Controllable preparation method and performance of three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide aerogel under mild conditions
-
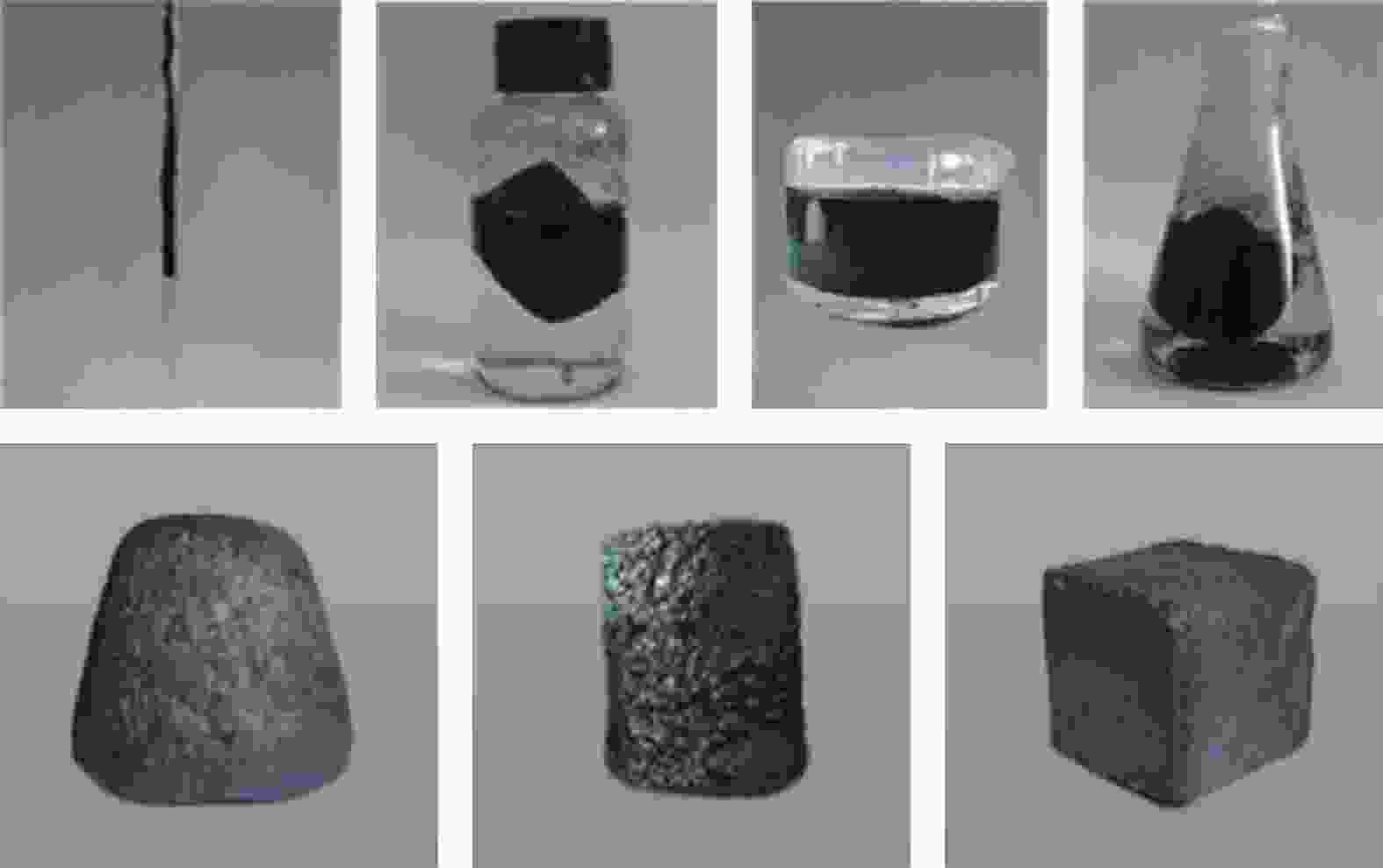
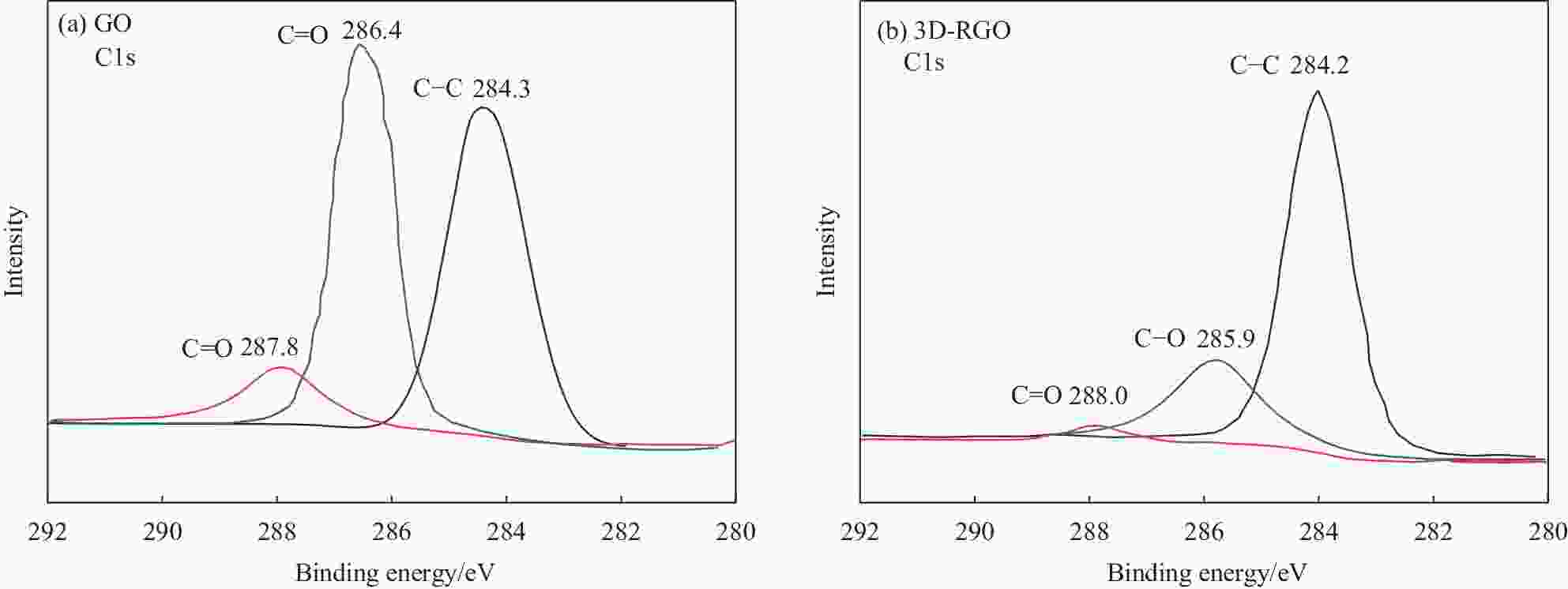
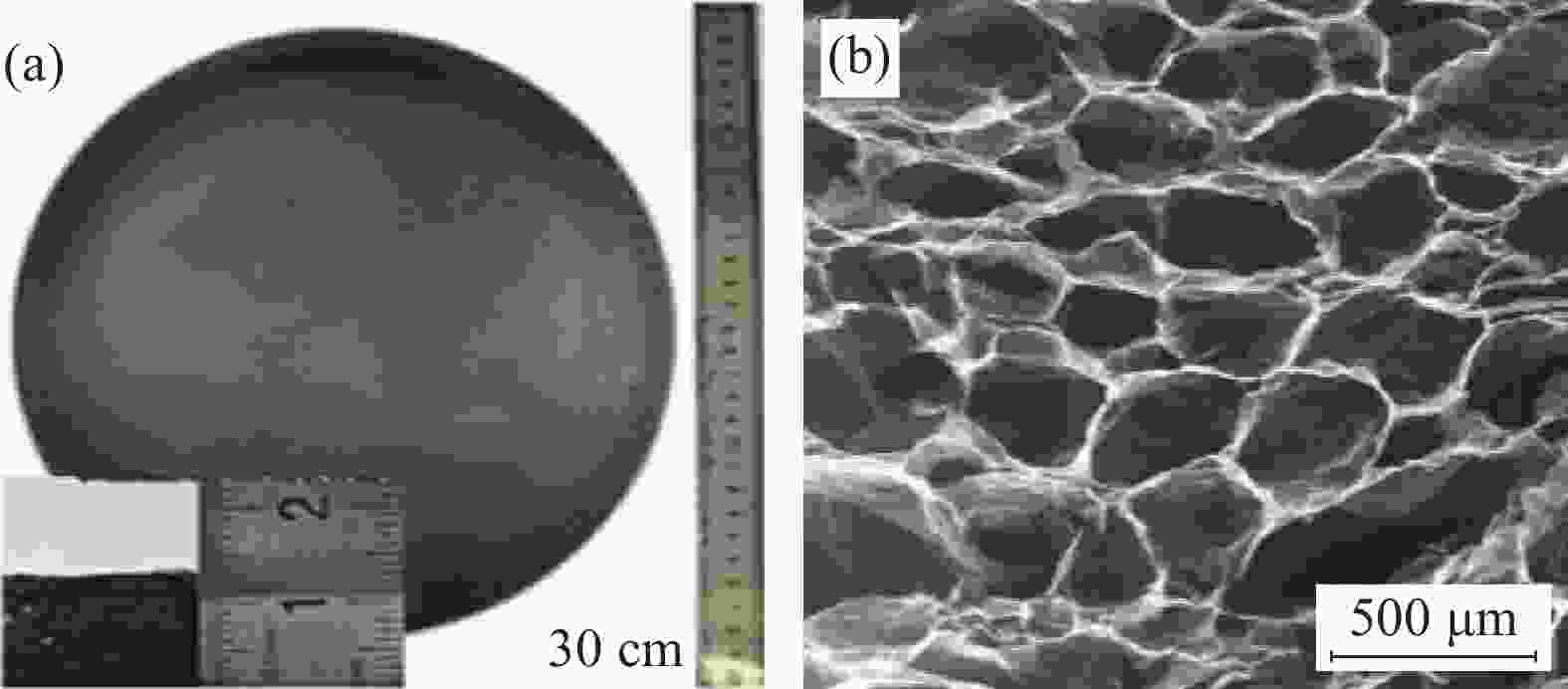
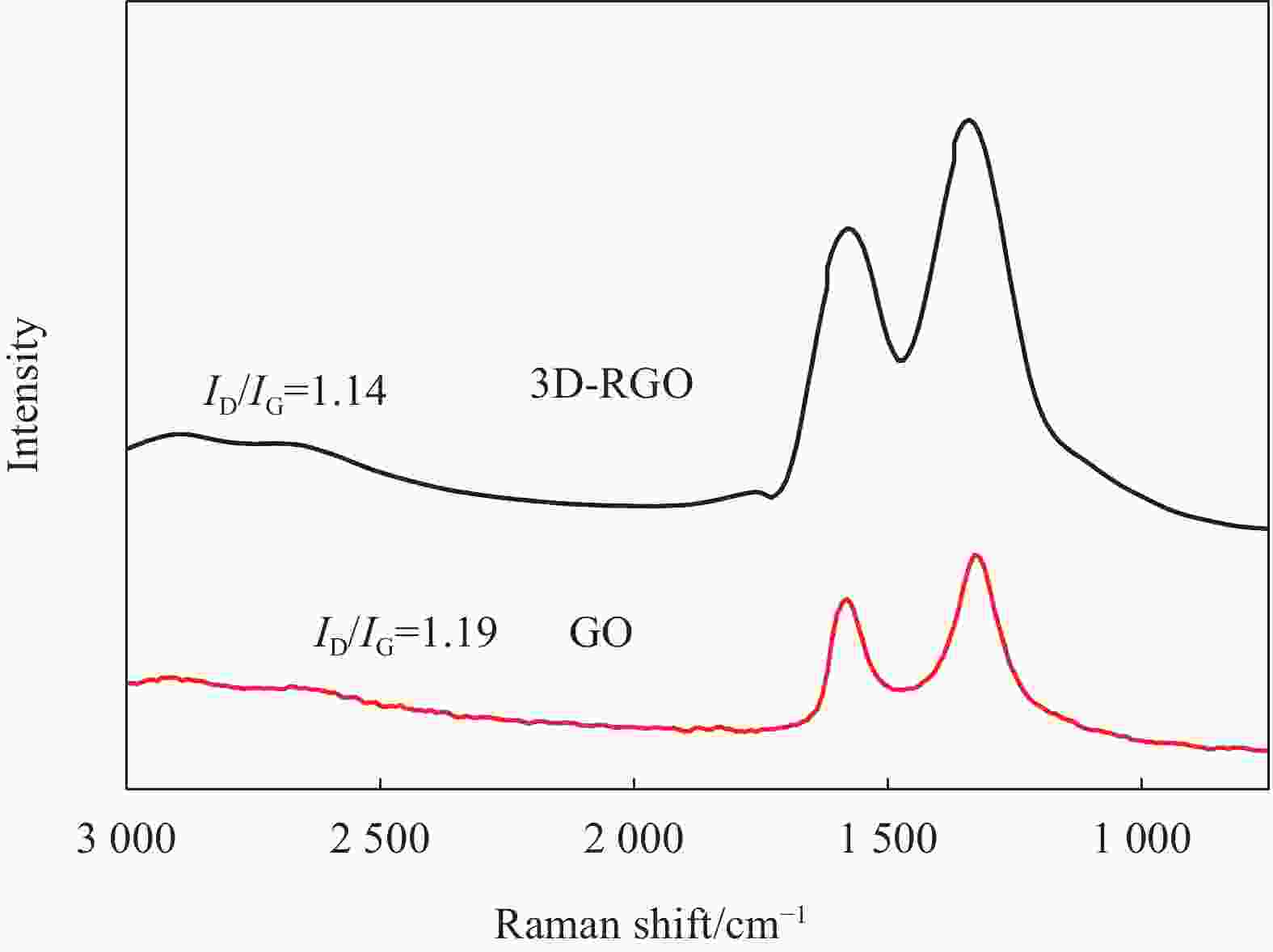
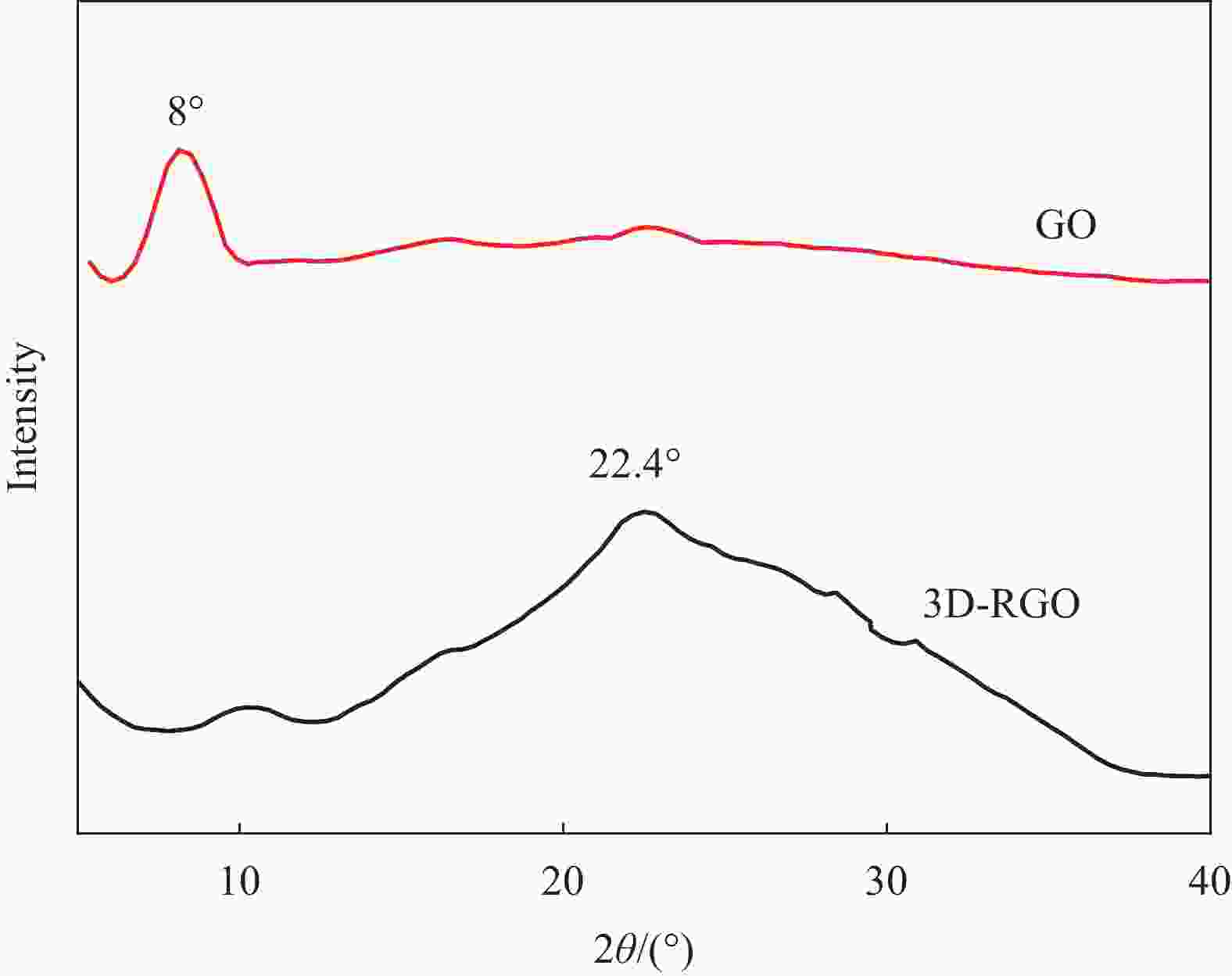
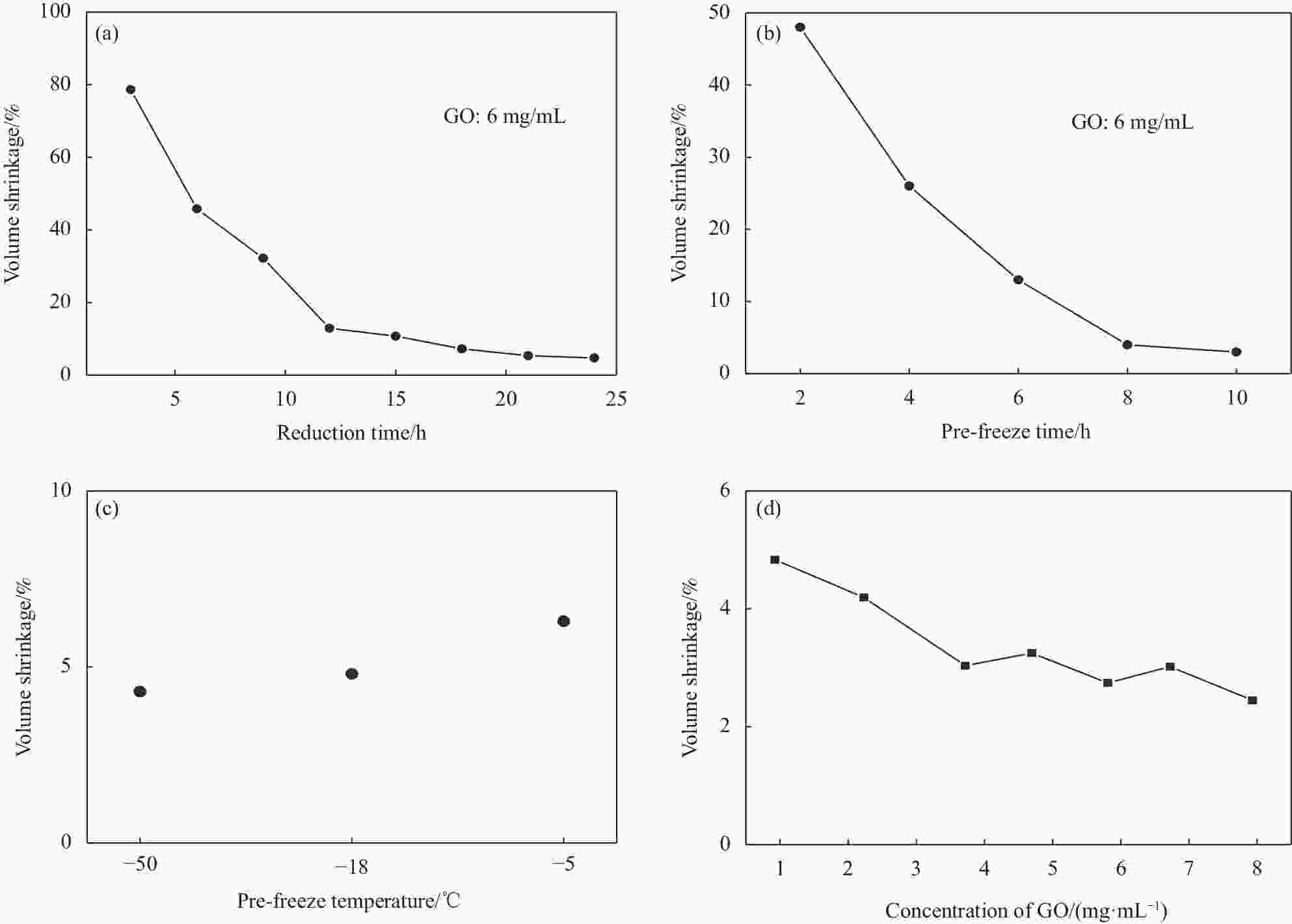
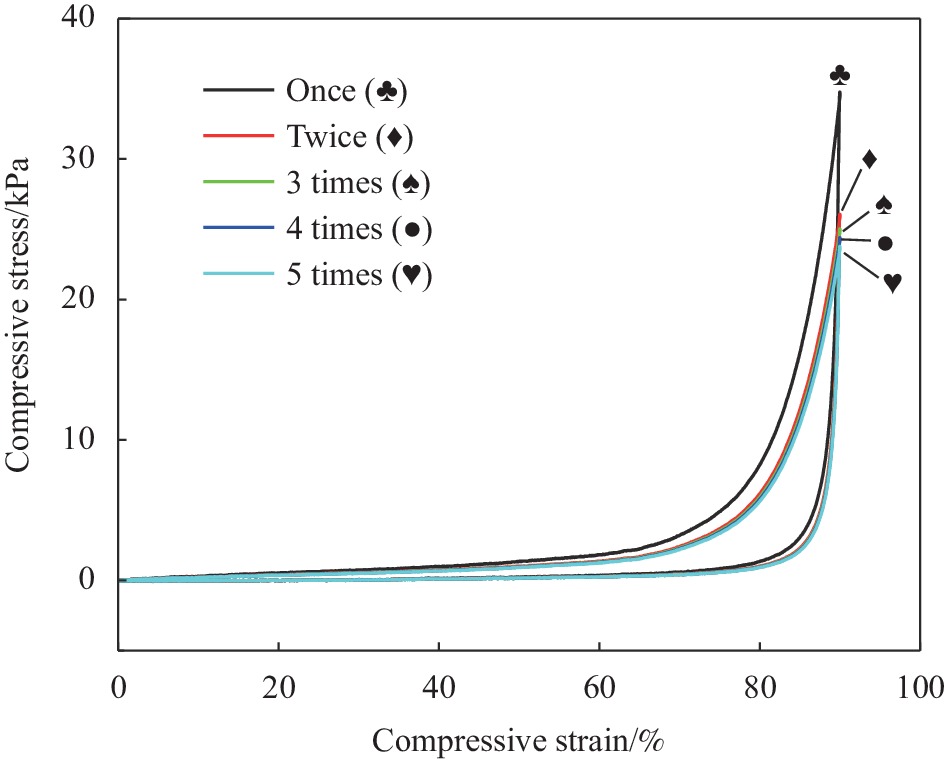
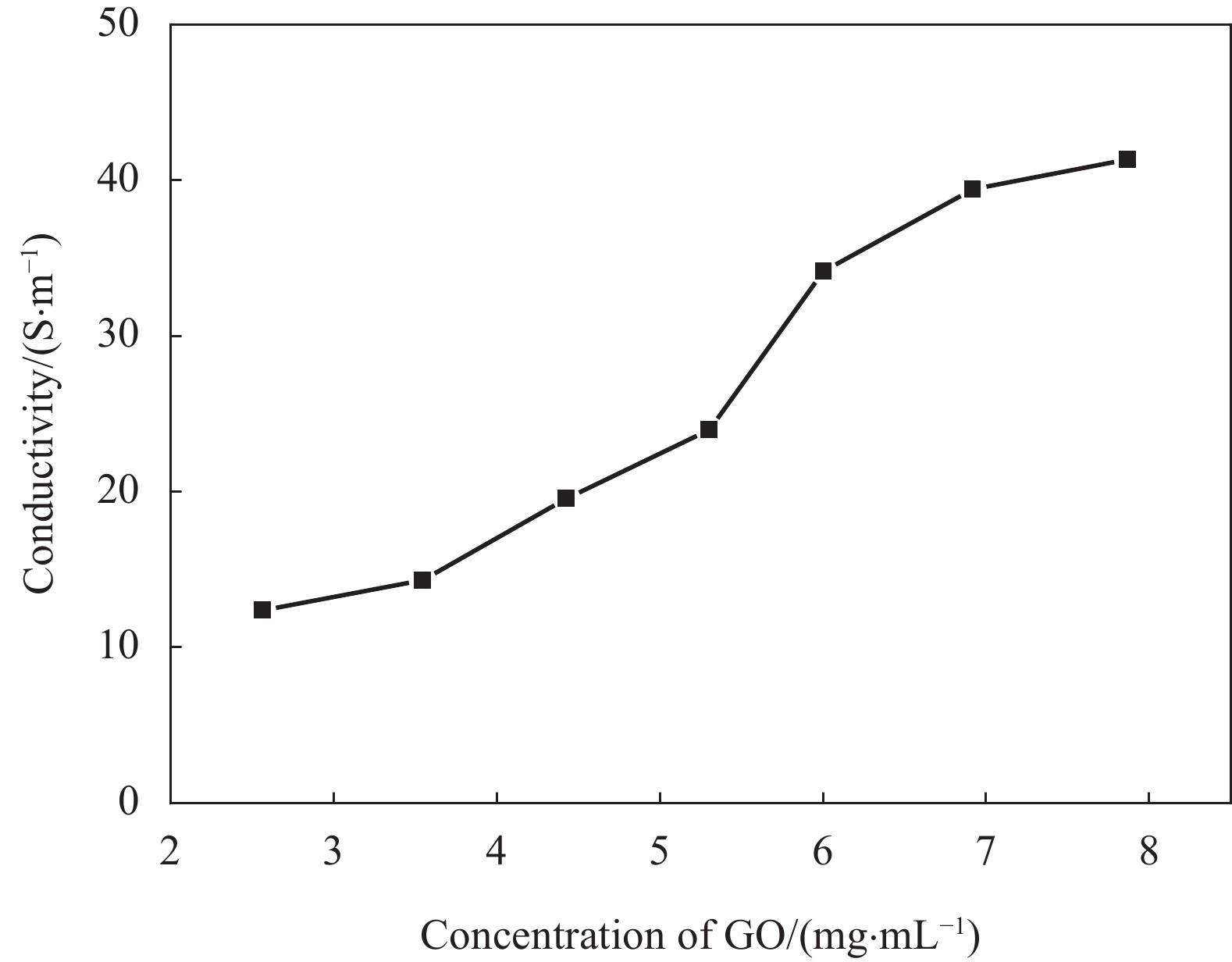
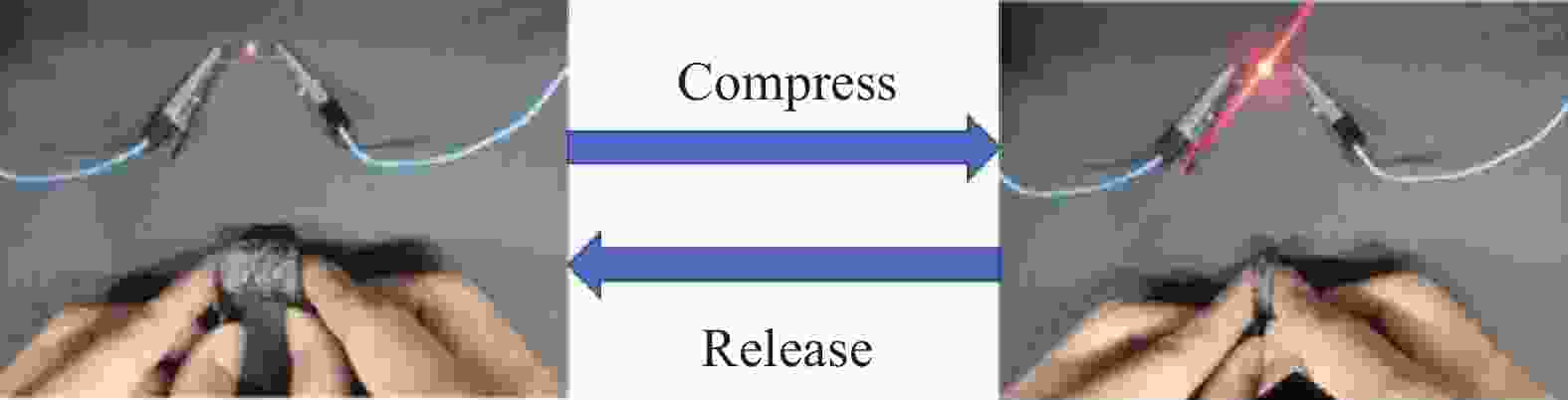
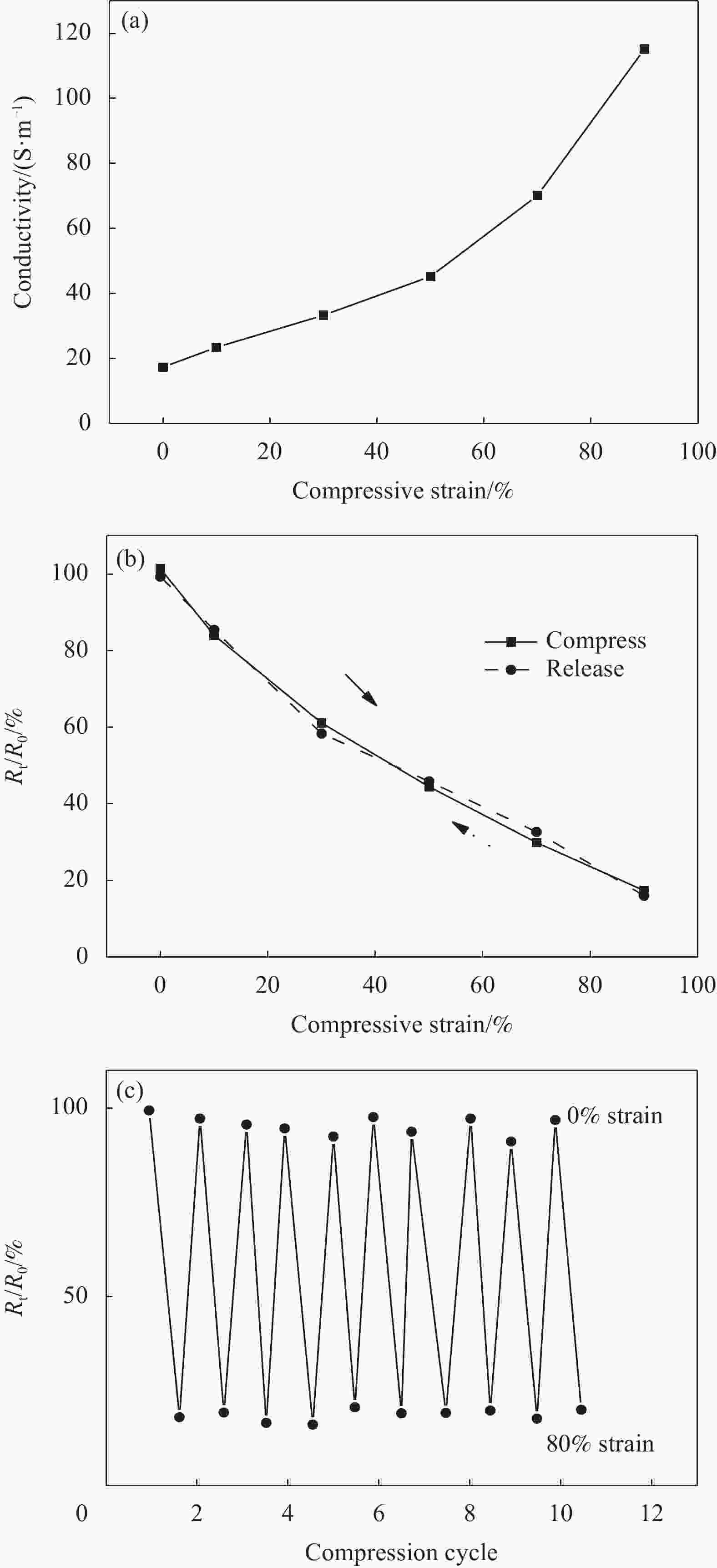
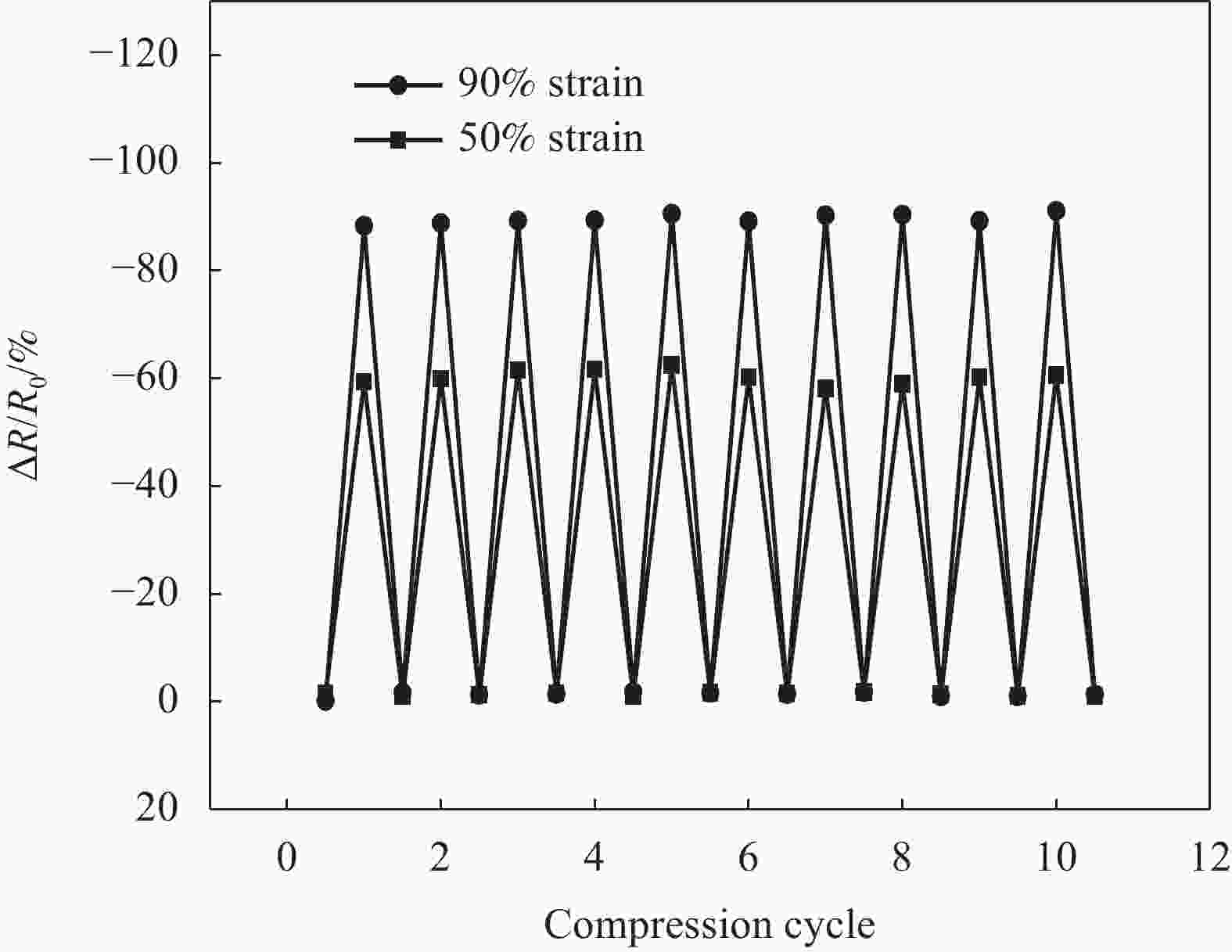
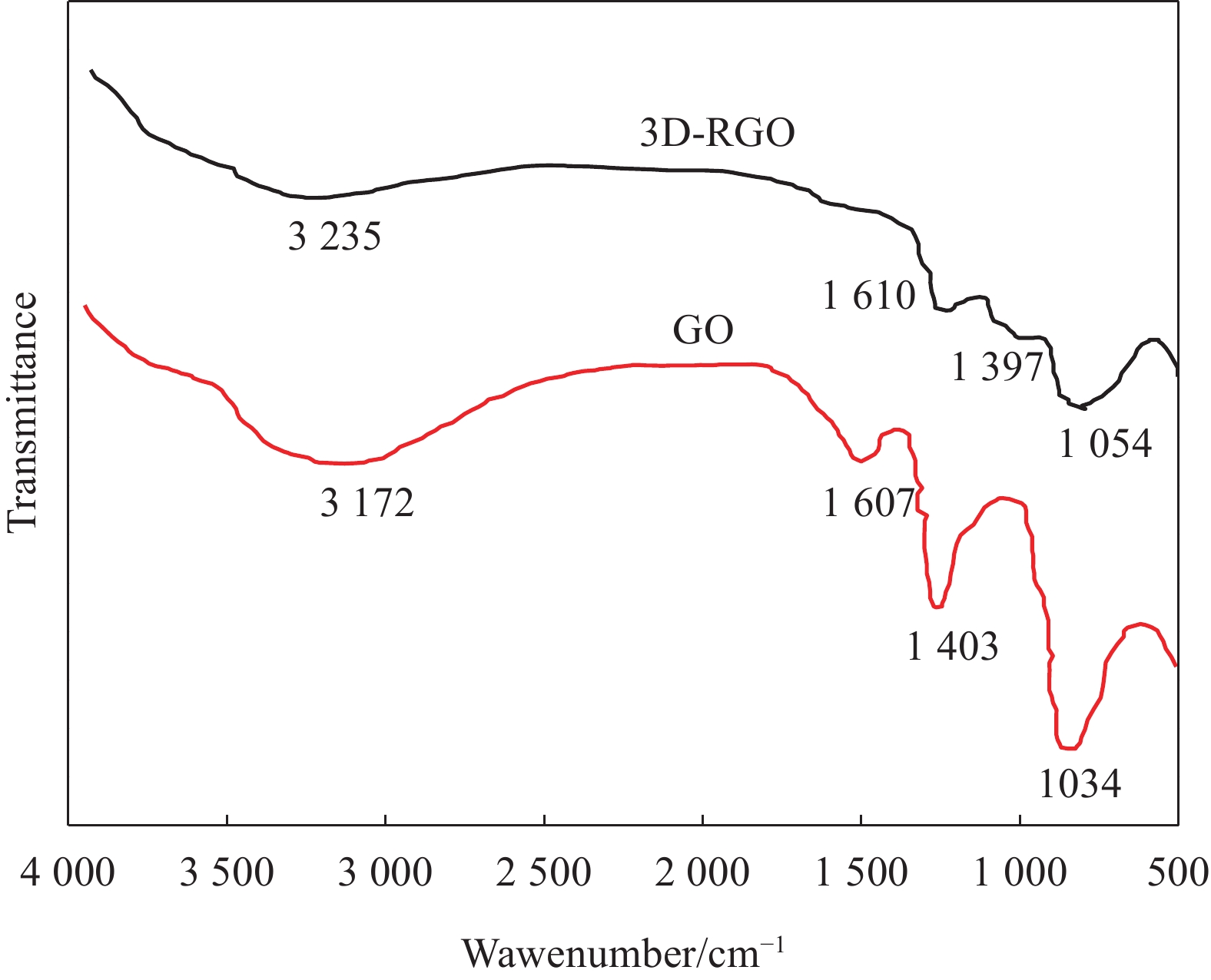
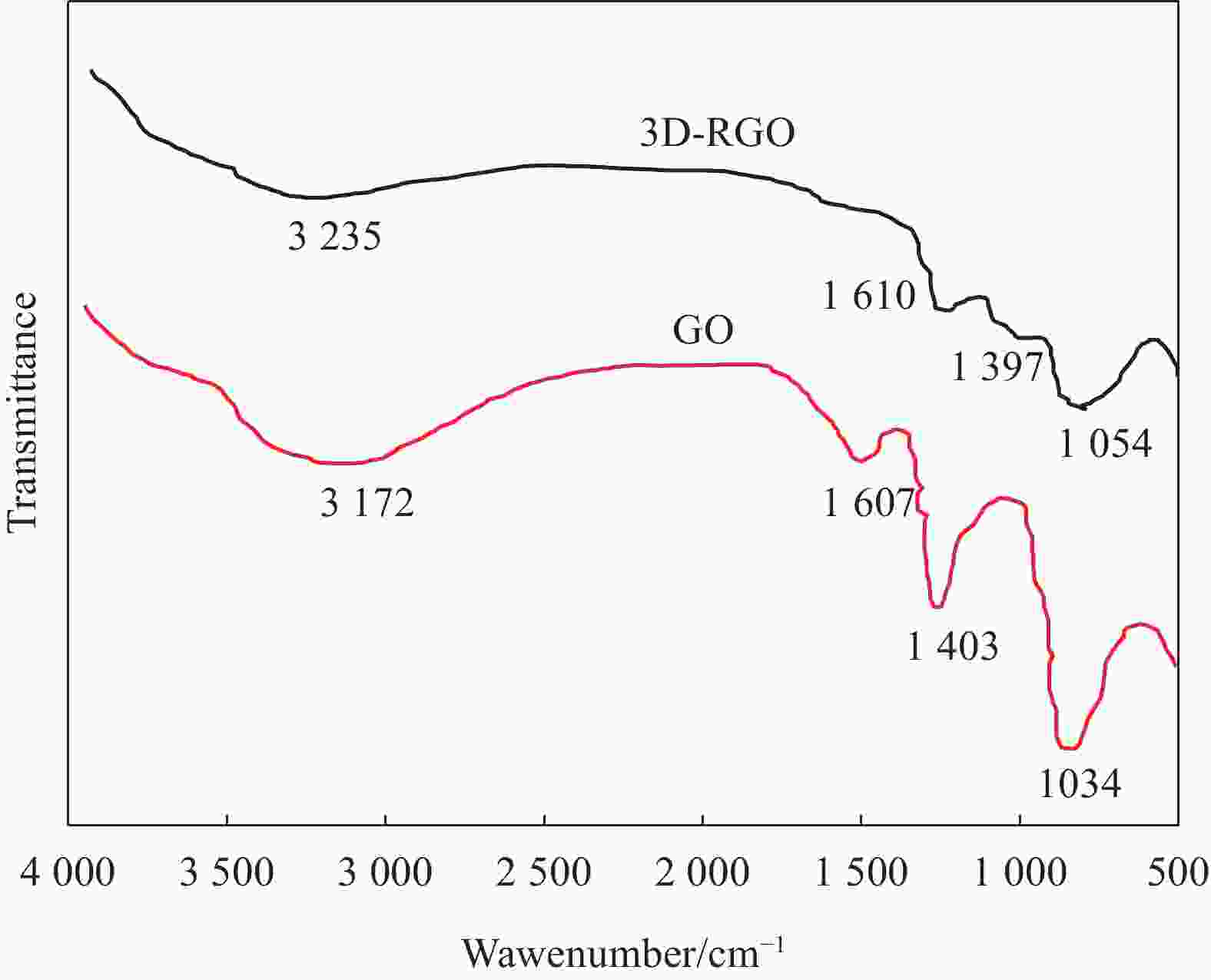
摘要: 为了实现石墨烯类三维气凝胶在温和环境条件下的大面积可控制备和高性能化,本文应用水合肼作为还原剂,通过低温预冷冻结合室温自然干燥,实现了室温还原自组装法可控制备直径30 cm的大面积三维还原氧化石墨烯(3D-RGO)气凝胶。该方法制备条件温和,不需任何加热条件和特殊冷冻干燥设备。通过对气凝胶制备过程中还原时间、预冷冻时间、预冷冻温度和反应容器进行控制,可以有效调节气凝胶的形状、表面浸润性、体积收缩率等,实现3D-RGO气凝胶的可控制备。该气凝胶不会出现明显的体积收缩和结构破裂,为具有约500 μm的稳定孔径和3.8 mg/cm3的低密度的蜂窝状结构,并能够从90%的压缩应变下快速地恢复到初始状态,其干燥过程体积收缩率<5%;同时该石墨烯气凝胶展现良好稳定的导电性,在压缩应变从0%增加到90%时,其导电率从17.3 S/m增加至115.2 S/m。这种方法经济高效且易于制备出大面积的3D-RGO。Abstract: In order to realize the large-area controllable preparation and high performance of graphene-based three-dimensional aerogels under mild environmental conditions, hydrazine hydrate is used as reducing agent in this paper. Through low-temperature pre-frozen combined with natural drying at room temperature, large-area three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide (3D-RGO) aerogels with a diameter of 30 cm can be prepared effectively and controlled. The method has mild preparation conditions and does not need any heating conditions or special freeze-drying equipment. By controlling the reduction time, pre-frozen time, pre-frozen temperature and reaction vessel during the preparation of 3D-RGO aerogel, the shape, surface wettability, volume shrinkage aerogel can be effectively adjusted to achieve controllable preparation of 3D-RGO aerogel. The 3D-RGO aerogel has no obvious volume shrinkage and structural cracks. The aerogels exhibit a stable honeycomb-like structure with a stable pore size of about 500 μm and a low density of 3.8 mg/cm3, and it can quickly undergo a compression strain of 90% and return to the initial state. The volume shrinkage rate of the aerogels is <5% in the drying process. At the same time, the graphene aerogel exhibits good and stable conductivity. When the compressive strain increases from 0% to 90%, its conductivity increases from 17.3 S/m to 115.2 S/m. This method is suitable for the cost-effective preparation of large-area graphene aerogels.
-
表 1 不同方法制备的3D-RGO气凝胶密度、压缩应变与尺寸比较
Table 1. Density, compressive strain and size ratio of 3D-RGO aerogel prepared by various methods
Sample Method Density/
(mg·cm−3)Compression strain Size/cm GFs[29] CVD ca. 5 No 17×22 Graphene aerogel[30] Supercritical drying 12-96 40% < 5 GF[31] Freeze-drying ca. 2.1 No < 5 UFAs[32] Freeze-drying 0.16 82% ca. 21 MGM[33] Freeze-drying 6.73 50% < 5 CMG-CNs[34] Freeze-drying 2.0 50% < 5 Graphene sponge [35] Freeze-drying 1.7 98% < 5 GFs [36] Sintering 11.3 10% ca. 10 Graphene aerogel [19] Vacuum-/air-drying 5.3 80% < 5 NDGA[2] Air-drying 6.7 99% ca. 10 ADGA[1] Air-drying 2.5 93% ca. 5 RGO/GNP[37] Air-drying ca. 100 50% < 5 GAB[38] Air-drying 2.8 99% >100 CNTS-GR[39] Freeze-drying 1.06 72% 5 3D-RGO
( This work)Air-drying 3.8 90% 30 Notes: GFs, GF—Graphene foams; UFAs—Ultra-flyweight aerogels; MGM—Macroporous graphene monoliths; CMG-CNs—Chemically modified graphene-cellular networks; NDGA—Naturally dried graphene aerogels; ADGA—Ambient pressure dried graphene aerogels; RGO/GNP—Reduced graphene oxide/graphene nanoplatelets; GAB—Graphene aerogel bulk; CNTS-GR—Carbon nanotubes-graphene aerogel; CVD—Chemical vapor deposition; ca.—About. -
[1] 郭奇, 高源, 荔栓红, 等. 石墨烯增强聚合物气密性的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3):896-906.GUO Qi, GAO Yuan, LI Shuanhong, et al. Research progress in the enhanced polymer airtightness of graphene[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(3):896-906(in Chinese). [2] XU X, ZHANG Q, YU Y, et al. Naturally dried graphene aerogels with superelasticity and tunable Poisson's ratio[J]. Advanced Materials,2016,28(41):9223-9230. doi: 10.1002/adma.201603079 [3] ZHAO X, YAO W, GAO W, et al. Wet-spun superelastic graphene aerogel millispheres with group effect[J]. Advanced Materials,2017,29(35):1701482. doi: 10.1002/adma.201701482 [4] MAO J, IOCOZZIA J, HUANG J, et al. Graphene aerogels for efficient energy storage and conversion[J]. Energy & Environmental Science,2018,11(4):772-799. [5] 朱薇, 江坤, 游峰, 等. 三维立体介孔结构的海藻酸钠/氧化石墨烯复合气凝胶的制备及其对亚甲基蓝的吸附[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(5):1696-1706.ZHU Wei, JIANG Kun, YOU Feng. Preparation of 3-dimensional mesoporous sodium alginate/graphene oxide composite aerogel for adsorption of methylene blue[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(5):1696-1706(in Chinese). [6] 张宏伟, 谢鸿, 肖欣荣, 等. 不同氧化程度氧化石墨烯/聚乙烯醇气凝胶对亚甲基蓝的吸附[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(9):2795-2802.ZHANG Hongwei, XIE Hong, XIAO Xinrong, et al. Adsorption of methylene blue by graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcoholaerogels with different oxidation degrees[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(9):2795-2802(in Chinese). [7] NINE M J, AYUB M, ZANDER A C, et al. Graphene oxide-based lamella network for enhanced sound absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2017,27(46):1703820. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201703820 [8] 朱世东, 赵乾臻, 王星海. 石墨烯/高分子功能复合材料制备与应用研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2):489-501.ZHU Shidong, ZHAO Qianzhen, WANG Xinghai. Research progress in preparation and application of graphene/polymer functional composite materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(2):489-501(in Chinese). [9] BI H, YIN K, XIE X, et al. Low temperature casting of graphene with high compressive strength[J]. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(37): 5124-5129. [10] WANG Z, SHEN X, AKBARI GARAKANI M, et al. Graphene aerogel/epoxy composites with exceptional anisotropic structure and properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(9):5538-5549. [11] BI H, CHEN I W, LIN T, et al. A new tubular graphene form of a tetrahedrally connected cellular structure[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(39): 5943-5949 [12] LV L, ZHANG P, CHENG H, et al. Solution-processed ultraelastic and strong air-bubbled graphene foams[J]. Small, 2016, 12(24): 3229-3234 [13] WANG C, CHEN X, WANG B, et al. Freeze-casting produces a graphene oxide aerogel with a radial and centrosymmetric structure[J]. ACS Nano,2018,12(6):5816-5825. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b01747 [14] WANG C, HE X, SHANG Y, et al. Multifunctional graphene sheet-nanoribbon hybrid aerogels[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(36):14994-15000. doi: 10.1039/C4TA02591A [15] WORSLEY M A, PAUZAUSKIE P J, OLSON T Y, et al. Synthesis of graphene aerogel with high electrical conductivity[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2010,132(40):14067-14069. doi: 10.1021/ja1072299 [16] LI J, LI J, MENG H, et al. Ultra-light, compressible and fire-resistant graphene aerogel as a highly efficient and recyclable absorbent for organic liquids[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(9):2934-2941. doi: 10.1039/c3ta14725h [17] 周浪, 王涛. 石墨烯/功能聚合物复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(5):997-1014.ZHOU Lang, WANG Tao. Graphene/functional polymer composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(5):997-1014(in Chinese). [18] 胡涵. 石墨烯气凝胶的控制制备、改性及性能研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2015.HU Han. Controlled preparation, modification and performance of graphene aerogel[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2015(in Chinese). [19] LI C, QIU L, ZHANG B, et al. Robust vacuum-/air-dried graphene aerogels and fast recoverable shape-memory hybrid foams[J]. Advanced Materials,2016,28(7):1510-1516. doi: 10.1002/adma.201504317 [20] ZHANG R, HU R, LI X, et al. A bubble-derived strategy to prepare multiple graphene-based porous materials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28(23):1705879. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201705879 [21] XIAO J, TAN Y, SONG Y, et al. A flyweight and superelastic graphene aerogel as a high-capacity adsorbent and highly sensitive pressure sensor[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2018,6(19):9074-9080. doi: 10.1039/C7TA11348J [22] XU X, ZHANG Q, YU Y, et al. Naturally dried graphene aerogels with superelasticity and tunable Poisson’s ratio[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(41): 9223-9230. [23] RUI C, TANAKA D, MENDES A. Reduced graphene oxide films as transparent counter-electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells [J]. Solar Energy, 2012, 86 (2): 716-724. [24] 郑晓明. 基于拉曼光谱的石墨烯研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2015.ZHENG Xiaoming. Research on graphene based on raman spectroscopy[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2015(in Chinese). [25] ZHANG J, YANG H, SHEN G, et al. Reduction of graphene oxide via L-ascorbic acid[J]. Chemical Communications,2010,46(7):1112-1114. doi: 10.1039/B917705A [26] RHEE J H, CHUNG C C, DIAU W G. A perspective of mesoscopic solar cells based on metal chalcogenide quantum dots and organometal-halide perovskites [J]. NPG Asia Materials, 2013, 5(10): e68. [27] MOON I K, YOON S, CHUN K Y, et al. Highly elastic and conductive N-doped monolithic graphene aerogels for multifunctional applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2015,25(45):6976-6984. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201502395 [28] LI C, DING M, ZHANG B, et al. Graphene aerogels that withstand extreme compressive stress and strain [J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(38): 18291-18299. [29] CHEN Z, REN W, GAO L, et al. Three-dimensional flexible and conductive interconnected graphene networks grown by chemical vapour deposition[J]. Nature Materials,2011,10(6):424-428. doi: 10.1038/nmat3001 [30] ZHANG X, SUI Z, XU B, et al. Mechanically strong and highly conductive graphene aerogel and its use as electrodes for electrochemical power sources[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2011,21(18):6494-6497. doi: 10.1039/c1jm10239g [31] ZHAO Y, HU C, HU Y, et al. A versatile, ultralight, nitrogen-doped graphene framework[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2012,51(45):11371-11375. doi: 10.1002/anie.201206554 [32] SUN H, XU Z, GAO C. Multifunctional, ultra-flyweight, synergistically assembled carbon aerogels [J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25 (18): 2554-2560. [33] LI Y, CHEN J, HUANG L, et al. Highly compressible macroporous graphene monoliths via an improved hydrothermal process[J]. Advanced Materials,2014,26(28):4789-4793. doi: 10.1002/adma.201400657 [34] BARG S, PEREZ F M, NI N, et al. Mesoscale assembly of chemically modified graphene into complex cellular networks[J]. Nature Communications,2014,5(1):4328. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5328 [35] WU Y, YI N, HUANG L, et al. Three-dimensionally bonded spongy graphene material with super compressive elasticity and near-zero poisson’s ratio[J]. Nature Communications,2015,6(1):6141. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7141 [36] LI Y, ZHANG H B, ZHANG L, et al. One-pot sintering strategy for efficient fabrication of high-performance and multifunctional graphene foams[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(15):13323-13330. [37] YANG J, LI X, HAN S, et al. Air-dried, high-density graphene hybrid aerogels for phase change composites with exceptional thermal conductivity and shape stability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4(46):18067-18074. doi: 10.1039/C6TA07869A [38] YANG H, LI Z, LU B, et al. Reconstruction of inherent graphene oxide liquid crystals for large-scale fabrication of structure-intact graphene aerogel bulk toward practical applications[J]. ACS Nano,2018,12(11):11407-11416. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b06380 [39] 刘亮, 鲍瑞, 易健宏. 碳纳米管-石墨烯气凝胶的制备与性能 [J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(10): 2296-2303.LIU Liang BAO Rui, YI Jianhong. Preparation and properties of CNTs-graphene aerogel[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(10): 2296-2303(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: