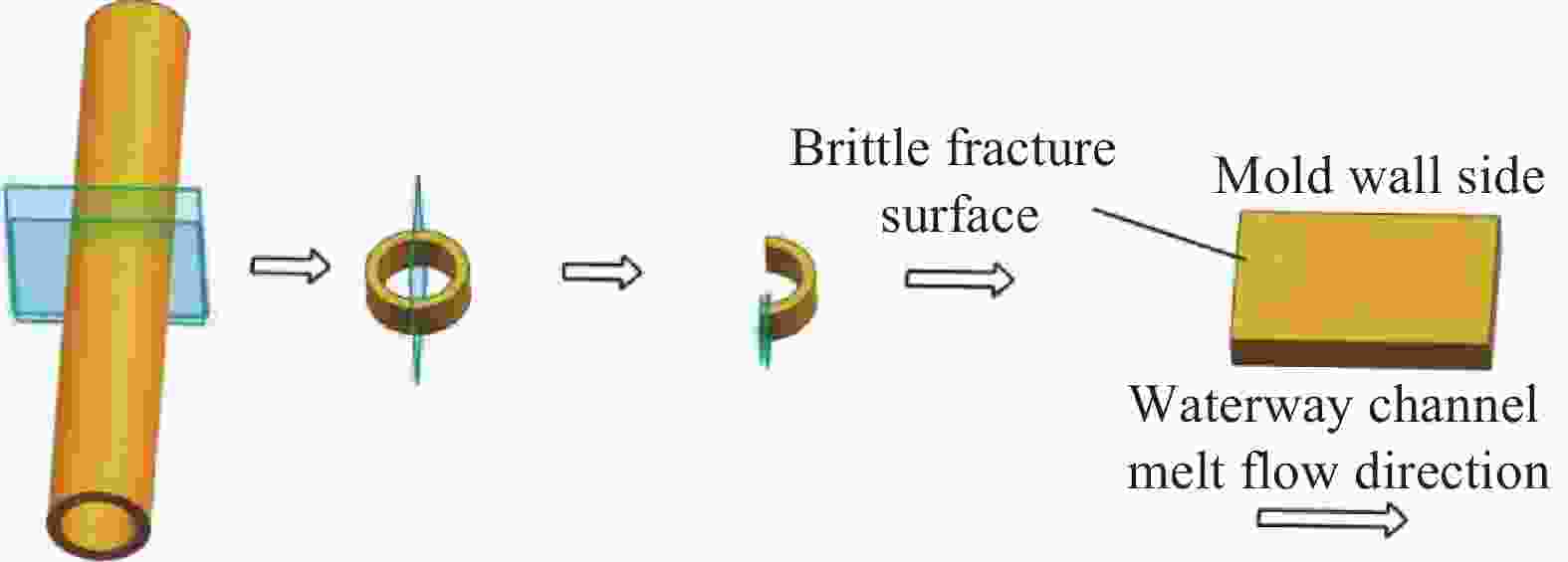
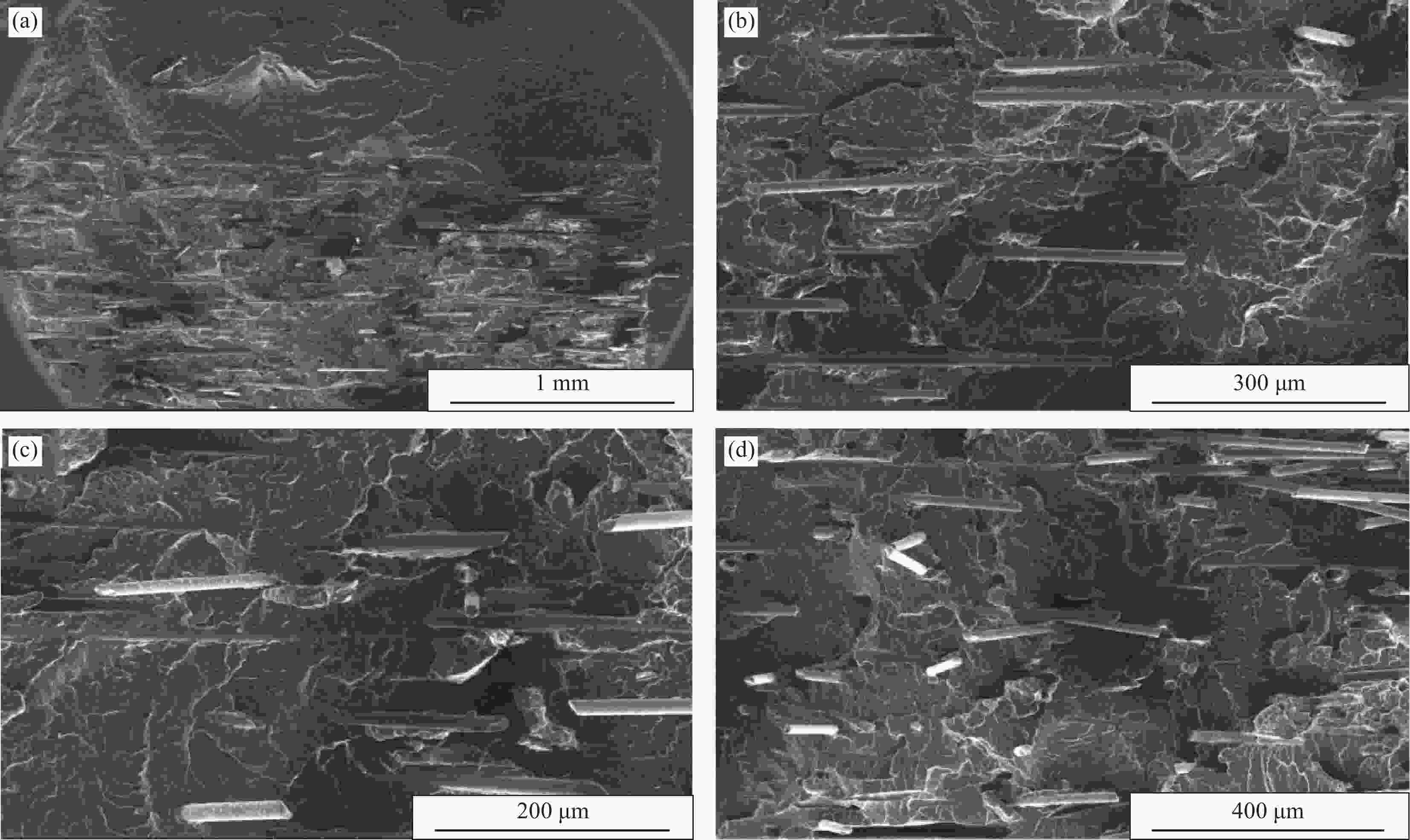
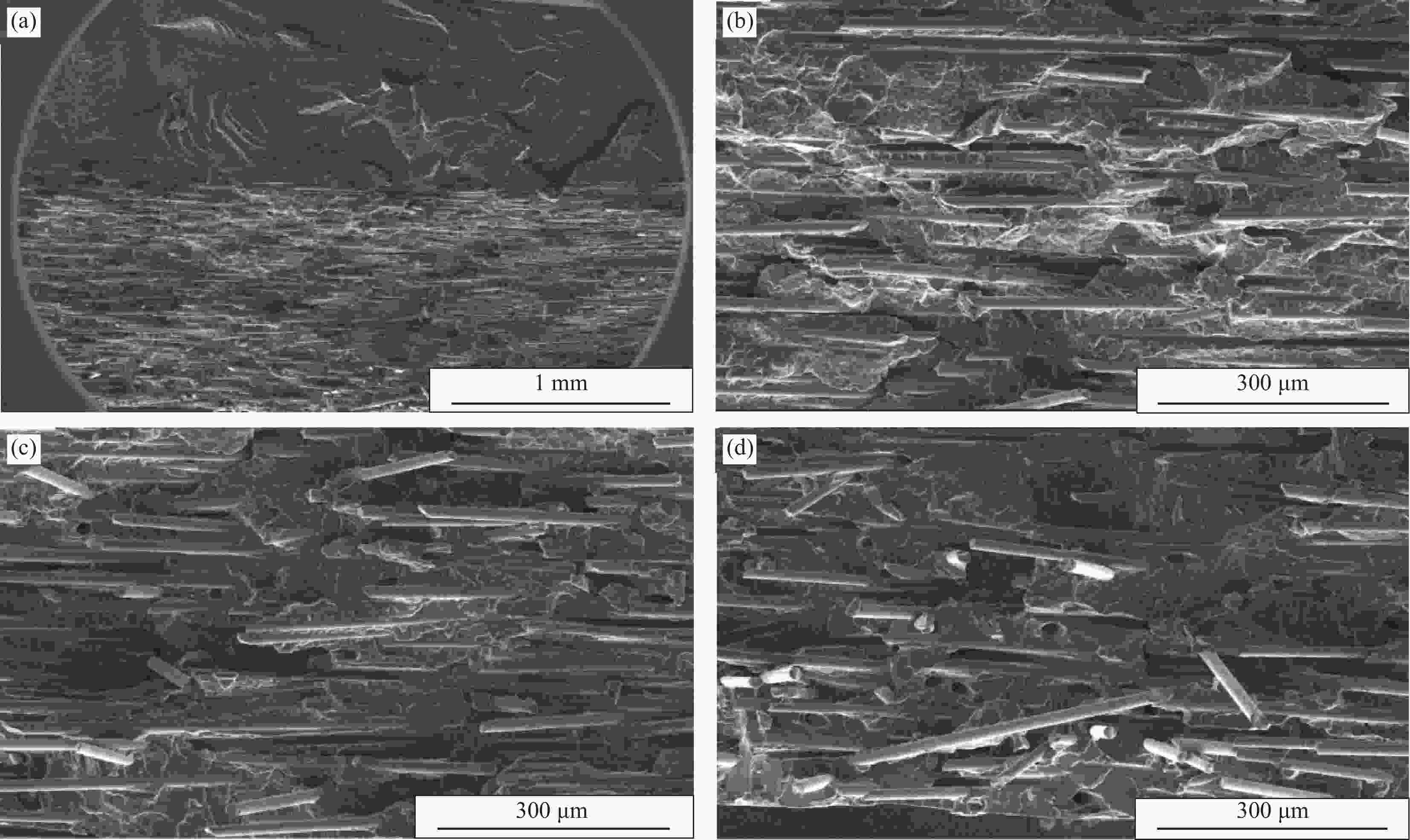
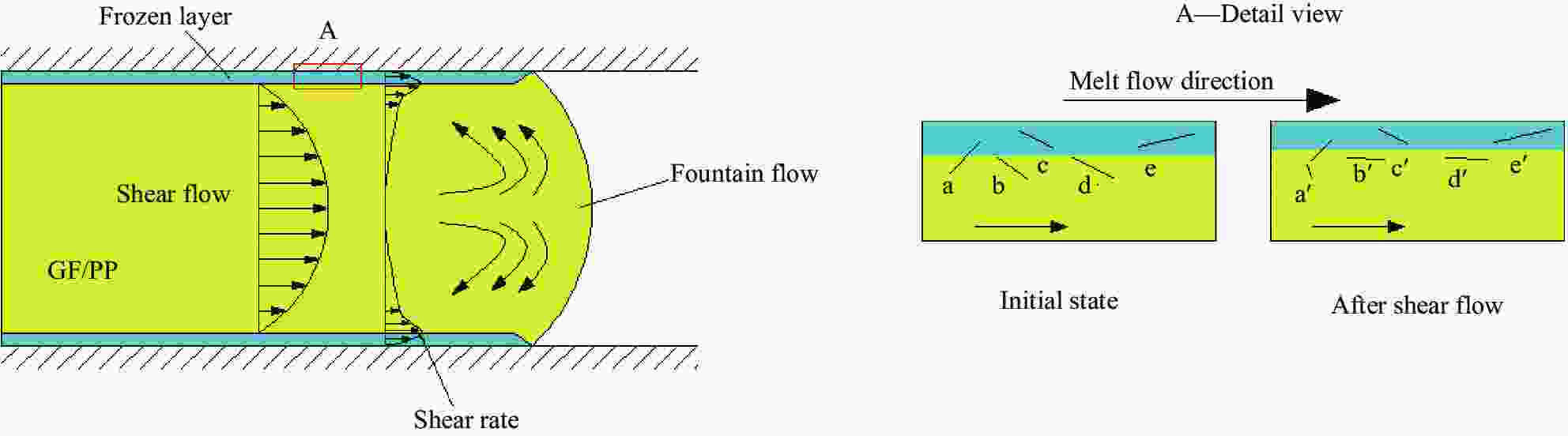
Effect of glass fiber mass fraction on the water assisted co-injection molding pipes of short glass fiber reinforced polypropylene
-
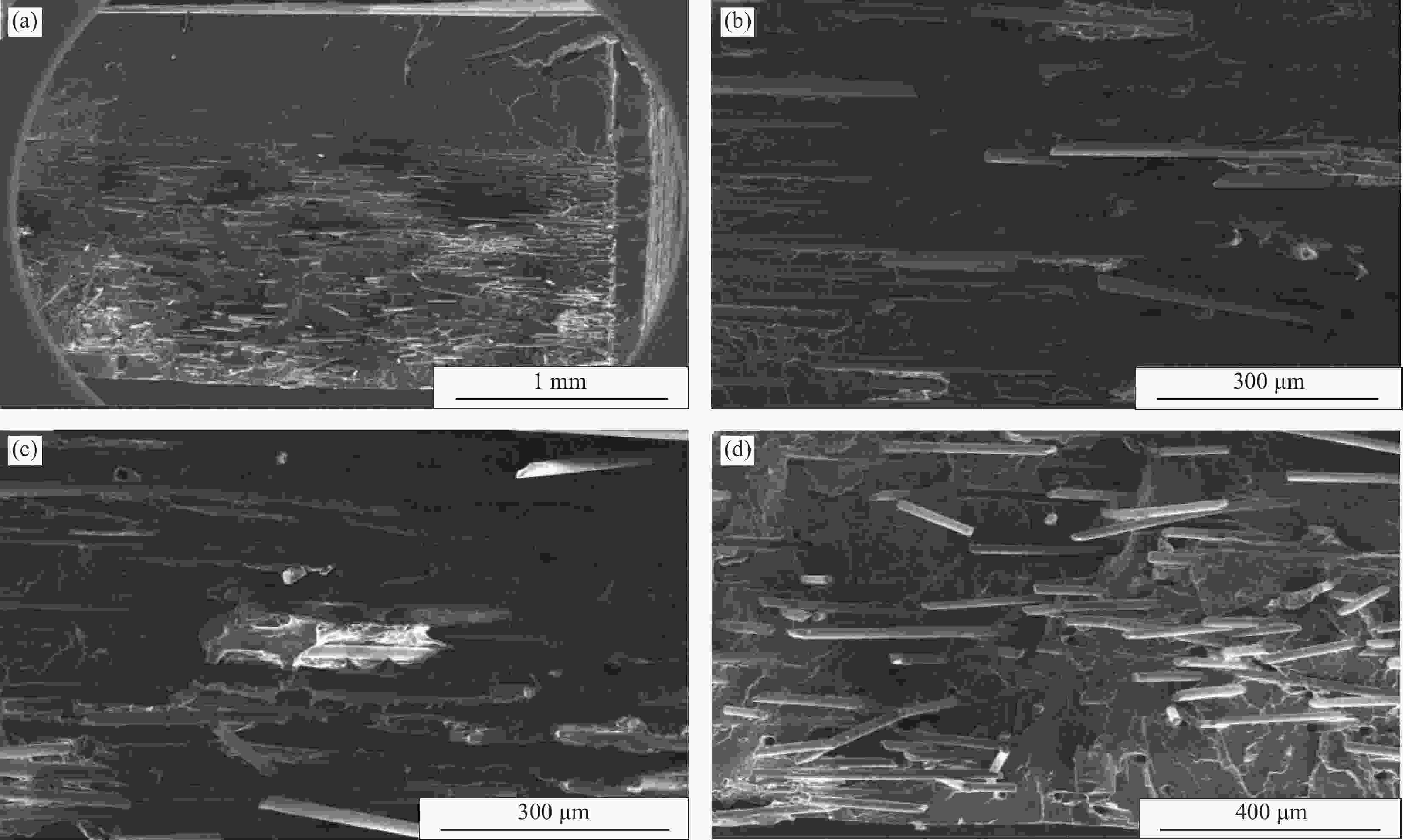
摘要: 水辅助共注塑成型技术(Water-assisted co-injection molding,WACIM)是一种结合共注塑技术和水辅助注塑技术的新型注塑工艺。特定的工艺过程使得玻纤增强复合材料应用于WACIM工艺时具有特定的玻纤取向规律和增强特点。以纯聚丙烯(PP)为内层材料、不同质量分数的短玻纤增强聚丙烯(GF/PP)为外层材料制备系列WACIM管件,比较分析了实验条件下玻纤质量分数对管件壁厚、玻纤取向分布及拉伸强度的影响规律与机制。研究发现在玻纤质量分数不超过30wt%时,管件壁厚差异不明显,当玻纤质量增加到40wt%时,管件内外壁厚均增大;WACIM管件外层按玻纤取向的分布特点均可分为近界面层、中间层和近模壁层,玻纤沿流动方向的取向程度由内向外依次降低;管件的拉伸性能随着玻纤质量分数的增加呈先增后减的趋势,玻纤质量分数为30wt%时管件拉伸强度最好。与玻纤增强聚丙烯的水辅助注塑成型(WAIM)管件比较,发现两种工艺中玻纤质量分数对壁厚、玻纤取向分布和拉伸强度的影响有差异,影响机制有所区别。Abstract: Water-assisted co-injection molding (WACIM) technology is an novel injection molding process that combines co-injection molding technology and water-assisted injection molding technology. Its special process makes the glass fiber reinforced composite used in the process have special characteristics of fiber orientation and enhancement. WACIM pipes with polypropylene (PP) as inner material and short glass fiber reinforced polypropylene (GF/PP) as outer material were prepared to investigate the effects of glass fiber mass fraction on the thicknesses of pipe inner and outer layers, glass fiber orientation and tensile strength. It is found that when the mass fraction of glass fiber is less than 30wt%, the variations of pipe inner and outer layer thicknesses are not obvious. When the mass fraction of glass fiber increases to 40wt%, both the inner and outer layer thicknesses of pipe increase. According to the distribution characteristics of glass fiber orientation, the outer layer of WACIM pipes can be divided into three layers: Near interface layer, intermediate layer and near mold wall layer. The orientation degree of glass fiber along the flow direction decreases from inside to outside. The tensile properties of pipes increased first and then decreased with the increase of glass fiber mass fraction. The highest tensile strength of pipes can be obtained when the glass fiber mass fraction is 30wt%. It is found by comparison that the influences of glass fiber mass fraction on thickness, glass fiber orientation and tensile strength of WACIM and water-assisted injection molding (WAIM) pipes are different, and the influence mechanism are different.
-
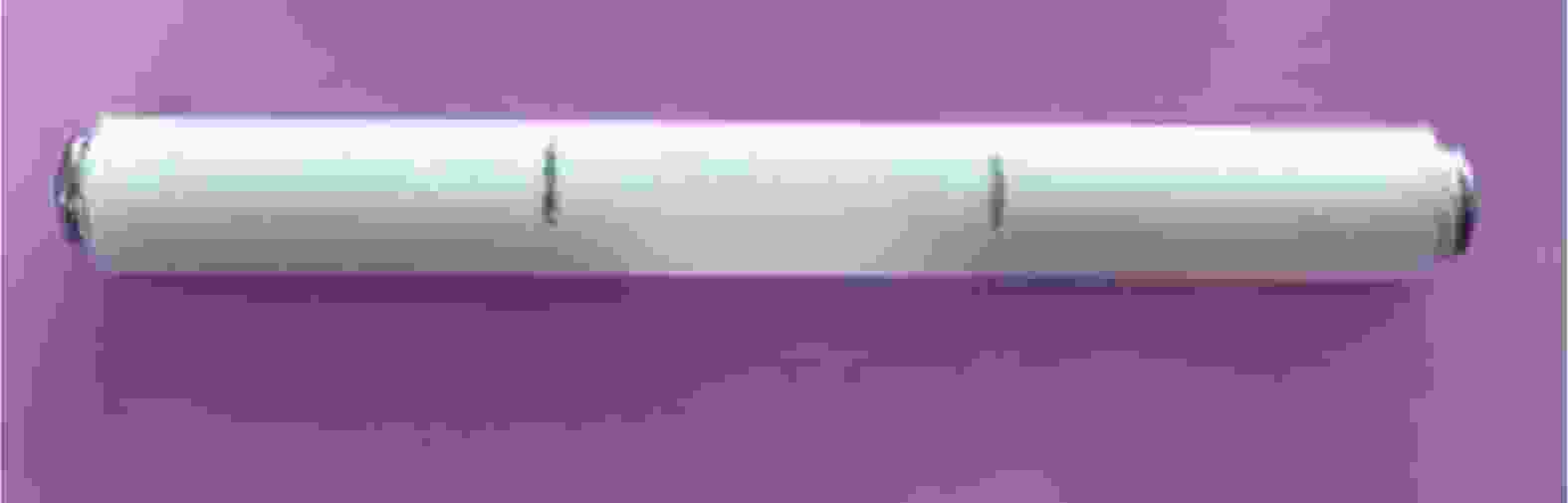
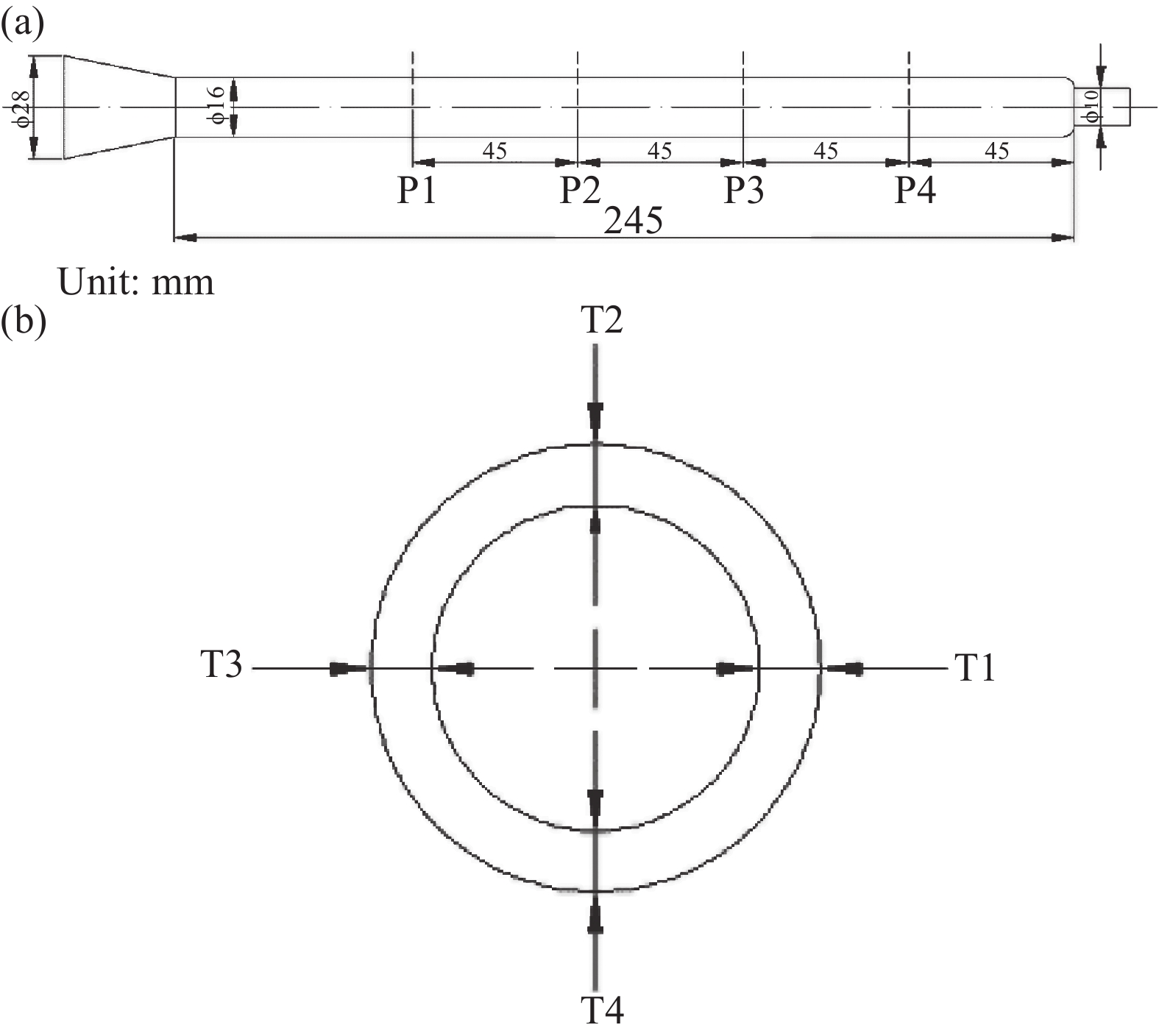
图 1 玻纤增强聚丙烯(GF/PP)水辅助共注塑(WACIM)管件 (a) 及其残余壁厚测量 (b)
Figure 1. Glass fiber reinforced polypropylene (GF/PP) water-assisted co-injection molding (WACIM) pipe (a) and measurement of its residual wall thickness (b)
P1-P4—Section positions of residual wall thickness measurement; T1-T4—Measurement positions of residual wall thickness
表 1 GF/PP WACIM管件制备工艺参数
Table 1. Processing parameters used to produce the test GF/PP WACIM samples
Process parameters Value Outer melt temperature/℃ 250 Inner melt temperature/℃ 210 Inner melt injection pressure/MPa 7 Inner melt injection delay time/s 3 Water injection delay time/s 4 Water injection pressure/MPa 6 Mold temperature/℃ 25 Holding time/s 4 -
[1] 黄丽. 聚合物复合材料[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2012.HUANG Li. Polymer composites[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2012(in Chinese). [2] 陈生超, 杨永良, 陈金涛, 等. 纤维含量对长玻纤增强聚丙烯注塑制品性能影响[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2013, 41(12):44-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2013.12.010CHEN Shengchao, YANG Yongliang, CHEN Jintao, et al. Effect of fiber content on properties of long glass fiber reinforced PP injection molded parts[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2013,41(12):44-48(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2013.12.010 [3] 王利霞, 李燕, 庄卫国. 注塑工艺和玻纤含量对玻纤增强PP注塑制品收缩的影响[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2009, 25(9): 135-137, 141.WANG Lixia, LI Yan, ZHUANG Weiguo. Influence of processing parameters and fiber content on shrinkage of fiber-reinforced PP injection-molded part[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2009, 25(9): 135-137, 141(in Chinese). [4] 匡唐清, 冯强, 徐盼, 等. 玻纤含量对短玻纤增强聚丙烯复合材料水辅注塑制品壁厚与微观形态的影响[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2020, 36(2): 105-111, 119.KUANG Tangqing, FENG Qiang, XU Pan, et al. Influence of glass fiber contents on the residual wall thickness and microscopic morphology of water-assisted injection molding pipes of short-glass-fiber reinforced polypropylene composites[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2020, 36(2): 105-111, 119(in Chinese). [5] 钟罗浩, 匡唐清, 赖家美, 等. 成型工艺对短玻璃纤维增强聚丙烯注塑管件的壁厚分布及玻璃纤维取向的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2021, 35(5):11-16.ZHONG Luohao, KUANG Tangqing, LAI Jiamei, et al. Effect of molding process on wall residual thickness distribution and glass-fiber orientation of short-glass-fiber reinforced polypropylene molded pipes[J]. China Plastics,2021,35(5):11-16(in Chinese). [6] 张宇, 段召华, 陈弦, 等. 注塑工艺参数对长玻纤增强PA66复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 塑料科技, 2011, 39(2):65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3360.2011.02.009ZHANG Yu, DUAN Zhaohua, CHEN Xian, et al. Effect of injection molding parameters on mechanical properties of long glass fiber reinforced PA66 composite[J]. Plastics Science and Technology,2011,39(2):65-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3360.2011.02.009 [7] TSENG H C, CHANG R Y, HSU C H. Numerical predictions of fiber orientation and mechanical properties for injection-molded long-glass-fiber thermoplastic composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,150:181-186. [8] ZHONG Y, LIU P, PEI Q, et al. Elastic properties of injection molded short glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites[J]. Composite Structures,2020,254:112850. [9] SADABADI H, GHASEMI M. Effects of some injection molding process parameters on fiber orientation tensor of short glass fiber polystyrene composites (SGF/PS)[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2007,26(17):1729-1741. doi: 10.1177/0731684407081352 [10] FOSS P H, TSENG H C, SNAWERDT J, et al. Prediction of fiber orientation distribution in injection molded parts using Moldex3D simulation[J]. Polymer Composites,2014,35(4):671-680. doi: 10.1002/pc.22710 [11] HOU X Q, CHEN X Y, LIU B C, et al. Fracture and orientation of long-glass-fiber-reinforced polypropylene during injection molding[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science,2019,60(1):13-21. [12] JAWALI N D. Physicomechanical properties, machinability, and morphological behavior of short glass fiber-reinforced Nylon 6 composites[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2006,25(13):1409-1418. [13] 黎三雄, 杨明华, 刘廷华. 水辅助注塑成型技术及其进展[J]. 塑料工业, 2003(2): 5-8, 12.LI Sanxiong, YANG Minghua, LIU Tinghua. Water-assisted injection molding technology[J]. China Plastics Industry, 2003(2): 5-8, 12(in Chinese). [14] LANG S, PARKINSON M J. Two-component water assisted injection moulding[J]. Plastics, Rubber and Composites,2005,34(5):232-235. [15] 黄业勤. 多物料共同注塑工艺[J]. 橡塑技术与装备, 2005(7):30-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-797X.2005.07.007HUANG Yeqin. Multi material co-injection molding process[J]. China Rubber/Plastics Technology and Equipment,2005(7):30-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-797X.2005.07.007 [16] MCROSKEY J J. Introduction to co-injection molding[C]//Technical Paper Society of Manufacturing Engineers. Novi, Michigan, 1999: 1-5. [17] LIU S J, CHEN Y S. The manufacturing of thermoplastic composite parts by water-assisted injection-molding technology[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2004, 35(2): 171-180. [18] KNIGHTS, TECHNOLOGY M J P. Water injection molding makes hollow parts faster, lighter[J]. Plastics Technology, 2002, 48(4): 42-47. [19] 徐盼. 聚丙烯/聚酰胺6共混物的水辅助共注塑工艺-形态-性能研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2020.XU Pan. Morphology and mechanical properties of water assisted co-injection polypropylene/polyamide 6 blend[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University, 2020(in Chinese). [20] 赖德炜. 玻纤增强聚丙烯水辅注塑制品的多相演变机理及质量控制[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2018.LAI Dewei. Evolution mechanism of multi-phase morphologies during water-assisted injection molding process of glass fiber reinforced polypropylene composite and the parts quality control[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University, 2018(in Chinese). [21] 钟明强, 濮阳楠, 益小苏, 等. 短玻纤增强聚丙烯注射压力对微观结构和力学性能影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2000, 17(4):6-10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.04.002ZHONG Mingqiang, PU Yangnan, YI Xiaosu, et al. Effects of injection pressure on the microstructures and mechanical properties of short glass fiber injection-molded reinforced polypropylene[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2000,17(4):6-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.04.002 [22] 王选伦, 张凌瑞, 尹皓, 等. 短玻纤和连续玻纤增强聚丙烯复合材料的性能比较研究[J]. 山东化工, 2016, 45(1):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2016.01.003WANG Xuanlun, ZHANG Lingrui, YIN Hao, et al. Comparative study on properties of polypropylene composites reinforced by short glass fiber and continuous glass fiber[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2016,45(1):6-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2016.01.003 [23] 庄卫国. 玻纤含量对玻纤增强聚丙烯拉伸性能的影响[J]. 精密成形工程, 2010, 2(2):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2010.02.005ZHUANG Weiguo. Study on influence of glass fiber content on glass fiber reinforced polypropylene part quality[J]. Precision Forming Engineering,2010,2(2):20-22(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2010.02.005 -






 下载:
下载: