Development and analysis of a novel collagen-sodium humate composite hydrogel
-
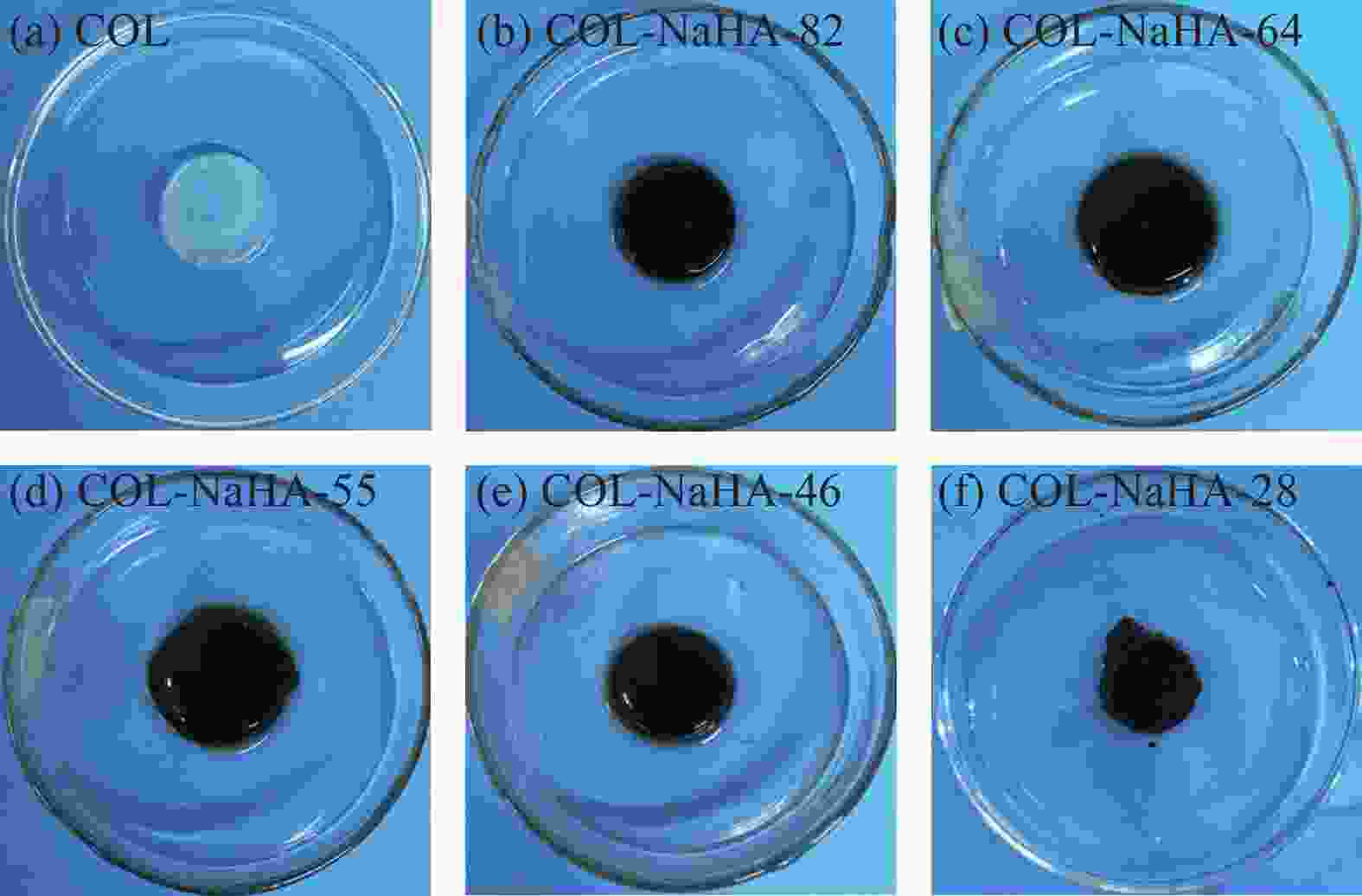
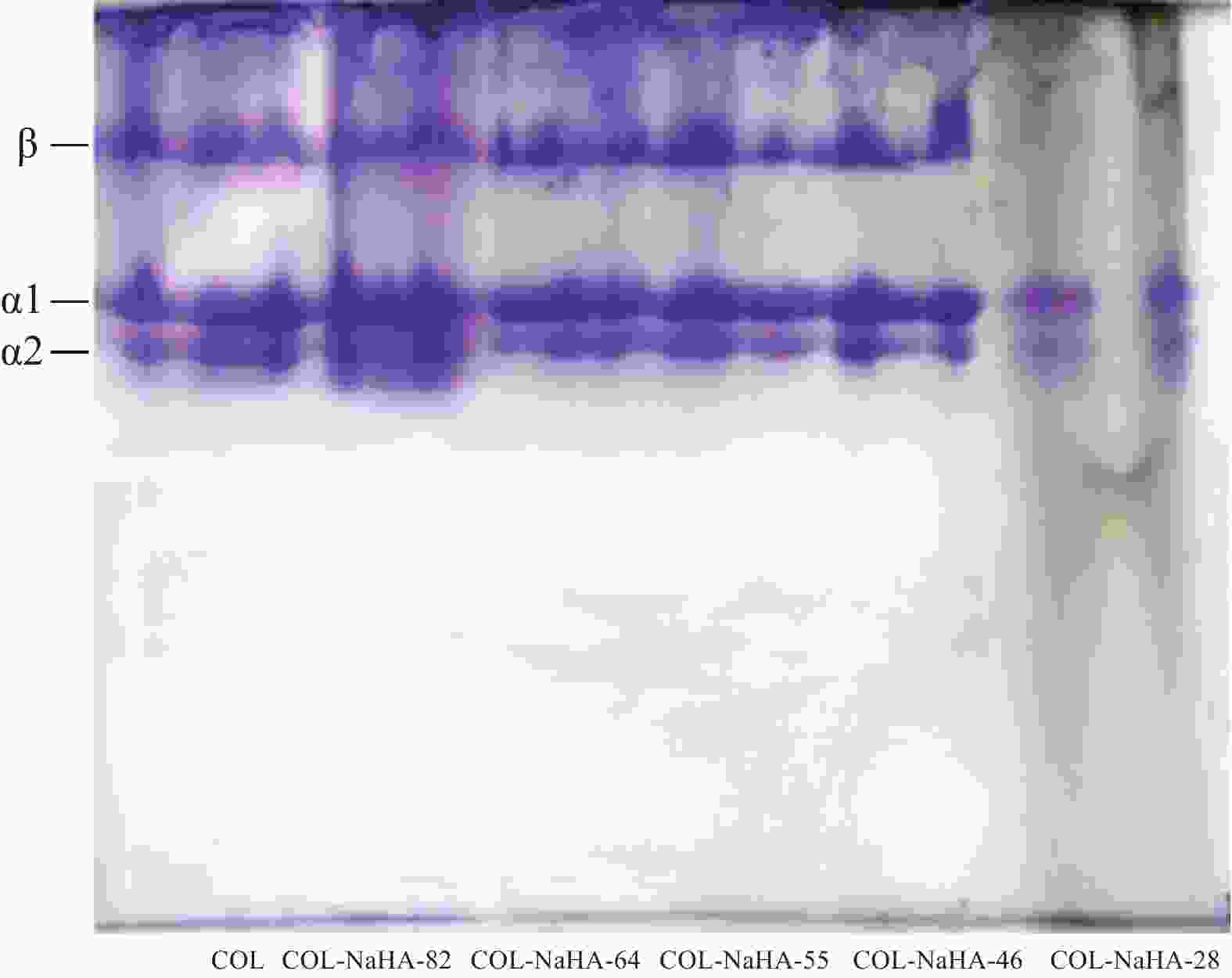
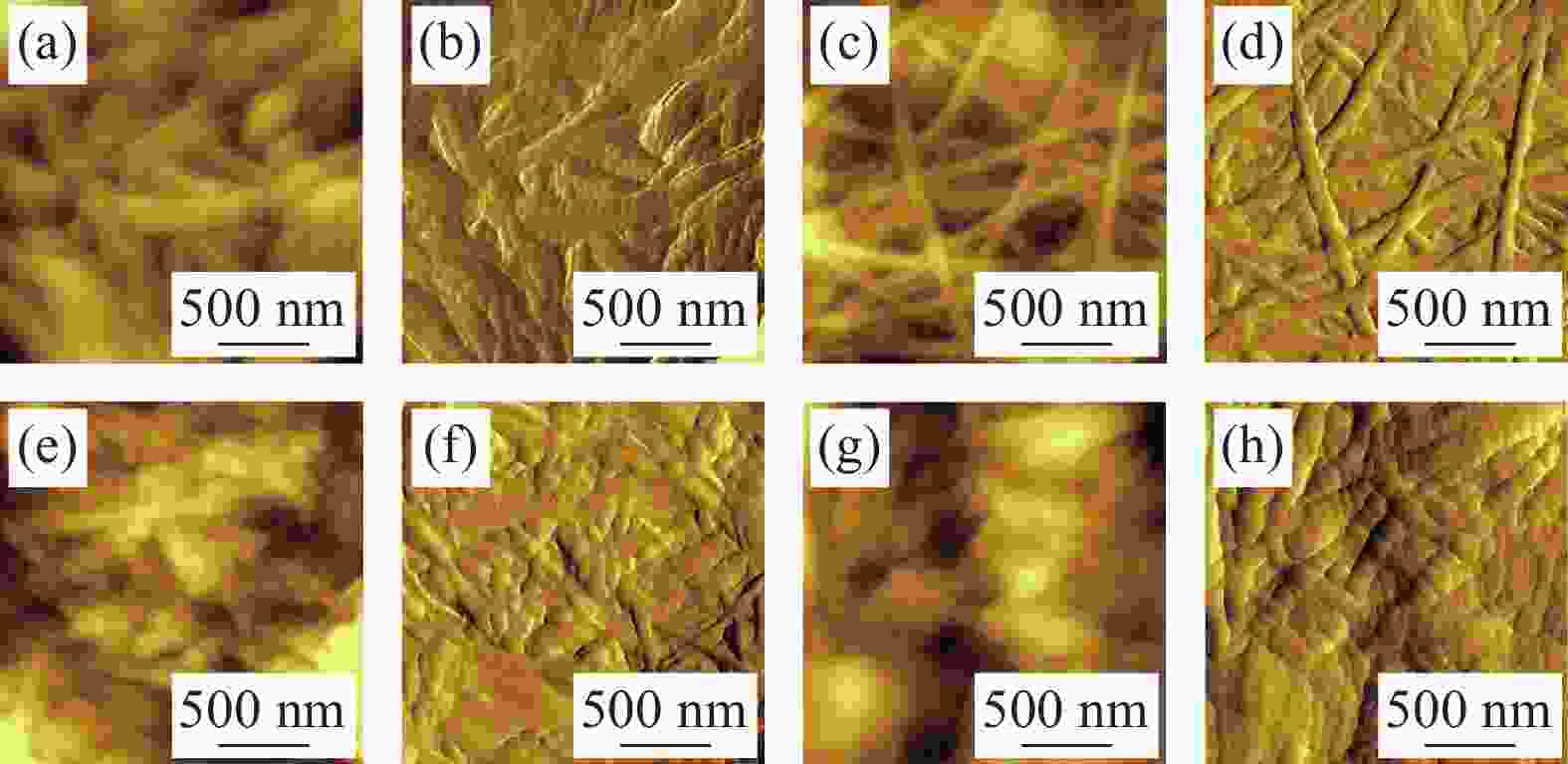
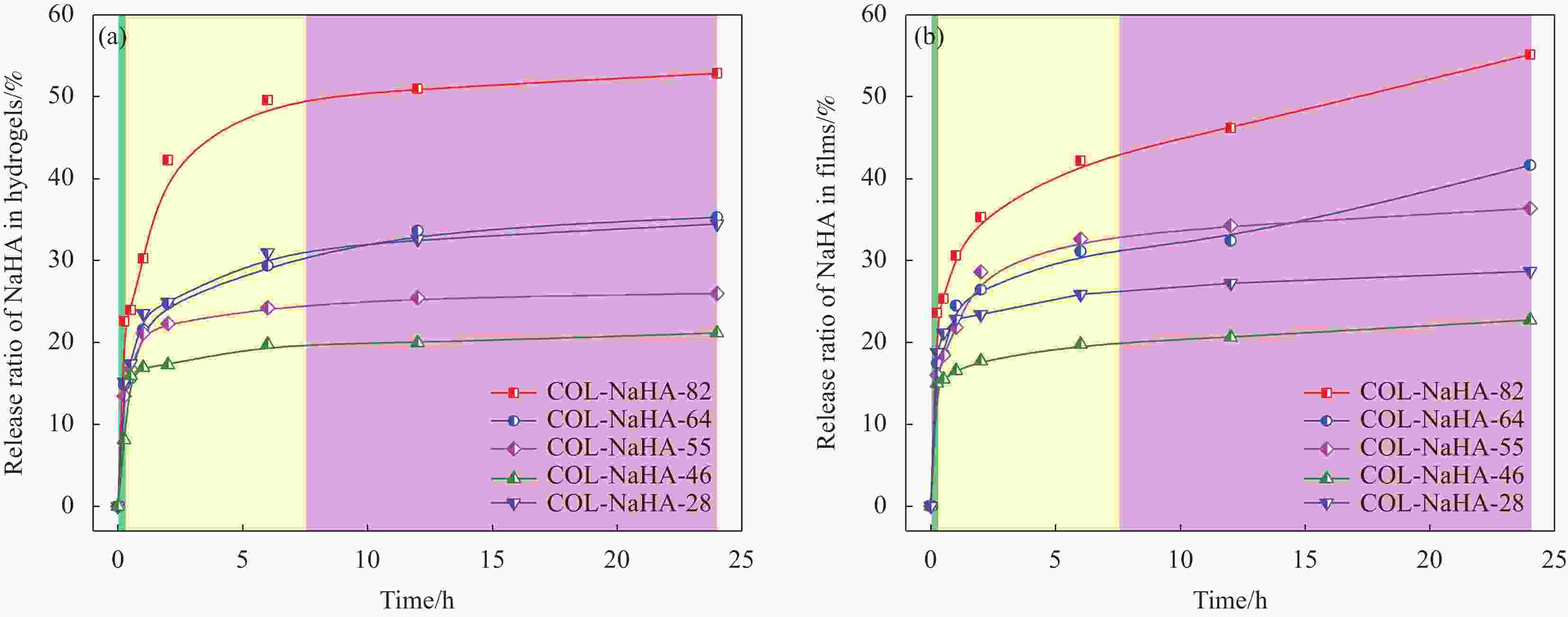
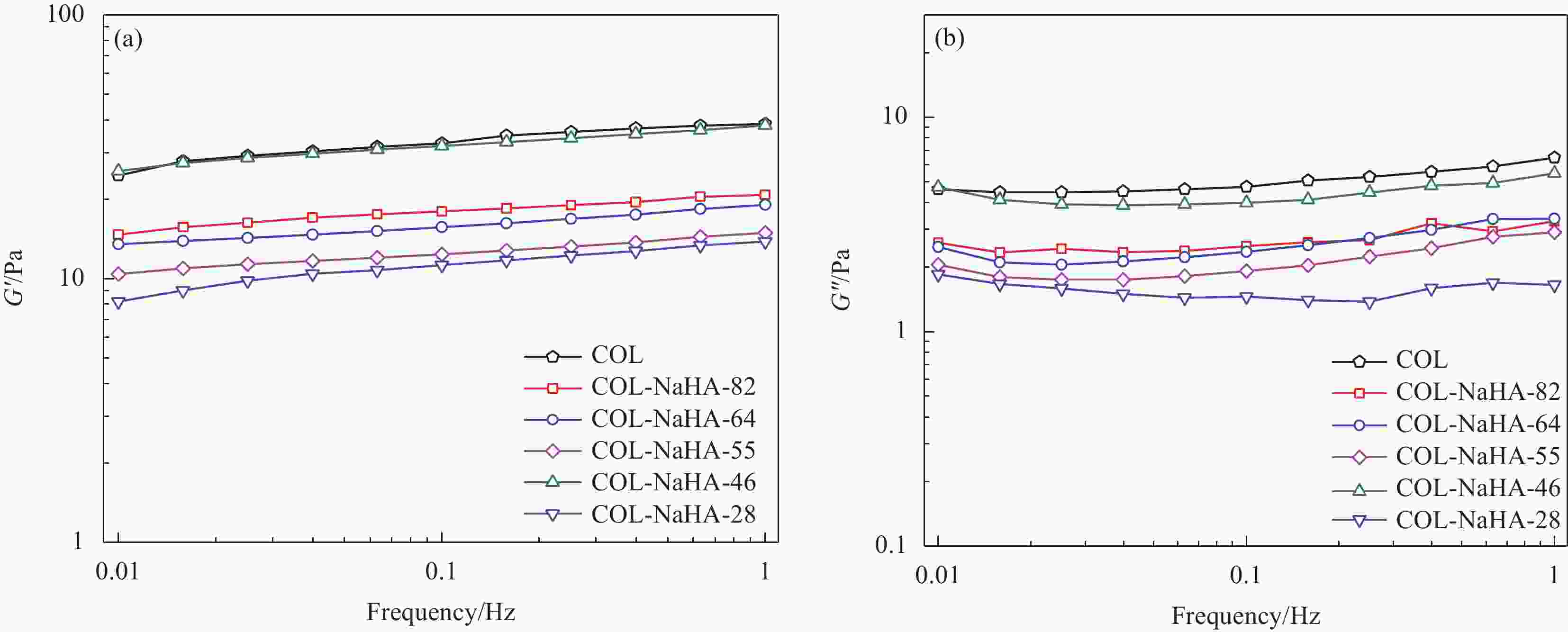
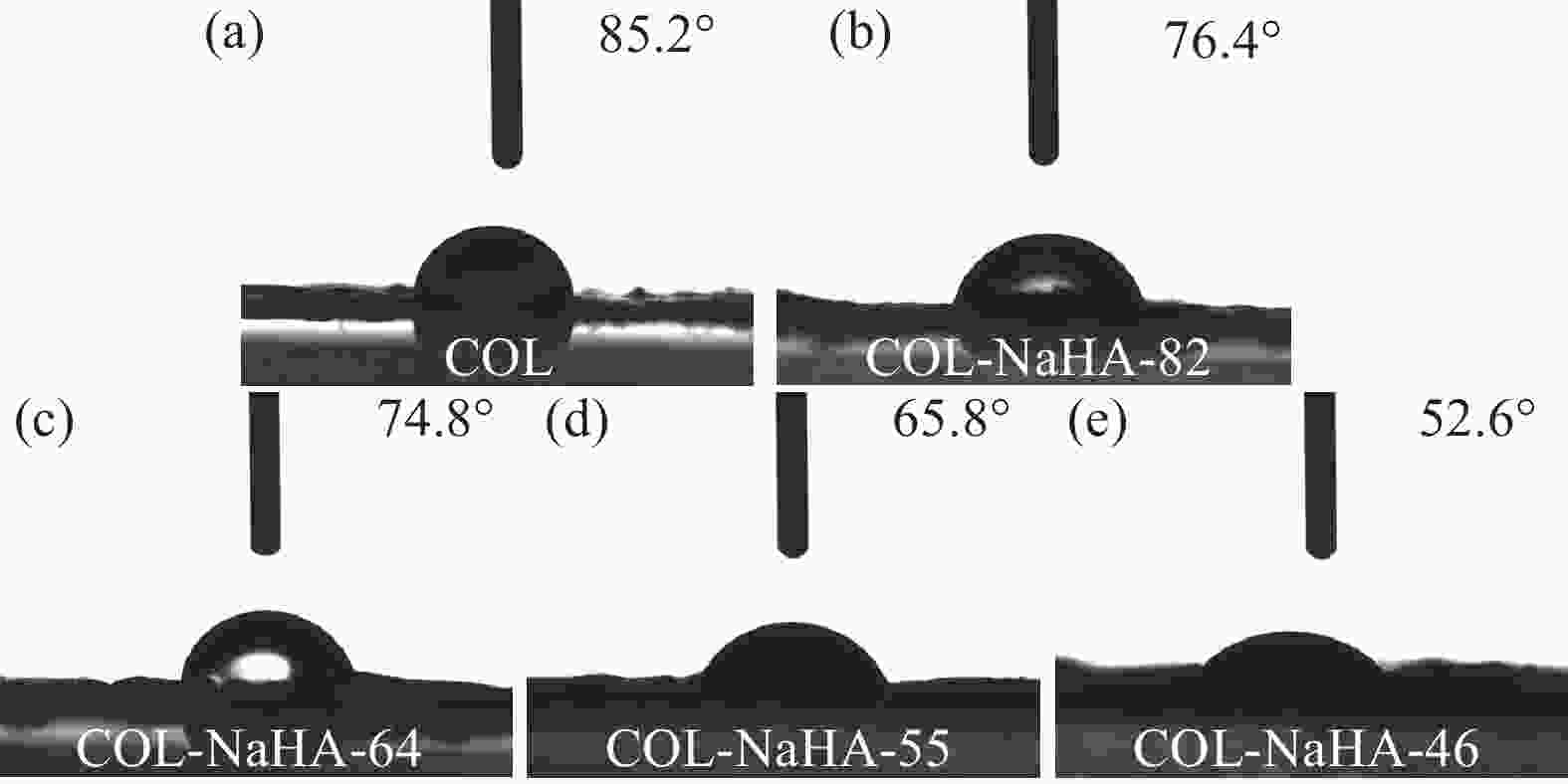
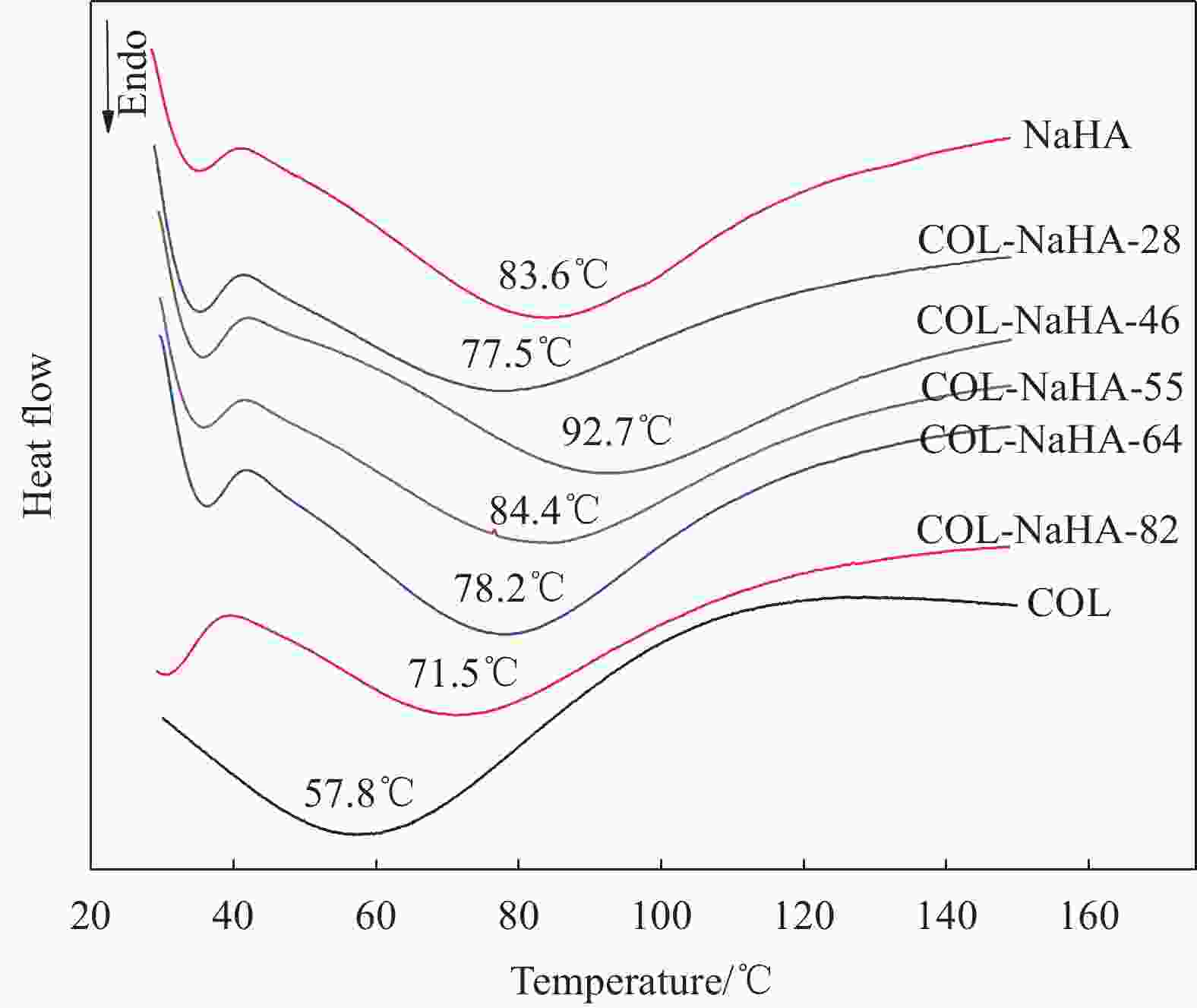
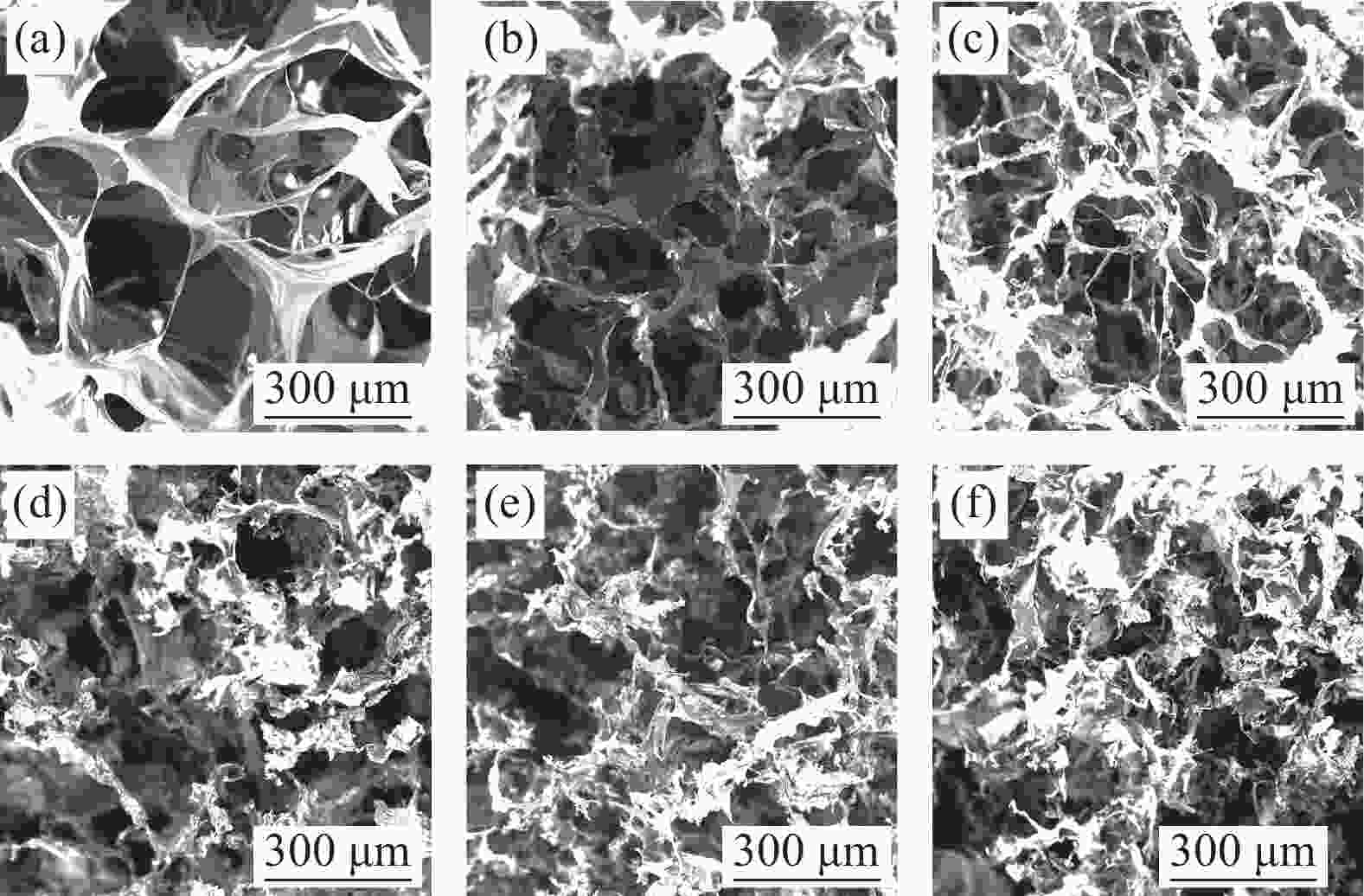
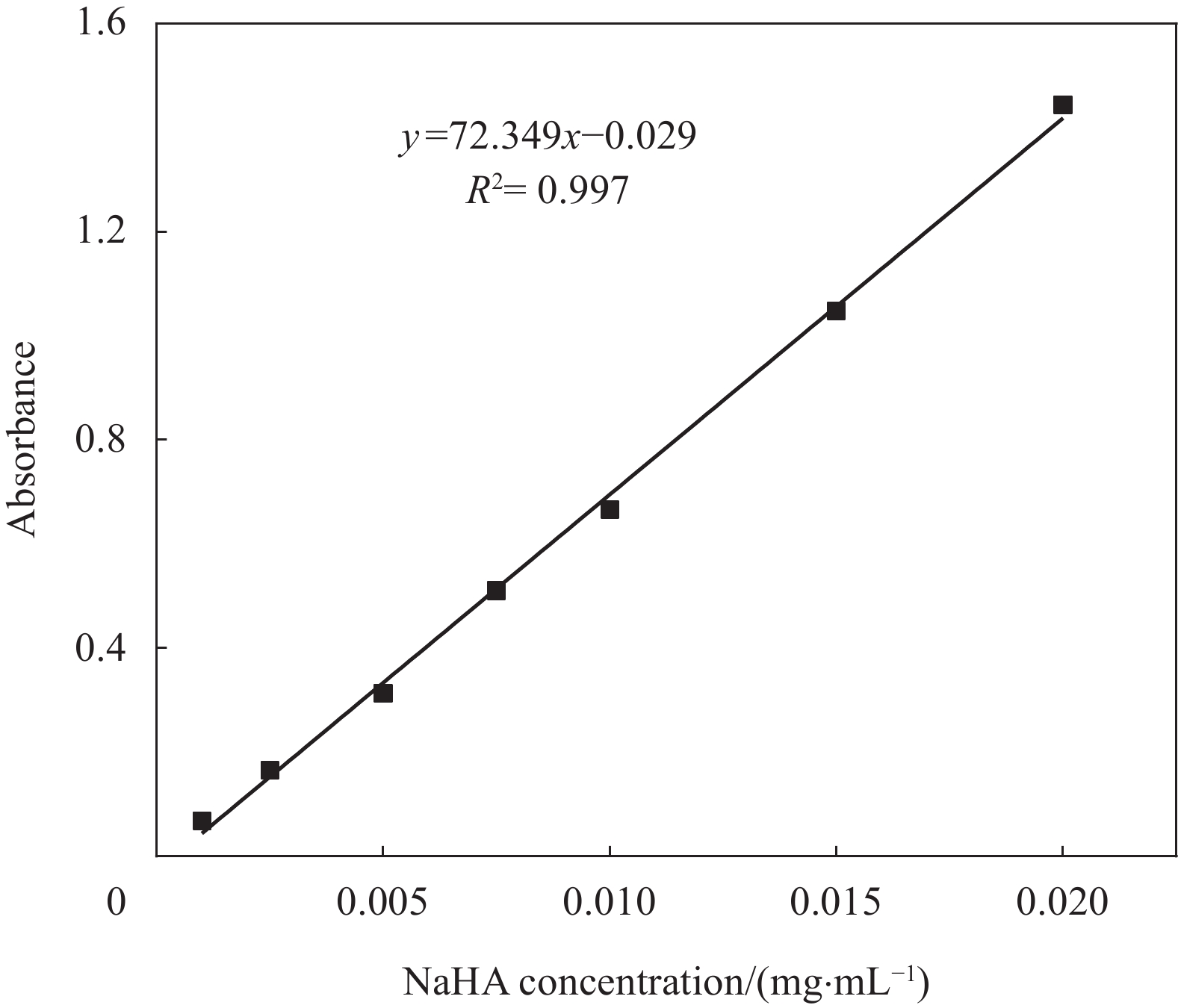
摘要: 水凝胶具有弹性高、含水量高,冷效应、保湿性强、形状多变等优点,是医用敷料的主要材料之一。将具有优良生物相容性、促细胞增殖功能的胶原(COL)与具有止血、消炎等作用的腐植酸钠(NaHA)按不同比例(COL∶NaHA)共混并采用自组装方式制备了一种新型胶原-腐植酸钠复合水凝胶,并考察两者间的相互作用及复合水凝胶的结构与性能,以期应用于医用敷料行业。NaHA不改变胶原的三股螺旋结构且两者之间存在氢键与静电作用。当COL∶NaHA ≥ 4∶6时,两者间的静电结合被NaCl所屏蔽,因此体系相容性较好;然而继续增加NaHA会引起聚沉现象。当COL∶NaHA=4∶6时,两者结合率最高,达到93.2%且相容性较好,复合水凝胶的纤维具有明显的D-周期且各方面性能最佳。NaHA的释放较缓慢,24 h后仍有约80%保留在水凝胶中;热稳定性较纯胶原提升了34.9℃;储能模量和损耗模量分别为31.89 Pa和3.99 Pa。此外,随着NaHA的加入,冻干复合水凝胶的孔径缩小、孔隙分布更加均匀;复合膜的亲水性明显提升。Abstract: Hydrogel was one of main materials for medical dressings due to the excellent performance such as high elasticity, high water content, cold effect, strong moisture retentiveness and variable shape. Collagen (COL) had good biocompatibility and can promote cell proliferation. And Sodium humate (NaHA) possessed hemostatic, anti-inflammatory and other biological functions. Therefore, a novel collagen-sodium humate composite hydrogel was prepared by mixing collagen and NaHA at various COL∶NaHA ratios and collagen self-assembly, which was expected to be applied as medical dressing. Then the interaction between collagen and NaHA and the microstructures and properties of composite hydrogels were investigated. The collagen triple helix is not affected, although hydrogen bonds and electrostatic interaction occur between collagen and NaHA. At COL∶NaHA≤4∶6, the hydrogels possess good compatibility due to the shielding effect of NaCl on electrostatic binding; however, the coagulation takes place with the further increase in NaHA content. At COL∶NaHA=4∶6, the percentage of NaHA incorporated into collagen fibrils is highest and 93.2%, and the compatibility between collagen and NaHA is good; therefore, the properties of composite hydrogel consisting of mature fibrils with D-periodicity are optimum. Moreover, about 80% of NaHA still remain in hydrogel, indicating its release is slow. The thermal stability improves by 34.9°C, and storge modulus and loss modulus are 31.89 Pa and 3.99 Pa, respectively. Furthermore, the pore sizes of the lyophilized composite hydrogels decrease and the pores become dense and well-distributed. The composite films have significant rises in hydrophilicity.
-
Key words:
- collagen /
- sodium humate /
- composite hydrogel /
- microstructure /
- percentage of binding /
- control release /
- thermal stability
-
表 1 胶原-腐植酸钠(COL-NaHA)复合水凝胶的制备配方
Table 1. Formulations of collagen-sodium humate (COL-NaHA) composite hydrogels
Sample cCOL/
(mg·mL−1)cNaHA/
(mg·mL−1)COL∶NaHA COL 5.00 0.00 10∶0 COL-NaHA-82 5.00 1.25 8∶2 COL-NaHA-64 5.00 3.33 6∶4 COL-NaHA-55 5.00 5.00 5∶5 COL-NaHA-46 5.00 7.50 4∶6 COL-NaHA-28 5.00 20.00 2∶8 Note: cCOL and cNaHA—Concentrations of collagen and NaHA in COL-NaHA hydrogels, respectively. -
[1] LI S, WANG L, ZHENG W, et al. Rapid fabrication of self-healing, conductive, and injectable gel as dressings for healing wounds in stretchable parts of the body[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(31):2002370. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002370 [2] MOHAMADI S, NOROOZNEZHAD A H, MOSTAFAEI S, et al. A randomized controlled trial of effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma gel and regular dressing on wound healing time in pilonidal sinus surgery: Role of different affecting factors[J]. Biomedical Journal,2019,42(6):403-410. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2019.05.002 [3] STEVENSON F J. Humus chemistry: Genesis, composition, reactions[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1994. [4] 顾刚果, 耿宝琴, 雍定国. 黄腐植酸钠的抗凝作用[J]. 现代应用药学, 1988, 4(5):8, 41.GU Gangguo, GENG Baoqin, YONG Dingguo. Anticoagulant effect of sodium xanthate[J]. Application of Modern Medicine,1988,4(5):8, 41(in Chinese). [5] JI Y, ZHANG A, CHEN X, et al. Sodium humate accelerates cutaneous wound healing by activating TGF-beta/smads signaling pathway in rats[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B,2016,6(2):132-140. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2016.01.009 [6] 张爱军, 顾慧莹, 闫志勇, 等. 不同基质和pH值的腐植酸钠凝胶剂对大鼠皮肤创伤愈合的影响[J]. 中国药房, 2013, 21(24):1933-1935.ZHANG Aijun, GU Huiying, YAN Zhiyong, et al. Effect of sodium humic gel with different matrix and pH on wound healing of rats[J]. China Drug Store,2013,21(24):1933-1935(in Chinese). [7] 顾其胜, 王帅帅, 王庆生, 等. 海藻酸盐敷料应用现状与研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014, 28(2):255-258. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.20140055GU Qisheng, WANG Shuaishuai, WANG Qingsheng, et al. Application status and research progress of alginate dressing[J]. Chinese Journal of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery,2014,28(2):255-258(in Chinese). doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.20140055 [8] JIN J, JI Z, XU M, et al. Microspheres of carboxymethyl chitosan, sodium alginate, and collagen as a hemostatic agent in vivo[J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering,2018,4(7):2541-2551. [9] LIU X, ZHENG M, WANG X, et al. Biofabrication and characterization of collagens with different hierarchical architectures[J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering,2020,6(1):739-748. [10] SUN L, LI B, SONG W, et al. Comprehensive assessment of nile tilapia skin collagen sponges as hemostatic dressings[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2020,109:110532. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110532 [11] 刘晨阳, 马建中, 张跃宏. 胶原蛋白基纳米复合材料的性能及界面研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(6):1691-1702.LIU Chenyang, MA Jianzhong, ZHANG Yuehong. Progress on properties and interface of collagen-based nanocomposites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(6):1691-1702(in Chinese). [12] MORGENSTERN L, MICHEL S L, AUSTIN E. Control of hepatic bleeding with microfibrillar collagen[J]. Archives of Surgery,1977,112:941-943. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1977.01370080039005 [13] DOILLON C J, WHYNE C F, BRANDWEIN S, et al. Collagen-based wound dressings: Control of the pore structure and morphology[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research,1986,20:1219-1228. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820200811 [14] DOILLON C J, SILVER F H. Collagen-based wound dressing: Effects of hyaluronic acid and firponectin on wound healing[J]. Biomaterials,1986,7(1):3-8. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(86)90080-3 [15] BHASKAR K, MOHAN C K, LINGAM M, et al. Development of SLN and NLC enriched hydrogels for transdermal deli-very of nitrendipine: In vitro and in vivo characteristics[J]. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy,2009,35(1):98-113. doi: 10.1080/03639040802192822 [16] TEZGEL Ö, DISTASIO N, LAGHEZZA-MASCI V, et al. Collagen scaffold-mediated delivery of NLC/siRNA as wound healing materials[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology,2020,55:101421. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101421 [17] LAGHEZZA M V, TADDEI A R, COURANT T, et al. Characterization of collagen/lipid nanoparticle-curcumin cryostructurates for wound healing applications[J]. Macromolecular Bioscience,2019,19(5):e1800446. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201800446 [18] RIEDE U N, JONAS I, KIRN B, et al. Collagen stabilization induced by natural humic substances[J]. Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery,1992,111:259-264. doi: 10.1007/BF00571520 [19] GERT J K, ROBERT E M H. Experiments on collagen-humic interactions speed of humic uptake, and effects of diverse chemical treatments[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science,1995,22:263-270. doi: 10.1006/jasc.1995.0028 [20] LAEMMLI U K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4[J]. Nature,1970,277:680-685. [21] PIETRUCHA K. Changes in denaturation and rheological properties of collagen-hyaluronic acid scaffolds as a result of temperature dependencies[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2005,36(5):299-304. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2005.07.004 [22] DING C, ZHANG M, LI G. Preparation and characterization of collagen/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) blend film[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,119:194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.11.057 [23] Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc, Informatics Division. Sadtler spectral handbooks[M]. Berkeley: Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc, 2004: 116. [24] 冯文坡, 祁元明, 汤克勇. 胶原-羟基磷灰石/阿拉伯树胶复合材料的制备与表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2010, 27(6):113-119.FENG Wenpo, QI Yuanming, TANG Keyong. Preparation and characterization of collagen-hydroxyapatite/gum Arabic composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2010,27(6):113-119(in Chinese). [25] 易菊珍, 梁子倩, 张黎明. 腐植酸钠/聚丙烯酰胺水凝胶吸水性能的研究[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 46(2):36-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2007.02.010YI Juzhen, LIANG Ziqian, ZHANG Liming. Studies on sodium humate/polyacrylamide hydrogels(I) synthesis and water absorption properties[J]. Journal of Sun Yat-sen University (Medical Sciences),2007,46(2):36-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2007.02.010 [26] 丁翠翠. 胶原/HPMC共混体系中大分子相互作用及相态转变特性研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2015.DING Cuicui. Macromolecular interaction and phase transition in collagen/HPMC blends[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2015(in Chinese). [27] LI Y P. The mechanism of collagen self-assembly: Hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions[D]. Gainesville: The University of Florida, 2009. [28] PIELESZ A. Temperature-dependent FTIR spectra of collagen and protective effect of partially hydrolysed fucoidan[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2014,118:287-293. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.08.056 [29] 田振华, 何静瑄, 王颖, 等. 基于二维红外技术研究氧化羧甲基纤维素钠/胶原的相互作用及热稳定性[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 9(41):2782-2788.TIAN Zhenhua, HE Jingxuan, WANG Ying, et al. Interaction and thermal stability of oxidized carboxymethyl cellulose/collagen based on two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2021,9(41):2782-2788(in Chinese). [30] TIAN H L, LI C H, LIU W T, et al. The influence of chondroitin 4-sulfate on the reconstitution of collagen fibrils in vitro[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2013,105:259-266. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.01.005 [31] DING C, ZHANG M, TIAN H, et al. Effect of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose on collagen fibril formation in vitro[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,52:319-326. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.10.003 [32] LEE H J, AHN S H, KIM G H. Three-dimensional collagen/alginate hybrid scaffolds functionalized with a drug delivery system (DDS) for bone tissue regeneration[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2011,24(5):881-891. [33] PARK J H, LEE G S, SHIN U S, et al. Self-hardening microspheres of calcium phosphate cement with collagen for drug delivery and tissue engineering in bone repair[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society,2011,94(2):351-354. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04314.x [34] ARAFAT M T, TRONCI G, WOOD D J, et al. In-situ crosslinked wet spun collagen triple helices with nanoscale-regulated ciprofloxacin release capability[J]. Materials Letters,2019,255:126550. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126550 [35] FRANCIS-SEDLAK M E, URIEL S, LARSON J C, et al. Characterization of type I collagen gels modified by glycation[J]. Biomaterials,2009,30(9):1851-1856. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.12.014 [36] WU K J, WANG C Y, LU H K. Effect of glutaraldehyde on the humoral immunogenicity and structure of porcine dermal collagen membranes[J]. Archives of Oral Biology,2004,49(4):305-311. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2003.10.002 -






 下载:
下载: