Wrinkles in fiber-reinforced resin composites: Micro-stress non-destructive testing
-
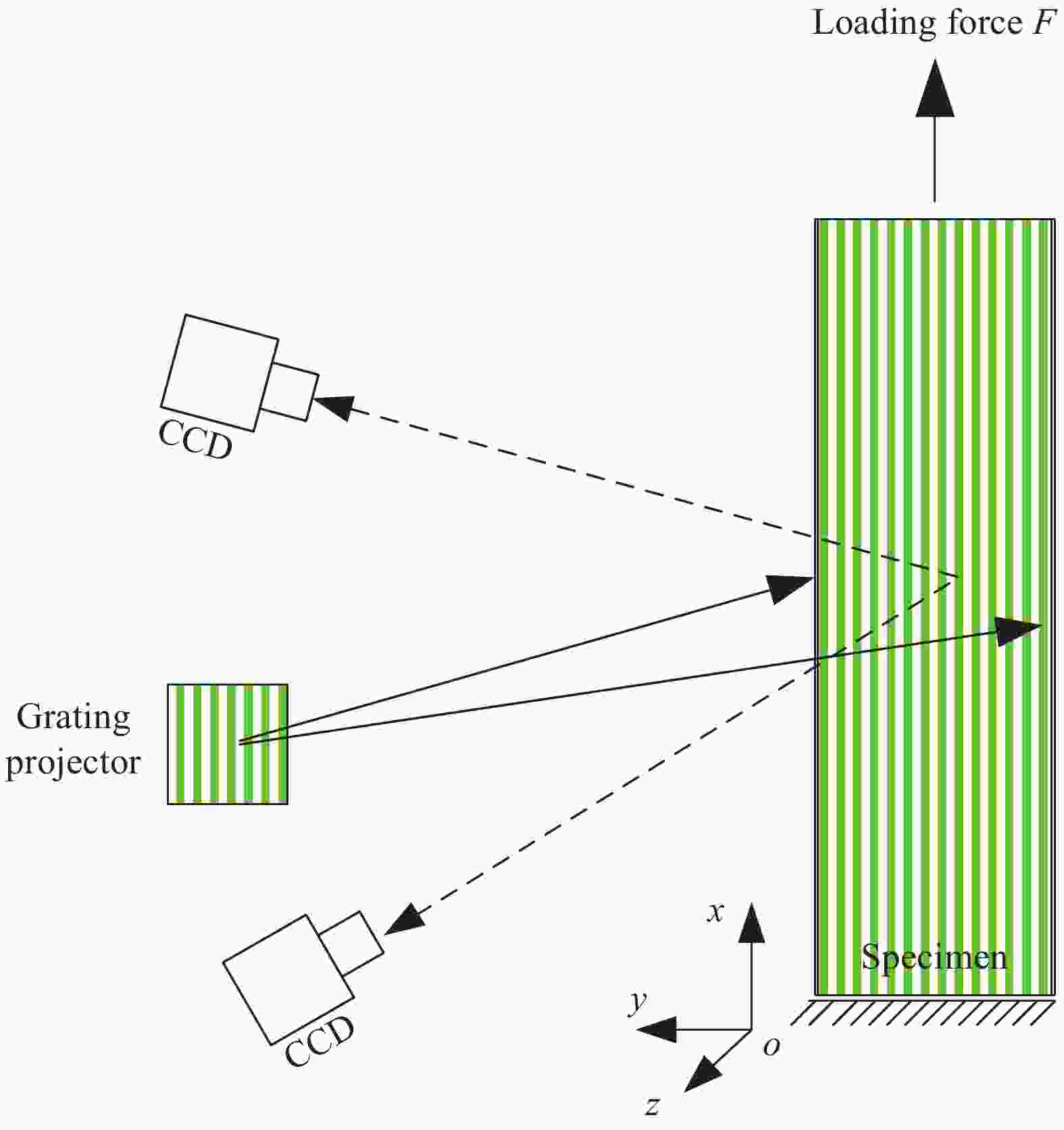
摘要: 纤维增强树脂复合材料在制造和服役过程中会不可避免地产生各类缺陷,且缺陷种类多、特征尺寸分散,检测难度大。缺陷检测的最终目的是对含缺陷构件的机械力学性能给出适应性评价,为此提出了一种特别适合于纤维增强树脂复合材料的集缺陷检测和性能评价为一体的微应力无损检测方法。该方法对构件施加一定的载荷使其处于微应力状态,结合全场位移的光学测量技术,捕捉缺陷导致的异常响应,以褶皱缺陷为例给出了具体的实施过程。首先基于褶皱缺陷特征响应的预测结果设计了特定的检测方案,并基于光栅投影测量技术创新性地提出了一种测量离面位移的新方法。试验结果表明,在轴向微应力加载下,利用提出的光栅投影测量方法可以探测到褶皱缺陷导致的离面位移畸变,畸变的位置和大小反映了缺陷的位置和严重程度。同时由于使用了光-力学的综合检测方法,可以跨越对缺陷具体形貌尺寸的探查,直接获得含缺陷构件在给定工况下的力学行为响应,为构件适应性评价提供参考依据。
-
关键词:
- 纤维增强树脂复合材料 /
- 褶皱缺陷 /
- 特征响应 /
- 光栅投影 /
- 无损检测
Abstract: Various defects with dispersive feature sizes can be accumulated inevitably in fiber-reinforced resin composites during their manufacturing and service processes, which are also difficult to be detected. The final objective of defects testing is to obtain the accuracy assessment of performance of defective structures. A micro-stress non-destructive defect detection and evaluation method is proposed for fiber-reinforced resin composites, which is especially suitable for composites measurement. Combing with the optical measurement technology for full-field displacement, the abnormal responses which caused by the defects of the structure under low stress level is able to be captured. The wrinkle defect detection is taken as an example to show the measurement processes. First, a specific detection scheme is designed based on the theoretical prediction of characteristic responses of wrinkles. Then, a new method of full-field displacement measurement is innovatively proposed based on the grating projection technology. Results show that under the axial tensile loading, the distorted out-of-plane displacements caused by wrinkles can be detected by the improved grating projection technology. The distorted displacements revealed the spatial distribution and severity of defects, and the influence on structural performance degradation can be evaluated based on the degree of displacement distortion. Further, by applying the optical-mechanical detection method, the mechanical responses of the defective component under a given working condition can be obtained directly, which can provide a reference for the adaptability evaluation of the component. -
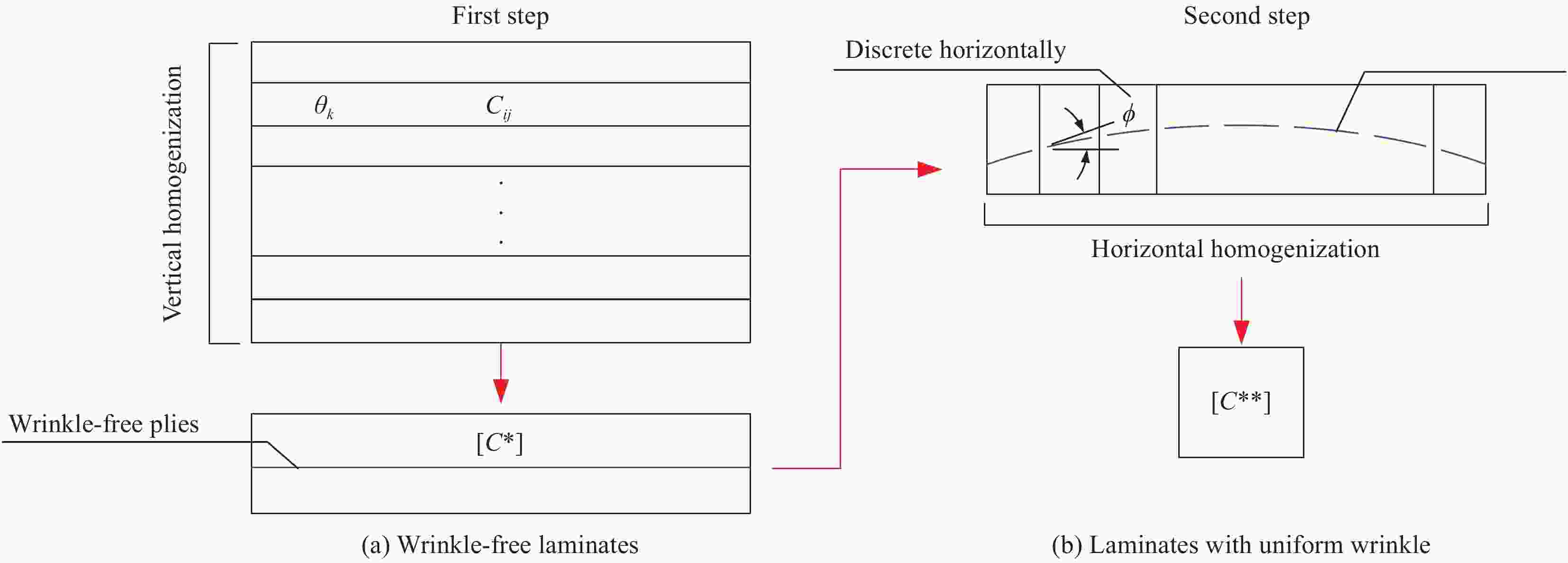
图 2 纤维增强树脂复合材料中含均匀型褶皱的RVE等效刚度计算模型
Figure 2. Calculation model of equivalent stiffness of RVE with uniform wrinkle in fiber-reinforced resin composites
Cij—Ply stiffness matrix; C*—Equivalent stiffness matrix of wrinkle-free laminates; C**—Equivalent stiffness matrix of laminates with uniform wrinkle; θk—Orientation angle of kth ply; φ—Out-of-plane misalignment
表 1 碳纤维(CF)/环氧树脂(EP)复合材料弹性参数
Table 1. Elastic parameters of carbon fiber (CF)/epoxy (EP) composites
E11 /GPa (E22 /E33) /GPa G23 /GPa G31 /GPa G12 /GPa ν21 ν32 ν31 133.3 9.09 3.16 7.24 7.23 0.261 0.436 0.261 Notes: E11, E22, E33—Elastic modulus (direction 11, 22, 33); G12, G23, G31—Shear modulus (direction 12, 23, 31); v21, v32, v31—Poisson’s ratio (direction 21, 32, 31). 表 2 CF/EP复材层合板中褶皱缺陷对不同载荷的响应敏感性
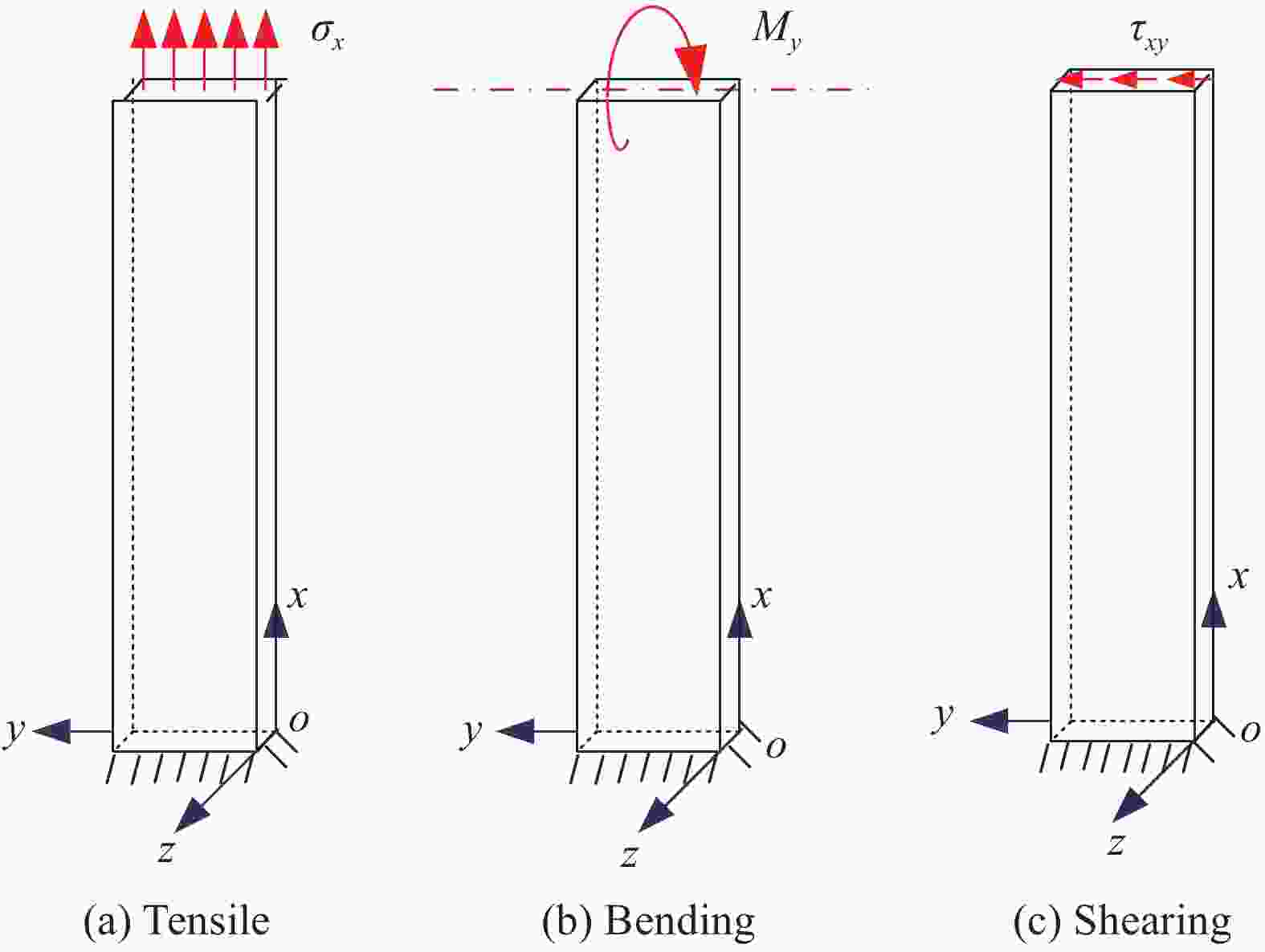
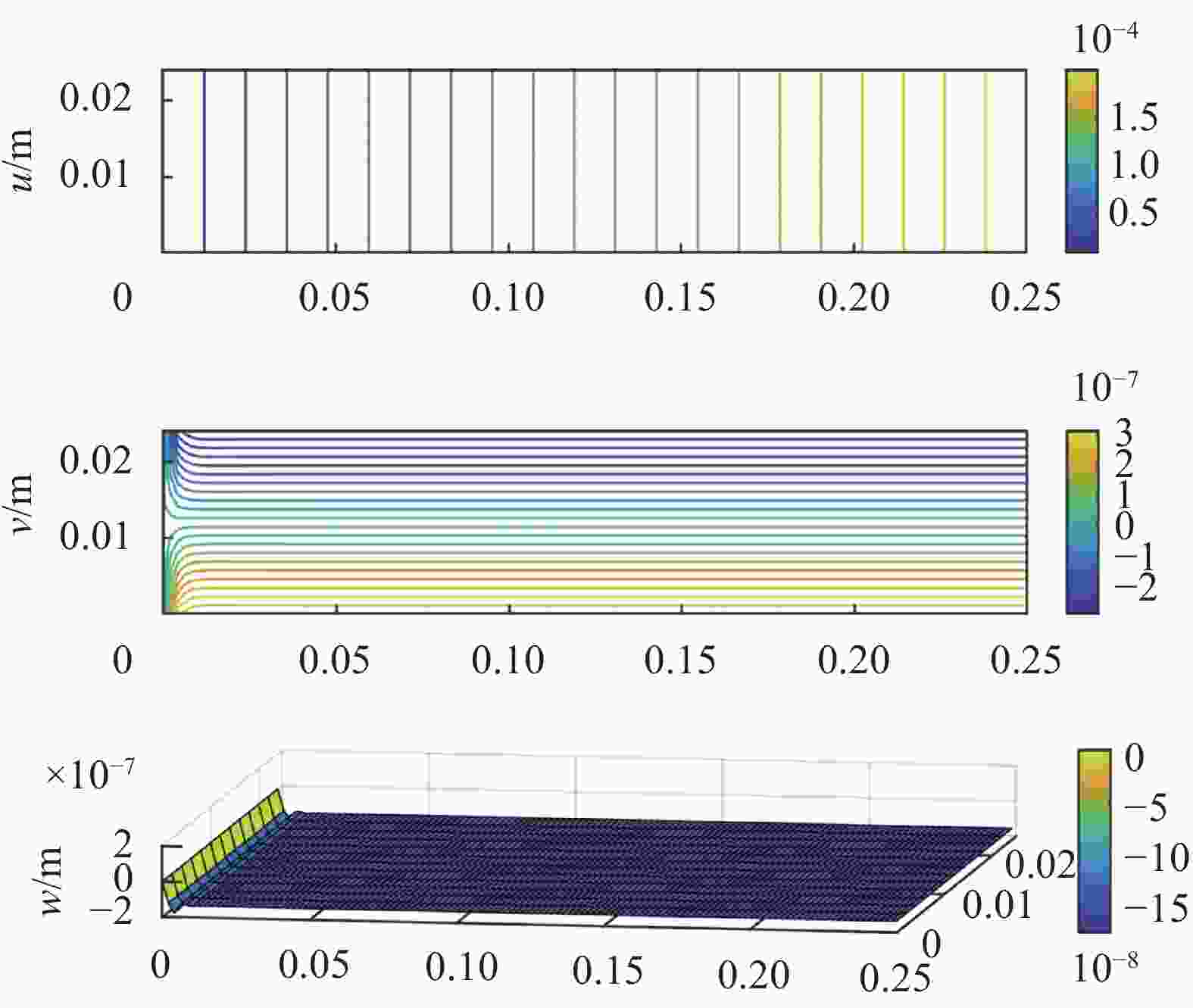
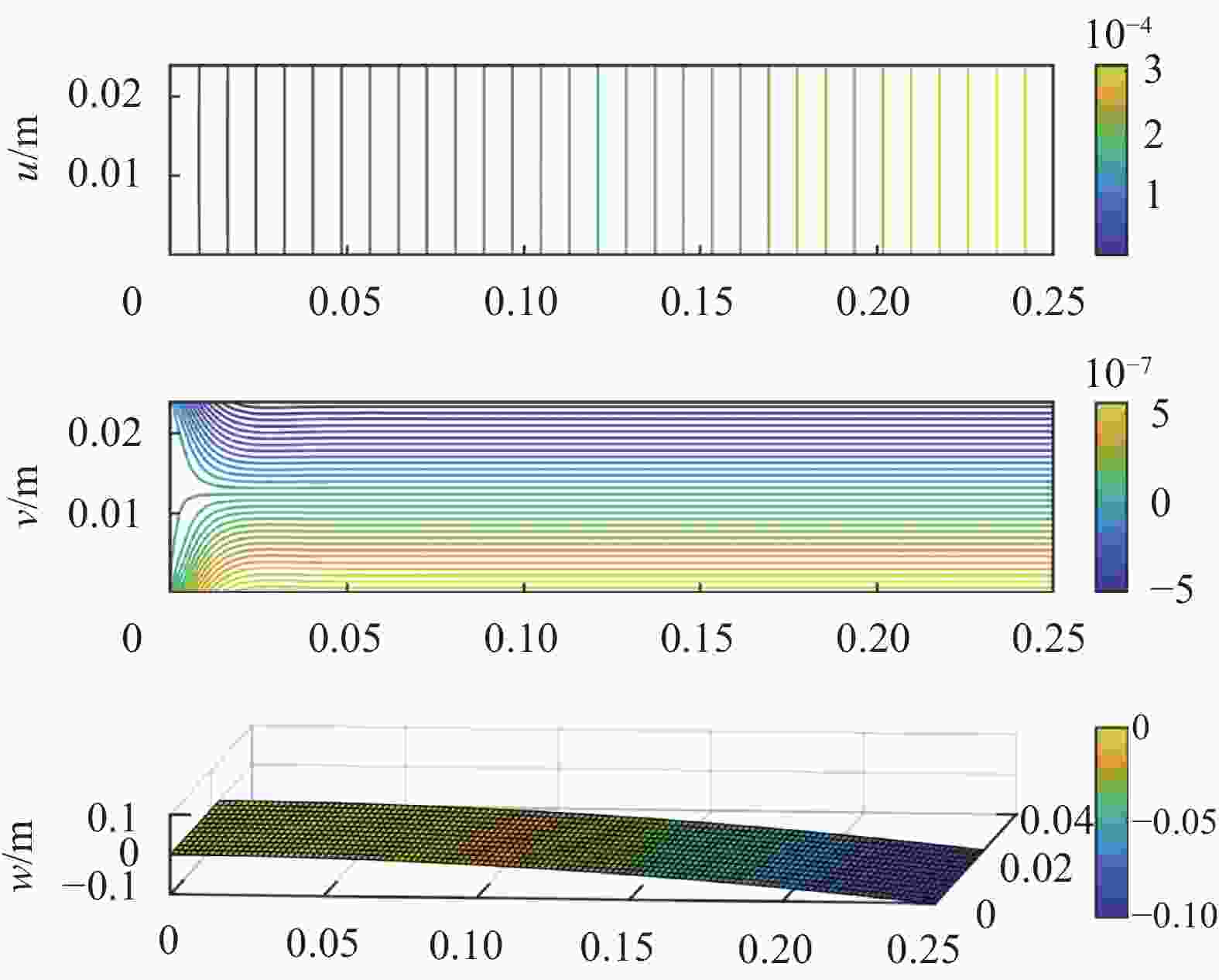
Table 2. Response sensitivity of wrinkle defects to different loading modes in CF/EP composite laminates
Loading mode Uniaxial tensile Bending Shearing Response sensitivity In-plane displacement u 


v 


Out-of-plane displacement w 


Note: *Sensitivity: 


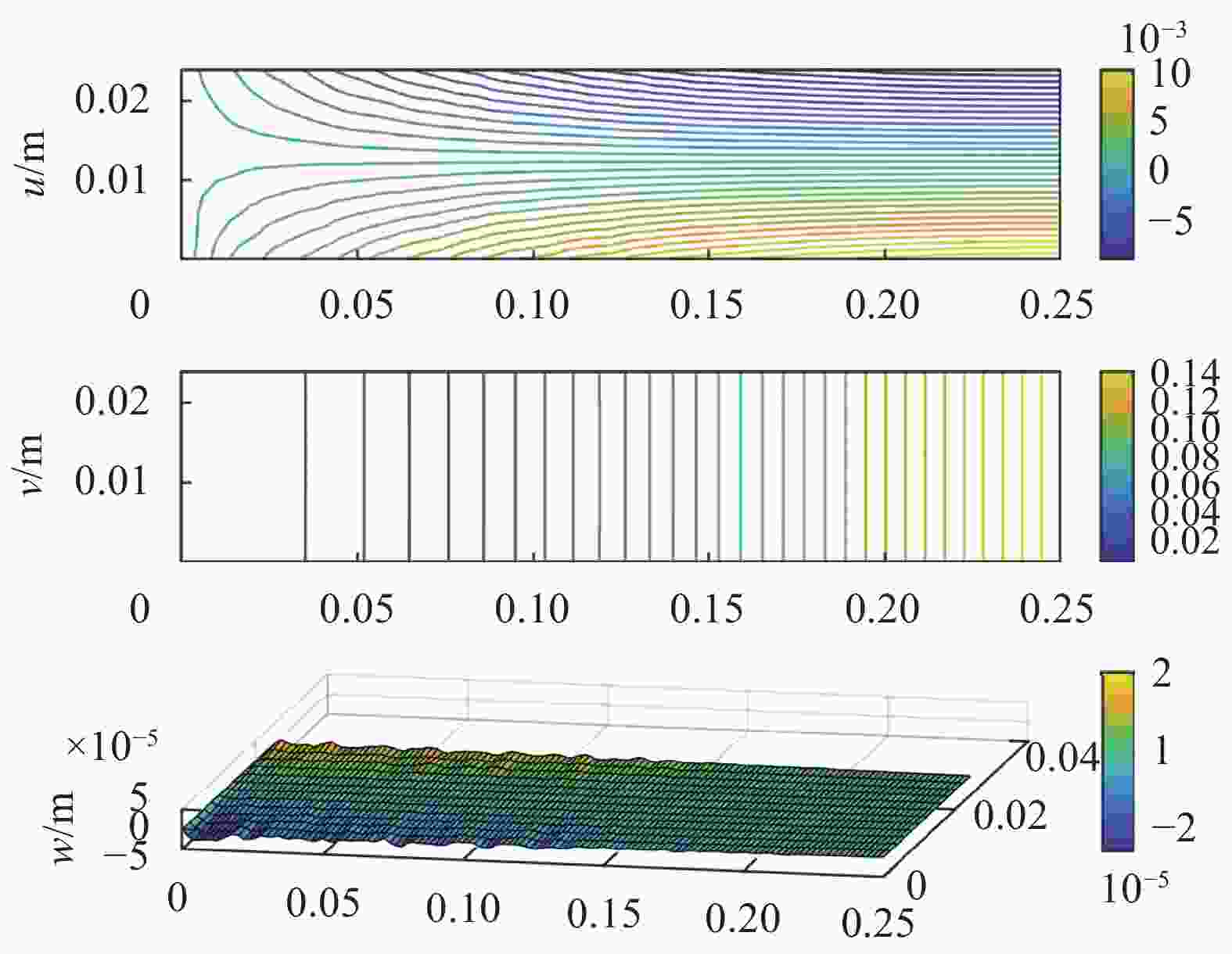
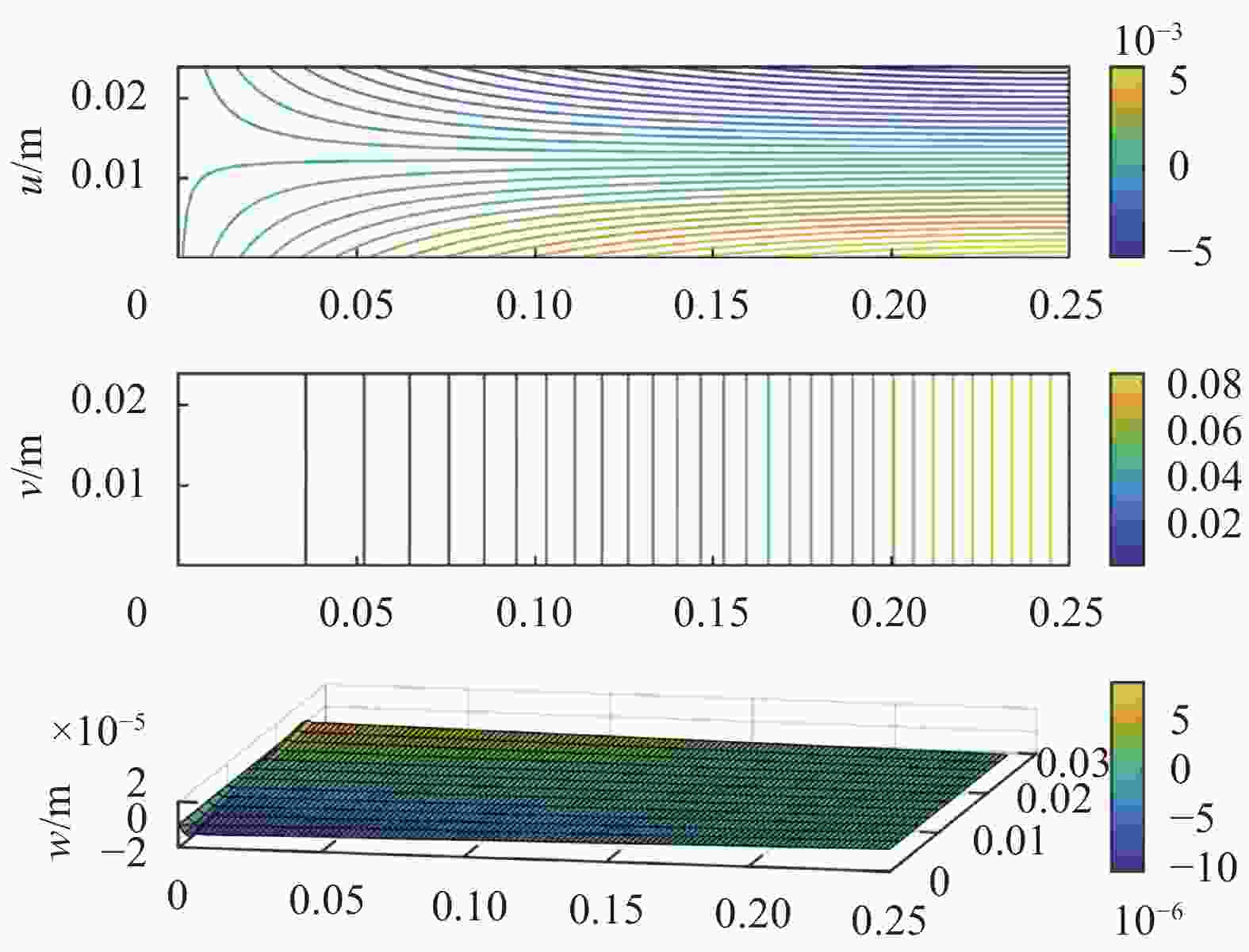
表 3 CF/EP复材层合板中层间弱粘结缺陷对不同载荷的响应敏感性[30]
Table 3. Response sensitivity of weak bonding defects to different loading modes in CF/EP composite laminates
Loading mode Uniaxial tensile Bending Shearing Response sensitivity In-plane displacement u 


v 


Out-of-plane displacement w 


表 4 CF/EP试样中的缺陷参数
Table 4. Defect parameters of the CF/EP specimens
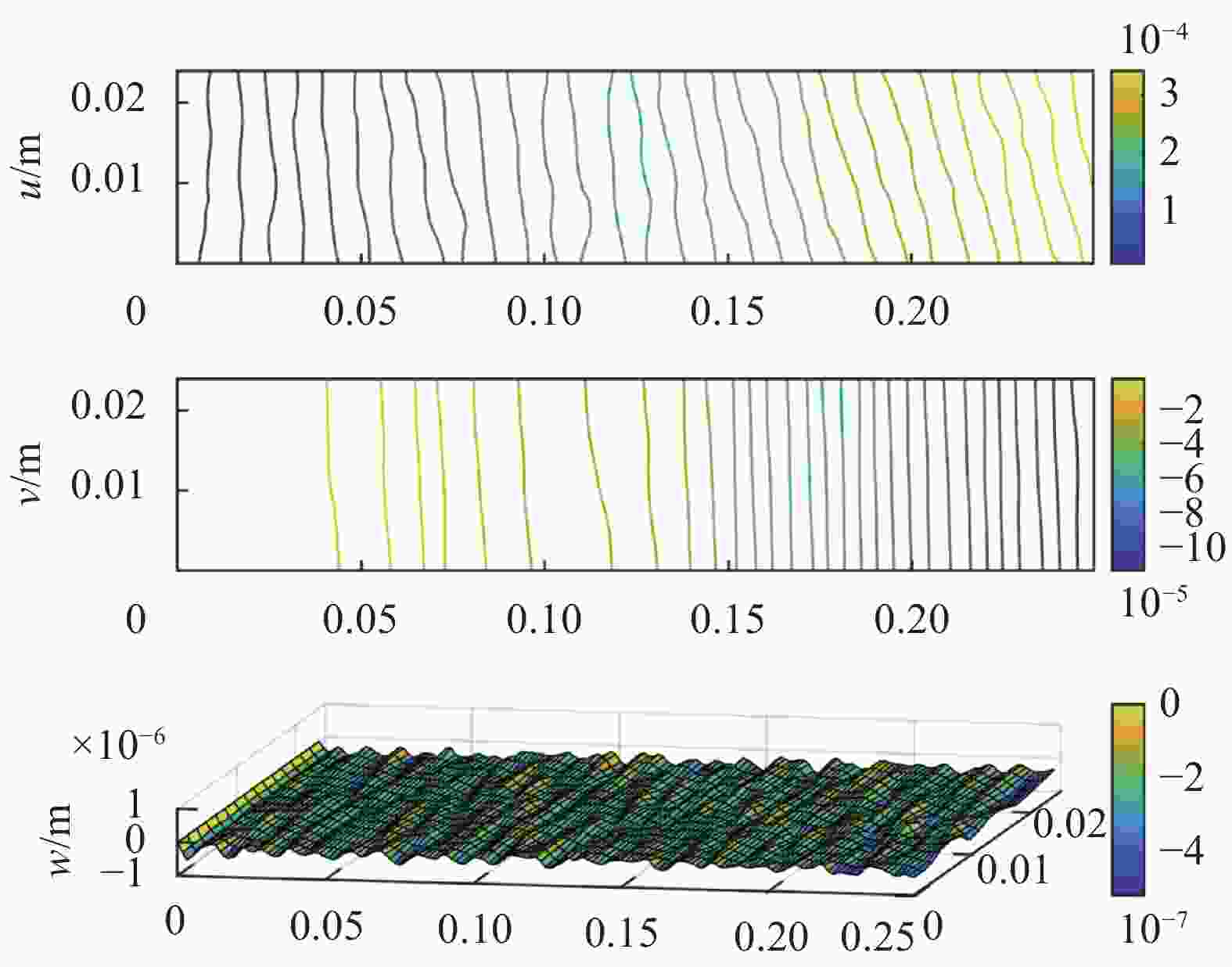
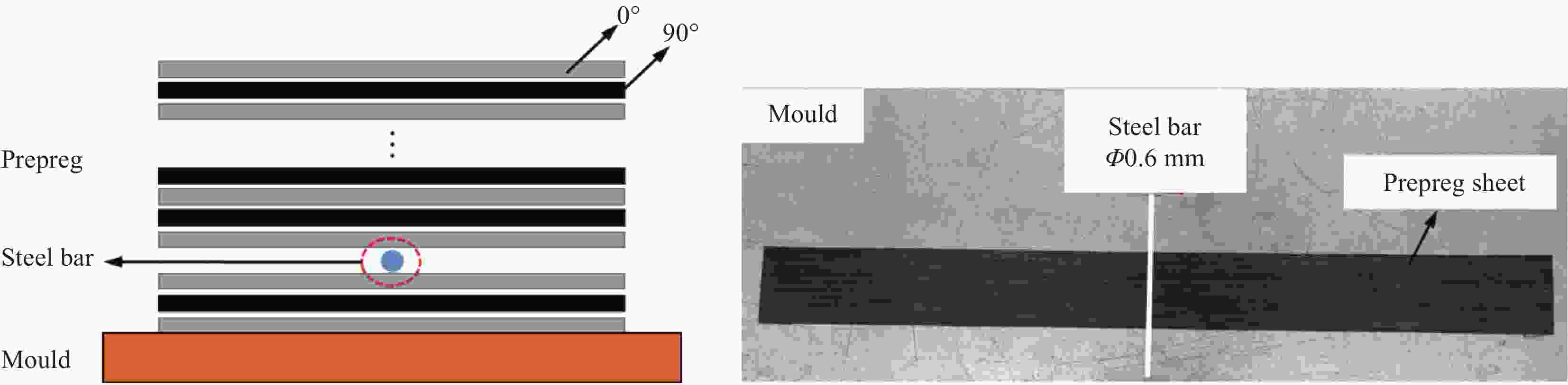
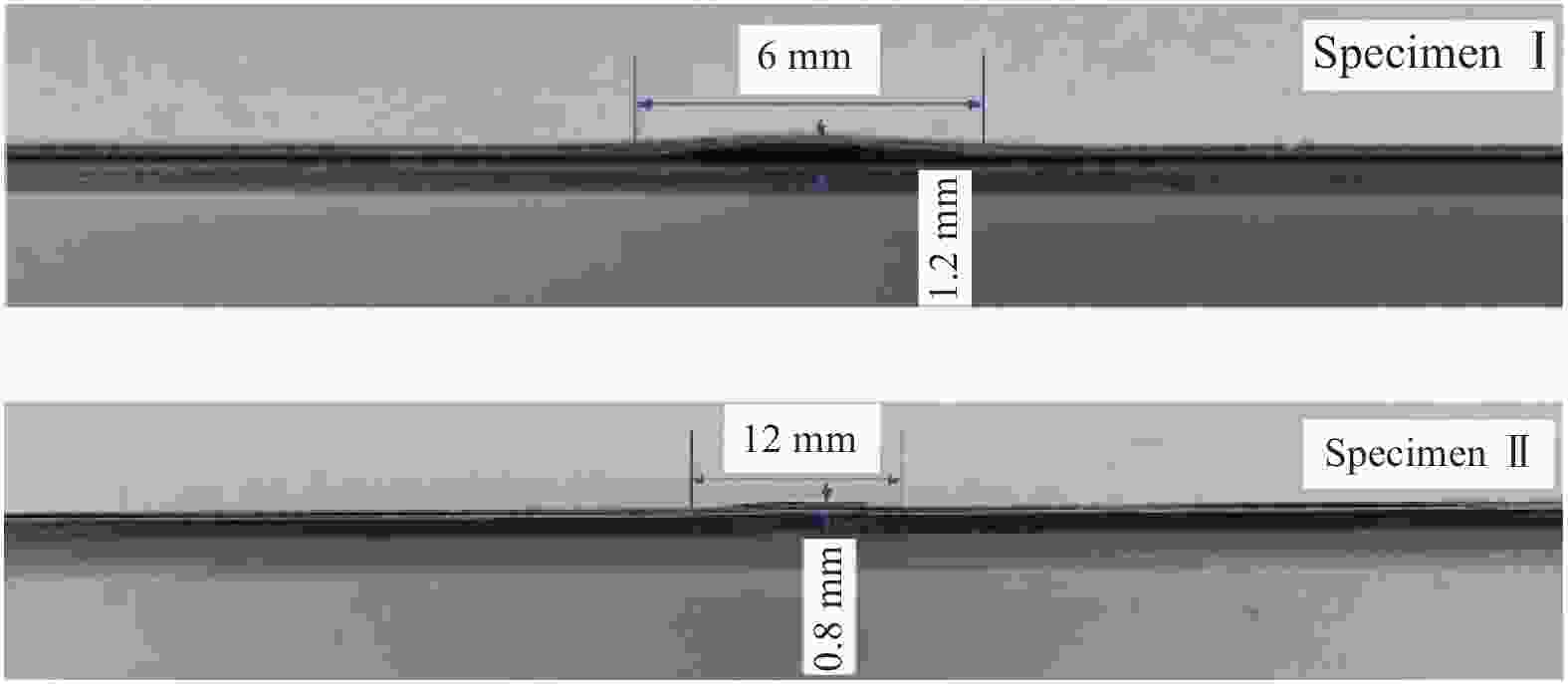
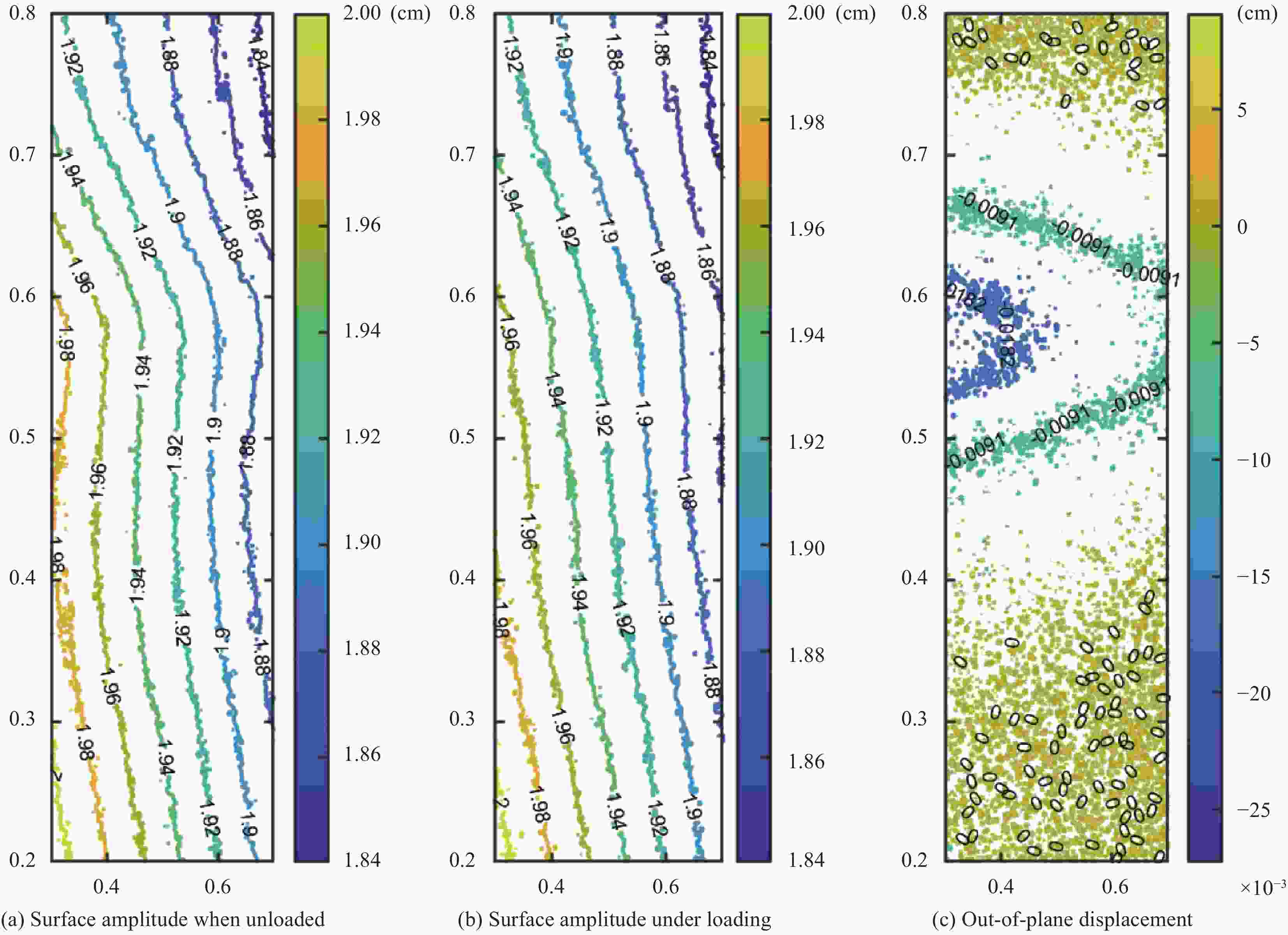
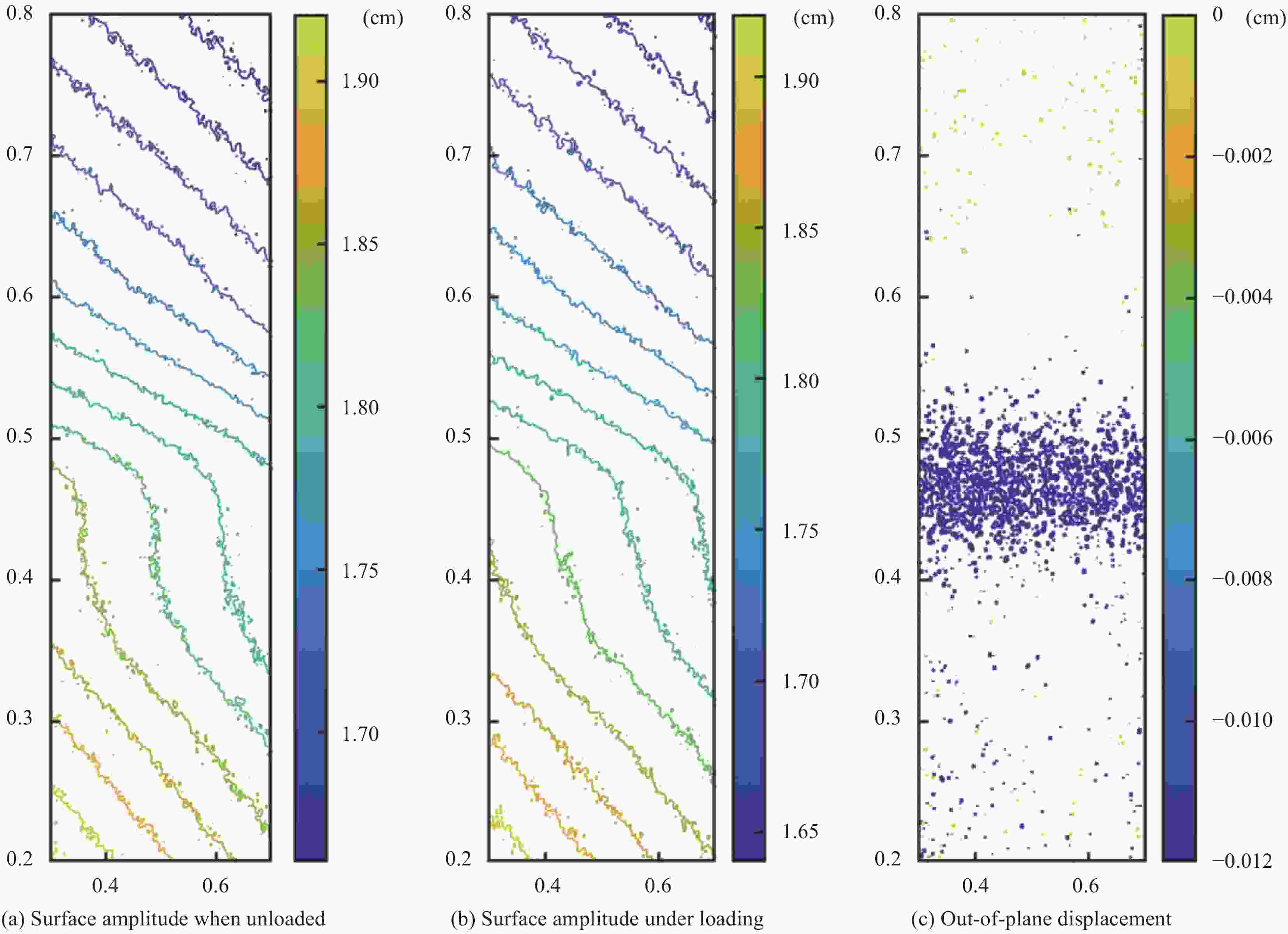
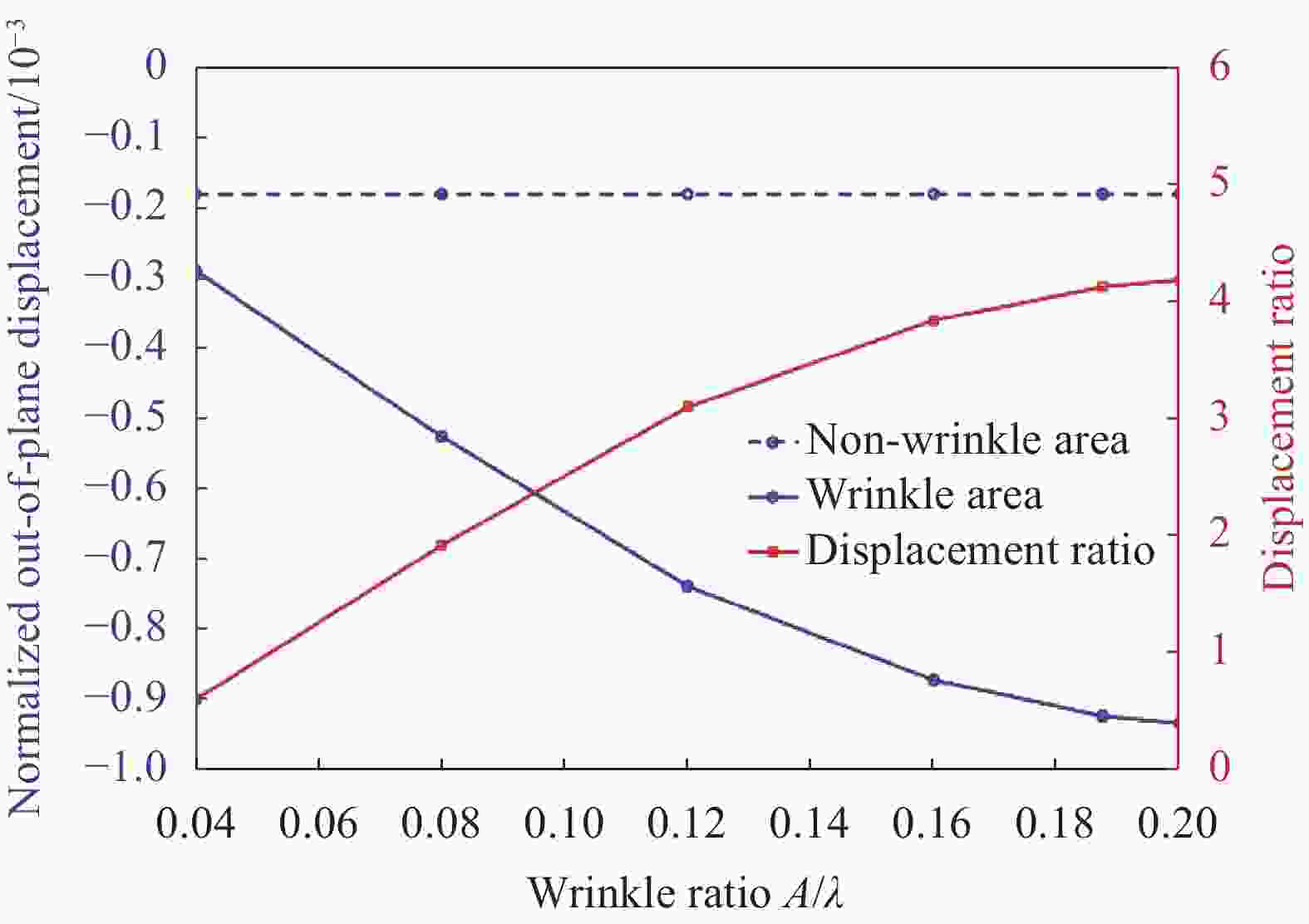
Specimen number Layup sequences Wrinkle parameters Wavelength/mm Amplitude/mm Wrinkle ratio I [0/90/0/90]s 6.0 1.2 0.200 II [0/90/0/90]s 12.0 0.8 0.067 表 5 CF/EP试样离面位移实测结果与有限元结果比较
Table 5. Comparison of out-of-plane displacement of CF/EP specimens between measurement results and finite element results
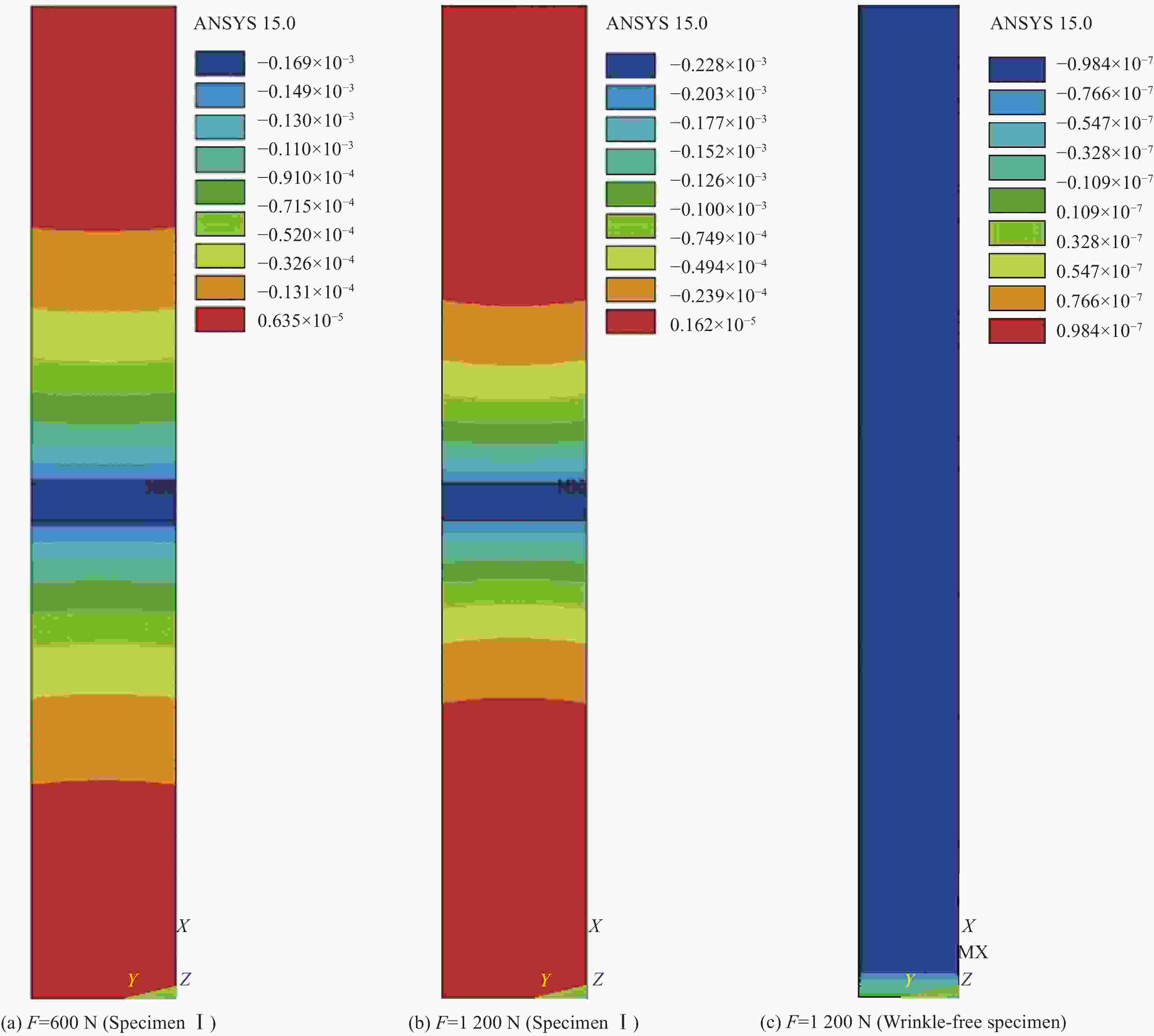
Specimen number Load/N Measurement results/cm Finite element results/cm Error I 200 0.01078 0.0089 17.7% 500 0.01806 0.0154 14.7% 800 0.02093 0.0193 7.8% 1 000 0.02359 0.0212 10.1% 1 200 0.02508 0.0228 10.0% Ⅱ 200 0.00218 0.0027 20.1% 500 0.00918 0.0101 8.6% 1 200 0.01361 0.0115 18.3% -
[1] 欧阳佳斯. 带波纹/褶皱类缺陷的纤维增强树脂基复合材料压缩性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.OUYANG Jiasi. Study on the compressive mechanical pro-perty of fiberreinforced composites with waviness defect[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [2] TAY T E, SHEN F. Analysis of delamination growth in lami-nated composites with consideration for residual thermal stress effects[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2002,36(11):1299-1320. doi: 10.1177/0021998302036011592 [3] 丁珊珊. 考虑孔隙形貌的CFRP复合材料超声散射机理及孔隙率检测方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2017.DING Shanshan. Ultrasonic scattering mechanism and porosity detection in CFRP composite materials considering void morphology[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [4] SAENZ-CASTILLO D, MARTÍN M I, CALVO S, et al. Effect of processing parameters and void content on mechanical properties and NDI of thermoplastic composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,121:308-320. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.03.035 [5] MUKHOPADHYAY S, JONES M I, HALLETT S R. Tensile failure of laminates containing an embedded wrinkle; numerical and experimental study[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,77:219-228. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.07.007 [6] NELSON L J, SMITH R A. Fibre direction and stacking sequence measurement in carbon fibre composites using Radon transforms of ultrasonic data[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,118:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.12.009 [7] SUTCLIFFE M P F, LEMANSKI S L, SCOTT A E. Measurement of fibre waviness in industrial composite components[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2012,72(16):2016-2023. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.09.001 [8] CREIGHTON C J, SUTCLIFFE M, CLYNE T W. A multiple field image analysis procedure for characterisation of fibre alignment in composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2001,32(2):221-229. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(00)00115-9 [9] REVOL V, PLANK B, KAUFMANN R, et al. Laminate fibre structure characterisation of carbon fibre-reinforced polymers by X-ray scatter dark field imaging with a grating interferometer[J]. NDT & E International,2013,58:64-71. [10] ZARDAN J P, GUEUDRE C, GORNELOUP G. Study of induced ultrasonic deviation for the detection and identification of ply waviness in carbon fibre reinforced polymer[J]. NDT & E International,2013,56(jun.):1-9. [11] LARRAÑAGA-VALSERO B, SMITH R A, TAYONG R B, et al. Wrinkle measurement in glass-carbon hybrid laminates comparing ultrasonic techniques: A case study[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,114:225-240. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.08.014 [12] ZHANG Z, LIU M, LI Q, et al. Visualized characterization of diversified defects in thick aerospace composites using ultrasonic B-scan[J]. Composites Communications,2020,22:100435. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2020.100435 [13] PARK B, AN Y, SOHN H. Visualization of hidden delamination and debonding in composites through noncontact laser ultrasonic scanning[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2014,100:10-18. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.05.029 [14] IBRAHIM M E, SMITH R A, WANG C H. Ultrasonic detection and sizing of compressed cracks in glass-and carbon-fibre reinforced plastic composites[J]. NDT & E International,2017,92:111-121. [15] ELHAJJAR R, HAJ-ALI R, WEI B. An infrared thermoelastic stress analysis investigation for detecting fiber waviness in composite structures[J]. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering,2014,53(12):1251-1258. doi: 10.1080/03602559.2014.886116 [16] KATUNIN A, DRAGAN K, DZIENDZIKOWSKI M. Damage identification in aircraft composite structures: A case study using various non-destructive testing techniques[J]. Composite Structures,2015,127:1-9. [17] LI Y, SUN B, GU B. Impact shear damage characterizations of 3D braided composite with X-ray micro-computed tomography and numerical methodologies[J]. Composite Structures,2017,176(9):43-54. [18] CHEN X. Fractographic analysis of sandwich panels in a composite wind turbine blade using optical microscopy and X-ray computed tomography[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis,2020,111:104475. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104475 [19] 洪友仁, 何浩培, 何小元. 剪切散斑: 一种光学测量技术及其应用[J]. 实验力学, 2006, 21(6):667-688. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4888.2006.06.001HONG Youren, HE Haopei, HE Xiaoyuan. Shearography: An optical measurement technique and applications[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics,2006,21(6):667-688(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4888.2006.06.001 [20] FERREIRA L M, GRACIANI E, PARÍS F. Three dimensional finite element study of the behaviour and failure mechanism of non-crimp fabric composites under in-plane compression[J]. Composite Structures,2016,149:106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.04.022 [21] LEONG M, HVEJSEL C F, THOMSEN O T, et al. Fatigue failure of sandwich beams with face sheet wrinkle defects[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2012,72(13):1539-1547. [22] AYMERICH F, DORE F, PRIOLO P. Prediction of impact-induced delamination in cross-ply composite laminates using cohesive interface elements[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2008,68(12):2383-2390. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.06.015 [23] TAKEDA T. Micromechanics model for three-dimensional effective elastic properties of composite laminates with ply wrinkles[J]. Composite Structures,2018,189:419-427. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.10.086 [24] 申川川, 马利, 文安戈, 等. 纤维增强树脂复合材料中的褶皱缺陷: 分散性与虚拟测试[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3):1332-1342. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210518.007SHEN Chuanchuan, MA Li, WEN Ange, et al. Wrinkles in fiber-reinforced resin composites (Part I): Heterogeneity and virtual test[J]. Acta Materiae Composites Sinica,2022,39(3):1332-1342(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210518.007 [25] MUKHOPADHYAY S, JONES M I, HALLETT S R. Compressive failure of laminates containing an embedded wrinkle; experimental and numerical study[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,73:132-142. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.03.012 [26] LEMANSKI S L, SUTCLIFFE M P F. Compressive failure of finite size unidirectional composite laminates with a region of fibre waviness[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(3):435-444. [27] RIDDLE T, CAIRNS D, NELSON J. Characterization of manu-facturing defects common to composite wind turbine blades: Flaw characterization[C]. 52nd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. Denver, 2011. [28] SHEN C, MA L, XU P, et al. Virtual testing of mechanical response of composite plates with normally distributed wrinkles[J]. Composite Structures,2019,229:111440. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111440 [29] MA L, SHEN C C, WEN A G, et al. Dependence between displacement distortion and heterogeneity of vegetable fiber composites[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 2022, 29: 1889079 . [30] SHEN C C, MA L, WEN A G, et al. Composite plates with randomly distributed weak bonding: Heterogeneity and virtual testing[J]. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures,2022,29:1928344. [31] FELIPE-SESÉ L, LÓPEZ-ALBA E, SIEGMANN P, et al. Integration of fringe projection and two-dimensional digital image correlation for three-dimensional displacements measurements[J]. Optical Engineering,2016,55(12):121711. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.55.12.121711 [32] WU Z J, GUO W B, PAN B, et al. A DIC-assisted fringe projection profilometry for high-speed 3D shape, displacement and deformation measurement of textured surfaces[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2021, 142: 106614. -






 下载:
下载: