Preparation and mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced 3D fabric reinforced epoxy foam sandwich composites
-
摘要: 为了进一步提高泡沫夹层复合材料的承载能力和综合性能,实现其在轨道交通及汽车等工业领域的应用,开展了玻璃纤维立体织物增强环氧树脂泡沫(GF-Fabric/EP)复合材料的制备及其力学性能的研究。制备GF-Fabric/EP复合材料及其夹层结构,探索了GF-Fabric/EP复合材料及其夹层结构的失效行为,以揭示立体织物的增强机制。结果表明:立体织物的引入可显著改善GF-Fabric/EP复合材料的强度、刚度及破坏应变;但在不同承载条件下,各纱线发挥承载作用和效果不同。面板、芯材各自的性能、尺寸及面/芯界面性能均是影响GF-Fabric/EP夹层复合材料力学性能及失效特征的重要因素。以三点加载下的弯曲性能为例,针对不同的GF-Fabric/EP夹层复合材料,需调整跨厚比和试样尺寸并获得理想的失效特征,方可对其弯曲性能或层间剪切性能进行有效、合理的评价。
-
关键词:
- 环氧树脂泡沫夹层复合材料 /
- 立体织物 /
- 力学性能 /
- 有限元模拟 /
- 失效机制
Abstract: The preparation and mechanical properties of glass fiber 3D fabric reinforced epoxy foam composites (GF-Fabric/EP composites) were studied in order to further improve the bearing capacity and comprehensive properties of foam sandwich composite materials and realize its application in rail transit and automobile industry. The GF-Fabric/EP composite and its sandwich structure were fabricated. The failure behavior of GF-Fabric/EP composite and its sandwich structure were explored to reveal the reinforcing mechanism of the 3D fabric. The results show that the introduction of 3D fabric can significantly improve the strength, stiffness and failure strain of GF Fabric/EP composites. However, under different load-bearing conditions, each yarn plays a different role and effect. The properties, dimensions and surface/core interface properties of panel and core materials are important factors affecting the mechanical properties and failure characteristics of GF Fabric/EP sandwich composites. Taking the bending properties under three-point loading as an example, for different GF Fabric/EP sandwich composites, it is necessary to adjust the span thickness ratio and specimen size and obtain ideal failure characteristics before effective and reasonable evaluation of their bending properties or interlaminar shear properties. -
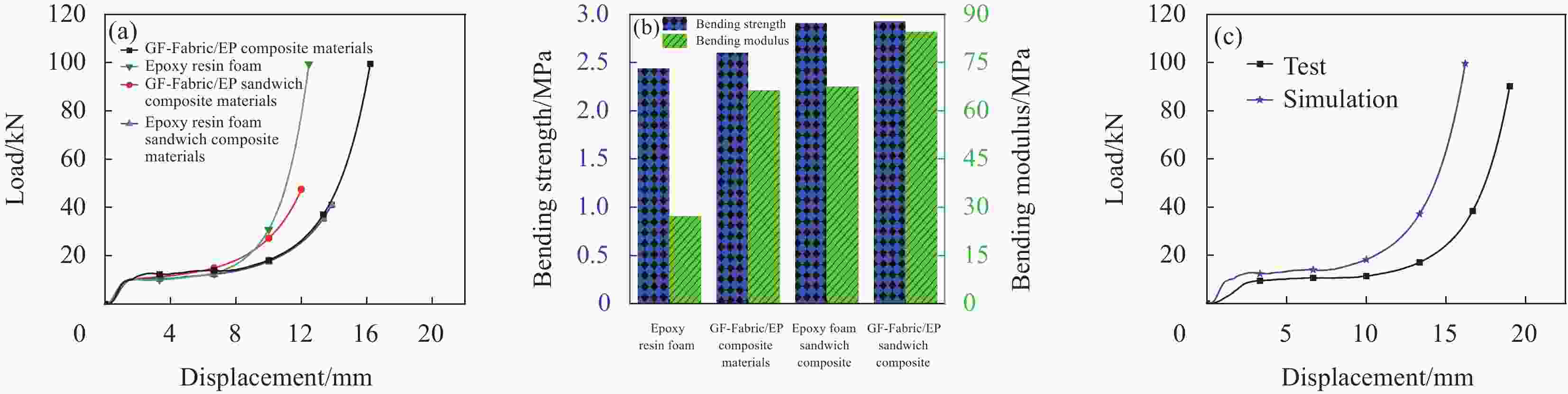
图 6 GF-Fabric/EP复合材料与环氧树脂泡沫及其夹层复合材料的对比:(a) 载荷-位移曲线;(b) 压缩强度、压缩模量对比;(c) 试验与模拟载荷-位移曲线对比
Figure 6. Comparison of GF-Fabric/EP composites with epoxy foams and their sandwich composites: (a) Load-displacement curves; (b) Comparison of compressive strength and modulus; (c) Comparison between test and simulated load-displacement curves
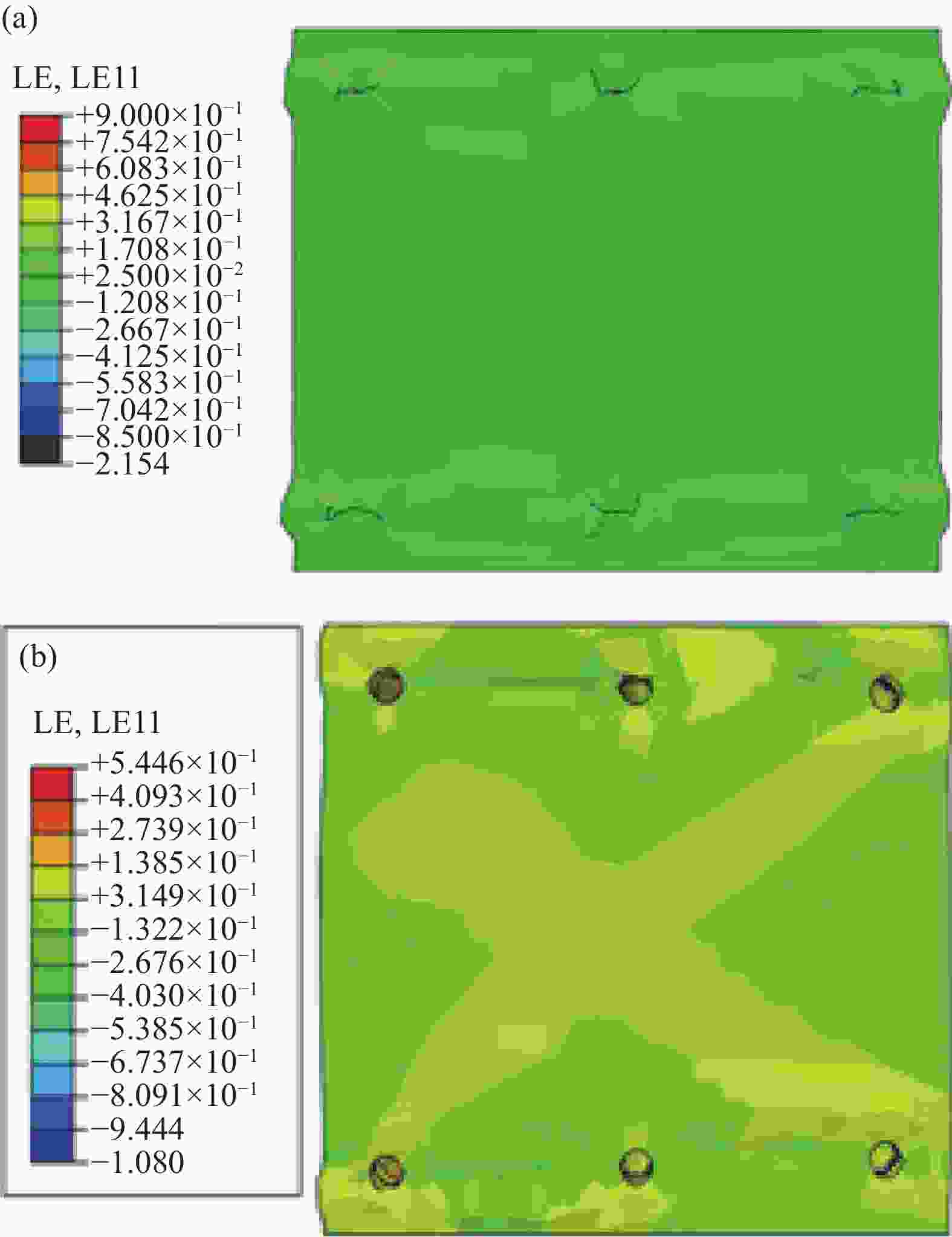
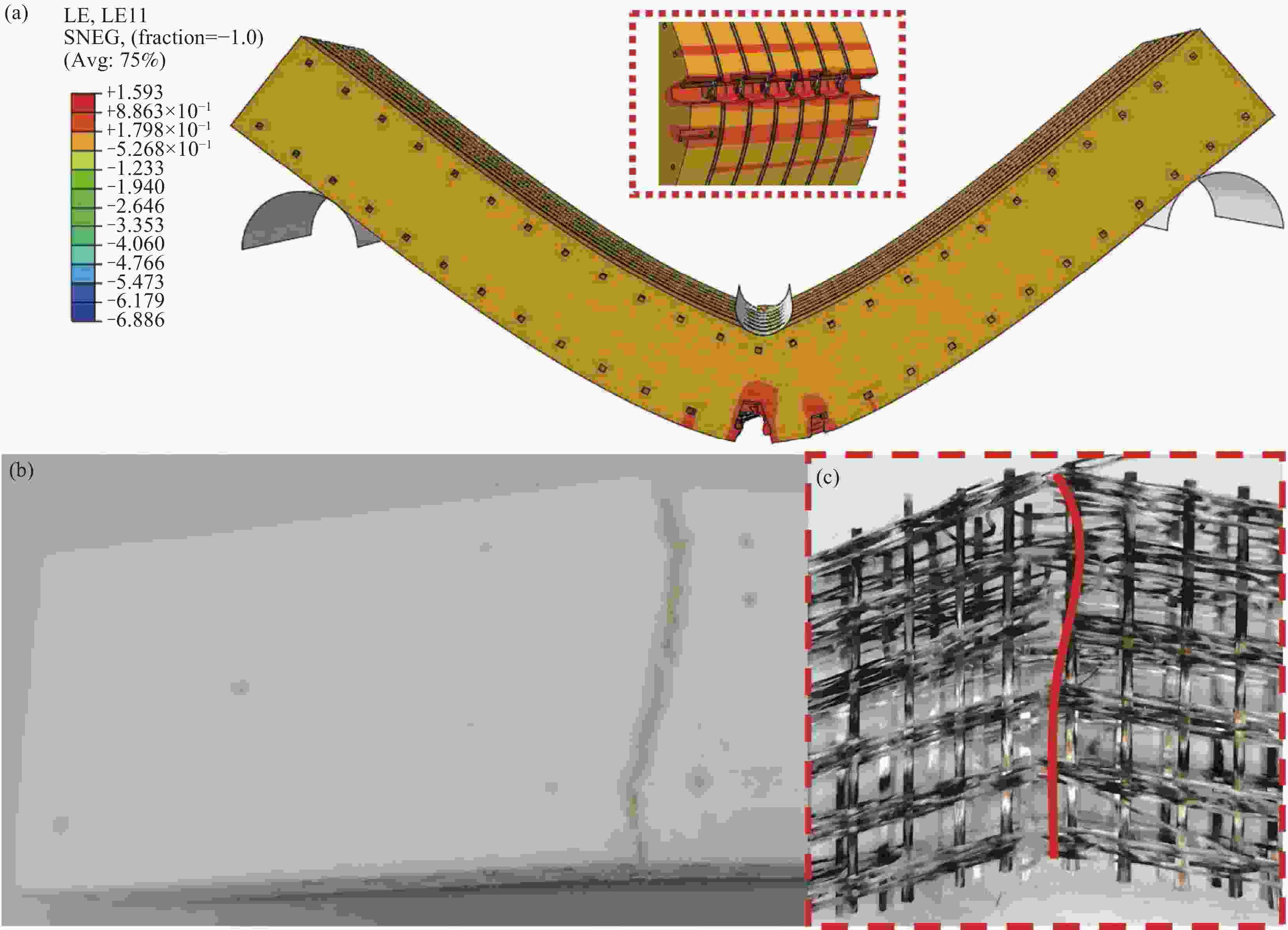
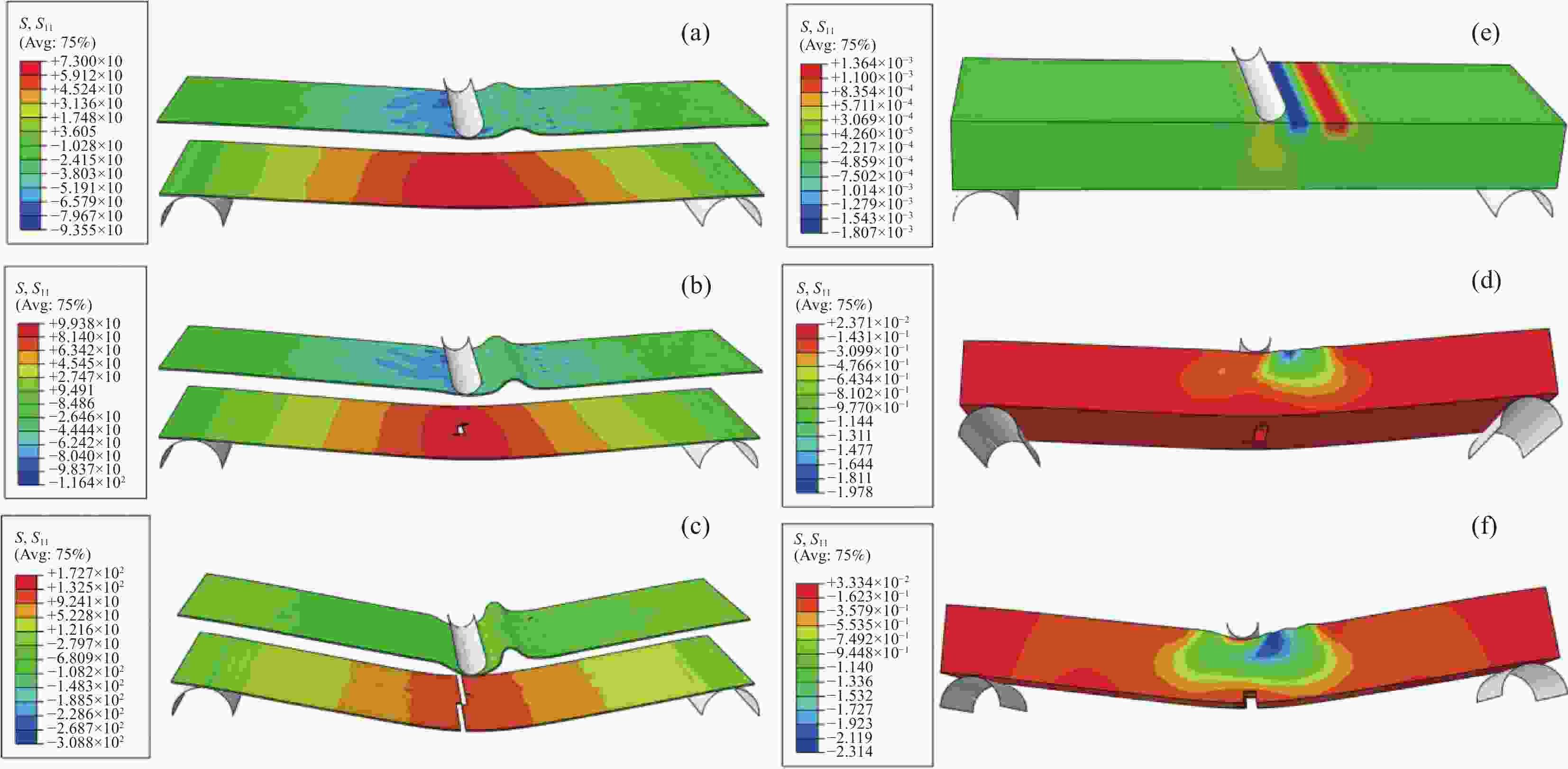
图 7 GF-Fabric/EP复合材料压缩仿真应力云图((a)~(c))及实际失效图(d)
Figure 7. Stress nephogram ((a)-(c)) and actual failure diagram (d) of GF-fabric/EP composite compression simulation
S—Stress (MPa); S11—0° fiber direction stress; SNEG—Distance from the middle plane of the unit to the reference plane; HSN—Hashin; MC—Matrix compressive; CRT—Criteria
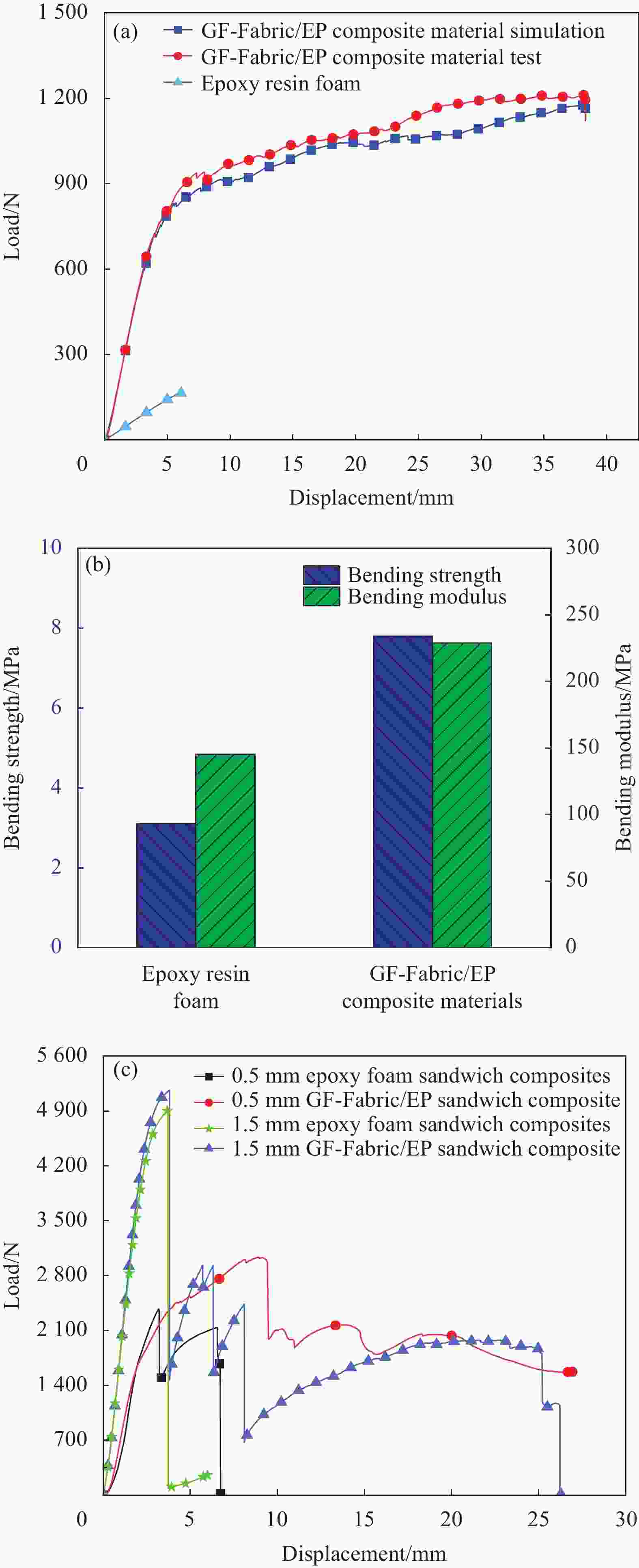
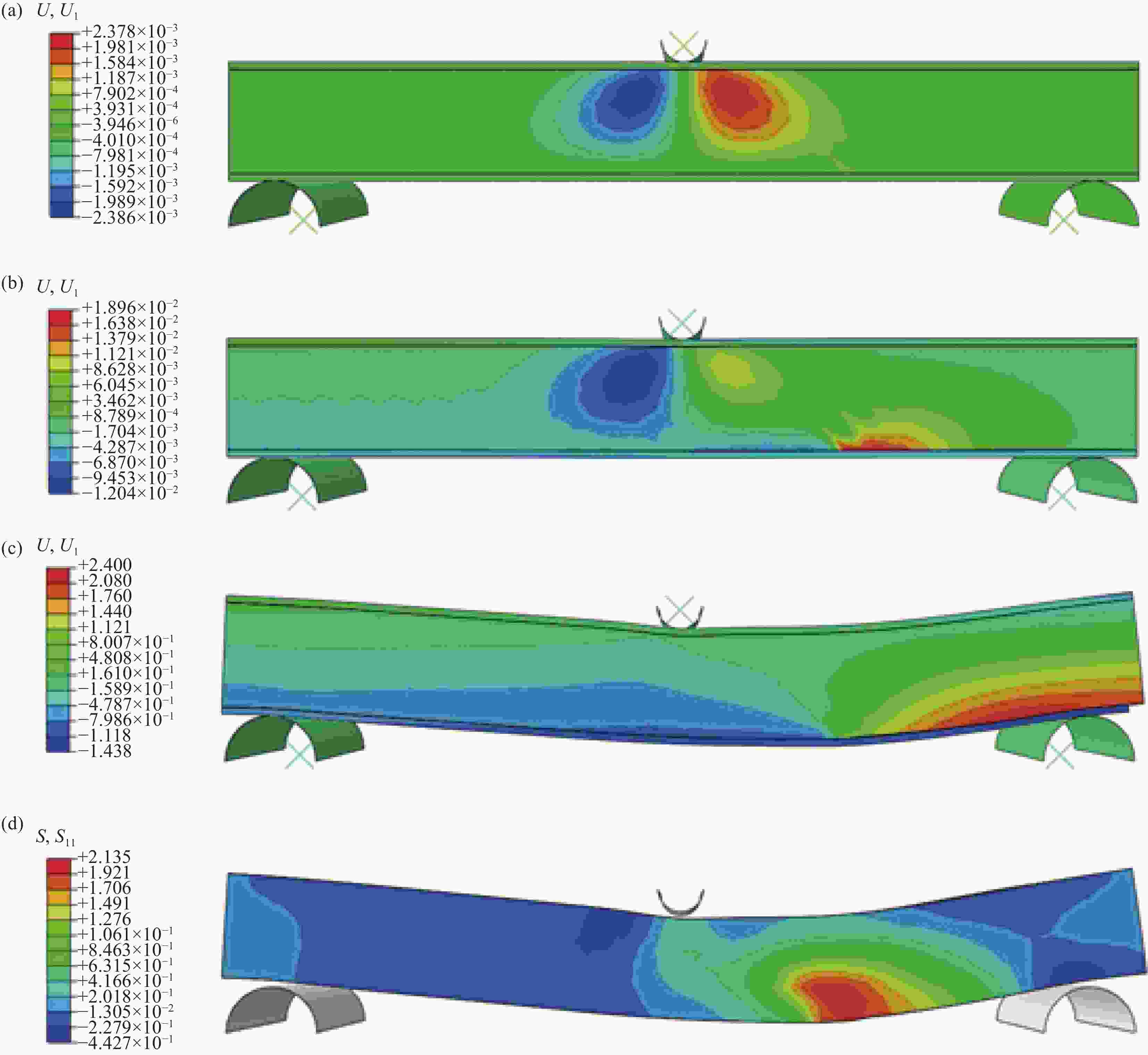
图 9 GF-Fabric/EP复合材料与环氧树脂泡沫及其夹层结构的弯曲性能:(a) 载荷-位移曲线;(b) 弯曲强度、弯曲模量对比;(c) 0.5 mm/1.5 mm厚铝合金面板夹层结构载荷-位移曲线对比
Figure 9. Bending performance of GF-Fabric/EP composite and epoxy foam and their sandwich structures: (a) Load-displacement curves; (b) Comparison of bending strength and modulus; (c) Comparison of load-displacement curves of 0.5 mm/1.5 mm thick aluminum alloy panel sandwich structures
表 1 环氧树脂泡沫的材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of epoxy foam
Property Performance Parameter value Elastic properties Young modulus/MPa 27.23 Poisson’s ratio 0 Crushable foam properties Compression yield stress ratio 0.75 Plastic Poisson’s ratio 0 表 2 玻璃纤维立体织物基本力学性能参数
Table 2. Basic mechanical property parameters of glass fiber 3D fabric
Performance Direction Parameter value Density/(g·mm−3) — 2.6×10−3 Elastic modulus/MPa E12 45000 E13 5000 E23 5000 Poisson’s ratio ν12 0.33 ν13 0.33 ν23 0.45 Shear modulus/MPa G12 5500 G13 5500 G23 3000 Notes: 1—Fiber direction; 2 and 3—Two normal directions of the fiber. 表 3 玻璃纤维立体织物的强度参数和损伤演化参数
Table 3. Strength parameters and damage evolution parameters of glass fiber 3D fabric
Performance Direction Parameter value Strength/MPa Xt 1500 Xc 1000 Yt 100 Yc 100 S 50 Fracture toughness/
(kJ·m−2)Gft 12.5 Gfc 12.5 Gmt 1.0 Gmc 1.0 Notes: Xt—Fiber direction stretching; Yt—Fiber direction compression; Xc—Stretching perpendicular to the fiber direction; Yc—Compression perpendicular to the fiber direction; S—Shearing stress; Three-dimensional Hashin criterion divides the material failure into four categories: Fiber tensile failure (Gft), fiber compression failure (Gfc), matrix tensile failure (Gmt) and matrix compression failure (Gmc). 表 4 玻璃纤维立体织物与环氧树脂泡沫界面层材料参数
Table 4. Material parameters of glass fiber 3D fabric and epoxy foam interface layer
Parameter Direction Parameter value Initial stiffness/(N·mm−1) Kn0
Ks0
Kt0106
106
106Interface strength/MPa τn0
τs0
τt06
6
6Notes: Kn0—Normal stiffness; Ks0—In-plane shear stiffness; Kt0—Transverse shear stiffness; n−Normal direction; s, t−Shear-sense. 表 5 铝合金/环氧树脂泡沫界面层材料参数
Table 5. Material parameters of aluminum alloy/epoxy foam interface layer
Parameter Direction Parameter value Initial stiffness/(N·mm−3) $ {K}_{\mathrm{n}\mathrm{n}}^{0}{=K}_{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{s}}^{0}{=K}_{\mathrm{t}\mathrm{t}}^{0} $ 106 Interface strength/MPa $ {t}_{\mathrm{n}}^{0} $ 2.82 $ {t}_{\mathrm{s}}^{0}={t}_{\mathrm{t}}^{0} $ 20.62 Fracture energy/(kJ·m−2) $ {G}_{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{C}} $ 0.20 $ {G}_{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{I}\mathrm{C}} $ 0.34 Mixed mode index η 1.45 Notes: IC—Type I interlayer energy release rate; IIC—Type II interlayer energy release rate. -
[1] 王宝芹, 王沫楠, 刘长喜. 基于多尺度方法的蜂窝夹层复合材料结构轴向压缩稳定性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(3):601-608. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190918.001WANG Baoqin, WANG Monan, LIU Changxi. Stability of honeycomb sandwich composite structure under axial compression based on multi-scale method[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(3):601-608(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190918.001 [2] HU Y, ZHU J, WANG J H, et al. Interfacial failure in stitched foam sandwich composites[J]. Matrials,2021,14(9):2275. doi: 10.3390/ma14092275 [3] CAPRICHO J C, FOX B, HAMEED N. Multifunctionality in epoxy resins[J]. Polymer Reviews,2020,60(1):1-41. doi: 10.1080/15583724.2019.1650063 [4] WANG Y, CHEN Z H, YU F. Preparation of epoxy-acrylic latex based on bisphenol f epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Macromolecular Science Part A: Pure and Applied Chemistry,2018,55(2):205-212. doi: 10.1080/10601325.2017.1410065 [5] ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG W H, LI D S, et al. Mechanical and anticorrosive properties of graphene/epoxy resin composites coating prepared by in-situ method[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2015,16(1):2239-2251. doi: 10.3390/ijms16012239 [6] 余为, 薛海龙, 钱蒙, 等. 浸泡腐蚀对玻璃纤维-空心玻璃微珠/环氧树脂复合泡沫材料弯曲性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(6):1688-1695.YU Wei, XUE Hailong, QIAN Meng, et al. Effect of immersion corrosion on the bending properties of glass fiber hollow glass bead/epoxy composite foam[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(6):1688-1695(in Chinese). [7] SHEN H B, NUTT S. Mechanical characterization of short fiber reinforced phenolic foam[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2003,34(9):899-906. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(03)00136-2 [8] YA B, WANG Y S, MENG L G, et al. Study on the performance of syntactic foam reinforced by hybrid functionalized carbon nanotubes[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2019,137(16):48586. doi: 10.1002/app.48586 [9] CHEN Q H, DU S R, JIANG Z Y, et al. Mechanical properties of foam sandwich with chopped-glass-fiber/carbon nanotube reinforced hierarchical structure interlayer[J]. Polymer Composites,2020,41(8):3411-3420. doi: 10.1002/pc.25630 [10] 张靠民, 顾轶卓, 李敏, 等. 快速固化环氧树脂及其碳纤维/环氧复合材料性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(6):21-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3851.2013.06.004ZHANG Kaomin, GU Yizhuo, LI Min, et al. Rapid curing epoxy resin and the properties of carbon fiber/epoxy composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(6):21-27(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3851.2013.06.004 [11] 马元春, 俸翔, 卢子兴, 等. 缝纫泡沫夹芯复合材料板的稳定性分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(2):201-205.MA Yuanchun, FENG Xiang, LU Zixing, et al. Stability analysis of stitched foam-core composite sandwich plates[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2011,28(2):201-205(in Chinese). [12] QUINTANA J M, MOWER T M. Thermomechanical behavior of sandwich panels with graphitic-foam cores[J]. Materials & Design,2017,135:411-422. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2017.09.021 [13] 王聪, 竺铝涛, 高晓平. 纳米增韧三维正交玻璃纤维机织物增强环氧树脂复合材料的力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(2):252-259.WANG Cong, ZHU Lvtao, GAO Xiaoping. Mechanical properties of nano toughened three-dimensional orthogonal glass fiber woven fabric reinforced epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(2):252-259(in Chinese). [14] 邓富泉, 张丽, 刘少祯, 等. 单向连续碳纤维-玻璃纤维层间混杂增强环氧树脂基复合材料的力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7):1857-1863.DENG Fuquan, ZHANG Li, LIU Shaozhen, et al. Mechanical properties of unidirectional continuous carbon fiber glass fiber interlayer hybrid reinforced epoxy resin matrix composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(7):1857-1863(in Chinese). [15] ZHANG T T, YAN Y, LI J F, et al. Low-velocity impact of honeycomb sandwich composite plates[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2015,35(1):8-32. doi: 10.1177/0731684415612573 [16] ANANDAN S, DHALIWAL G, GANGULY S, et al. Investigation of sandwich composite failure under three-point bending: Simulation and experimental validation[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2020,22(6):1838-1858. [17] KULKARNI N, MAHFUZ H, JEELANI S, et al. Fatigue crack growth and life prediction of foam core sandwich composites under flexural loading[J]. Composite Structure,2003,59(4):499-505. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(02)00249-0 [18] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 夹层结构或芯子平压性能试验方法: GB/T 1453—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Test method for flat compressive properties of sandwich structures or cores: GB/T 1453—2005[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2005(in Chinese). [19] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 夹层结构平拉强度试验方法: GB/T 1452—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Test method for flat tensile strength of sandwich structures: GB/T 1452—2005[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2005(in Chinese). [20] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 夹层结构弯曲性能试验方法: GB/T 1456—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Test method for flexural properties of sandwich structures: GB/T 1456—2005[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2005(in Chinese). [21] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硬质泡沫塑料 弯曲性能的测定 第2部分: 弯曲强度和表观弯曲弹性模量的测定: GB/T 8812.2—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2007.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Determination of flexural properties of rigid cellular plastics second parts: Determination of flexural strength and apparent flexural modulus of elasticity: GB/T 8812.2—2007[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2007(in Chinese). [22] HAN S H, LU A H, LIU Y J. Study on multi-axial mechanical properties of a polyurethane foam and experimental verification[C]//International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering. Guangzhou: Trans Tech Publications, 2011: 299-306. [23] BELINGARDI G, MEHDIPOUR H, MANGINO E, et al. Progressive damage analysis of a rate-dependent hybrid composite beam[J]. Composite Structures,2016,154:433-442. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.07.055 [24] 朱国华. 金属/碳纤维混合材料薄壁结构耐撞性研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2018.ZHU Guohua. Study on crashworthiness of thin-walled structures made of metal/carbon fiber composites[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2018(in Chinese). [25] HASHIN Z, ROTEM A. A fatigue failure criterion for fiber reinforced materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1973,7(4):448-464. doi: 10.1177/002199837300700404 [26] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test methods for tension testing of metallic materials: ASTM E8/E 8M-08[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials International, 2008. [27] YASAEE M, BOND I P, TRASK R S, et al. Mode I interfacial toughening through discontinuous interleaves for damage suppression and control[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(1):198-207. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.10.009 [28] KANG M S, JEON M H, KIM I G, et al. The characteristics for mode I interlaminar and intralaminar fractures of cross-ply carbon/epoxy composite laminates based on energy release rate[J]. Composites Research,2019,32(1):6-12. -





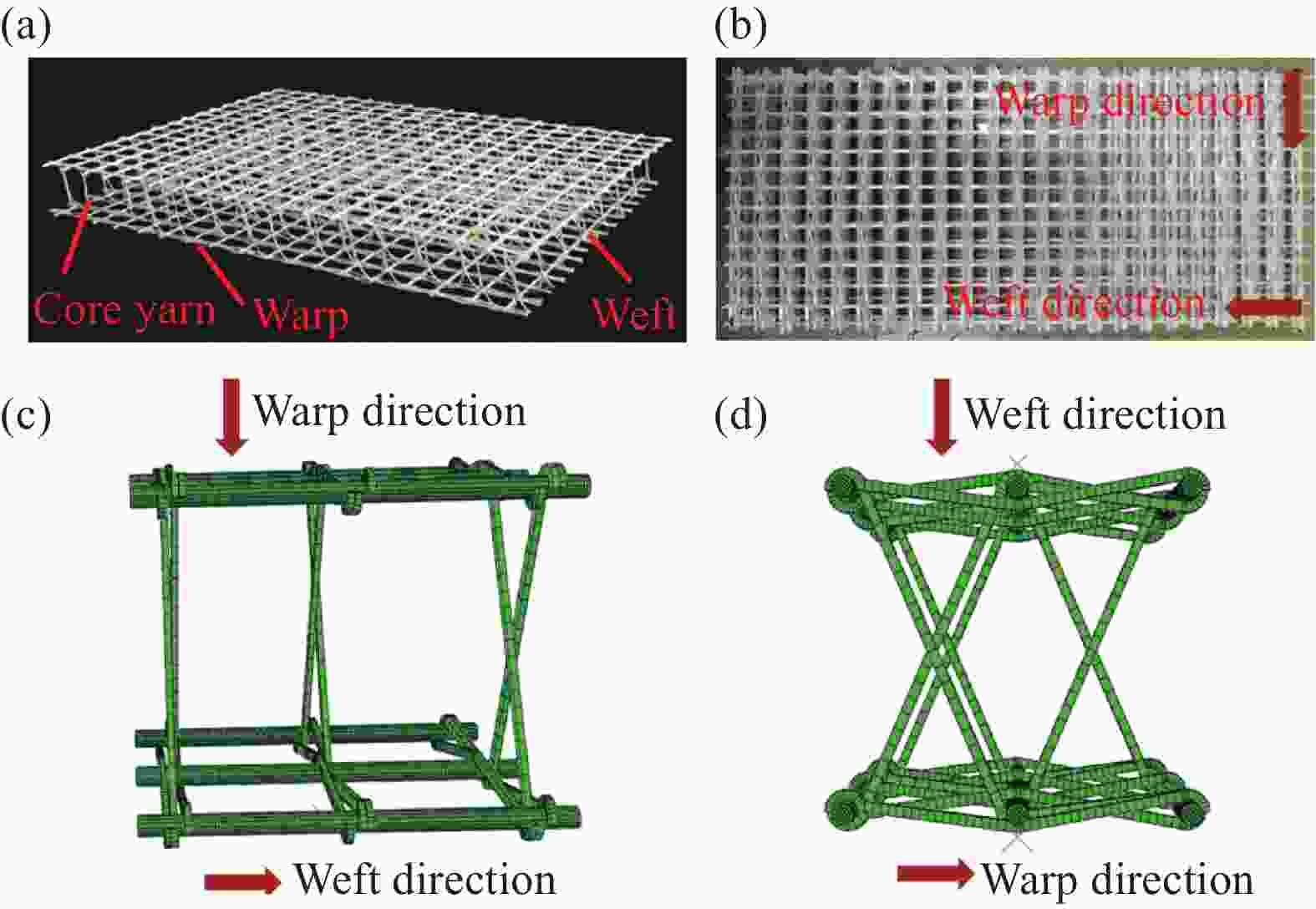
 下载:
下载: