Parametric effects of low-velocity impact response and damage mode of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels
-
摘要: 以铝蜂窝夹层板为对象,通过低速落锤试验及包含面板、胶层及蜂窝的细节仿真模型,探究了蜂窝胞元直径、蜂窝壁厚、面板厚度及冲头半径参数影响下低速冲击响应曲线及损伤模式的变化情况,确定在试验工况下的3种损伤模式:芯层屈曲、芯层剪切及夹层板穿透,其中芯层剪切模式具有更好的吸能分布。结果表明:蜂窝胞元直径与蜂窝壁厚对冲击响应与损伤模式具有类似的影响,面板厚度增加可以较大程度地提升抗冲击性能,冲头半径的大小会显著影响损伤模式。在此基础上建立与上述参数相关的损伤模式极限载荷公式,绘制相应的损伤模式图,为铝蜂窝夹层板的抗冲击设计提供参考。Abstract: Taking the aluminum honeycomb sandwich panel as the object, through the low-speed drop weight test and the detailed simulation model including the panel, the adhesive layer and the honeycomb, the changes of low-speed impact response curve and damage mode under the influence of the honeycomb cell diameter, honeycomb wall thickness, panel thickness and punch radius parameters were studied. Three damage modes under the test conditions were determined: Core buckling, core shear and sandwich panel penetration, among which the core shear mode has better energy absorption distribution. The results show that the honeycomb cell diameter and the honeycomb wall thickness have similar effects on the impact response and damage mode. The increase of the panel thickness can greatly improve the impact resistance, and the size of the punch radius will significantly affect the damage mode. On this basis, the damage mode limit load formula related to the above parameters was established, and the corresponding damage mode diagram was drawn to provide a reference for the impact resistance design of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels.
-
图 3 混合模式的牵引分离律
Figure 3. Mixed-mode traction-separation law
δI, δ3—Separate displacement in normal direction (mode I); δ1, δ2—Separate displacement in tangential plane; δII—Separate displacement in tangential direction (mode II); δ0—Mixed-mode damage initiation displacement; $\delta_{\mathrm{I}}^0, \delta_{\mathrm{II}}^0 $—Damage initiation separations of two modes; β—“Mode mixity”; $\delta_{\mathrm{I}}^{\mathrm{F}}, \delta_{\mathrm{II}}^{\mathrm{F}}, \delta^{\mathrm{F}} $—Final damage displacements of two modes and mixed mode; δm—Total mixed-mode separate displacement; $σ_I^max,σ_II^max $—Maximum traction stress of the two modes; EN, ET—Traction stiffness of the two modes; $G_{\mathrm{I}}^{\mathrm{C}}, G_{\mathrm{II}}^{\mathrm{C}} $—Energy release rates of the two modes
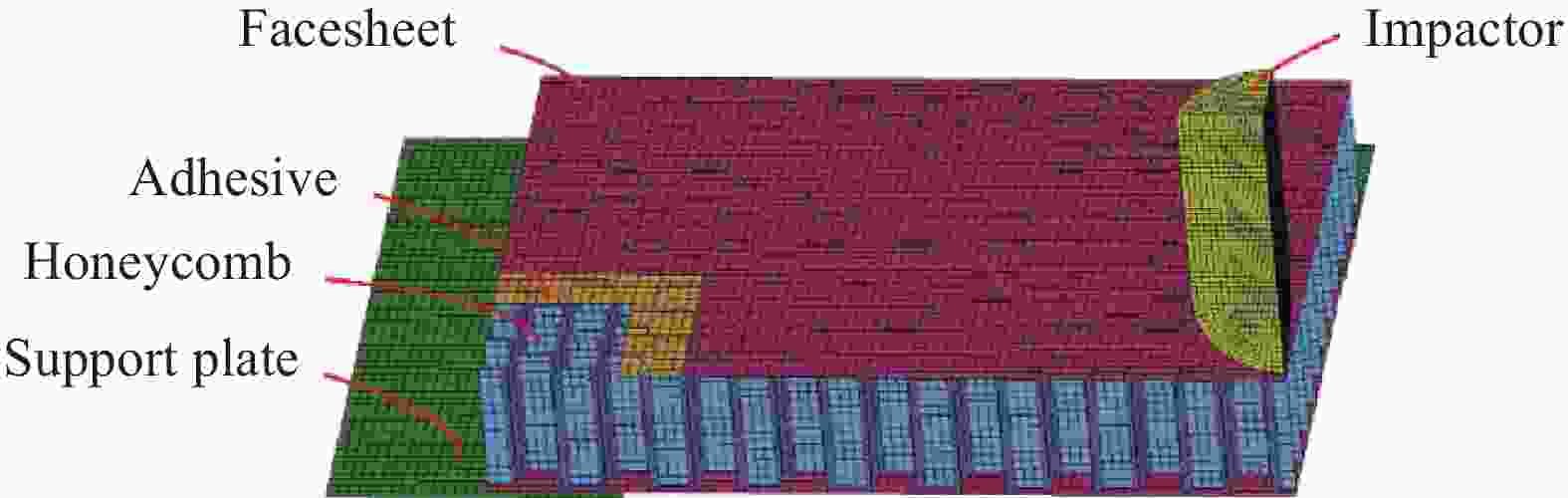
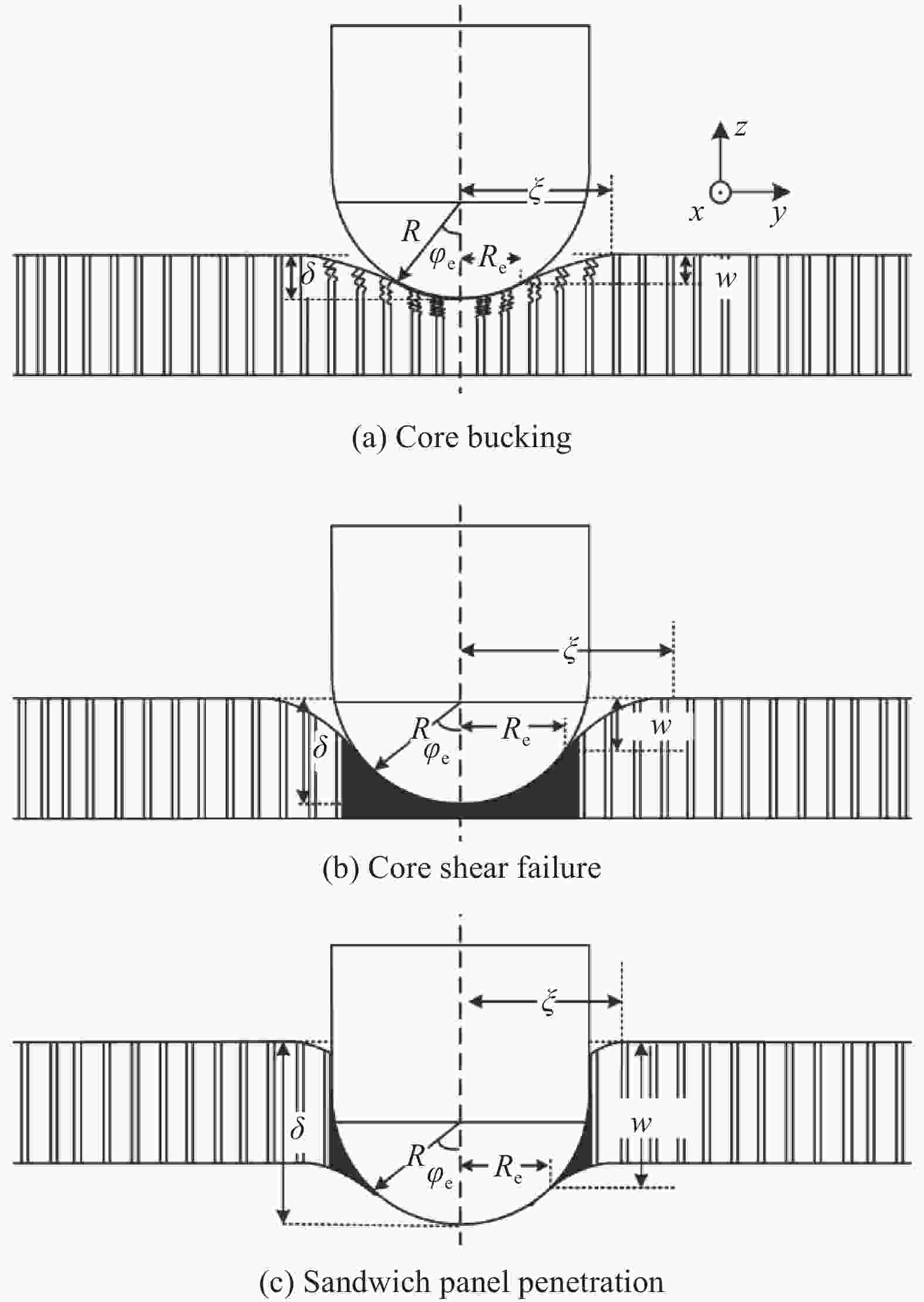
图 5 铝蜂窝夹层板冲击损伤模型
Figure 5. Impact damage model of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels
R—Punch radius; $ \xi $—Indentation deformation radius of the aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels by impact; $ \delta $—Damage depth caused by the punch; $ {R}_{\mathrm{e}} $—Contact radius between the punch and the top or back facesheets; $ {\varphi }_{\mathrm{e}} $—Angle between the contact radius position and the center line of the punch; $ w $—Lateral displacement of the aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels at the contact radius
表 1 冲击试验工况
Table 1. Experimental conditions
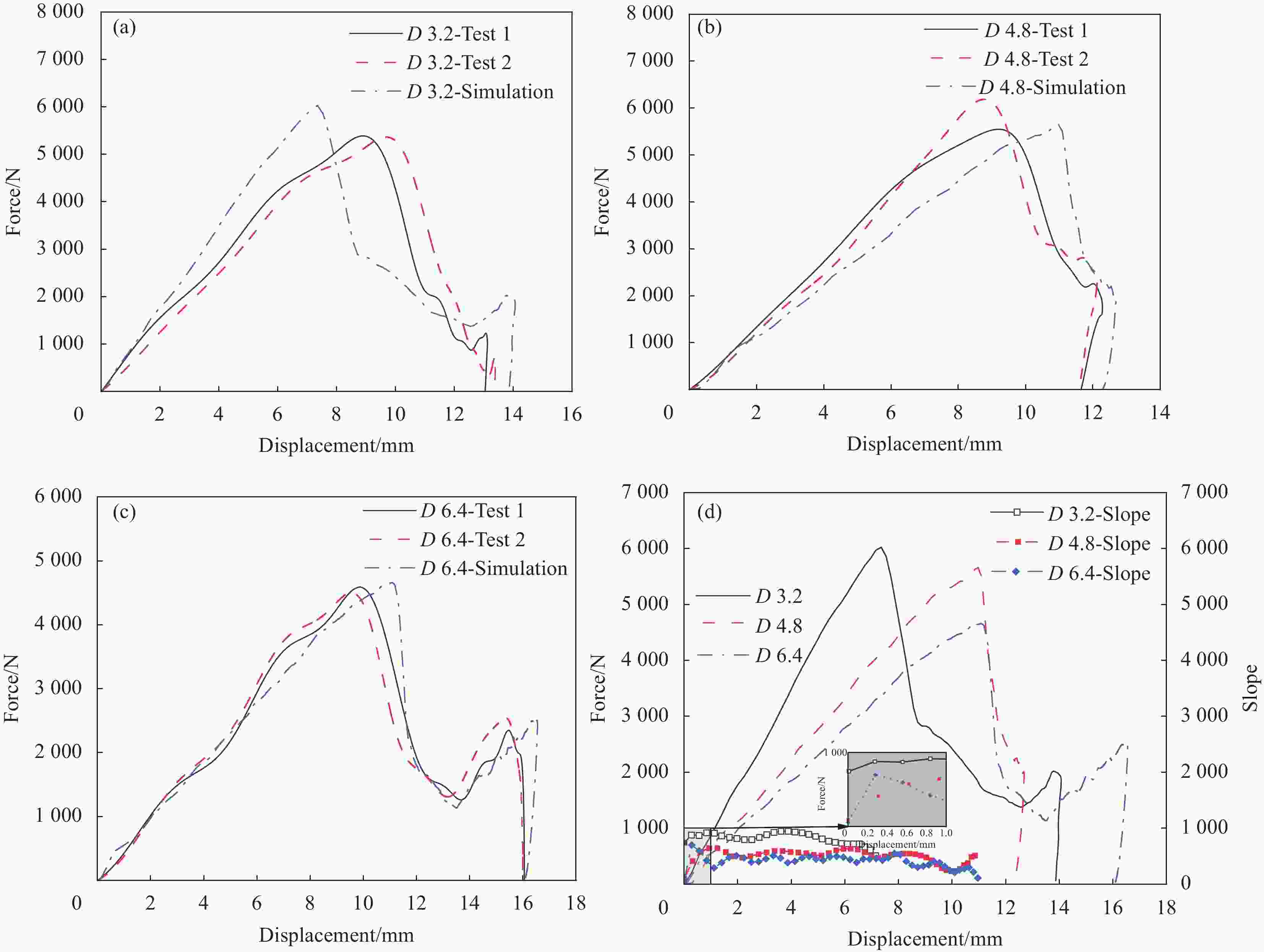
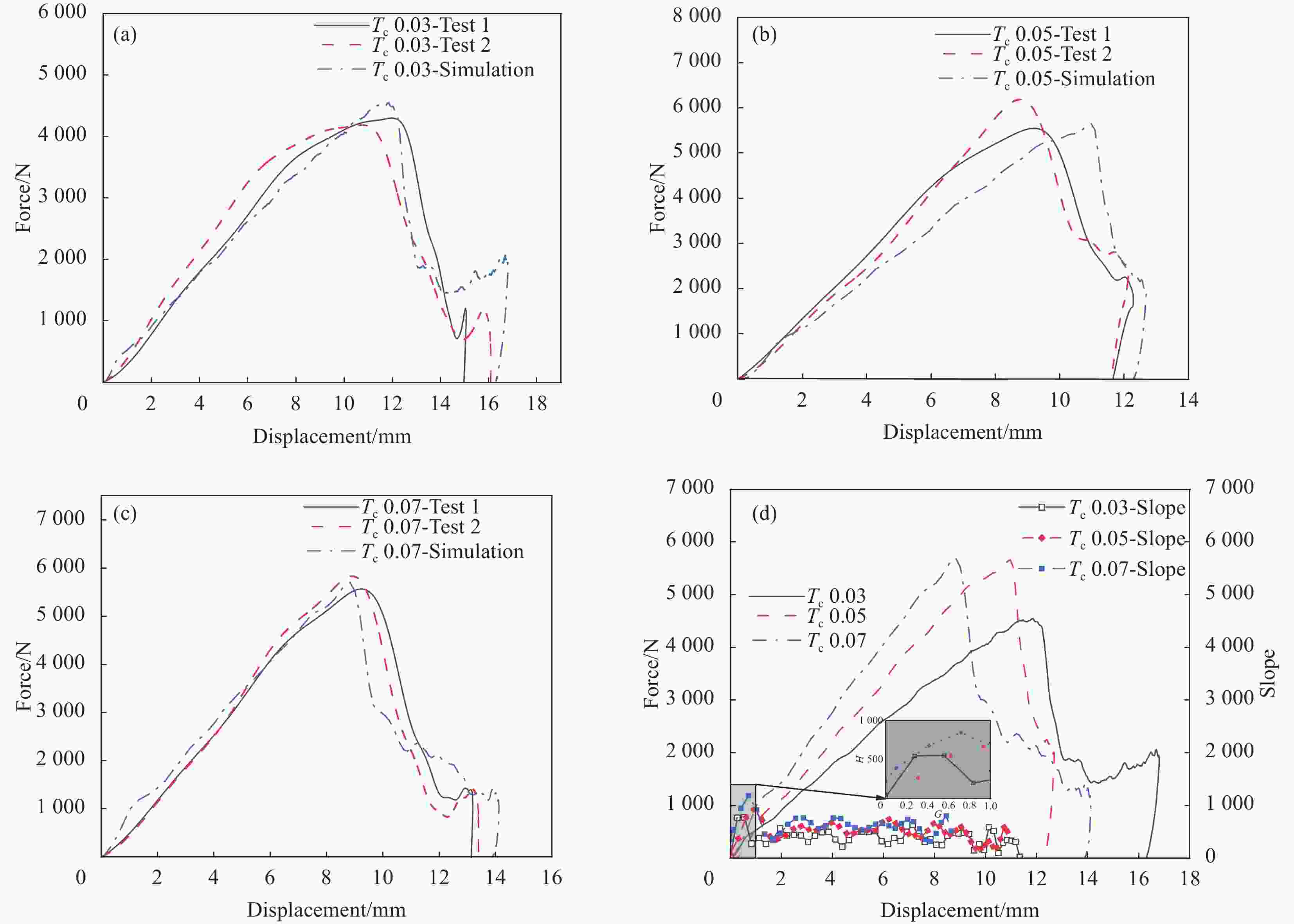
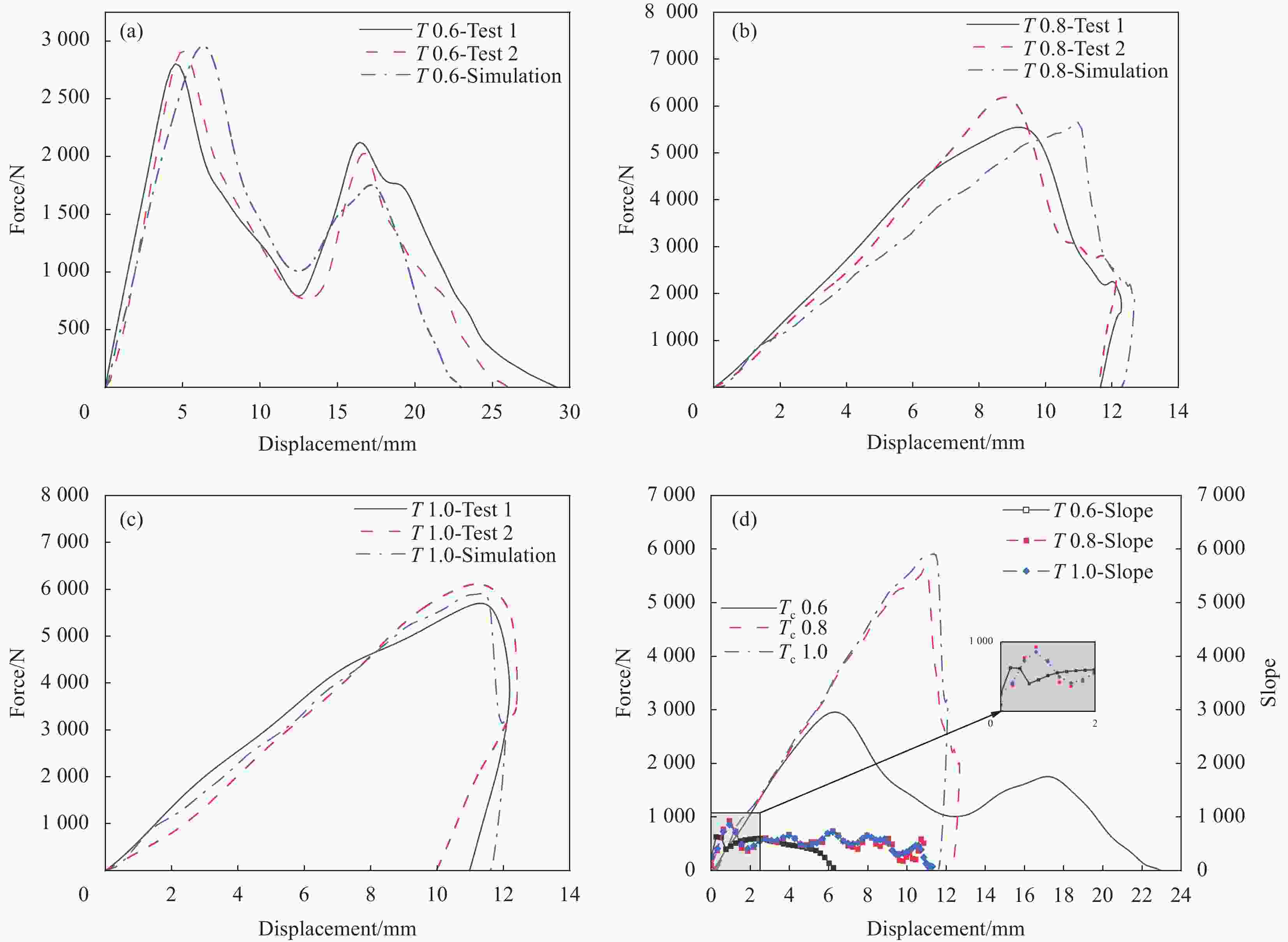
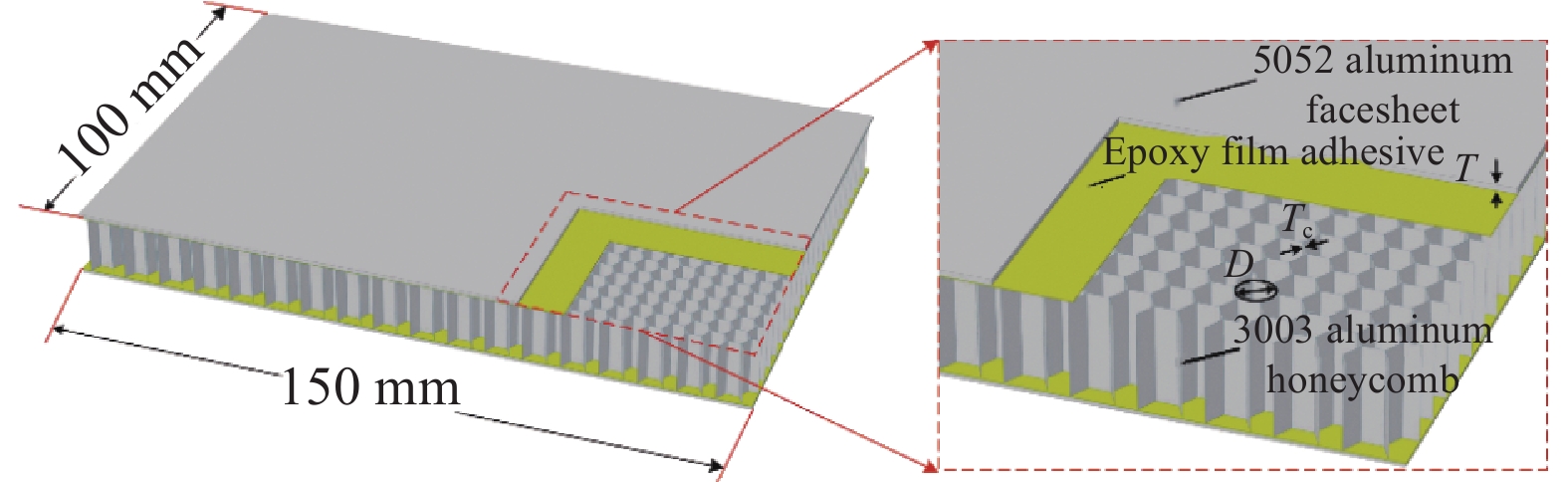
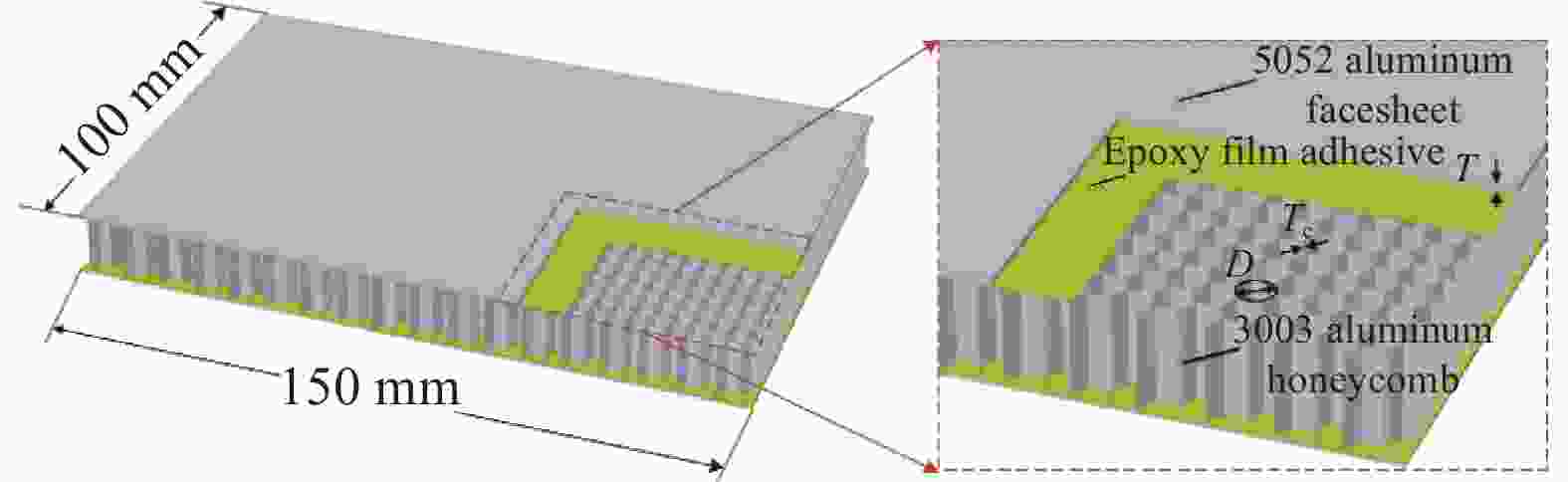
Variable Test label Honeycomb cell diameter D/mm Honeycomb wall thickness $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $/mm Facesheet thickness $ T $/mm Punch radius
R/mmHoneycomb cell diameter D 3.2 3.2 0.05 0.8 8 D 4.8 4.8 0.05 0.8 8 D 6.4 6.4 0.05 0.8 8 Honeycomb wall thickness $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 0.03 4.8 0.03 0.8 8 $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 0.05 4.8 0.05 0.8 8 $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 0.07 4.8 0.07 0.8 8 Facesheet thickness T 0.6 4.8 0.05 0.6 8 T 0.8 4.8 0.05 0.8 8 T 1.0 4.8 0.05 1.0 8 Punch radius R 6 4.8 0.05 0.8 6 R 8 4.8 0.05 0.8 8 R 10 4.8 0.05 0.8 10 表 2 铝合金材料参数
Table 2. Aluminum alloy parameters
Aluminum alloy grade Density/(kg·m−3) Young's modulus/GPa Poisson's ratio A B C n 5052 2685 70 0.33 138 231 0.015 0.63 3003 2740 69 0.33 214 143 0.015 0.36 Note: A, B, C, n—Material dependent constants of Johnson-Cook model. 表 3 环氧胶层性能参数
Table 3. Epoxy adhesive layer performance parameters
$ {E}_{\mathrm{N}} $/mm3 $ {E}_{\mathrm{T}} $/mm3 $ {G}_{\mathrm{I}}^{\mathrm{C}} $/mm $ {G}_{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{I}}^{\mathrm{C}} $/mm $ {\sigma }_{\mathrm{I}}^{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $/MPa $ {\sigma }_{\mathrm{I}\mathrm{I}}^{\mathrm{m}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{x}} $/MPa 1×105 1×105 0.26 1.002 30 60 表 4 铝蜂窝夹层板损伤模式汇总
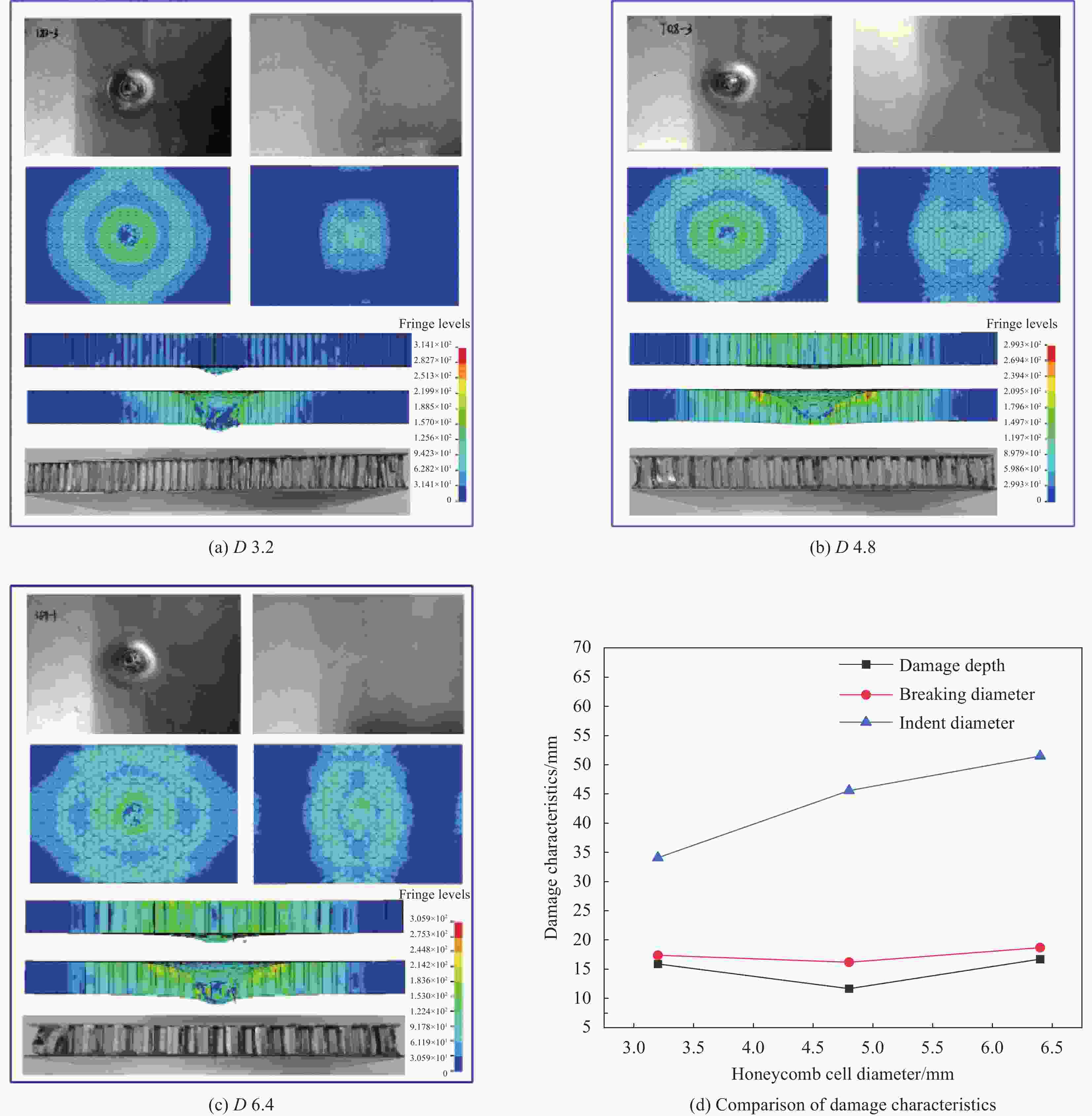
Table 4. Summary of damage modes of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels
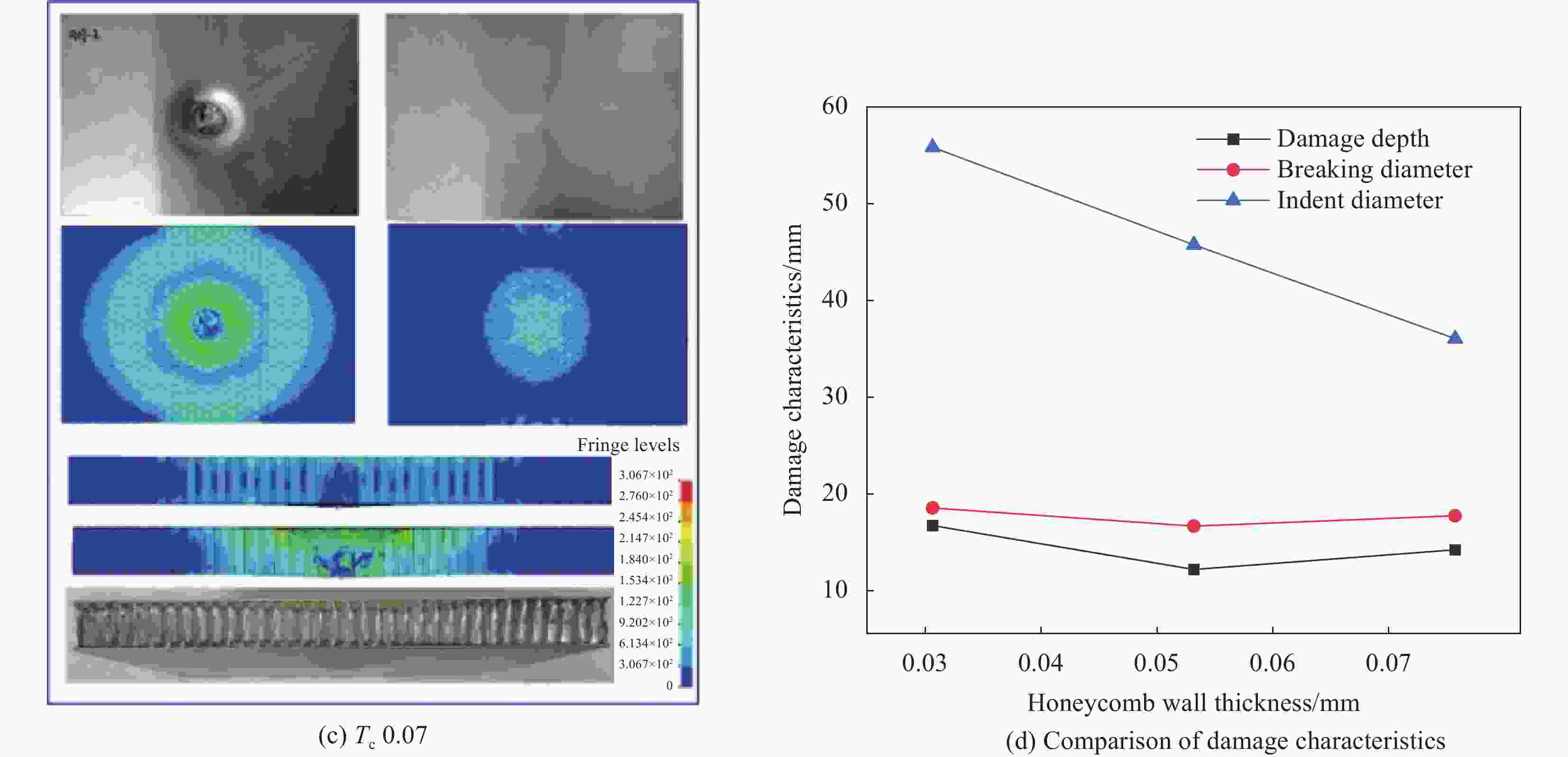
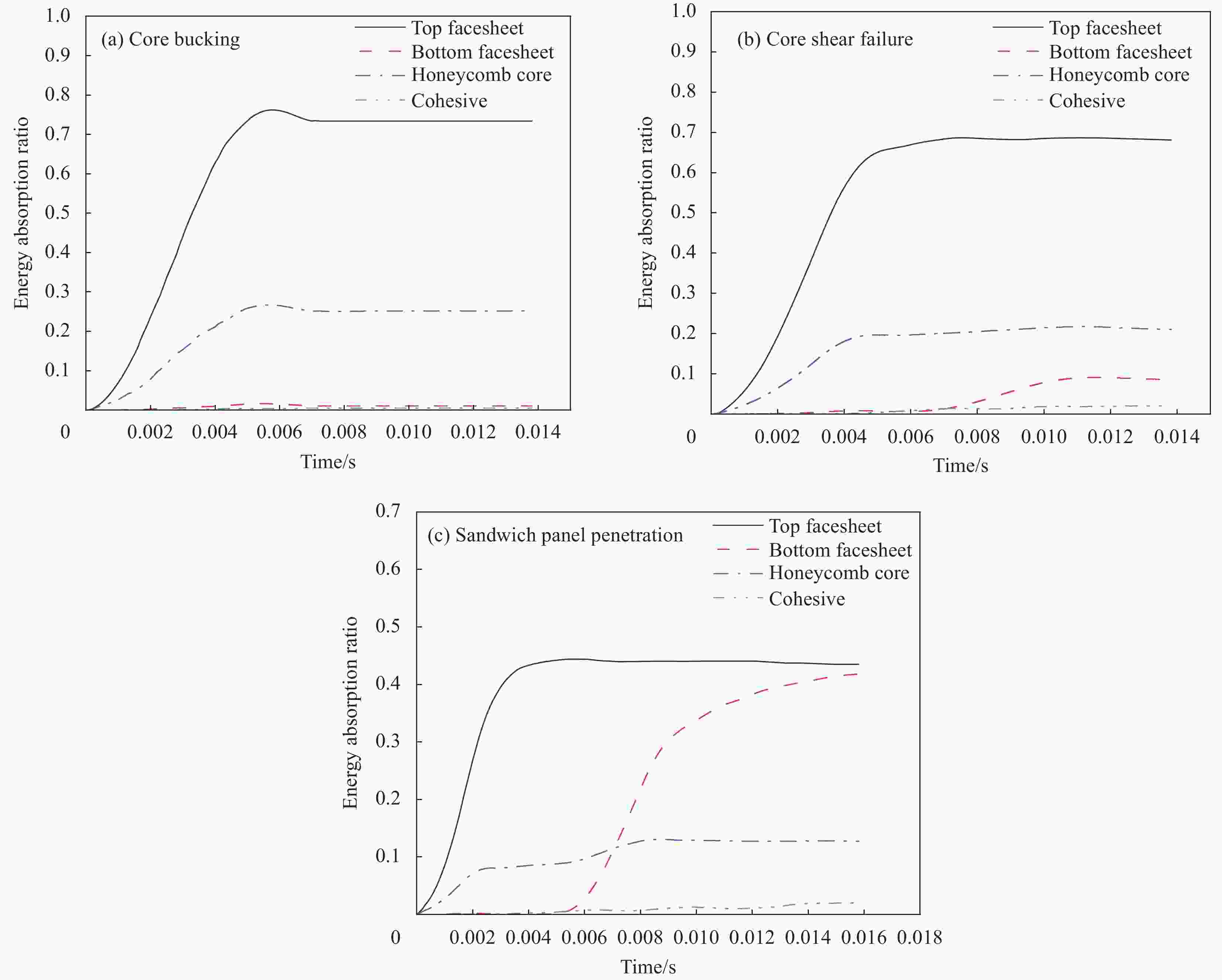
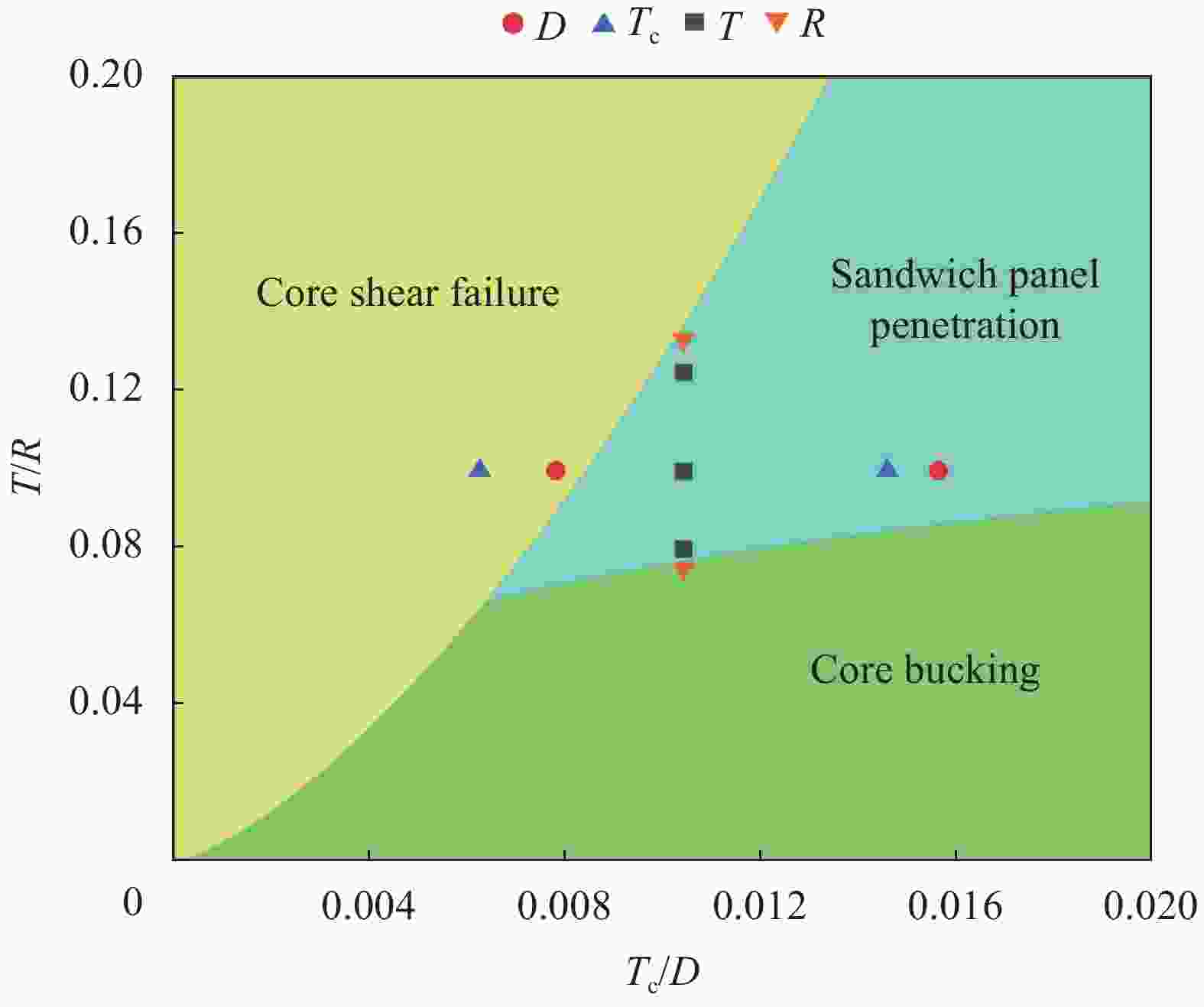
Specimen Core bucking Core shear failure Sandwich panel penetration D 3.2 — — √ D 6.4 — √ — $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 0.03 — √ — $ {T}_{\mathrm{c}} $ 0.07 — — √ T 0.6 — — √ T 0.8 — — √ T 1.0 — √ — R 6 — — √ R 10 √ — — 表 5 铝蜂窝夹层板的损伤模式和载荷预测
Table 5. Damage mode and load prediction of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels
Damage mode Threshold load Qualitative damage conditions Core bucking $ {P}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}}^{\mathrm{b}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{k}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}=3\sqrt{3}{\sigma }_{\mathrm{c}}\left(1+\sqrt{3}\dfrac{D}{R}\right){\left(\dfrac{2{D}_{\mathrm{f}}}{{E}_{3\mathrm{c}}}\right)}^{\frac{2}{3}} $ Honeycomb core strength ↑
Facesheet strength ↑
Punch radius ↑Core shear failure $ {P}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{e}}^{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{h}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{r}}=72\dfrac{{A}_{1}^{2}{\gamma }_{\mathrm{f}}^{6}}{{\sigma }_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{r}}}+{\text{π}}{\sigma }_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{r}}{R}_{\mathrm{e}}^{2} $ Honeycomb core strength ↓
Facesheet strength ↑
Punch radius ↑Sandwich panel penetration $ {P}_{\mathrm{f}}^{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{r}\mathrm{a}\mathrm{c}\mathrm{k}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}\mathrm{g}}=2{\text{π}}{R}_{\mathrm{e}}{A}_{1}\sqrt{2{\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{r}}}+{\text{π}}{q}_{\mathrm{c}}{\xi }^{2} $ Honeycomb core strength ↑
Facesheet strength ↓
Punch radius ↓Notes: $P_{\text {core }}^{\text {bucking }} $—Peak load of the buckling mode of the Core bucking; σc—Equivalent compressive strength in the out-of-plane direction of the honeycomb core; D—Honeycomb cell diameter; R—Punch radius; Df—Facesheet bending stiffness; E3c—Equivalent Young's modulus of the honeycomb core; $\mathrm{P}_{\text {core }}^{\text {shear }} $—Peak load of Core shear failure model; A1—Facesheet membrane stiffness; γc—Transverse shear strain of honeycomb core; σcr—Honeycomb compressive strength considering punch diameter; Re—Contact radius between the punch and the sandwich panel; $P_{\mathrm{f}}^{\text {cracking }} $—Peak load of the Sandwich panel penetration model; εr—Facesheet membrane strain; ξ—Indentation deformation radius of the aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels by impact. -
[1] SUN M Q, WOWK D, MECHEFSKE C, et al. Surface and honeycomb core damage in adhesively bonded aluminum sandwich panels subjected to low-velocity impact[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2022,230:109506. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109506 [2] ZHANG J X, ZHU Y Q, LI K K, et al. Dynamic response of sandwich plates with GLARE face-sheets and honeycomb core under metal foam projectile impact: Experimental and numerical investigations[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2022,164:104201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2022.104201 [3] IVAÑEZ I, MOURE M M, GARCIA S K, et al. The oblique impact response of composite sandwich plates[J]. Composite Structures,2015,133:1127-1136. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.08.035 [4] WANG S Y, XU Y X, ZHANG X G, et al. Design and fabrication of aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures by atmosphere protect brazing: Microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior[J]. Materialia,2022,22:101423. doi: 10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101423 [5] WANG H R, LONG S C, YAO X H, et al. Analytical study on the low-velocity impact penetration of the fully-clamped foam-core composite sandwich panels[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2021,224:109214. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109214 [6] ZHANG D H, JIANG D, FEI Q G, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on indentation and energy absorption of a honeycomb sandwich panel under low-velocity impact[J]. Finite Elements in Analysis and Design,2016,117-118:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.finel.2016.04.003 [7] SAFRI S N A, SULTAN M T H, YIDRIS N, et al. Low velocity and high velocity impact test on composite materials–A review[J]. The International Journal of Engineering and Science,2014,3(9):50-60. [8] WU Y H, LIU Q, FU J, et al. Dynamic crash responses of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP panels[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,121:122-133. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.03.030 [9] HE W T, YAO L, MENG X J, et al. Effect of structural parameters on low-velocity impact behavior of aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP face sheets[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2019,137:411-432. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2019.01.022 [10] 齐佳旗, 段玥晨, 铁瑛, 等. 结构参数对CFRP蒙皮-铝蜂窝夹层板低速冲击性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6):1352-1363.QI Jiaqi, DUAN Yuechen, TIE Ying, et al. Influence of structural parameters on low-velocity impact performance of CFRP skin-aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(6):1352-1363(in Chinese). [11] SUN G Y, HUO X T, WANG H X, et al. On the structural parameters of honeycomb-core sandwich panels against low-velocity impact[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2021,2016:108881. [12] ZHU S Q, CHAI G B. Damage and failure mode maps of composite sandwich panel subjected to quasi-static indentation and low velocity impact[J]. Composite Structures,2013,101:204-214. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.02.010 [13] EBRAHIMI H, GHOSH R, MAHDI E, et al. Honeycomb sandwich panels subjected to combined shock and projectile impact[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2016,95:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2016.04.009 [14] SABAH S H A, KUEH A B H, BUNNORI N M. Failure mode maps of bio-inspired sandwich beams under repeated low-velocity impact[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,182:107785. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107785 [15] ZHANG Y W, YAN L L, ZHANG C, et al. Low-velocity impact response of tube-reinforced honeycomb sandwich structure[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2021,158:107188. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107188 [16] LIU J F, CHEN W S, HAO H, et al. Numerical study of low-speed impact response of sandwich panel with tube filled honeycomb core[J]. Composite Structures,2019,220:736-748. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.04.023 [17] PALOMBA G, EPASTO G, CRUPI V, et al. Single and double-layer honeycomb sandwich panels under impact loading[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2018,121:77-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.07.013 [18] WANG Z G, WANG X X, LIU K, et al. Crash worthiness index of honeycomb sandwich structures under low-speed oblique impact[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2021,208:106683. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2021.106683 [19] ASTM. Standard test method for measuring the damage resistance of a fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event: ASTM D7136/D7136 M-2015[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2015. [20] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[C]//In: Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Ballistics. Hague: Scientific Research Publishing, 1983: 541-547. [21] SUN G Y, CHEN D D, WANG H X, et al. High-velocity impact behaviour of aluminium honeycomb sandwich panels with different structural configurations[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2018,122:119-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2018.08.007 [22] MUFLAHI S A, MOHAMED G F A, HALLETT S R. Investigation of delamination modeling capabilities for thin composite structures in LS-DYNA[C]//13th International LS-DYNA Users Conference. Dearborn: Bristol University Press, 2014: 1-14. [23] RAJU K S, SMITH B L, TOMBLIN J S, et al. Impact damage resistance and tolerance of honeycomb core sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2008,42(4):385-412. doi: 10.1177/0021998307088596 [24] RAJU K S, TOMBLIN J S. Damage characteristics in sandwich panels subjected to static indentation using spherical indentors[C]//19th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics. Anaheim: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2001: 103-111. [25] BERNARD M L, LAGACE P A. Impact resistance of composite sandwich pates[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,1989,8(5):432-445. doi: 10.1177/073168448900800502 [26] SCHUBEL P M, LUO J J, DANIEL I M. Impact and post impact behavior of composite sandwich panels[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2007,38(3):1051-1057. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2006.06.022 [27] KIM J K, YU T X. Indentation, penetration and perforation of composite laminate and sandwich panels under quasi-static and projectile loading[J]. Key Engineering Materials,1998,141(143):501-552. [28] PETRAS A, SUTCLIFFE M P F. Failure mode maps for honeycomb sandwich panels[J]. Composite Structures,1999,44:237-252. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(98)00123-8 [29] ZHU F, LU G, RUAN D, et al. Plastic deformation, failure and energy absorption of sandwich structures with metallic cellular cores[J]. International Journal of Protective Structures,2010,1(4):507-541. doi: 10.1260/2041-4196.1.4.507 [30] CHAI G B, ZHU S. A review of low-velocity impact on sandwich structures[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials: Design and Applications,2011,225(4):207-230. doi: 10.1177/1464420711409985 [31] LEE S M, TSOTSIS T K. Indentation failure behavior of honeycomb sandwich panels[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2000,60(8):1147-1159. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(00)00023-3 [32] OLSSON R. Engineering method for prediction of impact response and damage in sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2002,4:3-19. [33] CHATURVEDI R, TRIKHA M, SIMHA K R Y. Impact penetration through spacecraft honeycomb panels analytical, numerical and experimental study[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2020,21(2):1050-1058. [34] WIERZBICKI T, ALVAREZ A L, FATT M H. Impact energy absorption of sandwich plates with crushable core[C]//In: Proceedings of the ASME/AMD Symposium, Impact Waves, and Fracture. Los Angeles: U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information, 1995, 205: 391-411. [35] ZHOU G, HILL M, LOUGHLAN J. Damage characteristics of composite honeycomb sandwich panels in bending under quasi-static loading[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2006,8(1):55-90. [36] ZHOU G, HILL M. Investigation of parameters governing the damage and energy absorption characteristics of honeycomb sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2007,9(4):309-342. [37] ZHOU G, HILL M. Impact damage and energy-absorbing characteristics and residual in-plane compressive strength of honeycomb sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2009,11(4):329-356. [38] FATT M S H, PARK K S. Dynamic models for low-velocity impact damage of composite sandwich panels–Part B: Damage initiation[J]. Composite Structures,2001,52(3-4):353-364. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(01)00045-9 [39] LEE Y W, WOERTZ J C, WIERZBICKI T. Fracture prediction of thin plates under hemi-spherical punch with calibration and experimental verification[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2004,46(5):751-781. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2004.05.004 -





 下载:
下载: