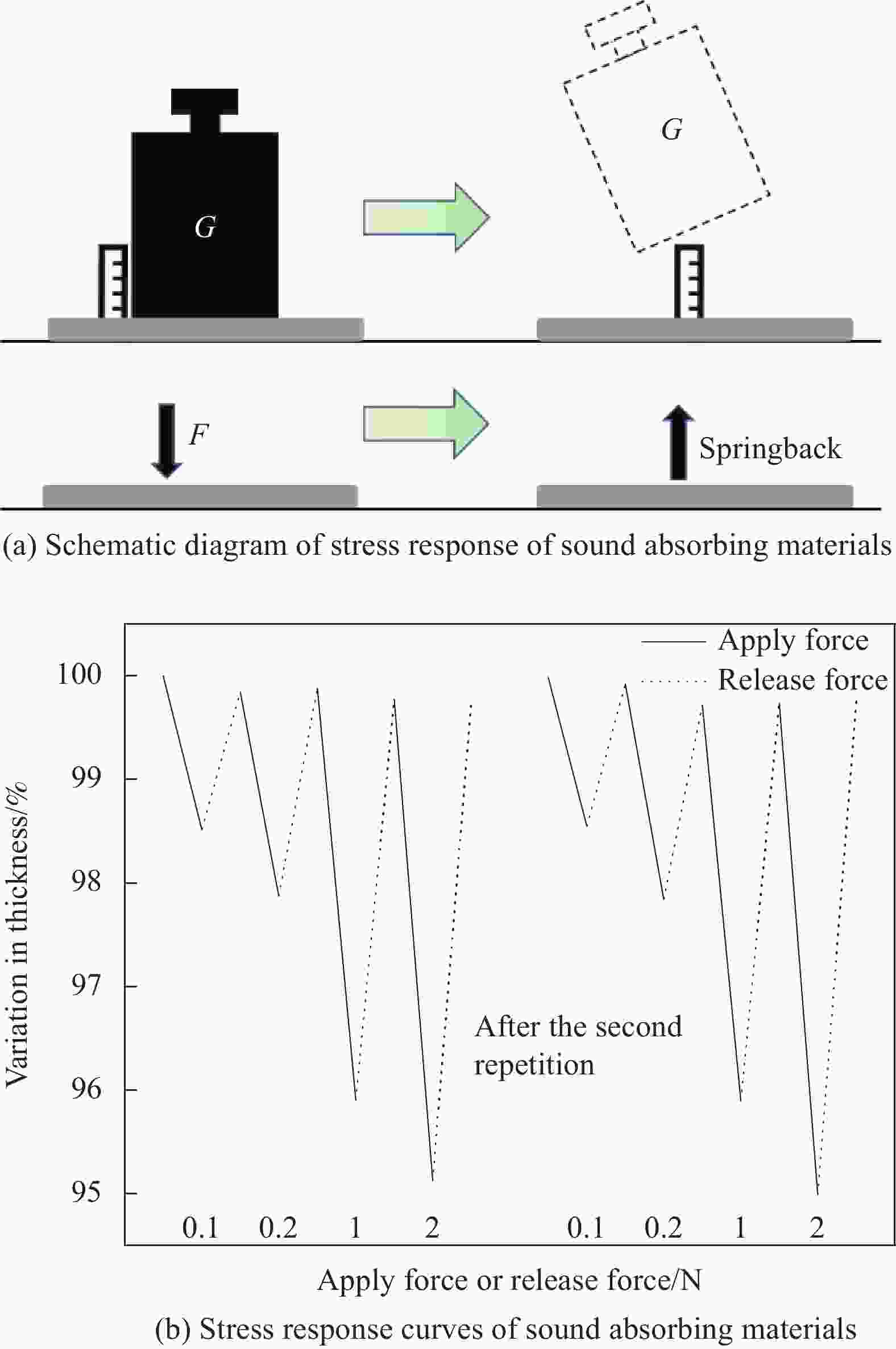
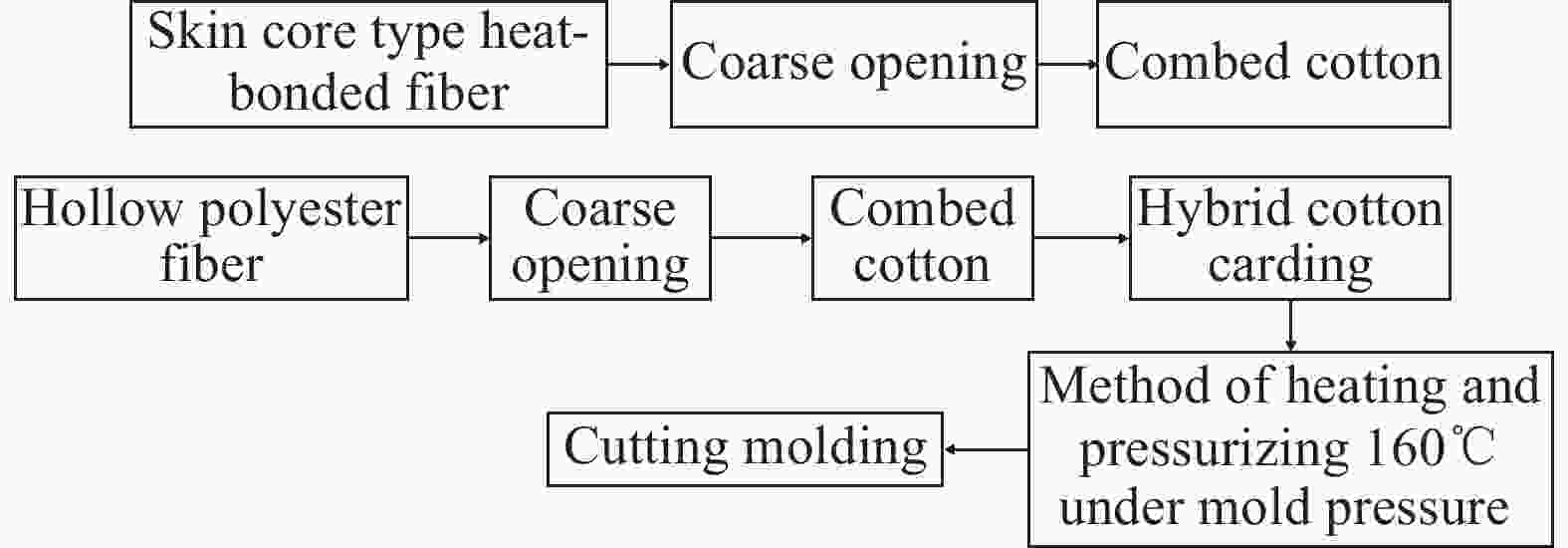
摘要: 随着环境污染问题的不断加剧,瓶片基再生聚酯纤维的开发和应用具有重要意义。本文以再生聚酯中空纤维和皮芯型热粘合纤维为原料,通过热风固结成型制备具有多尺度微孔的吸声材料,表征了聚酯中空纤维的结构与性能,此外采用驻波管法研究了中空纤维的线密度与吸声效果的关系,并提出了“多级”吸声理论。结果表明,线密度为10 D的中空纤维具有最大的中空度,最好的韧性,最优的吸声效果;吸声系数和降噪系数随厚度的增加线性增加,当厚度为2 cm时,降噪系数(NRC)大于0.5 ,有望成为理想的吸声材料。Abstract: With the aggravation of environmental pollution, the development and application of recycled polyester fibers based on bottle chip is of great significance. In this paper, recycled polyester hollow fibers and skin core type heat-bonded fibers were used as raw materials to prepare sound absorbing materials with multi-scale micropores by hot air consolidation. The structure and properties of polyester hollow fibers were characterized. Standing wave tube method was used to study the relationship between linear density and sound absorbing effect of hollow fibers, and a "multistage" sound absorbing theory was proposed. The results show that the hollow fibers with the linear density of 10 D has the largest hollowness, the best toughness and the best sound absorption effect. The sound absorption coefficient and noise reduction coefficient increase linearly with the increase of thickness. When the thickness is 2 cm, the noise reduction coefficient (NRC) is greater than 0.5, which is expected to become an ideal sound absorption material.
-
图 8 吸声材料的吸声机制图:(a) 驻波管;(b) 吸声材料;(c) 声波在纤维间孔洞中折损;(d) 声波在纤维中空的折损;(e) 纤维自身的振动
Figure 8. Sound absorbing mechanism diagram of sound absorbing material: (a) Standing wave tube; (b) Sound absorbing material; (c) Acoustic wave loss in interfiber holes; (d) Loss of acoustic wave in the hollow of the fiber; (e) Vibration of the fiber itself
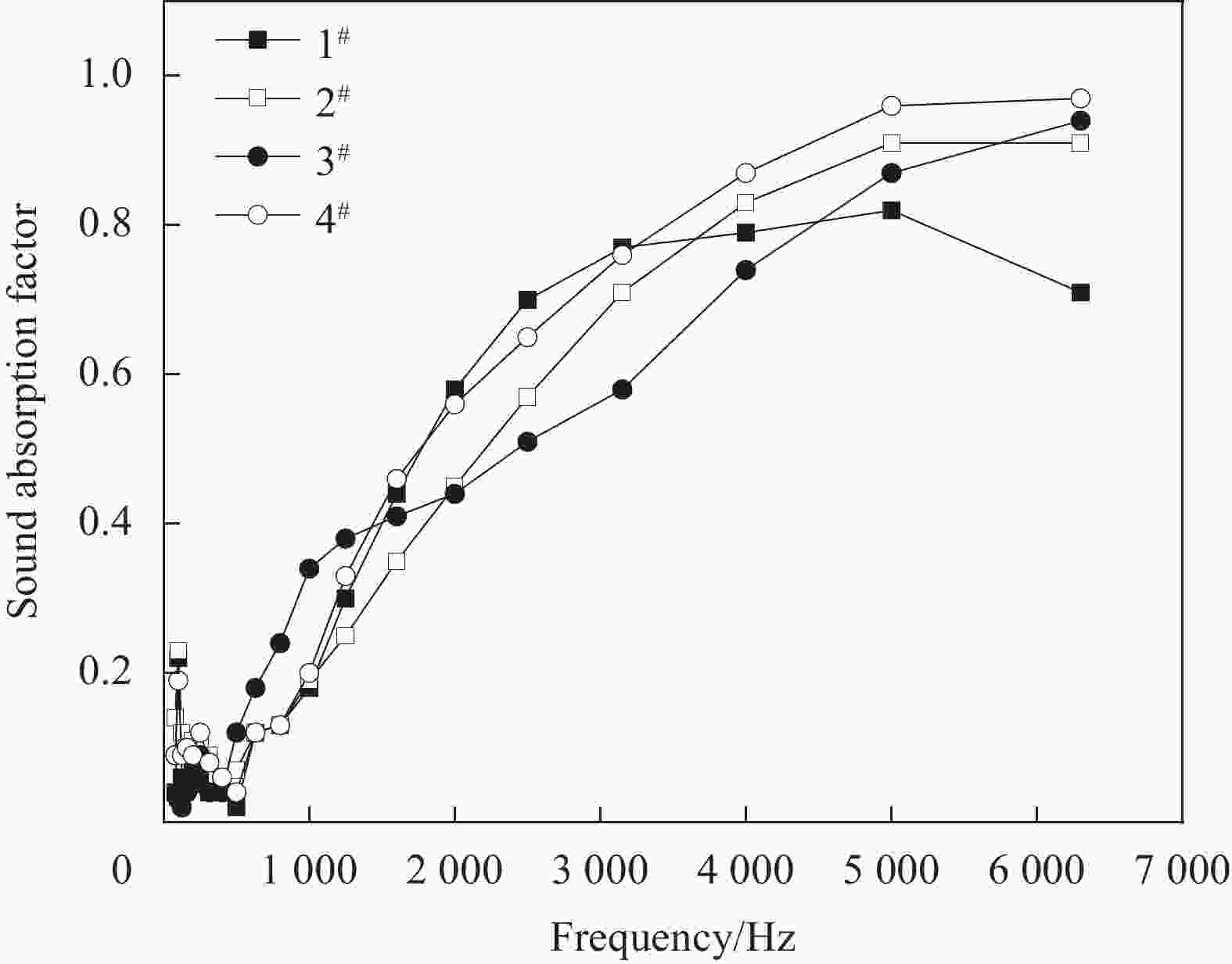
表 1 4种吸声材料的原料规格、厚度和密度
Table 1. Raw material specifications, thickness and density of 4 kinds of sound absorbing materials
Sample number Denier of hollow
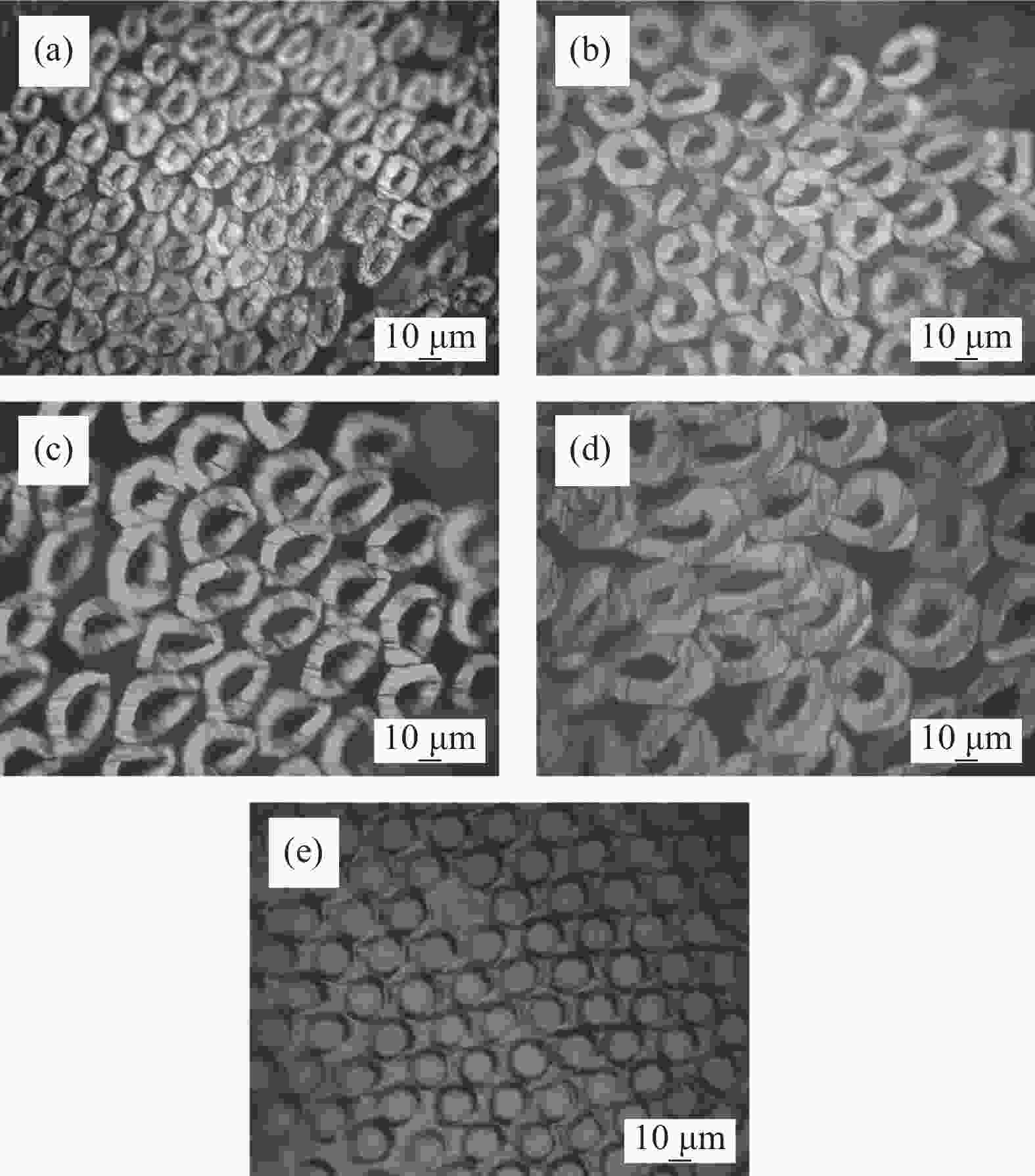
polyester fiber/DThickness/cm Density/(g·cm−3) 1# 3.3 0.64±0.002 0.25±0.020 2# 6.6 0.64±0.003 3# 10 0.64±0.001 4# 15 0.64±0.002 表 2 聚酯中空纤维的中空度
Table 2. Hollow degree of hollow polyester fibers
Fiber
denierHollow
degree/%Mean diameter of
hollow part/μm3.3 D 22.25 6.62 6.6 D 22.36 13.08 10 D 26.57 15.54 15 D 23.51 16.25 Note: 1 D×1.111=1 dtex. -
[1] VOSS S, SCHNEIDER A, HUTH C, et al. Long-term exposure to air pollution, road traffic noise, residential greenness, and prevalent and incident metabolic syndrome: Results from the population-based KORA F4/FF4 cohort in Augsburg, Germany[J]. Environment International,2021,147:106364. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106364 [2] 王笑笛. 玻璃纤维增强水泥基复合材料力学及吸声性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2018.WANG Xiaodi. Study on mechanical properties and sound absorption properties of glass fiber reinforced cement-based composites[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2018(in Chinese). [3] LEWIS R C, GERSHON R R, NEITZEL R L. Estimation of permanent noise-induced hearing loss in an urban setting[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(12):6393-6399. [4] CHEN Y, YUAN F, SU Q, et al. A novel sound absorbing material comprising discarded luffa scraps and polyester fibers[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,245:118917. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118917 [5] SHANG L, ZHAI J, ZHAO G. Stochastic dynamic analysis of acoustic-structural coupled systems under non-stationary random excitations[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures,2019,91:102742. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2019.102742 [6] YAO Z, CAI J, WANG X, et al. Application of equivalent diameter in sound absorption performance prediction of non-circular sectional polyester fibers[J]. Applied Acoustics,2021,182:108238. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108238 [7] LIU X T, JIANG J J,TANG X N, et al. Sound absorption of hollow polyester woven fabric with honeycomb weave[J]. Applied Acoustics,2021,180:108148. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108148 [8] 伍发元, 代小敏, 方铭, 等. 纤维截面形状对聚酯纤维材料吸声性能的影响研究[J]. 声学技术, 2020, 39(05):618-621.WU Fayuan, DAI Xiaomin, FANG Ming, et al. Research on the influence of polyester fiber cross-section shape on sound absorption performance of polyester fiber materials[J]. Technical Acoustics,2020,39(05):618-621(in Chinese). [9] SAKTHIVEL S, MELESE B, EDAE A, et al. Garment waste recycled cotton/polyester thermal and acoustic properties of air-laid nonwovens[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering,2020,2020:8304525. doi: 10.1155/2020/8304525 [10] PENG L, SONG B, WANG J, et al. Mechanic and acoustic properties of the sound-absorbing material made from natural fiber and polyester[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering,2015,2015:274913. doi: 10.1155/2015/274913 [11] SARI N H, FAJRIN J. Acoustic properties of sound absorber from modified polyester with filler sodium bicarbonate[J]. Oriental Journal of Chemistry,2018,34(4):2187-2191. doi: 10.13005/ojc/3404061 [12] YOON J W, JANG K S, CHO Y T. A study on the acoustic characteristics and absorption performance improvement method of double layered sound absorption system using high density polyester absorbing materials[J]. Transactions of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering,2016,26(3):331-339. doi: 10.5050/KSNVE.2016.26.3.331 [13] 王 灿, 朱 灿, 姚智敏, 等. 铝纤维/聚酯纤维复合结构的低频吸声性能研究[J]. 声学与振动, 2021, 9(1):30-35. doi: 10.12677/OJAV.2021.91004WANG Can, ZHU Can, YAO Zhimin , et al. Study on low frequency sound absorption performance of aluminum fiber/polyester fiber composites[J]. Open Journal of Acoustics and Vibration,2021,9(1):30-35(in Chinese). doi: 10.12677/OJAV.2021.91004 [14] 吴量, 刘淼, 刘学文, 等. 多层多孔吸声材料结构参数优化设计[J]. 应用声学, 2021, 40(3):449-456.WU Liang, LIU Miao, LIU Xuewen, et al. Optimal design of structural parameters of multi-layer porous sound-absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics,2021,40(3):449-456(in Chinese). [15] LEE T, CHEONG Y, BAAC H W, et al. Origin of Gouy phase shift identified by laser-generated focused ultrasound[J]. ACS Photonics,2020,7(11):3236-3245. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01313 [16] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 非织造布试验方法: GB/T 24218.2—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Test methods for nonwovens: GB/T 24218.2—2009[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2009(in Chinese). [17] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 阻抗管吸声系数和声阻抗的测量: GB/T 18696.1—2004 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2004.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of sound absorption coefficient and impedance in impedance tubes: GB/T 24218.2—2009[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2009(in Chinese). [18] BERTOCCHI M J, VANG P, BALOW R B, et al. Enhanced mechanical damping in electrospun polymer fibers with liquid cores: Applications to sound damping[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials,2019,1(8):2068-2076. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.9b00352 [19] CAO L, SI Y, YIN X, et al. Ultralight and resilient electrospun fiber sponge with a lamellar corrugated microstructure for effective low-frequency sound absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(38):35333-35342. [20] XIA B, YU D, LIU J. Interval and subinterval perturbation methods for a structural-acoustic system with interval parameters[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures,2013,38:146-163. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2012.12.003 [21] 周文璐, 林萍, 徐晓美, 等. 黄麻纤维毡吸声特性及其在汽车上的应用[J]. 林业工程学报, 2021, 6(03):113-119.ZHOU Luwen, LIN Ping, XU Xiaomei, et al. Sound absorption characteristics of the jute fiber felt and its application in automobiles[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2021,6(03):113-119(in Chinese). [22] BINBIN D, FEIHONG W, HAMIDREZA A, et al. Simple fabrication of concrete with remarkable self-cleaning ability, robust superhydrophobicity, tailored porosity, and highly thermal and sound insulation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(45):42801-42807. [23] 敖庆波, 王建忠, 李烨, 等. 低频吸声材料的研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2020, 51(12):12045-12050. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2020.12.007AO Qingbo, WANG Jianzhong, LI Ye, et al. Development of lower frequency sound absorption materials[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2020,51(12):12045-12050(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2020.12.007 [24] OH J H, KIM J, LEE H, et al. Directionally antagonistic graphene oxide-polyurethane hybrid aerogel as a sound absorber[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(26):22650-22660. [25] HE C, HUANG J, LI S, et al. Mechanically resistant and sustainable cellulose-based composite aerogels with excellent flame retardant, sound-absorption, and superantiwetting ability for advanced engineering materials[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6(1):927-936. -





 下载:
下载: