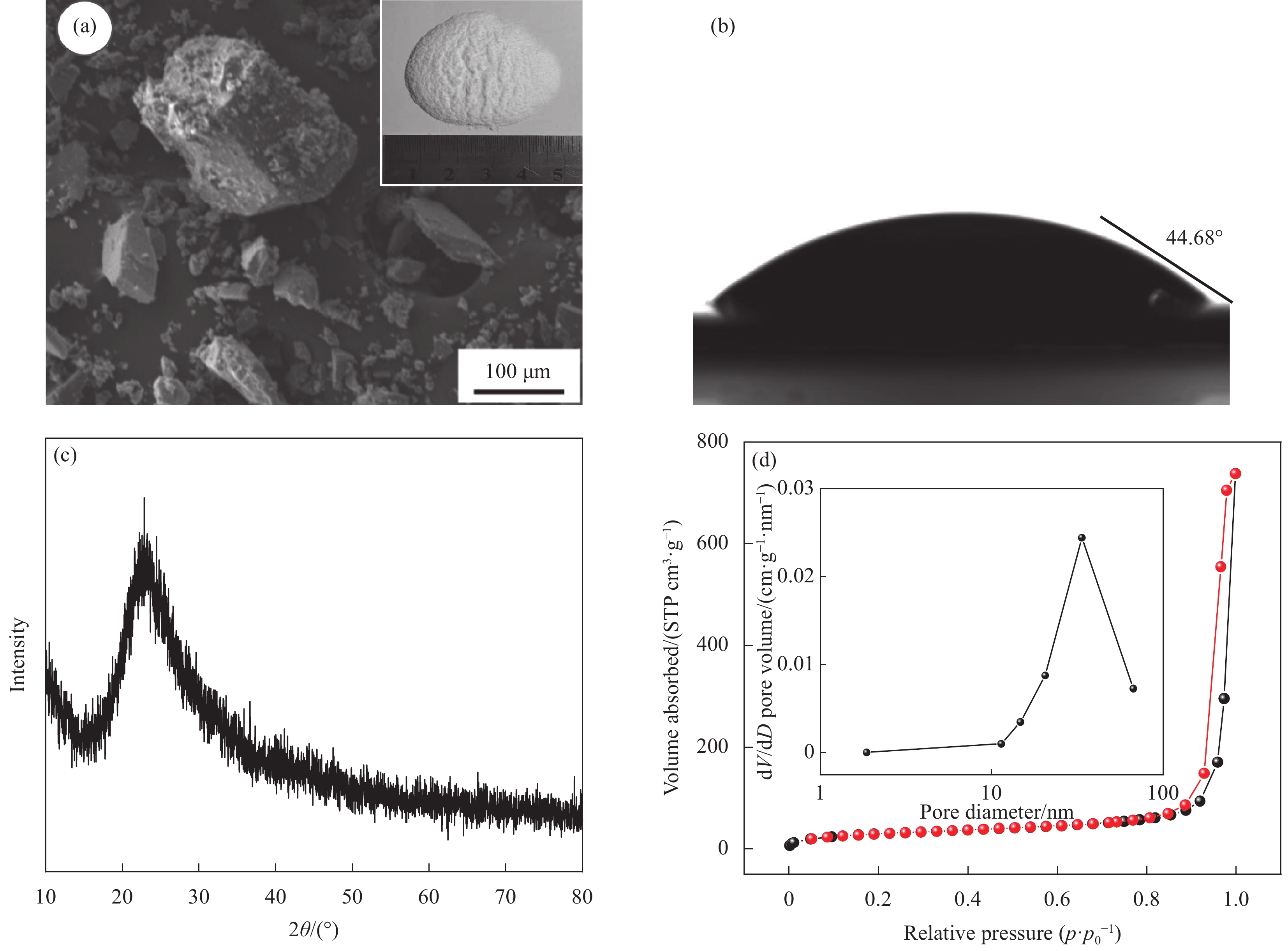
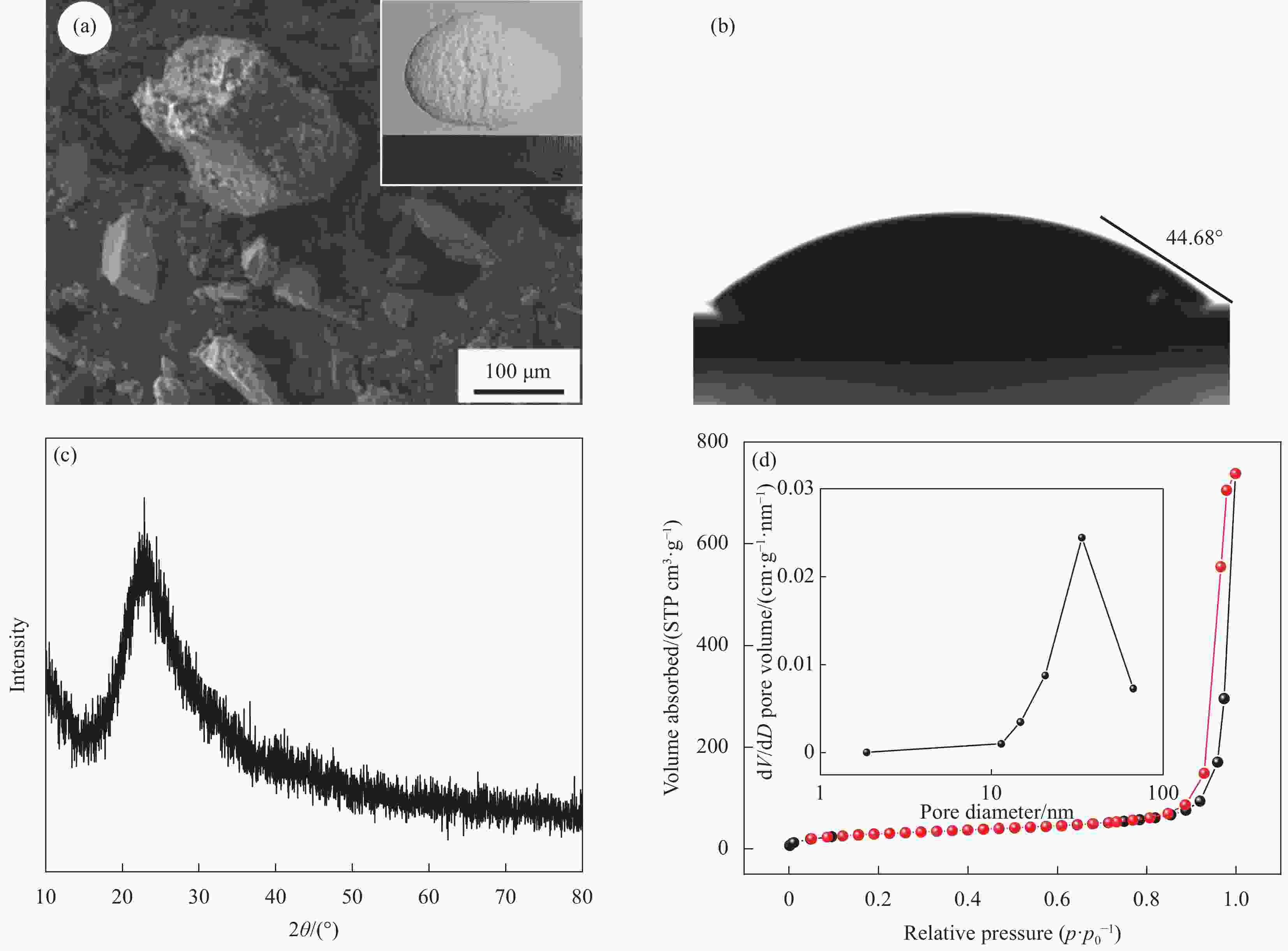
Performance and mechanism of the amine-modified silica aerogel for the removal of Cu(II)
-
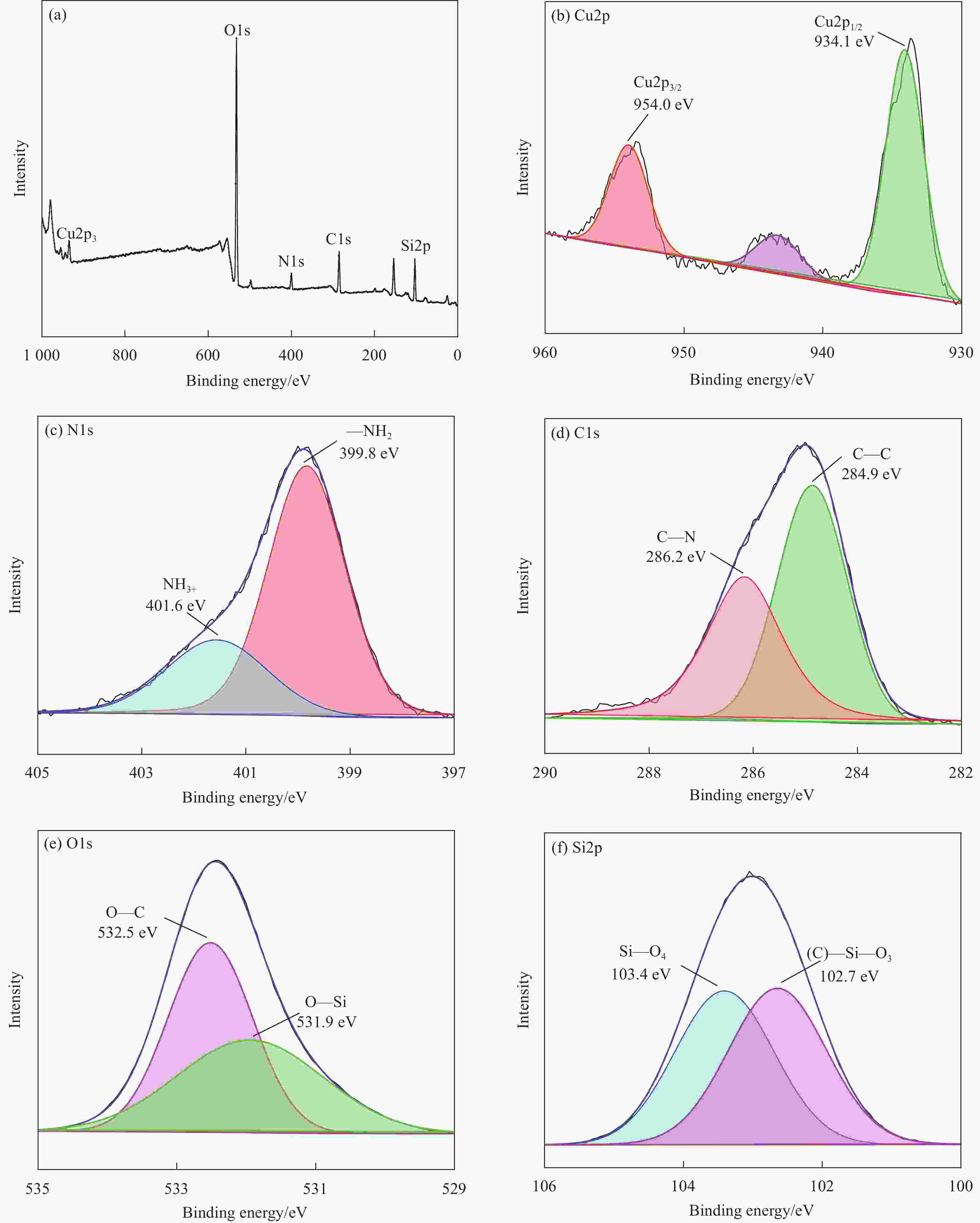
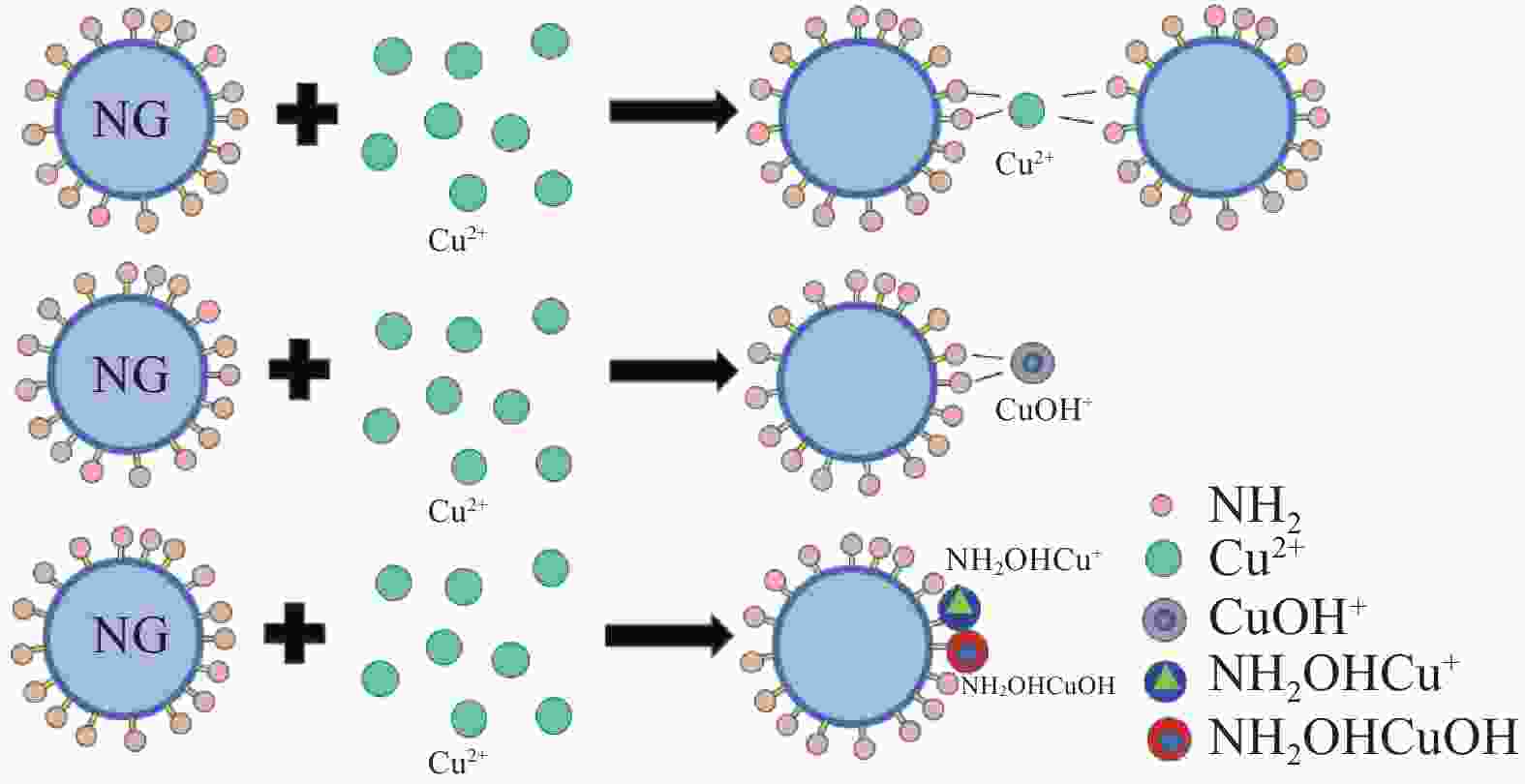
摘要: 为有效去除液相中重金属Cu(II),以正硅酸乙酯为原料、3-氨丙基三乙氧基硅烷为氨基化试剂,通过共缩聚法合成氨基改性SiO2气凝胶(NG)。系统考察pH、离子强度、时间、温度等因素对NG去除Cu(II)的影响,结合吸附动力学模型、吸附等温模型、吸附热力学、位点能量分布理论分析其吸附机制。研究结果表明:pH在3.00~6.00条件下,Cu(II)吸附量随pH升高而增大。离子强度由0 mol/L增至0.08 mol/L时,Cu(II)吸附量受抑制作用呈逐渐降低趋势,FTIR分析显示NG与Cu(II)主要形成外层络合物。NG吸附Cu(II)时间在8 h内基本达到平衡,其吸附主要经过边界层扩散、颗粒内扩散与化学吸附等过程,且该吸附过程最符合准二级动力学模型与Freundlich模型。温度升高有利于促进吸附反应发生,Cu(II)最大吸附量达到130.45 mg/g,其吸附过程属吸热、熵增加的自发反应。位点能量分布显示随吸附反应进行,Cu(II)优先占据NG上高能量吸附位点,再占据低能量吸附位点,NG吸附Cu(II)的主要机制是外层络合与静电作用。Abstract: In order to remove Cu(II) from the liquid phase efficiently, the amine-modified silica aerogel (NG) was prepared by co-condensation method using tetraethyl orthosilicate as raw material and 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane as amino agent. The effects of pH, ionic strength, time, temperature and other factors on the removal of Cu(II) by NG were systematically investigated. The adsorption mechanism of Cu(II) on the NG was analyzed by combining adsorption kinetics model, adsorption isotherm model, adsorption thermodynamics and site energy distribution theory. The results demonstrate that the adsorption capacity of Cu(II) increase with pH value from 3.00-6.00, and the adsorption is inhibited by the addition of ionic strength at the range of 0-0.08 mol/L. The outer-sphere complexes formed by Cu(II) and NG are confirmed by using FTIR analysis. Furthermore, the adsorption equilibrium is achieved within 8 h, and the adsorption process mainly go through boundary layer diffusion, intra-particle diffusion and chemisorption. The adsorption process is best fitted with the pseudo-second-order model and Freundlich model. The increase of temperature is beneficial to promote the adsorption reaction of Cu(II), and the maximum adsorption capacity reaches to 130.45 mg/g. The adsorption process is endothermic and entropy increasing spontaneous reaction. The energy distribution show that Cu(II) is preferentially adsorbed on the high-energy adsorption sites on NG and then occupied low-energy adsorption sites. Overall, the adsorption mechanism is mainly attributed to the electrostatic interaction and the outer-sphere complexation.
-
Key words:
- aerogel /
- adsorption /
- Cu(II) /
- kinetics /
- model /
- site energy distribution
-
图 2 pH对NG吸附Cu(II)的影响(ρ0=20 mg/L, I=0 mol, T=298 K, m=0.02 g, V=50 mL) (a)、水溶液中Cu(II)分布形态 (b)
ρ0—Initial mass concentration; I—Ionic strength; T—Adsorption temperature; m—Quality of the NG; V—Volume of solution
Figure 2. Effect of pH on absorption of Cu(II) by NG (ρ0=20 mg/L, I=0 mol, T=298 K, m=0.02 g, V=50 mL) (a), speciation of Cu(II) in the system (b)
图 3 离子强度对NG吸附Cu(II)的影响(ρ0=20 mg/L, pH=5.15, T=298 K, m=0.02 g, V=50 mL) (a)、NG吸附Cu(II)前后FTIR图谱(ρ0=20 mg/L, pH=5.15, I=0 mol, T=298 K, m=0.02 g, V=50 mL) (b)
Figure 3. Effect of ionic strength on absorption of Cu(II) by NG (ρ0=20 mg/L, pH=5.15, T=298 K, m=0.02 g, V=50 mL) (a), FTIR spectra of amine-modified silica aerogel before and after Cu(II) adsorption (ρ0=20 mg/L, pH=5.15, I=0 mol, T=298 K, m=0.02 g, V=50 mL) (b)
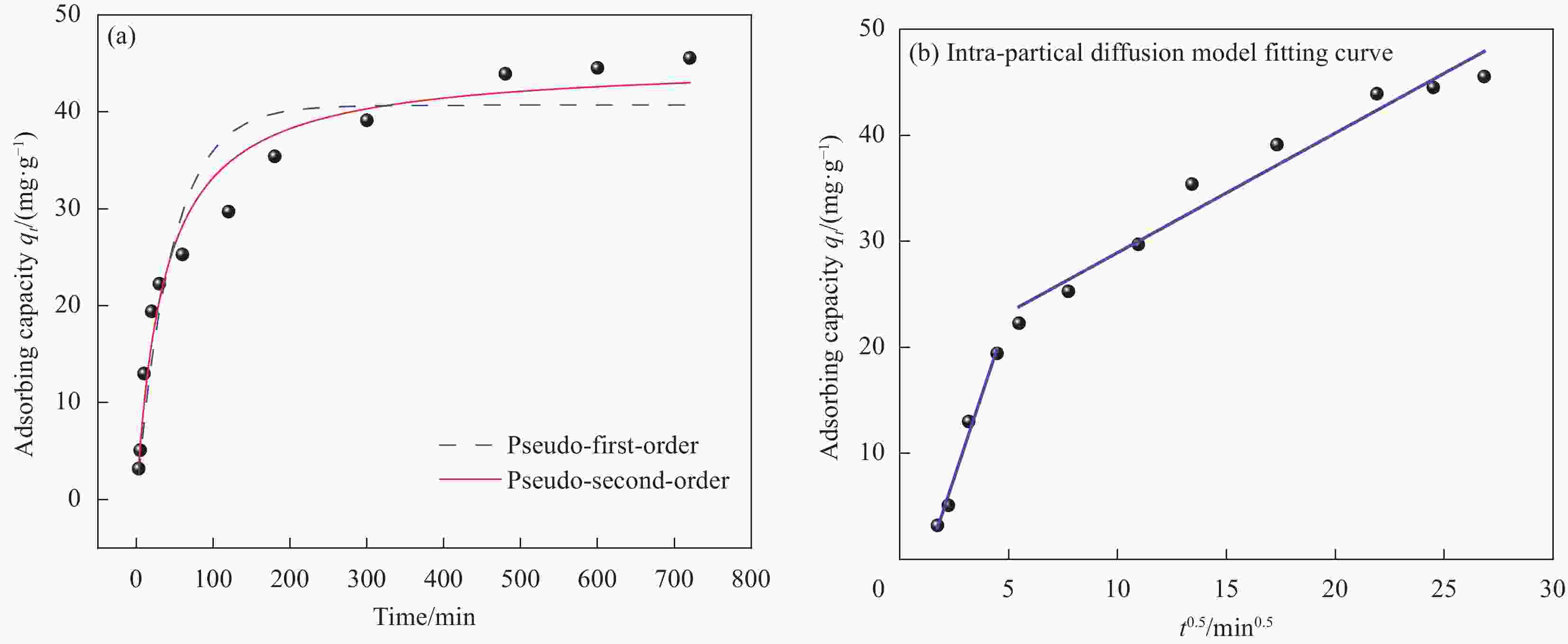
表 1 NG吸附Cu(II)的动力学模型参数
Table 1. Kinetic model parameters for Cu(II) adsorption onto NG
Kinetic model Parameter Result Pseudo-first order model qe,c/(mg·g−1) 40.6704 k1/(min−1) 0.0217 R2 0.9053 Pseudo-second order model qe,c/(mg·g−1) 45.1501 k2/(g·mg−1·min−1) 0.0006 R2 0.9653 Intra-partical diffusion model kp1, kp2/(mg·g−1·min−0.5) 6.1698, 1.1281 C1, C2 −7.7112, 17.6597 R12, R22 0.9760, 0.9538 Notes: qe,c—Theoretical calculation of adsorption capacity; k1, k2 and kp—Rate constans for the pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order and intraparticle diffusion, respectively; R2—Coefficient of determination; C—Desorption constant. 表 2 不同温度下Cu(II)在NG上吸附的等温模型参数
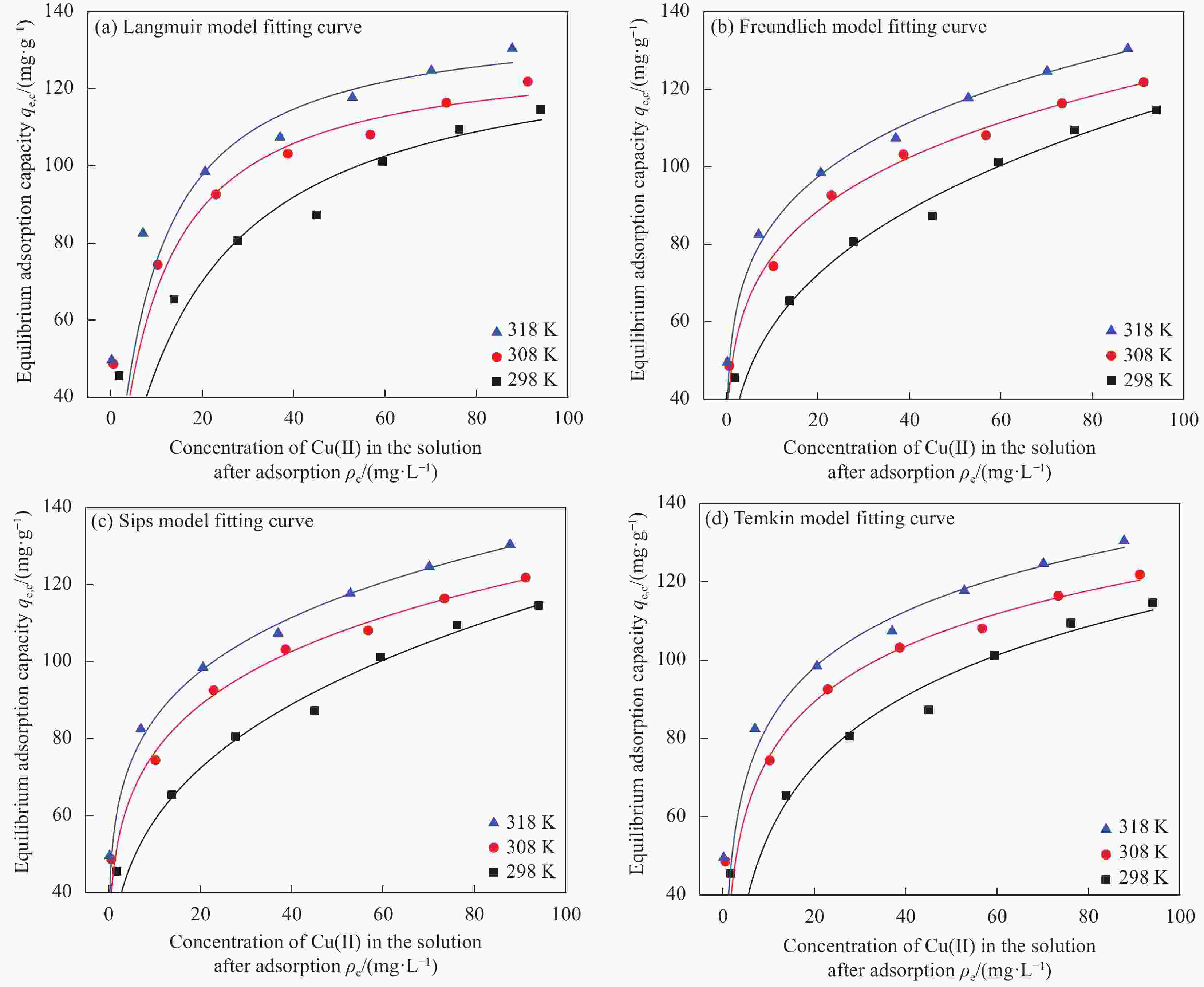
Table 2. Isotherm parameters of Cu(II) adsorption onto NG at varying temperatures
Model and parameter 298 K 308 K 318 K Langmuir nonlinear fit ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{7.39{\rho _{\text{e}}}}}{{1 + 0.05533{\rho _{\text{e}}}}}$ $ {q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{14.15{\rho _{\text{e}}}}}{{1 + 0.10868{\rho _{\text{e}}}}} $ ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{16.43{\rho _{\text{e}}}}}{{1 + 0.11819{\rho _{\text{e}}}}}$ R2 0.9913 0.9966 0.9958 Freundlich nonlinear fit ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = 29}}{\text{.55}}\rho _{\text{e}}^{0.2986}$ ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = 47}}{\text{.55}}\rho _{\text{e}}^{0.2080}$ ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = 54}}{\text{.45}}\rho _{\text{e}}^{0.1942}$ R2 0.9980 0.9995 0.9997 Sips nonlinear fit ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{29.55{\rho _{\text{e}}}^{0.2987}}}{{1 + 0.00004{\rho _{\text{e}}}^{0.2987}}}$ ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{49.26{\rho _{\text{e}}}^{0.2525}}}{{1 + 0.08598{\rho _{\text{e}}}^{0.2525}}}$ ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }}\dfrac{{54.45{\rho _{\text{e}}}^{0.1942}}}{{1 + 0.00006{\rho _{\text{e}}}^{0.1942}}}$ R2 0.9976 0.9994 0.9996 Temkin nonlinear fit ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }} - 3.86 + 25.67\ln {\rho _{\text{e}}}$ ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = 27}}{\text{.97}} + 20.49\ln {\rho _{\text{e}}}$ ${q_{{\text{e}},{\text{c}}}}{\text{ = }}35.97 + 20.74\ln {\rho _{\text{e}}}$ R2 0.9952 0.9992 0.9990 表 3 不同种类气凝胶对Cu(II)吸附效果
Table 3. Cu(II) adsorption by different aerogels
Number Sorbent Reaction condition Adsorption capacity/(mg·g-1) Reference 1 Carbon aerogel pH=7.00, T=298 K, t=10 min 86.27 [30] 2 MnFe2O4-cellulose aerogel pH=6.00, T=298 K, t=100 min 63.30 [31] 3 Graphene oxide aerogel pH=6.30, T=313 K, t=30 min 29.59 [32] 4 Porous alginate aerogel bead pH=4.50, T=298 K, t=950 min 126.82 [33] 5 Graphene oxide/carboxymethyl chitosan aerogel pH=5.00, T=303 K, t=600 min 95.37 [34] 6 Amine-modified sillica aerogel pH=5.00, T=318 K, t=720 min 130.45 Present study 表 4 NG吸附Cu(II)的热力学参数
Table 4. Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of Cu(II) onto NG
T/K KC ΔG/(kJ·mol−1) ΔH/(kJ·mol−1) ΔS/(J·(mol·K)−1) 298 29550 −25.50 24.21 167.27 308 47550 −27.58 318 54450 −28.83 Notes: T—Temperature; ΔG—Gibbs free energy; ΔH—Change in enthalpy during adsorption; ΔS—Adsorption process entropy change; KC—Modified constant. -
[1] HUANG Y Y, ZHU S Y, WU P F, et al. Gold nanoclusters inhibit the male reproductive toxicity of Cu2+[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials,2021,4(12):13919-13926. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c03227 [2] SHAO H, YIN D D, LI D, et al. Simultaneous visual detection and removal of Cu2+ with electrospun self-supporting flexible amidated polyacrylonitrile/branched polyethyleneimine nanofiber membranes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(41):49288-49300. [3] LIU S, LI J Y, OSHITA S, et al. Formation of a hydrogen radical in hydrogen nanobubble water and its effect on copper toxicity in chlorella[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2021,9(33):11100-11109. [4] CHEE D N A, AZIZ F, AMIN M A M, et al. Copper adsorption on ZIF-8/alumina hollow fiber membrane: A response surface methodology analysis[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering,2021,46(7):6775-6786. doi: 10.1007/s13369-021-05636-1 [5] 林本兰, 吴兰兰, 崔升, 等. 新型重金属离子吸附剂的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2015, 29(19):18-23.LIN Benlan, WU Lanlan, CUI Sheng, et al. Research progress of novel adsorbents of heavy metal ions[J]. Materials Reports,2015,29(19):18-23(in Chinese). [6] CHEN Y N, LIU Y H, LI Y P, et al. Functional wastepaper-montmorillonite composite aerogel for Cd2+ adsorption[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(31):38644-38653. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09907-6 [7] LI H T, ZHANG L J, CHEN J H, et al. Reduced graphene oxide based aerogels: Doped with ternary Prussian blue analogs and selective removal of Cs+ from effluent[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering,2022,47:1-12. [8] JING L M, YANG S, LI X, et al. Effective adsorption and sensitive detection of Cr6+ by degradable collagen-based porous fluorescent aerogel[J]. Industrial Crops& Products,2022,182:1-9. [9] EHGARTNER C R, WERNER V, SELZ S, et al. Carboxylic acid-modified polysilsesquioxane aerogels for the selec-tive and reversible complexation of heavy metals and orga-nic molecules[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Material,2021,312:1-11. [10] 张明. 增强改性 SiO2气凝胶复合材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11):2674-2683.ZHANG Ming. Research progress of reinforced SiO2 aerogel composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(11):2674-2683(in Chinese). [11] 刘双, 张洋, 张天蒙, 等. 氨基功能化纳米纤维素气凝胶的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11):3180-3188. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180316.004LIU Shuang, ZHANG Yang, ZHANG Tianmeng, et al. Preparation and characterization of 3-(2-aminoethylamino) propylmethyldimethoxysilane-nano cellulose aerogels[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(11):3180-3188(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180316.004 [12] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 粉末产品振实密度测定通用方法: GB/T 21354—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Powders-Determination of tap density: GB/T 21354—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese). [13] HASSANZADEH-AFRUZI F, ESMAILZADEHS F, ASGHARNASL S, et al. Efficient removal of Pb (II)/Cu(II) from aqueous samples by a guanidine-functionalized SBA-15/Fe3O4[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2022,291:1-15. [14] SINGH S, KAPOOR D, KHASNABIS S, et al. Mechanism and kinetics of adsorption and removal of heavy metals from wastewater using nanomaterials[J]. Environmental Che-mistry Letters,2021,19(3):2351-2381. doi: 10.1007/s10311-021-01196-w [15] WADHAWAN S, JAIN A, NAYYAR J, et al. Role of nanomaterials as adsorbents in heavy metal ion removal from waste water: A review[J]. Journal of Water Process Engi-neering,2020,33:1-17. [16] LI J, ZHANG S, CHEN C, et al. Removal of Cu(II) and fulvic acid by graphene oxide nanosheets decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2012,4(9):4991-5000. [17] 吴志坚, 刘海宁, 张慧芳. 离子强度对吸附影响机理的研究进展[J]. 环境化学, 2010(6):997-1003.WU Zhijian, LIU Haining, ZHANG Huifang. Research progress on mechanisms about the effect of ionic strength on adsorption[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2010(6):997-1003(in Chinese). [18] 张晋京, 王帅, 窦森, 等. 土壤粗胡敏素对铜离子的吸附作用及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(12):2527-2533. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.12.020ZHANG Jinjing, WANG Shuai, DOU Sen, et al. Adsorption of copper(Ⅱ) on crude humin from soils[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2008,28(12):2527-2533(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.12.020 [19] HAYES K, PAPELIS C, LECKIE J. Modeling ionic strength effects on anion adsorption at hydrous oxide/solution interfaces[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,1988,125(2):717-726. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(88)90039-2 [20] PEAK D, FORD R G, SPARKS D L. An in situ ATR-FTIR investigation of sulfate bonding mechanisms on goethite[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,1999,218(1):289-299. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1999.6405 [21] 刘秀芸, 王刚, 雷雨昕, 等. 巯基改性玉米秸秆对水中Cu(II)的吸附特性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(3):1220-1229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.03.027LIU Xiuyun, WANG Gang, LEI Yuxin, et al. Adsorption performance and mechanism of mercaptoacetyl corn straw for Cu(II) in aqueous solution[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(3):1220-1229(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.03.027 [22] TRAN H N, YOU S J, HOSSEINI-BANDEGHARAEI A, et al. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review[J]. Water Research,2017,120:88-116. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014 [23] 李海斌, 张克华, 陈庆典, 等. 氨基磷酸螯合树脂(D418)高效去除Cu(II)的性能与机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(4):1128-1138.LI Haibin, ZHANG Kehua, CHEN Qingdian, et al. Performance and mechanism of the amino methylene phosphonic acid chelating resin (D418) for the efficient removal of Cu(II)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(4):1128-1138(in Chinese). [24] LIU Y, CHEN Q, SINGH R P. Low-cost RSAC and adsorption characteristics in the removal of copper ions from wastewater[J]. Applied Sciences,2022,12(11):1-16. [25] LIU J L, BECKERMAN J. Application of sustainable biosorbents from hemp for remediation copper (II)-containing wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engi-neering,2022,10(3):1-12. [26] MOUBAYED N M S, AL-HOURI H J. Characterization of adsorption ability of spirulina platensis for copper ions removal from aqueous solutions[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2022,250:118-125. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2022.28111 [27] WANG R H, ZOU H Y, ZHENG R J, et al. Molecular dynamics beyond the monolayer adsorption as derived from Langmuir curve fitting[J]. Inorganic Chemistry,2022,61(20):7804-7812. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c00301 [28] MORADI H, AZIZPOUR H, BAHMANYAR H, et al. Molecular dynamic simulation of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrogen adsorption on Faujasite zeolite[J]. Chinese Jour-nal of Chemical Engineering,2022,43:70-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2021.05.034 [29] LI X D, WEN B A, LI Y J. Adsorption of the malachite green by magnetic clam shell powder[J]. Polish Journal of Envi-ronmental Studies,2021,31(1):717-726. [30] LI J, ZHENG L, LIU H B. A novel carbon aerogel prepared for adsorption of copper(II) ion in water[J]. Journal of Porous Materials,2017,24(6):1575-1580. doi: 10.1007/s10934-017-0397-y [31] CUI S, WANG X, ZHANG X, et al. Preparation of magnetic MnFe2O4-cellulose aerogel composite and its kinetics and thermodynamics of Cu(II) adsorption[J]. Cellulose,2018,25(1):735-751. doi: 10.1007/s10570-017-1598-x [32] MI X, HUANG G B, XIE W S, et al. Preparation of graphene oxide aerogel and its adsorption for Cu2+ ions[J]. Carbon,2012,50(13):4856-4864. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.06.013 [33] DEZE E G, PAPAGEORGIOU S K, FAVVAS E P, et al. Porous alginate aerogel beads for effective and rapid heavy metal sorption from aqueous solutions: Effect of porosity in Cu2+ and Cd2+ ion sorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,209:537-546. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.133 [34] LUO J Q, FAN C J, XIAO Z, et al. Novel graphene oxide/carboxymethyl chitosan aerogels via vacuum-assisted self-assembly for heavy metal adsorption capacity[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2019,578:1-11. [35] LOMBARDO S, THIELEMANS W. Thermodynamics of adsorption on nanocellulose surfaces[J]. Cellulose,2019,26(1):249-279. doi: 10.1007/s10570-018-02239-2 [36] KUMAR I A, JEYAPRABHA C, VISWANATHAN N. Effect of polyvalent metal ions encrusted biopolymeric hybrid beads on nitrate adsorption[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2020,8(4):1-11. [37] XIA C F, HUANG H H, LIANG D R, et al. Adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride on layered double hydroxide loaded carbon nanotubes and site energy distribution analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,443:1-10. [38] ZHAO F, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Z L, et al. Synthesis of an absorption material based on oil shale semi-coke: Discussion to adsorption mechanism and corresponding site energy distribution analysis[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2022,637:1-10. [39] BERGER J M, WINAND R. Solubilities, densities, and electrical conductivities of aqueous copper(I) and copper(II) chlorides in solutions containing other chlorides such as iron, zinc, sodium and hydrogen chlorides[J]. Hydrometallurgy,1984,12(1):61-81. doi: 10.1016/0304-386X(84)90048-3 [40] 蒋晖, 刘秀丽, 孙娇霞, 等. BPA和EE2在PA微塑料上竞争吸附的位点能量[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(12):5736-5746. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.12.030JIANG Hui, LIU Xiuli, SUN Jiaoxia, et al. Competitive adsorption characteristics of BPA and EE2 on PA microplastics by site energy distribution theory[J]. China Envi-ronmental Science,2021,41(12):5736-5746(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.12.030 [41] BELACHEW N, BEKELE G. Synergy of magnetite intercalated bentonite for enhanced adsorption of congo red dye[J]. Silicon,2020,12(3):603-612. doi: 10.1007/s12633-019-00152-2 [42] ZHOU Y Y, HE Y Z, XIANG Y J, et al. Single and simultaneous adsorption of pefloxacin and Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions by oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,646:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.267 [43] XU L, LIU Y N, WANG J G, et al. Selective adsorption of Pb2+ and Cu2+ on amino-modified attapulgite: Kinetic, thermal dynamic and DFT studies[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,404:1-10. [44] ZHOU T Z, LI C P, JIN H L, et al. Effective adsorption/reduction of Cr(VI) oxyanion by halloysite@polyaniline hybrid nanotubes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(7):6030-6043. [45] SHAO Z D, CHENG X, ZHENG Y M. Facile co-precursor sol-gel synthesis of a novel amine-modified silica aerogel for high efficiency carbon dioxide capture[J]. Journal of Colloid Interface Science,2018,530:412-423. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.06.094 [46] WANG J H, ZHANG D, LIU S C, et al. Enhanced removal of chromium(III) for aqueous solution by EDTA modified attapulgite: Adsorption performance and mechanism[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2020,720:1-8. [47] ZHANG L B, ZHANG G W, WANG S X, et al. Sulfoethyl functionalized silica nanoparticle as an adsorbent to selectively adsorb silver ions from aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers,2017,71:330-337. doi: 10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.001 [48] LI H, XIAO D L, HE H, et al. Adsorption behavior and adsorption mechanism of Cu(II) ions on amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2013,23(9):2657-2665. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62782-X -





 下载:
下载: