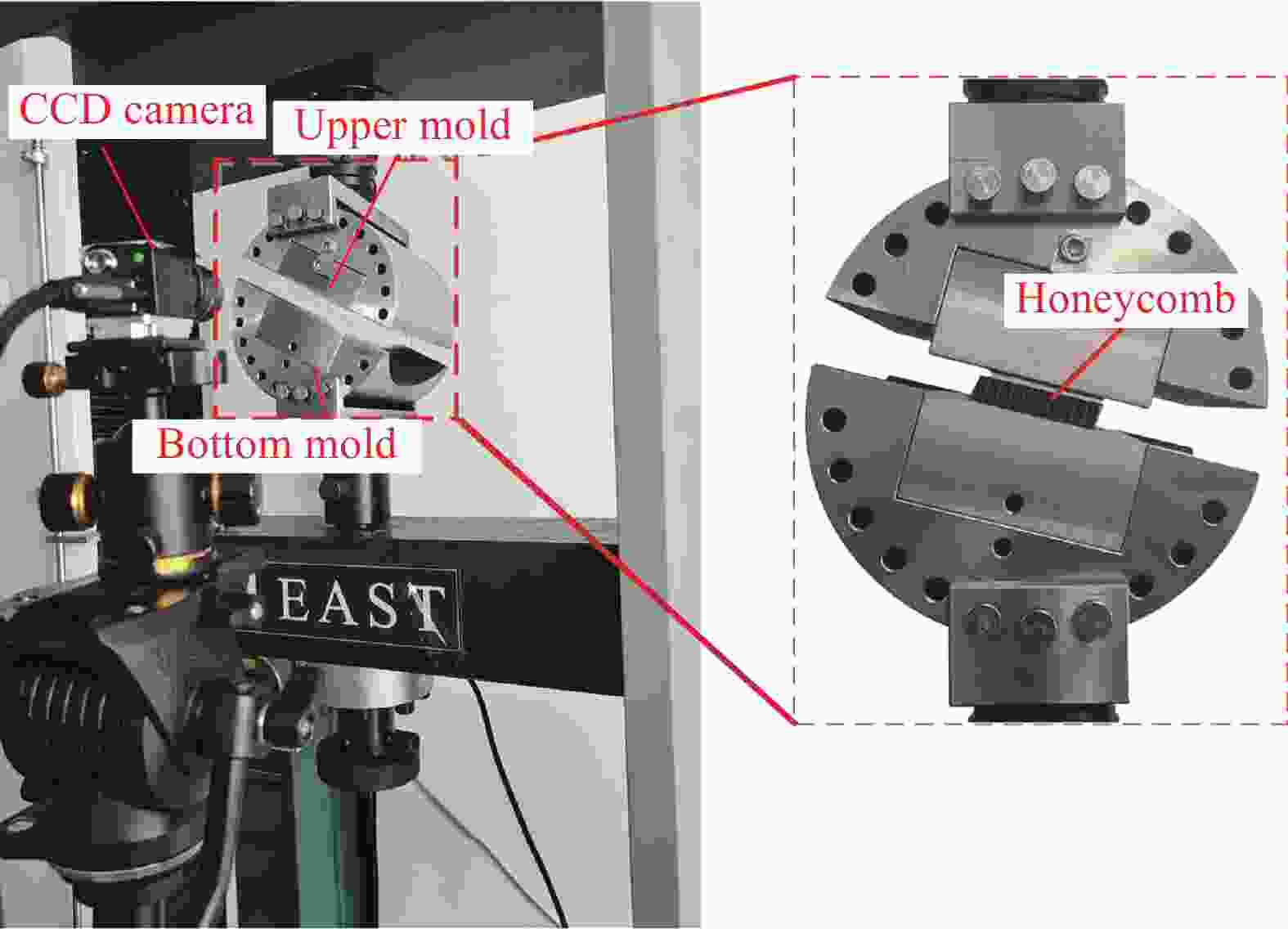
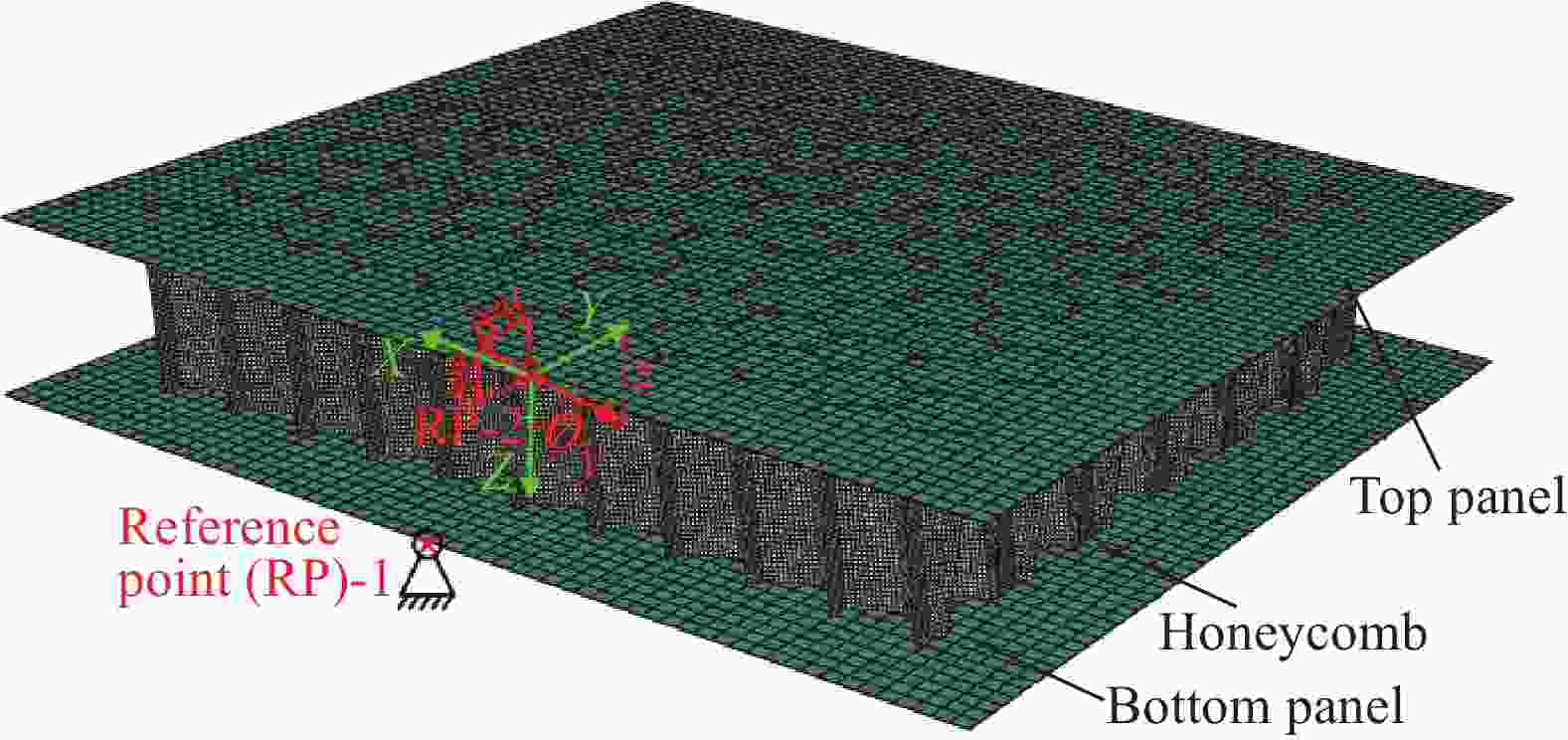
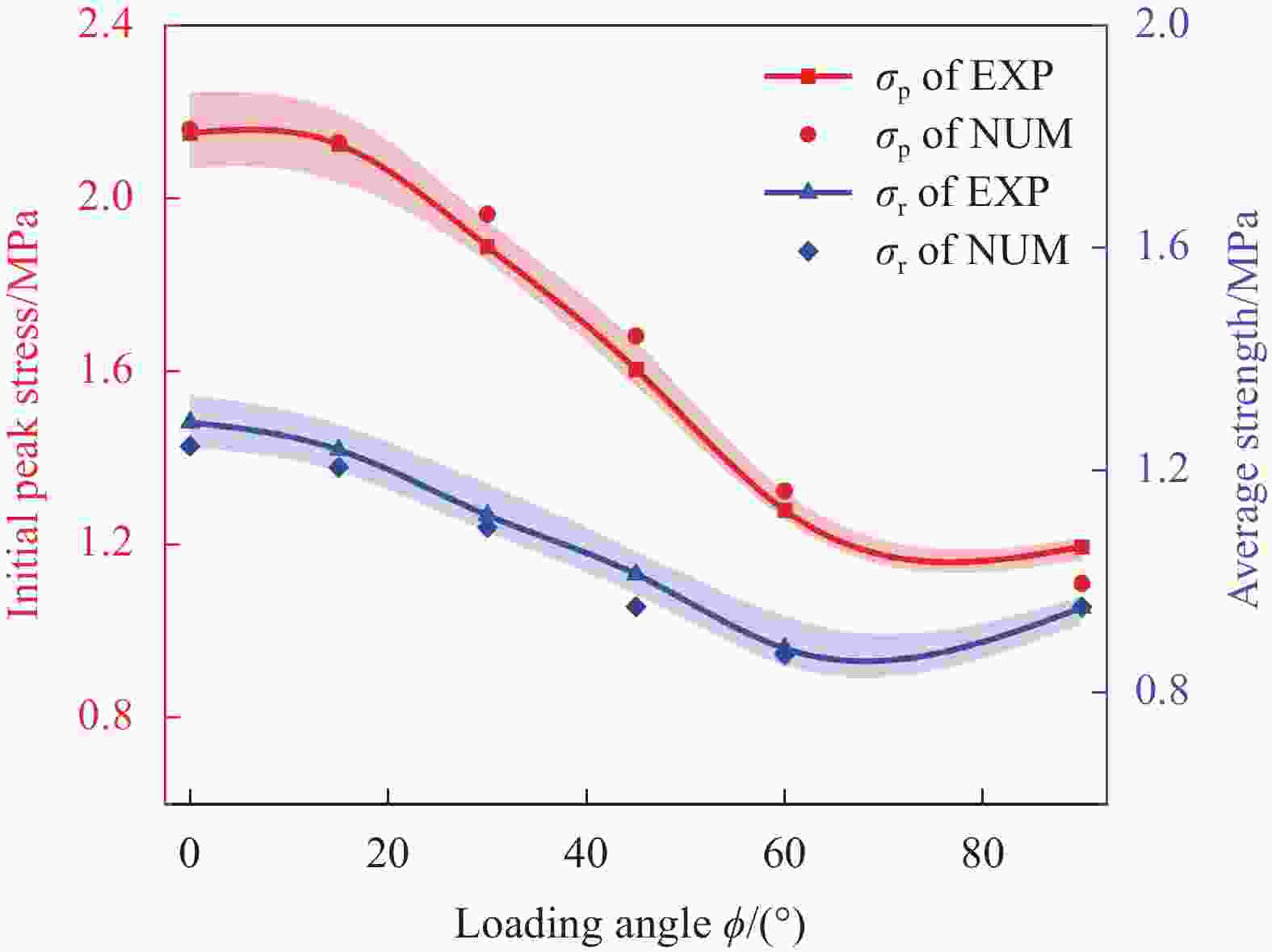
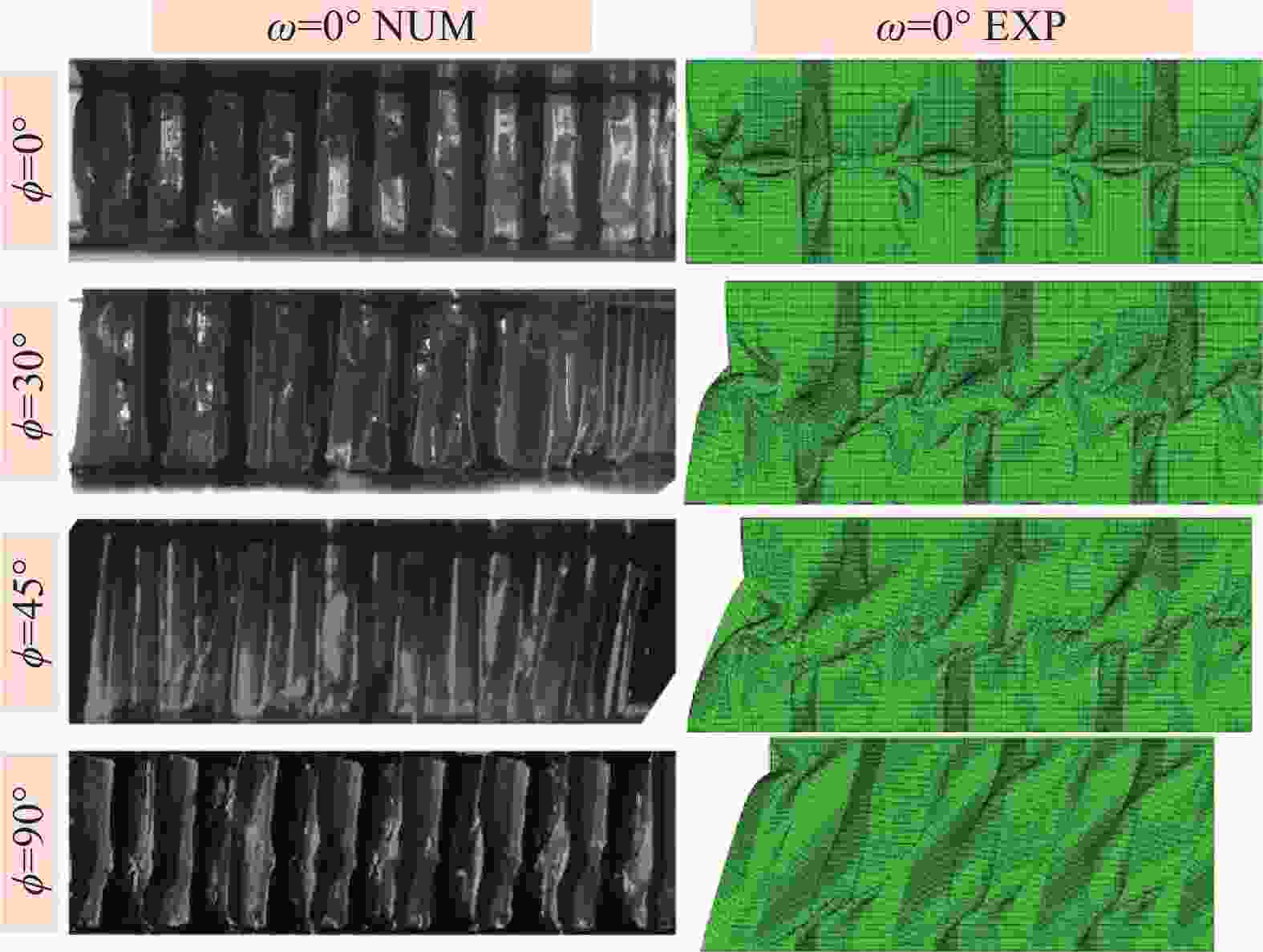
Mechanical response of inclined Nomex honeycombs under combined shear-compression loads
-
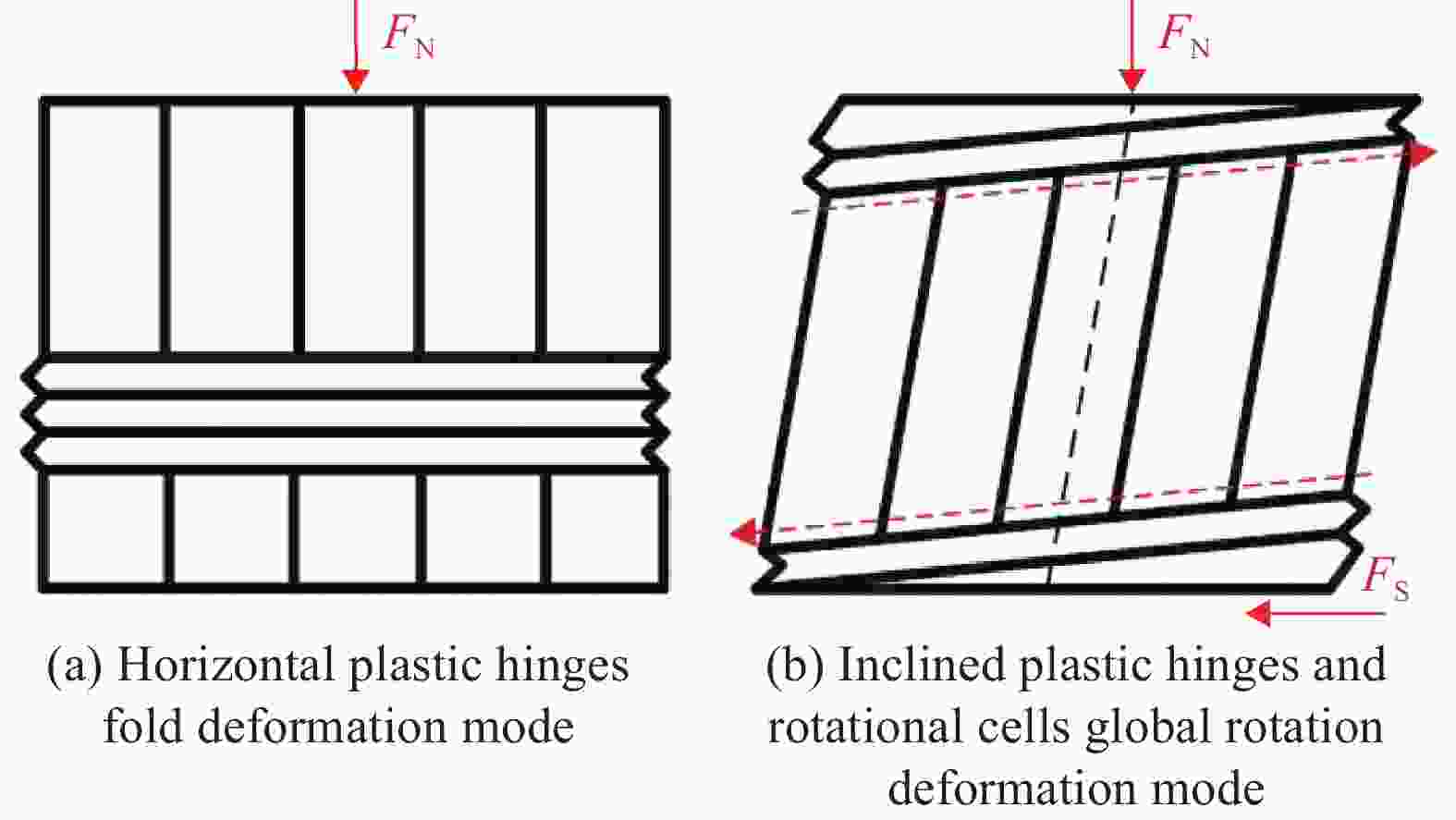
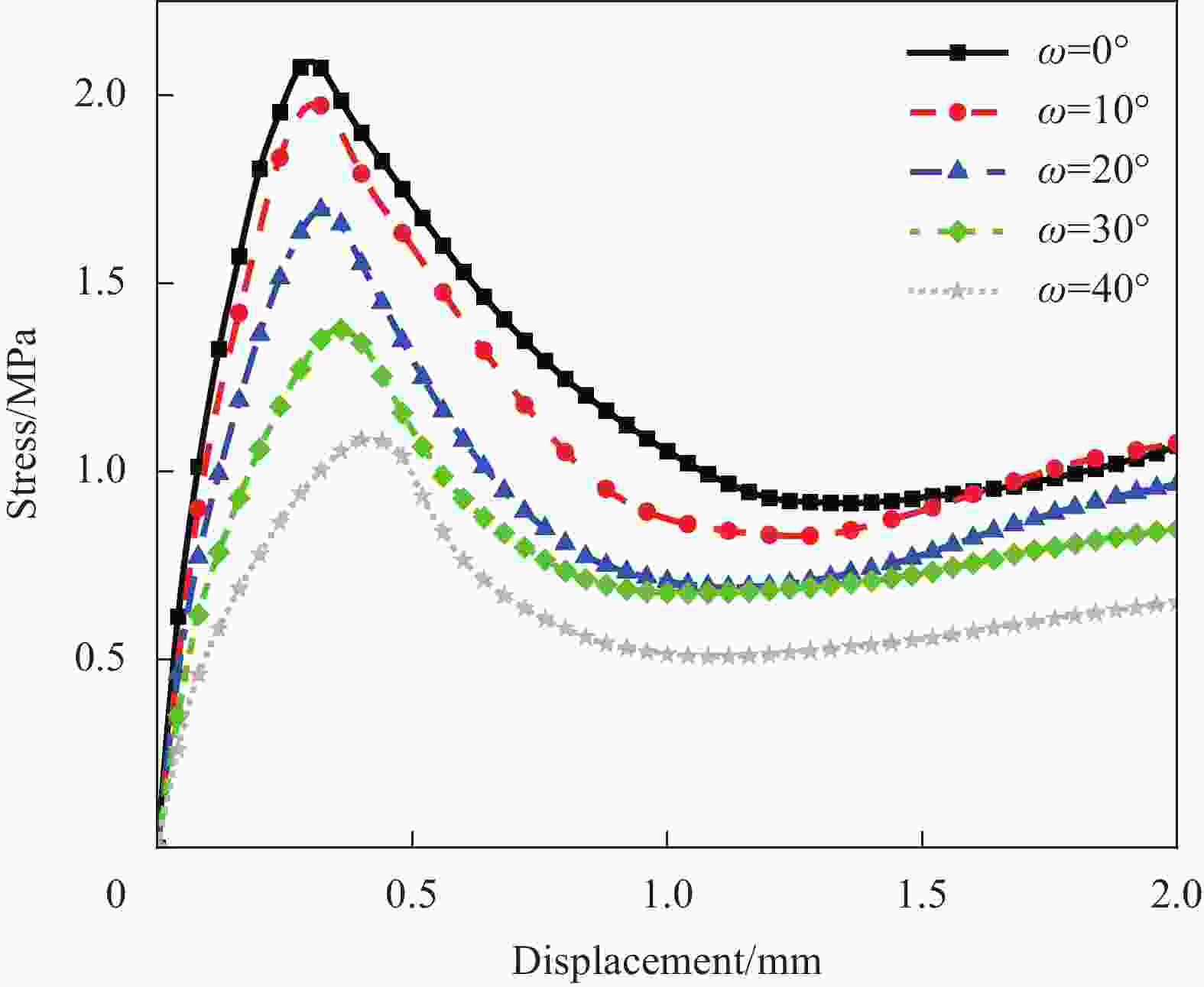
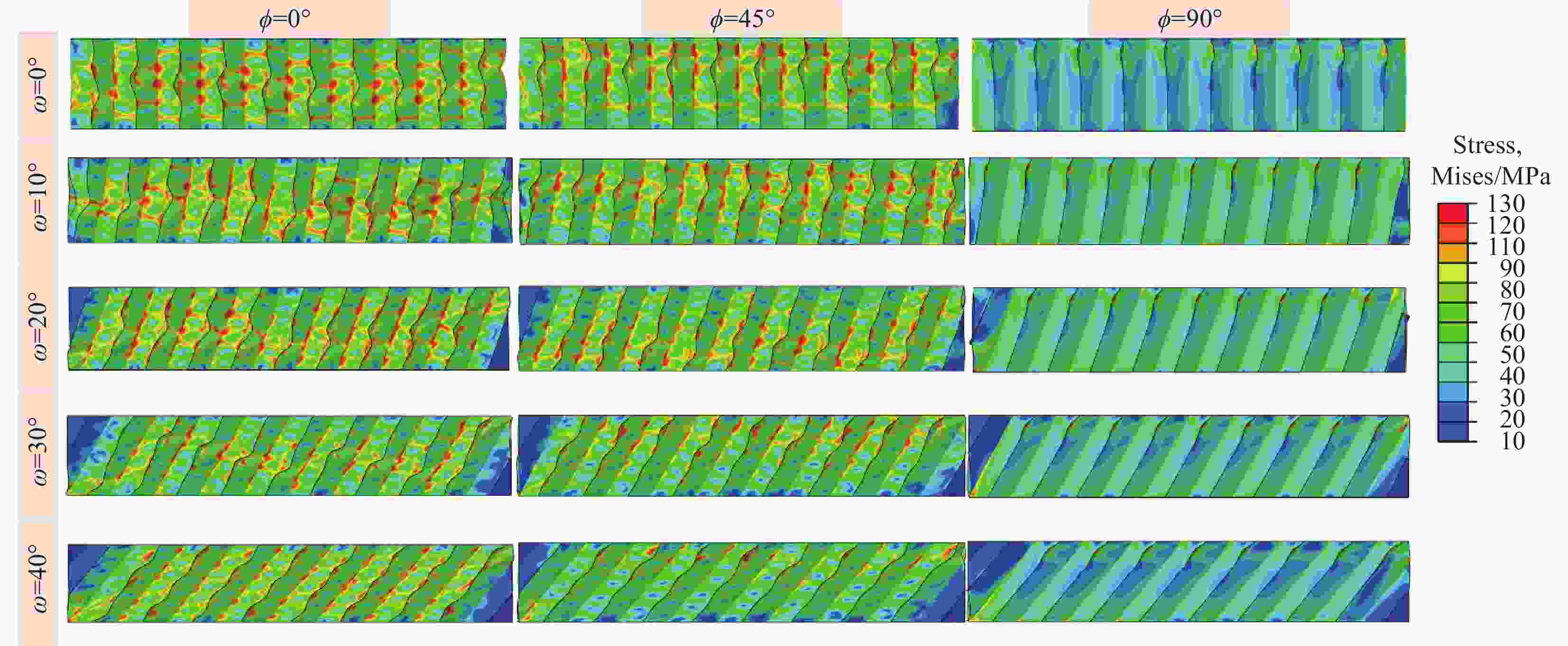
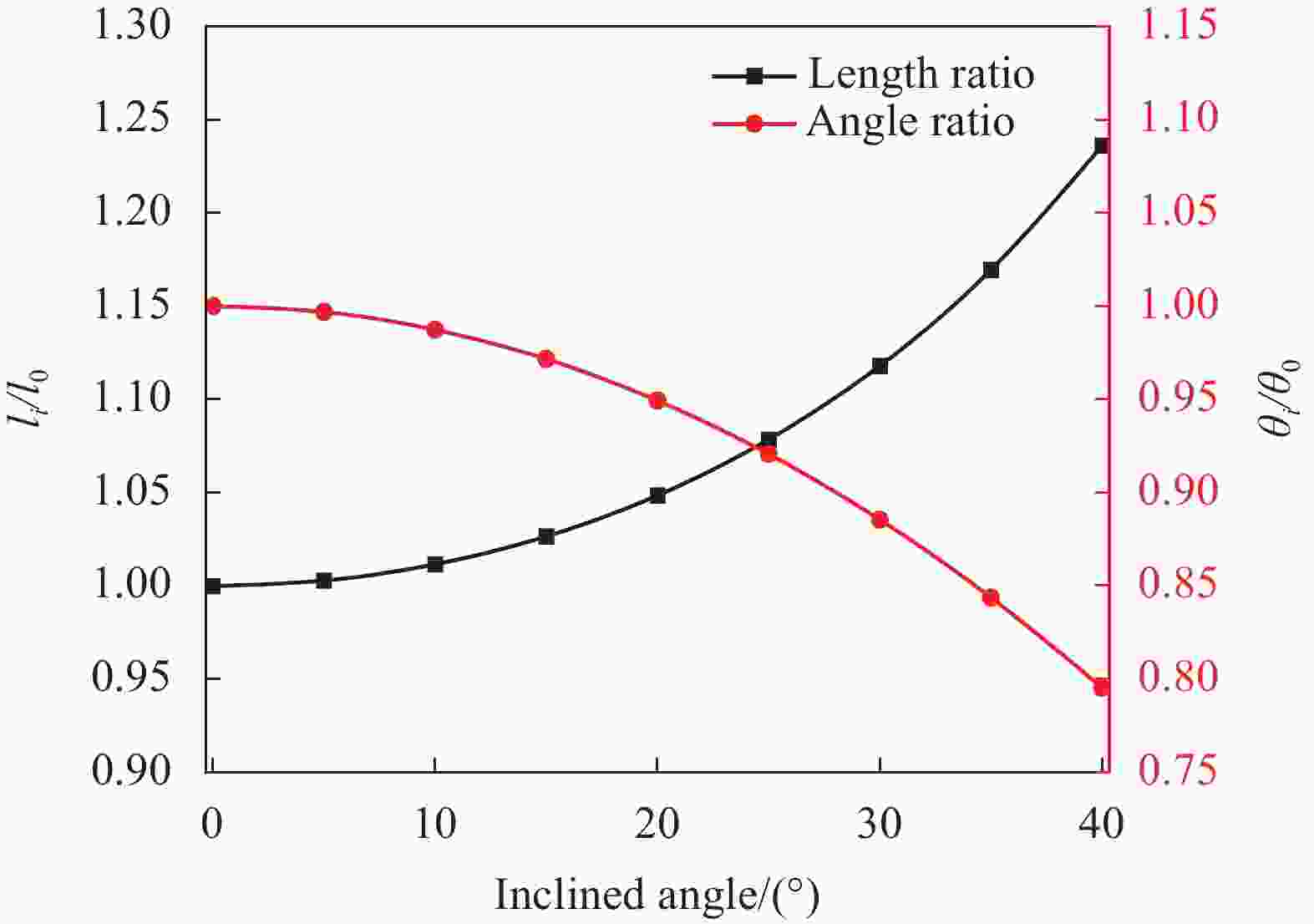
摘要: 成形具有一定曲率的夹层结构时,需要将蜂窝芯铣削成曲面形状,造成蜂窝胞壁呈一定倾角,进而降低蜂窝夹芯结构面外承载能力。为了定量化分析面外载荷作用下倾斜胞壁蜂窝芯的力学性能,建立了倾斜胞壁蜂窝芯面外压剪复合有限元模型,并通过设计专用Arcan夹具实现蜂窝芯的面外压剪复合加载,用于验证模型的有效性。对比仿真与实验结果,发现蜂窝芯压剪响应及胞壁变形模式吻合较好。利用验证的有限元模型对胞壁倾角范围为0°~40°的蜂窝芯在面外压剪复合载荷下的力学响应进行了研究,结果表明随着蜂窝胞壁倾角的增大,蜂窝芯面外承载能力逐渐降低;当胞壁倾斜角由0°增加到40°,初始应力峰值下降最大幅度为47.7%,平原阶段强度下降幅度为29%;进一步分析了倾斜胞壁蜂窝芯截面芯格尺寸与胞壁倾角的几何关系,将倾斜胞壁蜂窝芯等效为具有相同截面尺寸的垂直胞壁蜂窝芯,推导了倾斜胞壁蜂窝芯在面外压缩及剪切载荷作用下的坍塌强度,揭示了胞壁倾角对蜂窝芯坍塌强度影响机制。Abstract: When forming curved honeycomb sandwich structures, it needs to mill the honeycomb core into a curved shape, resulting in inclined cell walls of honeycombs and reducing its mechanical properties. A detailed finite element model was introduced to analyze the mechanical response and deformation mechanism of inclined honeycombs, and then verified by means of experiments using a specially designed set-up. The simulated results agree well with the experimental ones in terms of the crushing behavior and collapse mechanism. After that, the validated model was used to evaluate the effect of the inclined cell wall angle range from 0° to 40° on the crushing behavior of honeycombs. It is found that the inclined cell wall angle has a significant effect on the crushing response, and the mechanical properties of honeycomb decrease as the inclined cell wall angle increases. When the inclined cell wall angle varies from 0º to 40º, the maximum reduction of initial peak stress and the plateau strength is 47.7% and 29%, respectively. Moreover, the relationship between the dimension of cross-section about inclined cell wall honeycomb cores and the inclined angle was analyzed. The collapse stress of honeycomb under out-of-plane compression and shear loading is deduced by equivalent the inclined cell wall honeycomb as a vertical cell wall honeycomb with the same cross-section dimension, which reveals the influence mechanism of inclined cell wall angle on the properties of honeycombs.
-
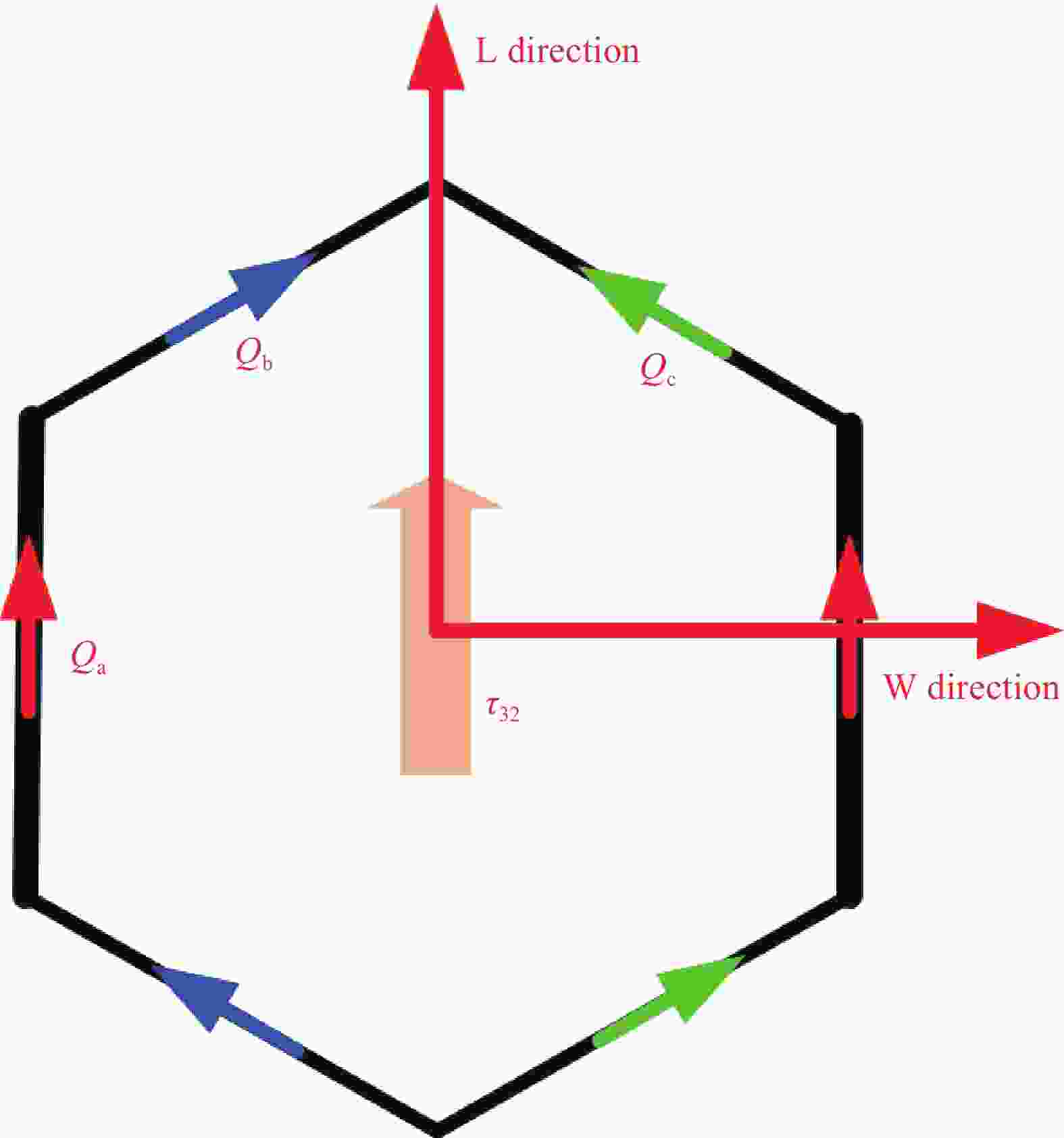
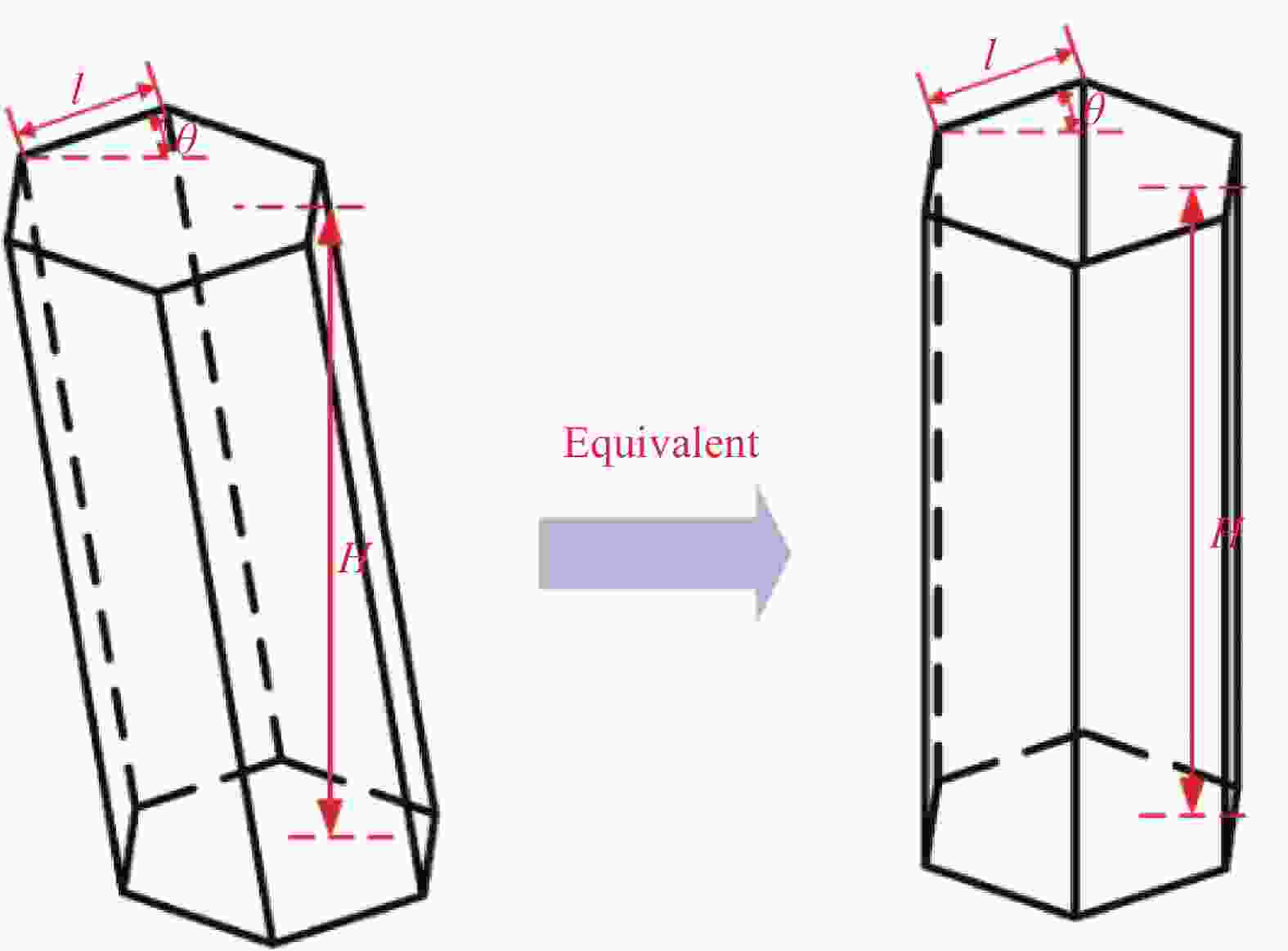
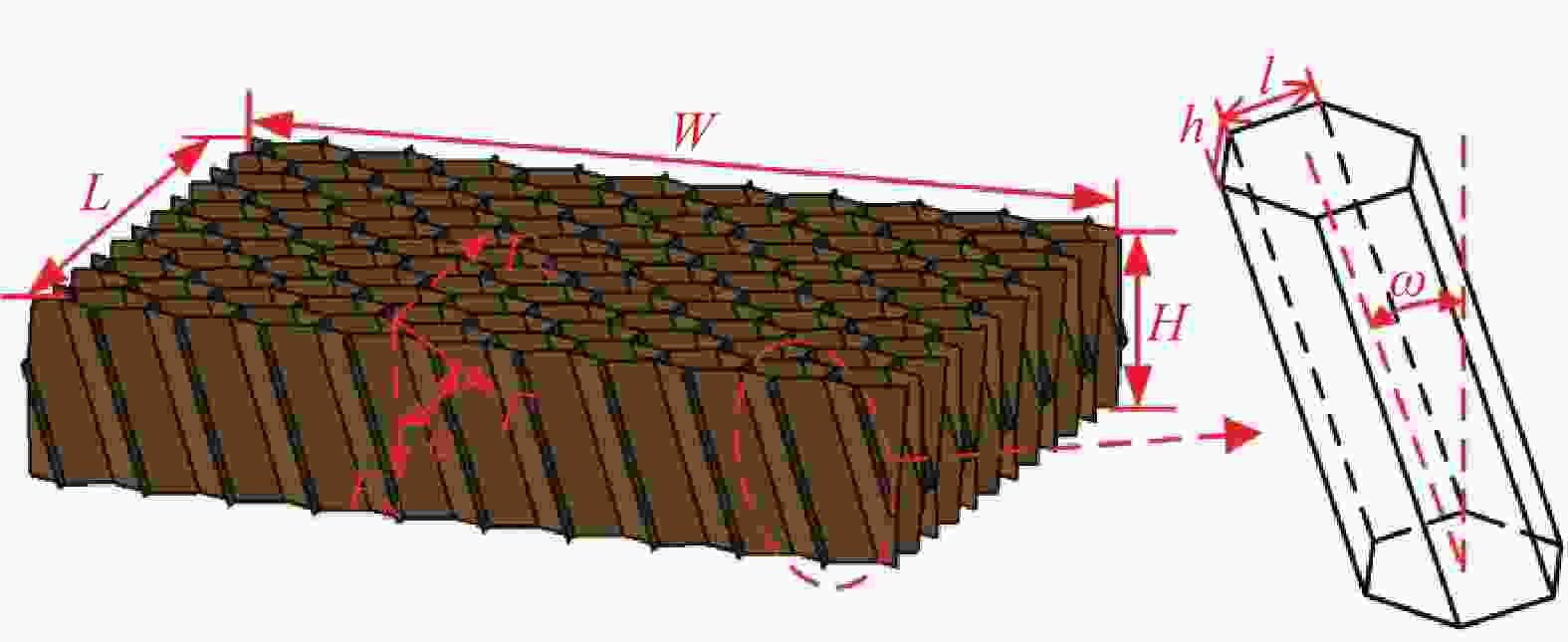
图 1 倾斜胞壁Nomex蜂窝芯几何构型示意图
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the inclined Nomex honeycomb
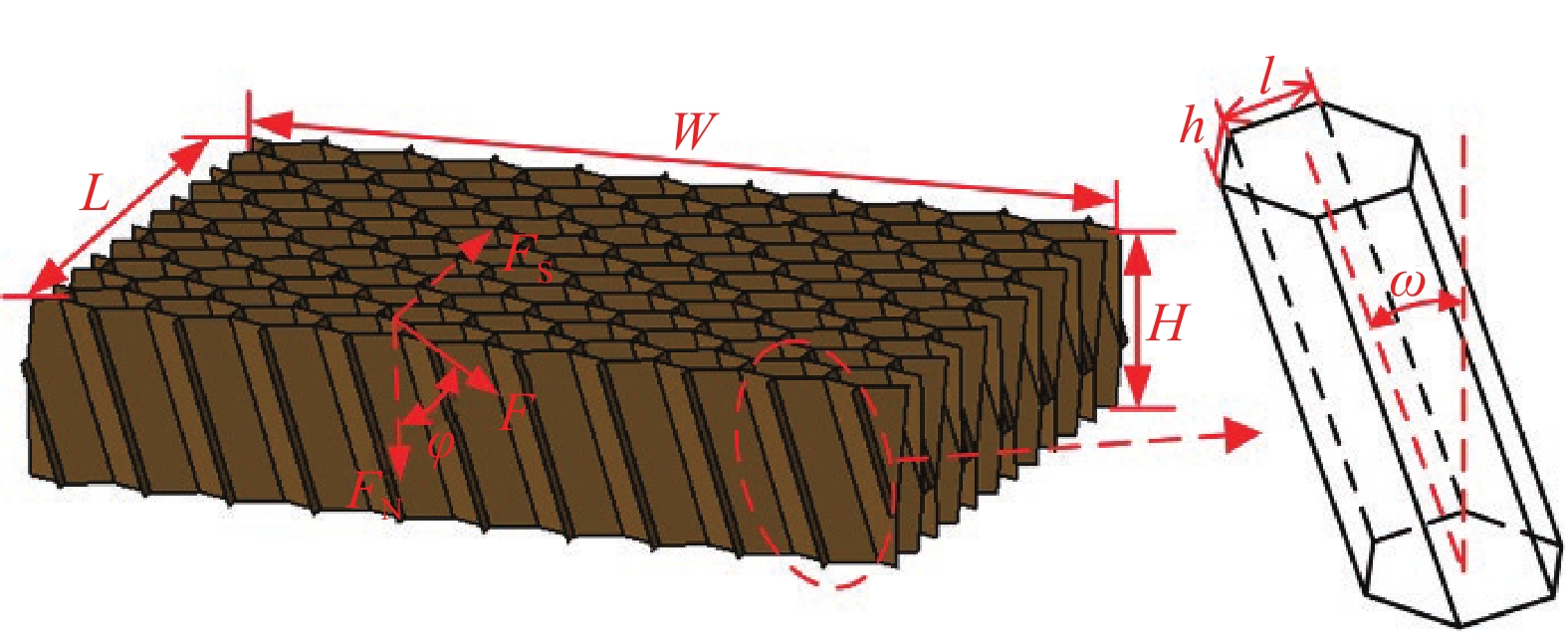
L—Length of the honeycomb; W—Width of the honeycomb; H—Hight of the honeycomb; F—Out-of-plane load; FN—Normal load; FS—Shear load; ϕ—Loading angle; h—Vertical cell wall length; l—Inclined cell wall length; ω—Inclined angle
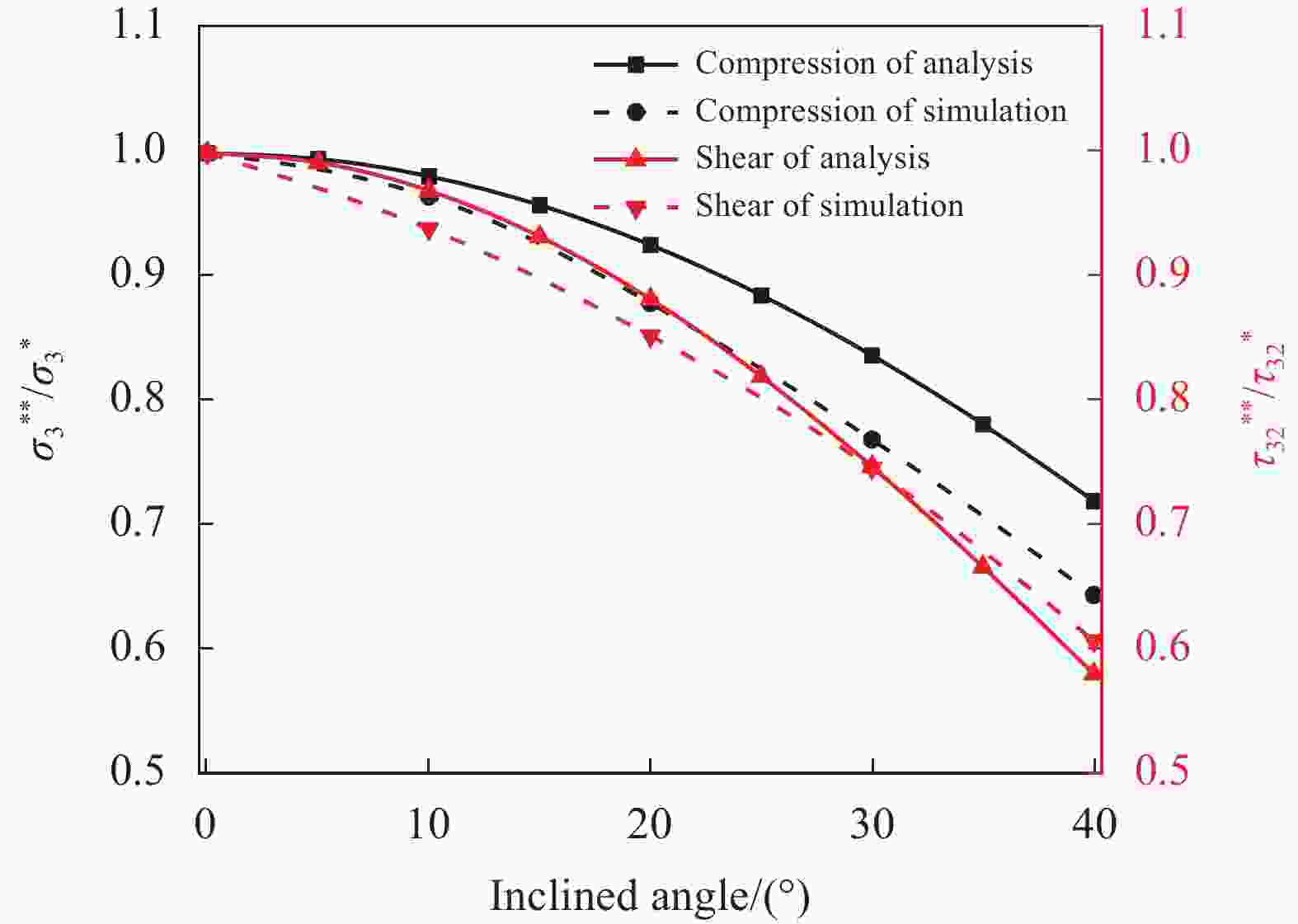
图 15 胞壁倾角对倾斜胞壁蜂窝芯坍塌应力与垂直胞壁蜂窝芯坍塌应力比值的影响
Figure 15. Effect of inclined angle on the ratio about the collapse stress of inclined cell wall honeycomb to the vertical cell wall honeycomb
$ \sigma _3^{ * * } $, $ \tau _{32}^{ * * } $—Collapse compression stress and shear stress of inclined cell wall honeycomb; $ \sigma _3^ * $, $ \tau _{32}^ * $—Collapse compression stress and shear stress of the vertical cell wall honeycomb
表 1 蜂窝胞壁的材料属性
Table 1. Material properties of the honeycomb cell wall
Elastic property Value Yield property Value EMD/MPa 5000.0 σMD/MPa 115.0 ECD/MPa 3500.0 σCD/MPa 105.0 G12/MPa 520.0 σ12/MPa 72.0 v 0.2 Notes: EMD and ECD—Young’s modulus in machine direction and cross machine direction; G12—Shear modulus; v—Poisson’s ratio; σMD and σCD—Tensile yield strength in machine direction and cross machine direction; σ12—Shear yield strength. -
[1] CASTANIE B, BOUVET C, GINOT M. Review of composite sandwich structure in aeronautic applications[J]. Composites Part C: Open Access,2020,1:100004. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomc.2020.100004 [2] HA N S, LU G X. A review of recent research on bio-inspired structures and materials for energy absorption applications[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,181:107496. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107496 [3] 齐佳旗, 段玥晨, 铁瑛, 等. 结构参数对 CFRP 蒙皮-铝蜂窝夹层板低速冲击性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6):1352-1363.QI Jiaqi, DUAN Yuechen, TIE Ying, et al. Effect of structural parameters on the low-velocity impact performance of aluminum honeycomb sandwich plate with CFRP face sheets[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(6):1352-1363(in Chinese). [4] SEEMANN R, KRAUSE D. Numerical modelling of Nomex honeycomb sandwich cores at meso-scale level[J]. Composite Structures,2017,159:702-718. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.09.071 [5] JANG W Y, KYRIAKIDES S. On the buckling and crushing of expanded honeycomb[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2015,91:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2014.02.008 [6] LI X, LU F, ZHANG Y, et al. Experimental study on out-of-plane mechanical and energy absorption properties of combined hexagonal aluminum honeycombs under dynamic impact[J]. Materials & Design,2020,194:108900. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108900 [7] LIU L, WANG H, GUAN Z. Experimental and numerical study on the mechanical response of Nomex honeycomb core under transverse loading[J]. Composite Structures,2015,121:304-314. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.11.034 [8] 王宝芹, 王沫楠, 刘长喜. 基于多尺度方法的蜂窝夹层复合材料结构轴向压缩稳定性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(3):601-608. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190918.001WANG Baoqin, WANG Monan, LIU Changxi. Stability of honeycomb sandwich composite structure under axial compression based onmulti-scalemethod[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(3):601-608(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190918.001 [9] LIU L, MENG P, WANG H, et al. The flatwise compressive properties of Nomex honeycomb core with debonding imperfections in the double cell wall[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2015,76:122-132. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.02.017 [10] RODRIGUEZ-RAMIREZ J D D, CASTANIE B, BOUVET C. Experimental and numerical analysis of the shear nonlinear behaviour of Nomex honeycomb core: Application to insert sizing[J]. Composite Structures,2018,193:121-139. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.03.076 [11] 冯威, 徐绯, 寇剑锋, 等. 考虑弹性支撑时蜂窝芯剪切屈曲强度的插值求解方法[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(6):1394-1399.FENG Wei, XU Fei, KOU Jianfeng, et al. Interpolation method for calculating the shear buckling strengths of honeycomb core considering elastic supports[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(6):1394-1399(in Chinese). [12] SHAFIQ M, AYYAGARI R S, EHAAB M, et al. Multiaxial yield surface of transversely isotropic foams: Part II—Experimental[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,2015,76:224-236. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2014.10.009 [13] ZHANG D, FEI Q. Effect of bird geometry and impact orientation in bird striking on a rotary jet-engine fan analysis using SPH method[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology,2016,54:320-329. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2016.05.003 [14] MOHR D, DOYOYO M. Experimental investigation on the plasticity of hexagonal aluminum honeycomb under multiaxial loading[J]. International Journal of Applied Mechanics,2004,71(3):375-385. doi: 10.1115/1.1683715 [15] HONG S T, PAN J, TYAN T, et al. Quasi-static crush behavior of aluminum honeycomb specimens under compression dominant combined loads[J]. International Journal of Plasticity,2006,22(1):73-109. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2005.02.002 [16] ZHANG D, LU G, RUAN D, et al. Quasi-static combined compression-shear crushing of honeycombs: An experimental study[J]. Materials & Design,2019,167:107632. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.107632 [17] HONG S T, PAN J, TYAN T, et al. Dynamic crush behaviors of aluminum honeycomb specimens under compression dominant inclined loads[J]. International Journal of Plasticity,2008,24(1):89-117. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2007.02.003 [18] HOU B, ONO A, ABDENNADHER S, et al. Impact behavior of honeycombs under combined shear-compression. Part I: Experiments[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2011,48(5):687-697. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.11.005 [19] TOUNSI R, MARKIEWICZ E, HAUGOU G, et al. Dynamic behaviour of honeycombs under mixed shear-compression loading: Experiments and analysis of combined effects of loading angle and cells in-plane orientation[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2016,80:501-511. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.10.010 [20] ASHAB A S M, RUAN D, LU G, et al. Quasi-static and dynamic experiments of aluminum honeycombs under combined compression-shear loading[J]. Materials & Design,2016,97:183-194. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.02.074 [21] OLYMPIO K R, GANDHI F. Flexible skins for morphing aircraft using cellular honeycomb cores[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures,2010,21(17):1719-1735. doi: 10.1177/1045389X09350331 [22] ZHAO Z, LIU C, SUN L, et al. Experimental and numerical study on the constrained bending-induced collapse of hexagonal honeycomb[J]. Composite Structures,2021,277:114604. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.114604 [23] WANG Z, LIU J, HUI D. Mechanical behaviors of inclined cell honeycomb structure subjected to compression[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,110:307-314. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.10.062 [24] MACRO G, GILIOLI A, MANES A. Numerical investigation of a three point bending test on sandwich panels with aluminum skins and Nomex™ honeycomb core[J]. Computational Materials Science,2012,56:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.01.007 [25] ZHANG J, ASHBY M F. The out-of-plane properties of honeycombs[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,1992,34(6):475-489. doi: 10.1016/0020-7403(92)90013-7 -





 下载:
下载: