Thermal conduction mechanism and heat dissipation effect of compression molded boron nitride/polyethylene terephthalate composites
-
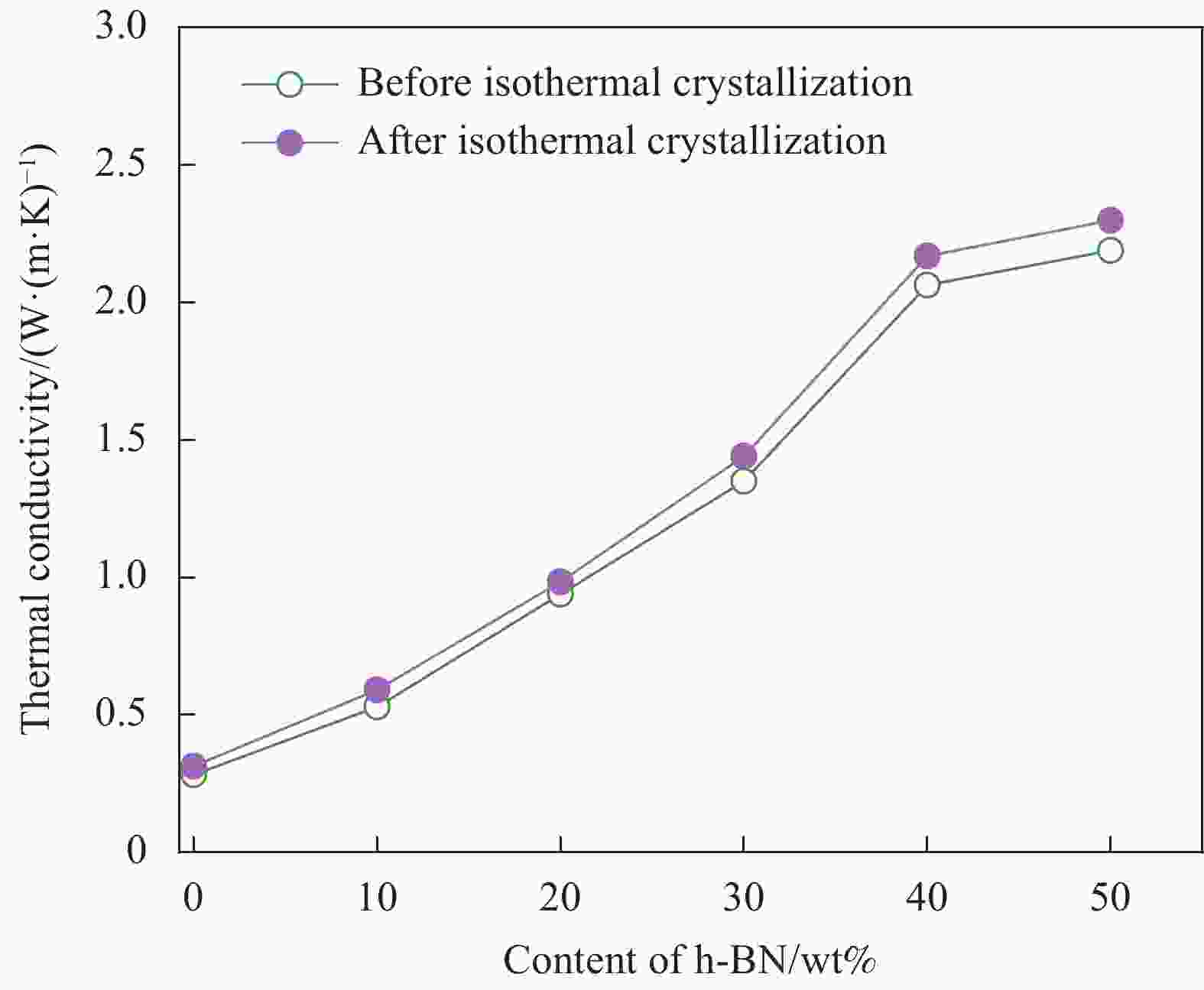
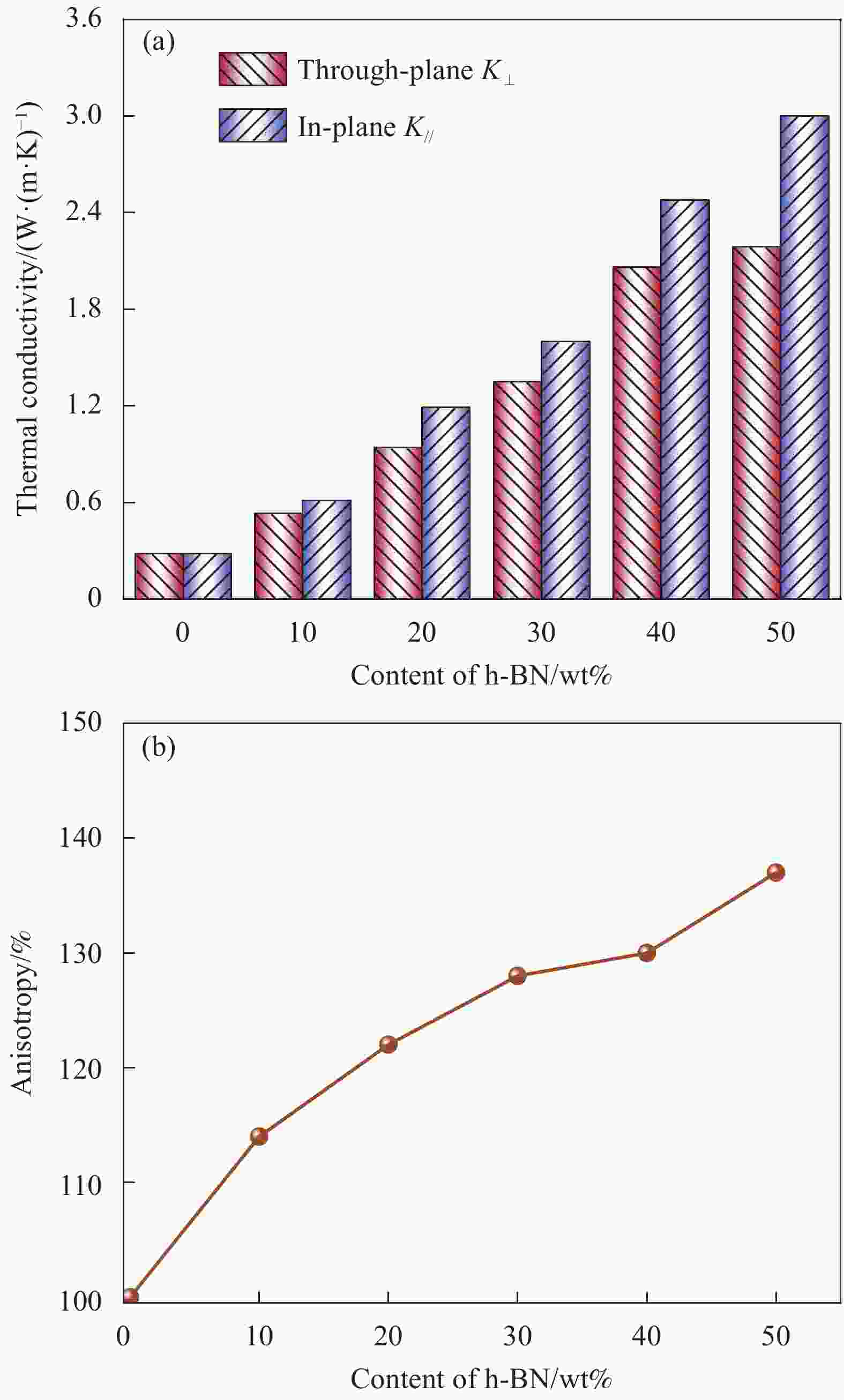
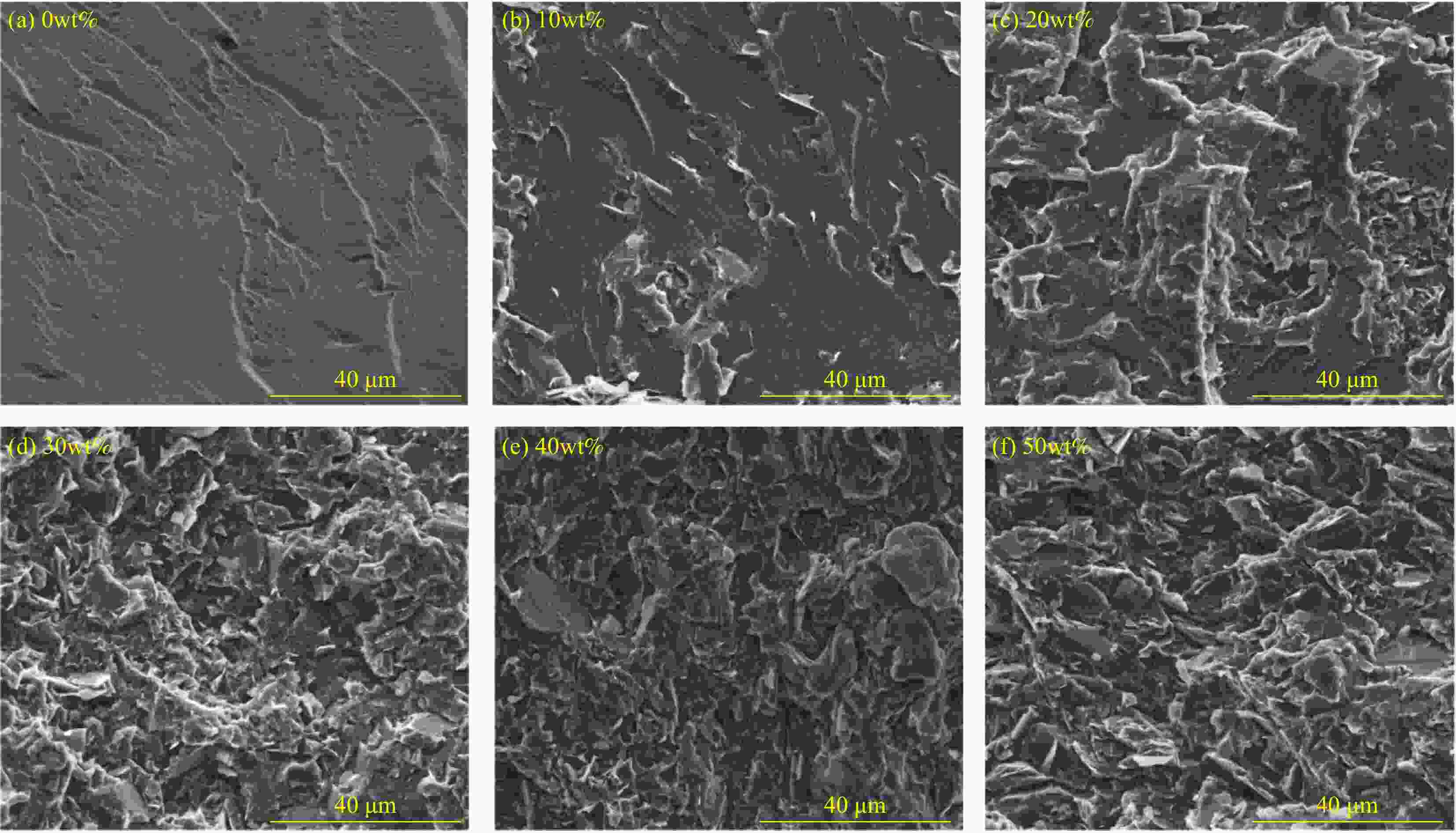
摘要: 电子电器设备中元器件的高密度集成使得散热问题日益突出,对导热材料的需求不断增长。本文以聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)为基体,六方氮化硼(h-BN)作为导热填料,通过熔融共混法制备h-BN/PET复合材料,考察了h-BN含量和PET基体聚集态结构对复合材料导热性能的影响,分析了复合材料的导热机制,并从材料应用的角度探讨了复合材料导热系数的温度依赖性和散热效果。结果表明,PET基体的结晶度和h-BN含量对复合材料的最终导热系数均有贡献,复合材料的导热系数随结晶度和h-BN含量的增加而提升。h-BN发挥了异相成核作用,显著加快了PET的结晶速度,提高了PET的结晶度。模压成型中h-BN受剪切应力驱使在PET基体中沿流动方向取向,导致复合材料呈现明显的各向异性特征。面内方向h-BN的有序排列为声子提供了更为通畅的传导通道。当h-BN含量为50wt%时,复合材料的面内与面间导热系数分别达到最大值3.00 W·(m·K)−1和2.19 W·(m·K)−1。h-BN/PET复合材料具有良好的散热效果,h-BN含量越高,复合材料的冷却速率越快,散热过程中温度下降符合指数函数规律。Abstract: The high density integration of components in electronic and electrical equipment makes the problem of heat dissipation increasingly prominent, and the demand for thermal conductive materials is increasing. In this paper, polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) were used as the matrix and thermally conductive filler, respectively, a series of h-BN/PET composites were prepared by melt blending method. The effect of the h-BN content and the crystallinity of the PET matrix on the thermal conductivity of the composites were investigated, and the thermal conduction mechanism of the composites was analyzed. The temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity and heat dissipation effect of the composites were explored from the perspective of material application. The results show that both the crystallinity of the PET matrix and the content of h-BN both contribute to the final thermal conductivity of the composites, and the thermal conductivity of the composites increases with the increase of the crystallinity and h-BN content. h-BN plays a role of heterogeneous nucleation, significantly accelerates the crystallization rate of PET and improves the crystallinity of PET. In compression molding, h-BN is driven by shear stress to oriented in the direction of flow in the PET matrix, resulting in the composite material showing obvious anisotropic characteristics. The orderly arrangement of h-BN in the in-plane direction provides more channels for phonons transmission. When the filling amount of h-BN reaches to 50wt%, the in-plane and through-plane thermal conductivity of the composites reach the maximum values of 3.00 W·(m·K)−1 and 2.19 W·(m·K)−1, respectively. h-BN/PET composites have good heat dissipation effect. The higher the h-BN content, the faster the cooling rate. The rule of temperature drop conforms to the exponential function during the heat dissipation process.
-
表 1 h-BN/PET复合材料的结晶参数
Table 1. Crystallization parameters of h-BN/PET composites
Content of h-BN/wt% $ {T}_{\mathrm{m}} $/℃ $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $/℃ $ {X}_{\mathrm{c}} $/% 0 256.2 207.9 28.6 10 256.5 224.2 36.8 20 257.4 228.4 37.4 30 256.3 229.6 36.3 40 257.8 233.6 36.0 50 257.7 235.5 36.1 Notes: $ {T}_{\mathrm{m}} $—Melting peak temperature; $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $—Crystallization peak temperature; $ {X}_{\mathrm{c}} $—Crystallinity. 表 2 不同h-BN含量的h-BN/PET复合材料在220℃下的等温结晶动力学参数
Table 2. Isothermal crystallization kinetic parameters of h-BN/PET composites with different h-BN contents at 220℃
Content of h-BN/wt% $ K $/min−n $ {t}_{1/2} $/min $ n $ 0 0.0045 8.73 2.32 10 0.0227 6.06 1.90 20 0.0321 5.68 1.77 30 0.0349 5.21 1.81 40 0.0502 4.63 1.71 50 0.0611 4.39 1.64 Notes: $ K $—Crystallization rate constants; $ {t}_{1/2} $—Crystallization half-time; $ n $—Avrami index. 表 3 20wt%h-BN含量的h-BN/PET复合材料于220℃下不同等温时间的结晶度
Table 3. Crystallinity of h-BN/PET composites with 20wt%h-BN at 220℃ with different isothermal crystallization time
Isothermal time/min 0 5 10 20 30 Crystallinity/% 37.4 38.2 39.8 41.1 44.5 表 4 h-BN/PET复合材料散热效果的指数拟合参数
Table 4. Index fitting parameters of the heat dissipation effect of h-BN/PET composites
Content of h-BN/wt% Parameter $ A $ $ b $ $ C $ $ \mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{D} $ 0 179.75 75.33 24.05 99.87% 10 172.23 58.91 27.78 99.90% 20 171.32 53.15 27.84 99.96% 30 169.93 49.75 28.31 99.93% 40 169.73 44.75 28.61 99.86% 50 166.41 29.97 31.69 99.83% Notes: A, b and C—Correction factor; $ \mathrm{C}\mathrm{O}\mathrm{D} $—Curve fitting degree. -
[1] LUYT A S, MOLEFI J A, KRUMP H. Thermal, mechanical and electrical properties of copper powder filled low-density and linear low-density polyethylene composites[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2006,91(7):1629-1636. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2005.09.014 [2] SIM L C, RAMANAN R R, ISMAIL H, et al. Thermal characterization of Al2O3 and ZnO reinforced silicone rubber as thermal pads for heat dissipation purposes[J]. Thermochimica Acta,2005,430(1-2):155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2004.12.024 [3] XU Y, LUO X, CHUNG D. Lithium doped polyethylene-glycol-based thermal interface pastes for high thermal contact conductance[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging,2002,124(3):188-191. doi: 10.1115/1.1477191 [4] HUANG X, JIANG P, TANAKA T. A review of dielectric polymer composites with high thermal conductivity[J]. IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine,2011,27(4):8-16. doi: 10.1109/MEI.2011.5954064 [5] YAO Y, ZENG X, SUN R, et al. Highly thermally conductive composite papers prepared based on the thought of bioinspired engineering[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(24):15645-15653. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b04636 [6] 曾凡坤, 孟正华, 郭巍. 碳化硅颗粒增强石墨/铝复合材料的热物理性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10):4918-4926. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211103.004ZENG Fankun, MENG Zhenghua, GUO Wei. Thermophysical properties of SiC particles reinforced graphite flakes/Al composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(10):4918-4926(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211103.004 [7] WANG Z, FU Y, MENG W, et al. Solvent-free fabrication of thermally conductive insulating epoxy composites with boron nitride nanoplatelets as fillers[J]. Nanoscale Research Letters,2014,9(1):1-7. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-1 [8] WEN B Y, ZHENG X L. Effect of the selective distribution of graphite nanoplatelets on the electrical and thermal conductivities of a polybutylene terephthalate/polycarbonate blend[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,174:68-75. [9] 林夏泽, 温变英. 界面效应对功能复合材料热传导行为的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(4):1498-1510. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211009.002LIN Xiaze, WEN Bianying. Influence of interfacial effect on heat conduction behavior of functional composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(4):1498-1510(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211009.002 [10] 吴宇明, 虞锦洪, 曹勇, 等. 高导热低填量聚合物基 复合材料研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(4):760-766. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170607.001WU Yuming, YU Jinhong, CAO Yong, et al. Review of polymer-based composites with high thermal conductivity and low filler loading[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(4):760-766(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170607.001 [11] JIN S H, PARK Y B, YOON K H. Rheological and mechanical properties of surface modified multi-walled carbon nanotube-filled PET composite[J]. Composites Science & Technology, 2007, 67(15-16): 3434-3441. [12] HANSEN D, BERNIER G A. Thermal-conductivity of polyethylene: The effects of crystal size, density and orientation on thermal-conductivity[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science,1972,12(3):204-208. doi: 10.1002/pen.760120308 [13] BAI L, ZHAO X, BAO R Y, et al. Effect of temperature, crystallinity and molecular chain orientation on the thermal conductivity of polymers: A case study of PLLA[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2018,53(14):10543-10553. doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-2306-4 [14] 周文英, 王蕴, 曹国政, 等. 本征导热高分子材料研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(7):2038-2055. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210312.001ZHOU Wenying, WANG Yun, CAO Guozheng, et al. Progress in intrinsic thermally conductive polymers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(7):2038-2055(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210312.001 [15] PAPAGEORGIOU G Z, KARANDREA E, GILIOPOULOS D, et al. Effect of clay structure and type of organic modifier on the thermal properties of poly(ethylene terephthalate) based nanocomposites[J]. Thermochimica Acta,2014,576:84-96. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2013.12.006 [16] WANG X, BIAN H, NI S, et al. BNNS/PVA bilayer composite film with multiple-improved properties by the synergistic actions of cellulose nanofibrils and lignin nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,157:259-266. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.178 [17] 秦国锋, 张婧婧, 徐子威, 等. BN纤维对石墨烯微片/聚丙烯复合材料导热绝缘性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(3):546-552. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190917.005QIN Guofeng, ZHANG Jingjing, XU Ziwei, et al. Effect of BN fiber on thermal conductivity and insulation properties of graphene nanoplatelets/polypropylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(3):546-552(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190917.005 [18] ZHANG F, FENG Y Y, FENG W. Three-dimensional inter-connected networks for thermally conductive polymer composites: Design, preparation, properties, and mechanisms[J]. Materials Science & Engineering R-Reports,2020,142:100580. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2020.100580 [19] 石林, 马忠雷, 景佳瑶, 等. 双导热网络功能化氮化硼纳米片/聚氨酯复合材料的制备与导热性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10):4531-4539. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211028.007SHI Lin, MA Zhonglei, JING Jiayao, et al. Preparation and thermally conductive properties of functionalized boron nitride nanosheets/polyurethane composites with double heat-conduction networks[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(10):4531-4539(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211028.007 [20] 王海花, 冯佳, 赵敏. 氮化硼纳米片的制备及其增强环氧树脂复合材料导热性能的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3):956-968. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211015.001WANG Haihua, FENG Jia, ZHAO Min. Research progress on the preparation of boron nitride nanosheets and its reinforcement on the thermal conductivity of epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(3):956-968(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211015.001 [21] CUI L, WANG P, ZHANG Y, et al. Combined effect of α-nucleating agents and glass fiber reinforcement on a polypropylene composite: A balanced approach[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7(68):42783-42791. doi: 10.1039/C7RA08322J [22] MCR A, ET A, MA A, et al. Enthalpy-based determination of crystalline, mobile amorphous and rigid amorphous fractions in semicrystalline polymers[J]. Thermochimica Acta,2007,462(1-2):15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2007.06.003 [23] American Society for Testing and Materials. Standard test method for thermal diffusivity by the flash method: ASTM-E1461-13[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials, 2013. [24] ZHENG X, WEN B. Practical PBT/PC/GNP composites with anisotropic thermal conductivity[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(62):36316-36323. doi: 10.1039/C9RA07168G [25] WEN B, MA L, ZOU W, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity of poly(lactic acid)/alumina composite by synergistic effect of tuning crystallization of poly(lactic acid) crystallization and filler content[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2020,31(8):6328-6338. doi: 10.1007/s10854-020-03189-x [26] YOO Y, LEE H L, HA S M, et al. Effect of graphite and carbon fiber contents on the morphology and properties of thermally conductive composites based on polyamide 6[J]. Polymer International,2013,63(1):151-157. [27] 张一铭, 郑小磊, 温变英. PBT/PC/GNP复合材料导电导热性能的温度依赖性[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2019, 47(10):18-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2019.10.004ZHANG Yiming, ZHENG Xiaolei, WEN Bianying. Temperature dependence of electrical and thermal conductivity of PBT/PC/GNP composites[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2019,47(10):18-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2019.10.004 -






 下载:
下载: