Formulation and properties of UV crosslinked low voltage ethylene propylene diene monomer cable insulation material
-
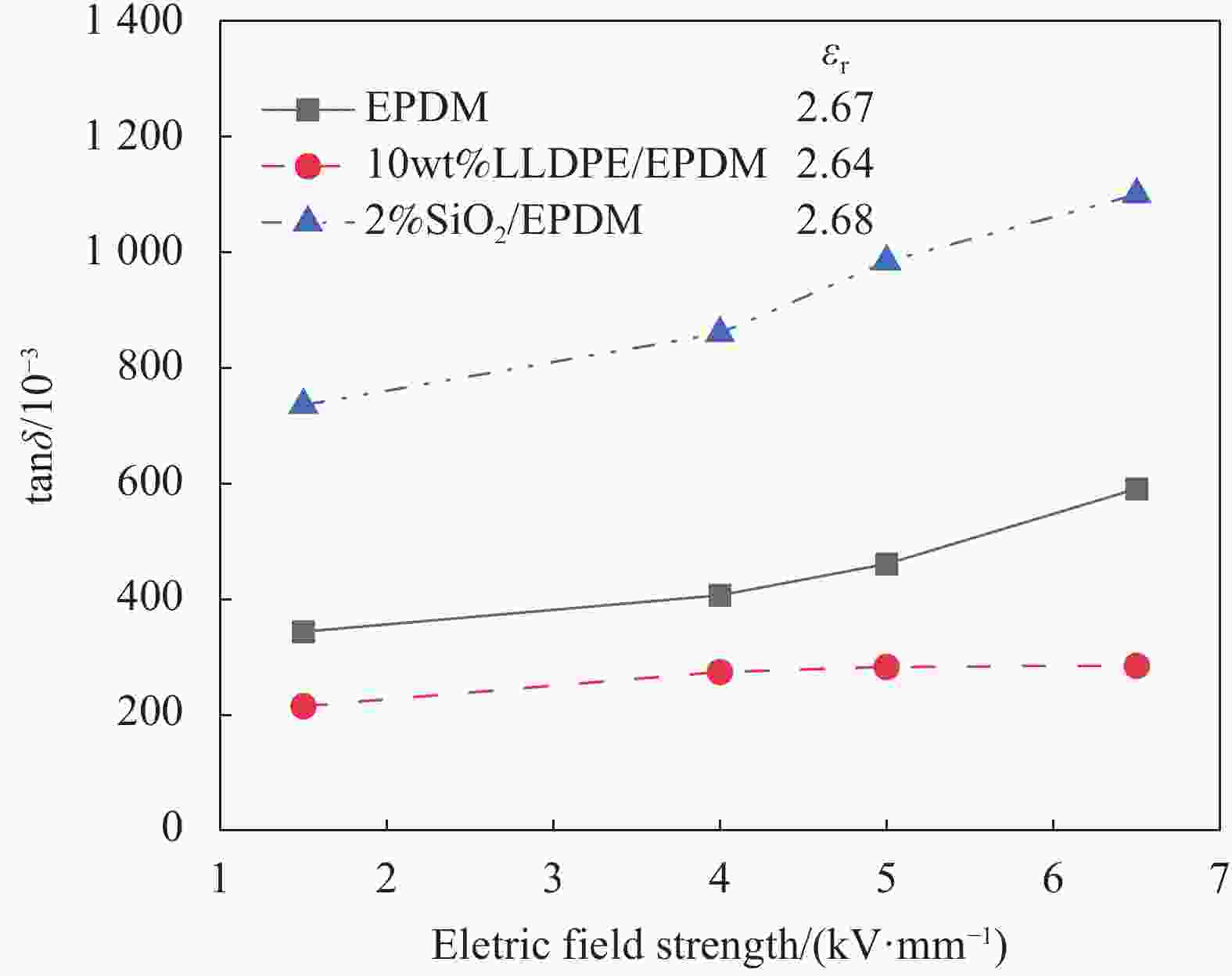
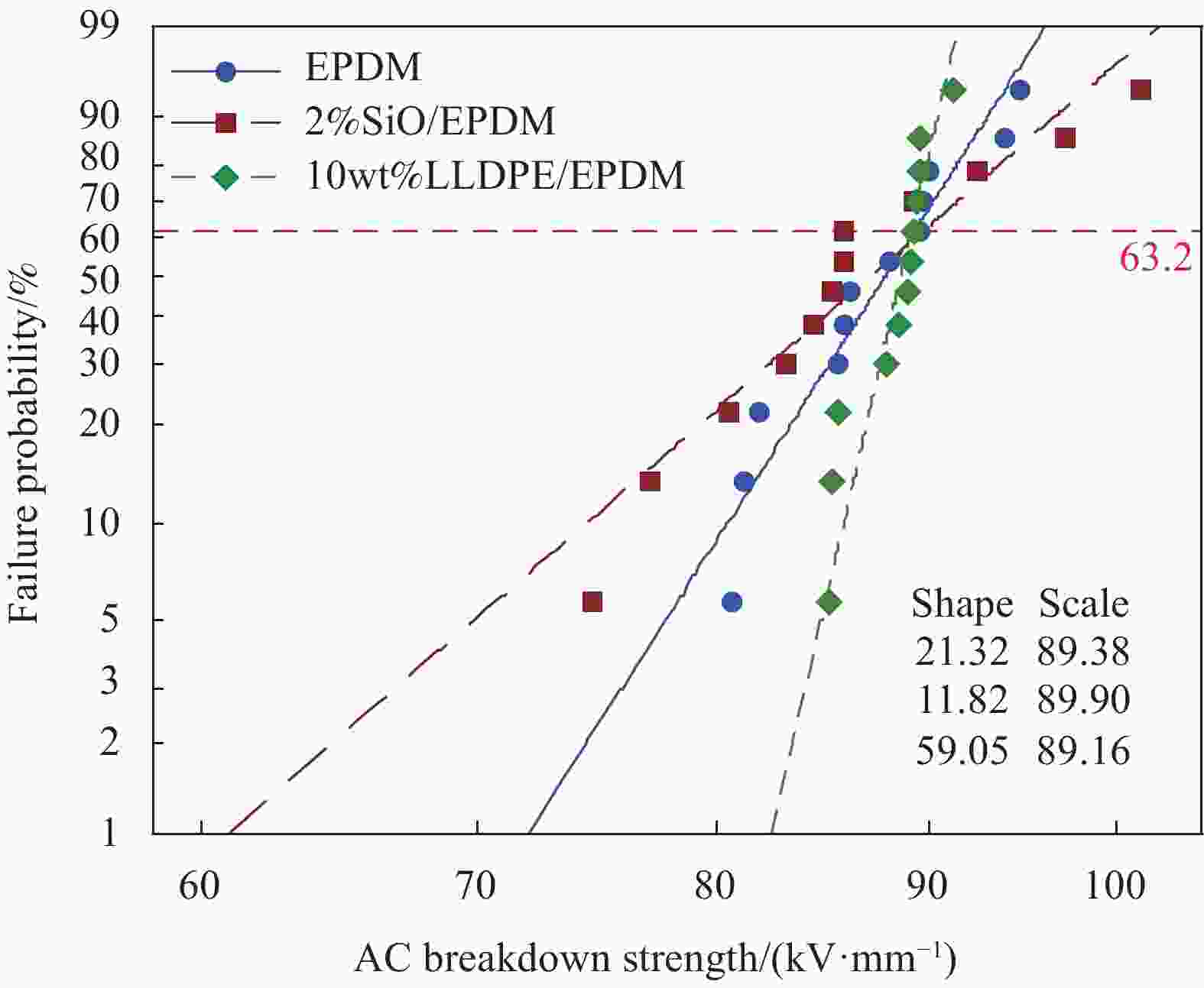
摘要: 为了将具有更高效率、更低功耗的紫外光交联技术用于三元乙丙橡胶(EPDM)电缆绝缘层生产,以达到节能减排、高效生产的目标,需研发低固体填料配方体系的EPDM绝缘材料。本文分别通过添加线性低密度聚乙烯(LLDPE)和少量纳米SiO2两种方法对EPDM进行补强。设计了可光交联的EPDM绝缘材料配方,并系统研究了紫外光交联EPDM材料的力学性能、交联性能、电学性能。结果表明,随着辐照时间的延长,EPDM力学性能明显下降,交联度迅速上升。与EPDM相比,LLDPE/EPDM材料交联程度和力学性能明显升高,当LLDPE含量为10wt%时,LLDPE/EPDM材料断裂伸长率为539%,拉伸强度为12 MPa,邵氏硬度为80 A,可以满足使用要求。对于SiO2/EPDM材料,当SiO2含量为4%(与橡胶的质量比,下同)时,力学性能最优,断裂伸长率为596%,拉伸强度为14 MPa。与EPDM相比,SiO2/EPDM复合材料的硬度变化不大,但交联程度降低,当辐照时间为12 s时,延伸率为40%,但仍可满足使用要求。添加0.5%抗氧剂1010可以抑制材料辐照交联过程中的降解,复合材料的力学性能大幅度提升,同时可以为EPDM绝缘材料提供较好的耐热老化性能。两种适用于紫外光交联技术的EPDM电缆绝缘材料均可满足电缆绝缘使用要求。其中,LLDPE补强材料的交联度和电学性能更优,但是对材料的硬度影响较大,而SiO2对复合材料的硬度几乎没有影响,但是交联度与电学性能略有下降。Abstract: In order to employ the high-efficiency, low-power-consumption ultraviolet light technology for the cross-linking of the ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber cable insulation layer and achieve the goal of energy conservation, pollution reduction and efficient production, it is necessary to develop EPDM insulation formulation with low content of solid fillers. In this paper, EPDM was reinforced by adding linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) and a small amount of nano SiO2. The formula of photo crosslinkable EPDM insulating material was designed, and the mechanical, crosslinking and electrical properties of UV crosslinked EPDM were systematically studied. The results show that, with the irradiation time increasing, the mechanical properties of EPDM are significantly decreased, and the crosslinking degree is rapidly increased. Compared with EPDM, the crosslinking degree and mechanical properties of LLDPE/EPDM materials are significantly higher. When the LLDPE content is 10wt%, the elongation at break of the LLDPE/EPDM material is 539%, the tensile strength is 12 MPa, and the Shore hardness is 80 A, which can meet the requirements of use. For SiO2/EPDM composite, when the SiO2 content is 4% (mass ratio to rubber), the mechanical properties are the best, the elongation at break is 596% and the tensile strength is 14 MPa. Compared with EPDM, the hardness of SiO2/EPDM composite is almost unchanged, but the crosslinking degree is reduced. When the irradiation time is 12 s, the loading elongation of SiO2/EPDM is 40%, which still meets the requirements of use. The degradation of the material during irradiation can be suppressed after 0.5% mass ratio of Irganox1010 is added, and the mechanical properties of the composite material are improved. Moreover, Irganox1010 can improve the thermo-oxidative aging resistance of the composite. Both two kinds of modified EPDM composites which are designed for UV cross-linking technology can meet the requirements of cable insulation. The blending of LLDPE increases the crosslinking degree and electrical properties of the material, but bring the negative impact on the hardness of EPAM, while the doping of SiO2 has almost no effect on the hardness of the composite, but the crosslinking degree and electrical properties are slightly weakened.
-
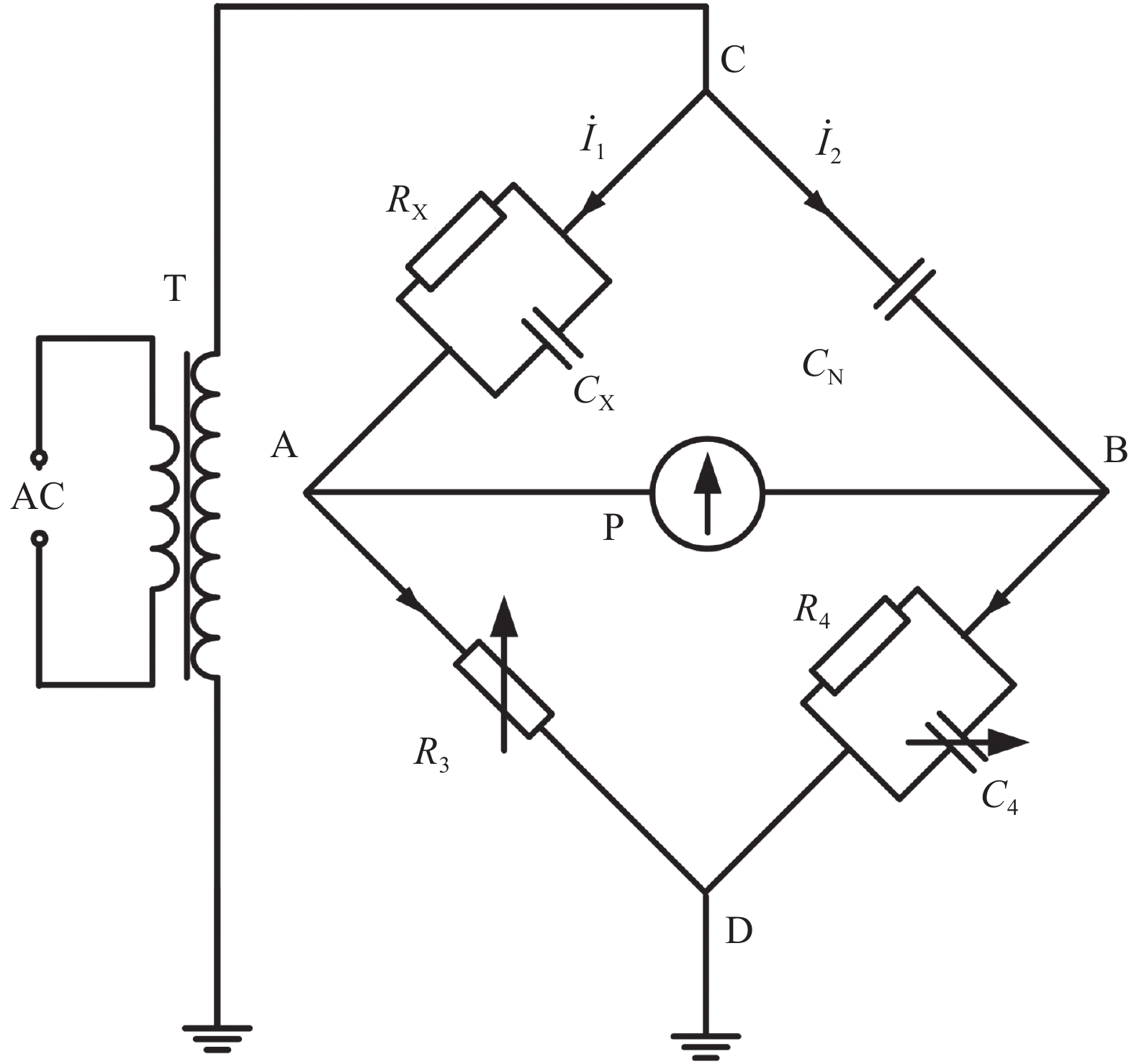
图 1 西林电桥电路图
Figure 1. Circuit diagram of West Linn Bridge
RX—Sample resistance; CX—Sample capacitance; R4—Fixed resistance; CN—Standard capacitance; R3—Adjustable resistance; C4—Adjustable capacitance; AC—AC power supply; T—AC transformer; ${{\dot{I}}_{1}} $—Sample arm current; ${{\dot{I}}_{2}} $—Bridge arm current of standard capacitor;P—Balance indicator; A, B, C, D—Node A, B, C, D
表 1 三元乙丙橡胶(EPDM)电缆绝缘复合材料配比
Table 1. Ratio of ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) cable insulation composite materials
g Material EPDM LLDPE Nano SiO2 BP TAIC 10wt%LLDPE/EPDM 36 4 0 0.8 0.4 20wt%LLDPE/EPDM 32 8 0 0.8 0.4 30wt%LLDPE/EPDM 28 12 0 0.8 0.4 40wt%LLDPE/EPDM 24 16 0 0.8 0.4 2%SiO2/EPDM 40 0 0.8 0.8 0.4 4%SiO2/EPDM 40 0 1.6 0.8 0.4 6%SiO2/EPDM 40 0 2.4 0.8 0.4 EPDM 40 0 0 0.8 0.4 Notes: LLDPE—Linear low density polyethylene; BP—Benzophenone; TAIC—Triallyl isocyanurate ester. 表 2 低压EPDM绝缘材料的性能要求
Table 2. Performance requirements for low voltage EPDM insulating materials
Project Standard requirements Tensile strength before aging/MPa ≥5.0 Elongation at break before aging/% ≥250 Thermal oxygen aging test: Tensile strength after aging/MPa ≥4.2 Maximum change rate of tensile strength/% ±25 Elongation at break after aging/% 200 Maximum change rate of elongation at break/% ±25 Thermal elongation/% ≤100 Permanent elongation/% ≤25 Shore hardness/A ≤84 Loss factor tanδ ≤0.04 Dielectric constant - Breakdown strength/(kV·mm−1) ≥25 表 3 EPDM在不同辐照时间下热延伸率
Table 3. Thermal elongation of EPDM under different irradiation time
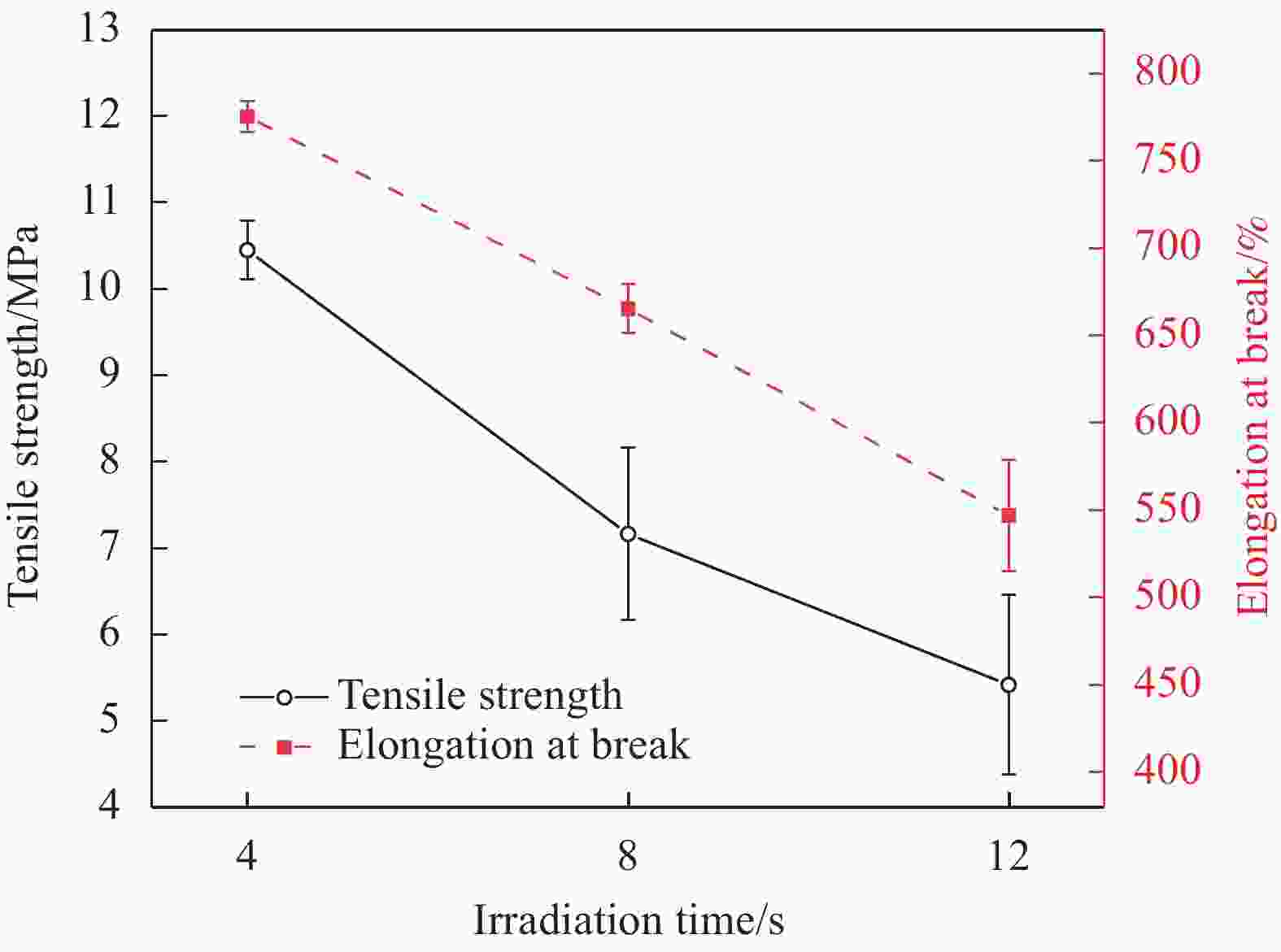
Irradiation
time/sThermal elongation/% Permanent elongation/% 4 Fuse − 8 85 0 12 25 0 表 4 10wt%LLDPE/EPDM复合材料热延伸率
Table 4. Thermal elongation of 10wt%LLDPE/EPDM composites
Irradiation
time/sThermal elongation/% Permanent elongation/% 4 Fuse − 8 35 0 12 20 0 表 5 SiO2/EPDM材料热延伸率
Table 5. Thermal elongation of SiO2/EPDM composites
Mass ratio of nano SiO2/% Thermal elongation/% Permanent elongation/% 0 25 0 2 35 0 4 40 0 6 40 0 表 6 EPDM材料抗氧剂配比与热延伸测试结果
Table 6. Test results of antioxidant ratio and thermal extension of EPDM materials
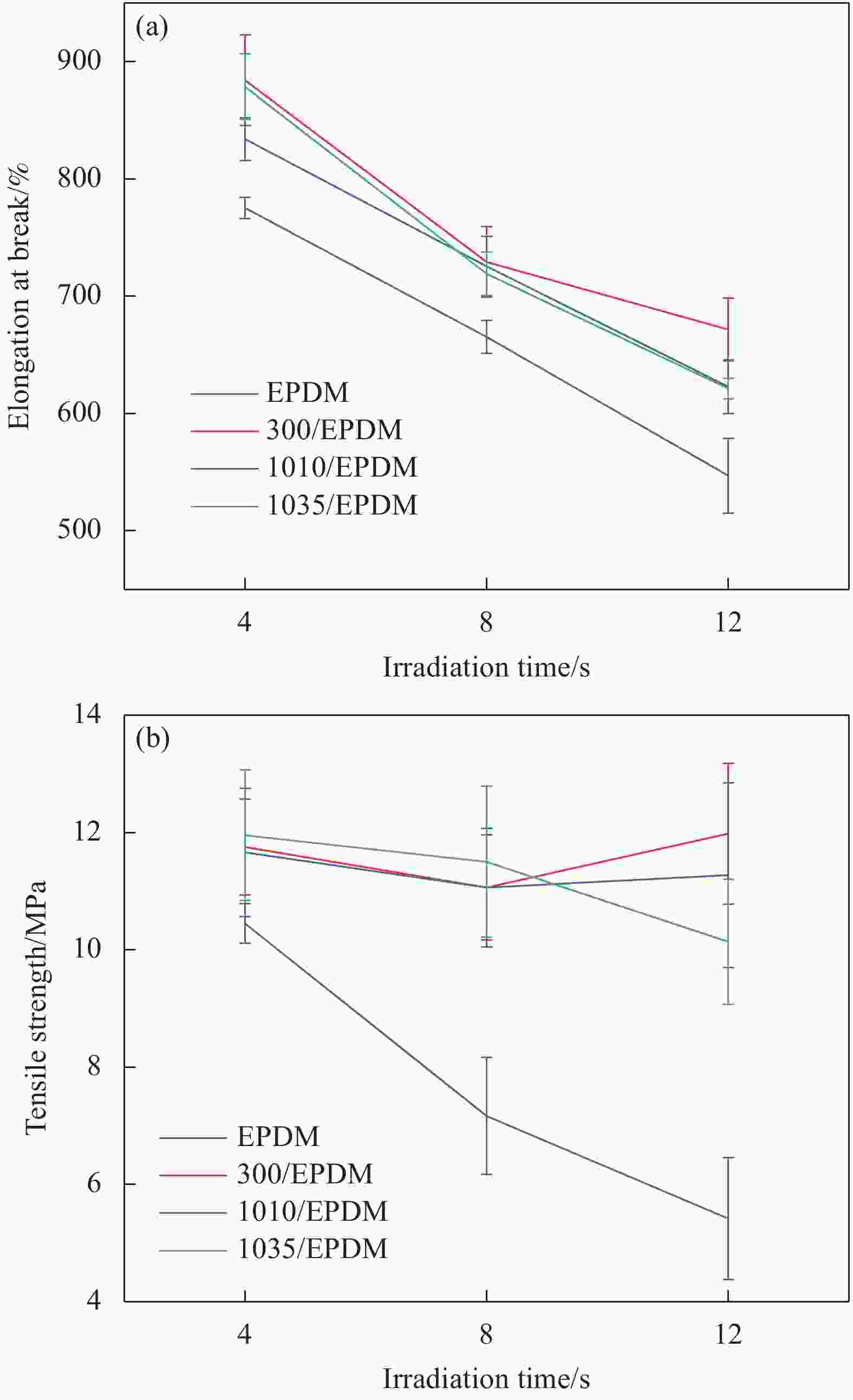
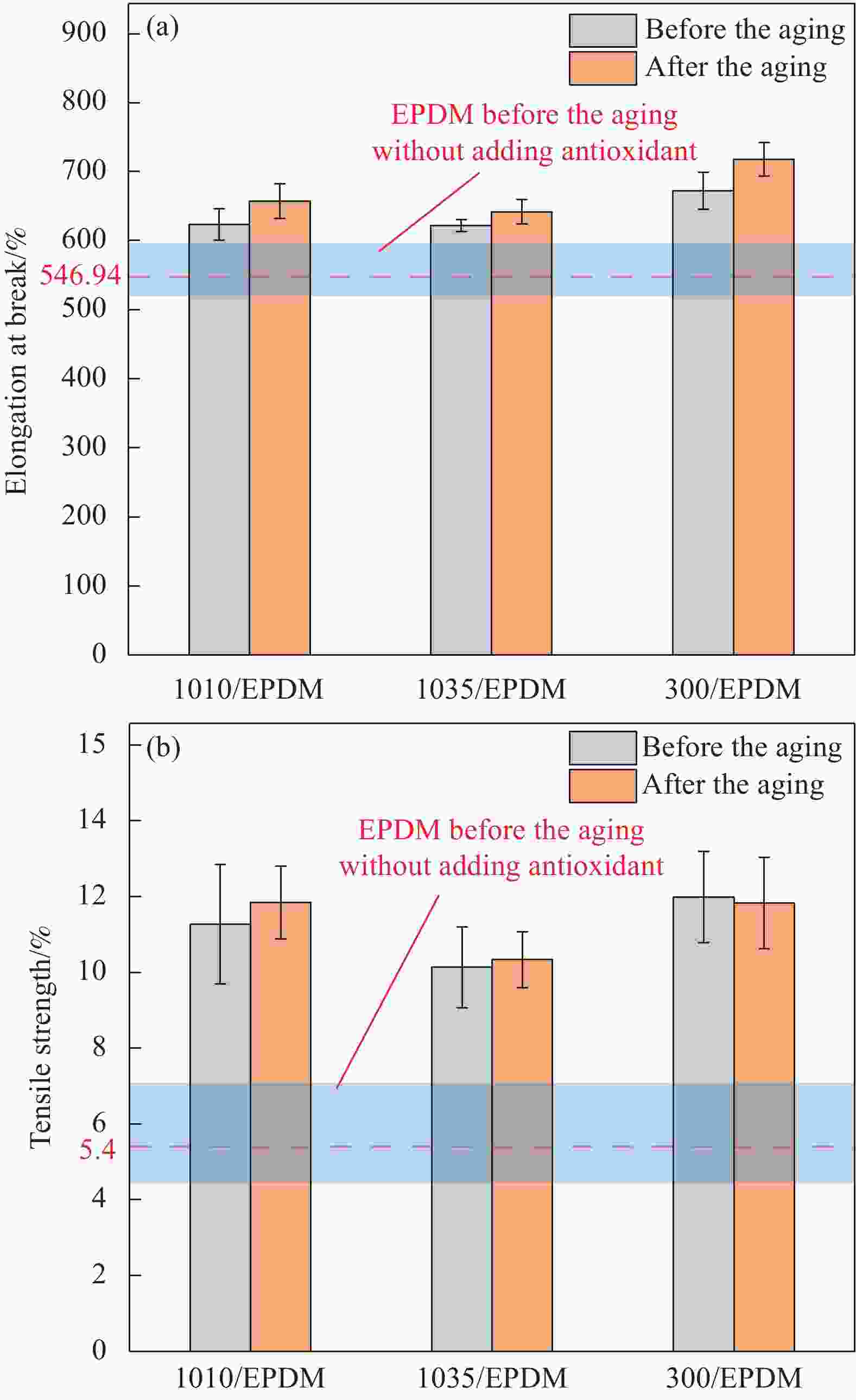
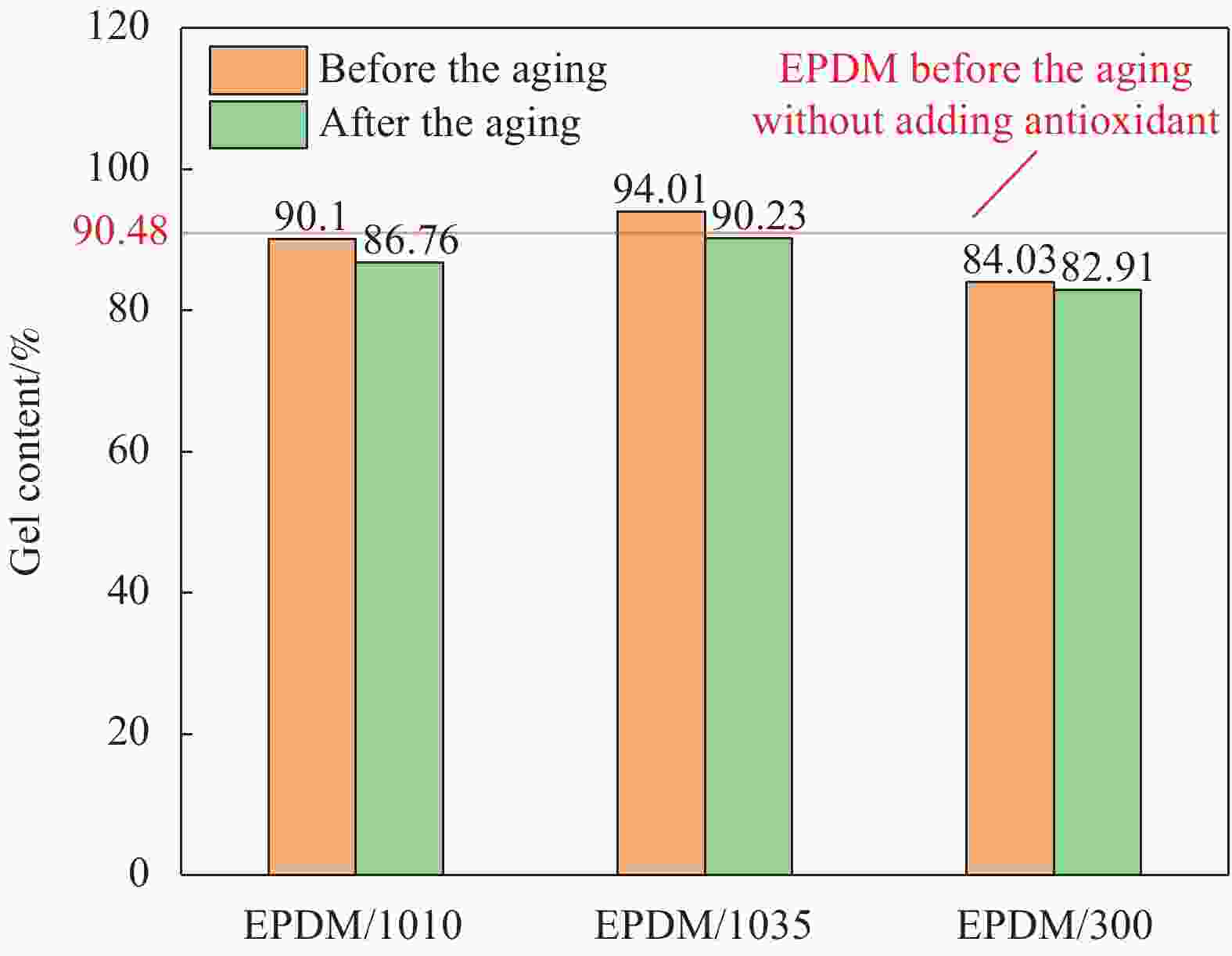
Sample name Antioxidant content/% Thermal elongation/% Permanent elongation/% 4020/EPDM 0.5 Fuse − 300*/EPDM 0.5 110 30 300/EPDM 0.3 45 0 1010/EPDM 0.5 35 0 1035/EPDM 0.5 35 0 Notes: 4020—Antioxidant 4020; 300—Antioxidant 300; 1010—Antioxidant 1010; 1035—Antioxidant 1035. -
[1] 王启丰, 王强, 潘龙, 等. 低压橡皮电缆用CM/EPDM绝缘配方研究[J]. 电线电缆, 2015(5):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6901.2015.05.007WANG Qifeng, WANG Qiang, PAN Long, et al. Research of CM/EPDM insulating cement formulation for low-tension rubber cable[J]. Wire and Cable,2015(5):24-27(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6901.2015.05.007 [2] ZUIDEMA C, KEGERISE W, FLEMING R, et al. A short history of rubber cables[J]. IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine,2011,27(4):45-50. doi: 10.1109/MEI.2011.5954068 [3] 林晨, 吝伶艳, 雷志鹏, 等. 基于 PDC的多应力老化乙丙橡胶电缆绝缘状态评估[J]. 绝缘材料, 2020, 53(1):70-75.LIN Chen, LIN Lingyan, LEI Zhipeng, et al. State evaluation of multi-stress aged EPR cable insulation based on PDC[J]. Insulating materials,2020,53(1):70-75(in Chinese). [4] 李冬梅. 橡皮绝缘电缆产品技术及制造工艺[M]. 北京: 力学工业出版社, 2017.LI Dongmei. Rubber insulated cable product technology and manufacturing process[M]. Beijing: Machinery Industry Press, 2017(in Chinese). [5] CHEN J, HUANG W, JIANG S B, et al. Flame-retardant EPDM compounds containing phenanthrene to enhance radiation resistance[J]. Radiation Physics & Chemistry,2016,130(1):400-405. [6] 李晨晨, 李培军. 煅烧陶土在三元乙丙橡胶电线电缆胶料中的应用[J]. 橡胶科技, 2019, 17(3):168-172.LI Chenchen, LI Peijun. Application of calcined clay in EPDM wire and cable compound[J]. Rubber Science and Technology,2019,17(3):168-172(in Chinese). [7] 郭尚振. EPDM/ZDMA复合材料的制备、结构与性能的表征[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2016.GUO Shangzhen. The preparation and characterization of EPDM/ZDMA materials[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [8] 万明顺, 信晓庆. 无机填料对过氧化物硫化EPDM性能的影响[J]. 特种橡胶制品, 2018, 39(6):28-30.WAN Mingshun, XIN Xiaoqing. Effect of inorganic fillers on the properties of peroxide vulcanized EPDM[J]. Special Purpose Rubber Products,2018,39(6):28-30(in Chinese). [9] 陈伟. 紫外光交联聚合物的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2014.CHEN Wei. Studies on UV-photocrosslinking of polymers[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese). [10] 马宝红, 鲍文波, 姜国发, 等. 紫外光交联对低烟无卤阻燃电缆绝缘材料性能的影响[J]. 中国塑料, 2017, 31(6):95-99.MA Baohong, BAO Wenbo, JIANG Guofa, et al. Influence of UV crosslinking on properties of insulation materials used for low-smoke halongen-free flame-retardant cables[J]. China Plastics,2017,31(6):95-99(in Chinese). [11] QU B J, BAO W B, WU Q H, et al. Recent devolpments on photoinitiated crosslinking of polyethylene and its applications for manufacturing insulated wire and cable[C]. 2009 IEEE 9th International Conference on the Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials. Harbin, 2009: 33-36. [12] WU Q, QU B. Photoinitiating characteristics of benzophenone derivatives as new initiators in the photocrosslinking of polyethylene[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science,2001,41(7):1220-1226. doi: 10.1002/pen.10823 [13] 郑宁来. 2019年全球热塑弹性体(TPE)需求将达到6700 kt[J]. 橡胶参考资料, 2016, 46(4): 45.ZHENG N L. The global demand for thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) will reach 6700 kt in 2019[J]. Rubber Reference, 2016, 46(4): 45(in Chinese). [14] 程实, 胡凌骁, 丁玉梅, 等. PP/EPDM/滑石粉微孔发泡复合材料的制备和性能[J]. 塑料, 2014, 43(5):75-77, 74.CHENG Shi, HU Lingxiao, DING Yumei, et al. Preparation and properties of PP/EPDM/Talc microporous foam composites[J]. Plastics,2014,43(5):75-77, 74(in Chinese). [15] 宋旭鹏. 三元乙丙橡胶/无机填料共混物的紫外光光交联及其阻燃材料的研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2009.SONG Xupeng. Study on ultraviolet light crosslinking and flame retardant materials of EPDM/inorganic filler blends[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2009(in Chinese). [16] 林文莉. 线性低密度聚乙烯及其紫外光辐照交联材料老化特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2017.LIN Wenli. Study on aging characteristics of linear low density polyethylene and its UV irradiated crosslinked materials[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [17] 荆彦宽. 功能性乙丙橡胶/SiO2复合材料的合成[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019.JING Yankuan. Functional ethylene propylene rubber/SiO2 synthesis of composites[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [18] 吴来利, 周志宇, 徐华胜, 等. 中低压电缆用乙丙橡胶绝缘材料配方设计概述[J]. 光纤与电缆及其应用技术, 2021(3):6-9, 14.WU Laili, ZHOU Zhiyu, XU Huasheng, et al. Summary of formulation design of EPR insulation material for medium and low voltage cables[J]. Optical Fiber & Electric Cable and Their Applications,2021(3):6-9, 14(in Chinese). [19] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶压入硬度实验方法第一部分: 邵氏硬度计法(邵尔硬度): GB/T 531.1—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermmoplastic—Determination of indentation hardness—Part 1: Duromerer method (Shore hardness): GB/T 531.1—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese). [20] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡拉伸应力应变性能的测定: GB/T 528—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic—Determination of tensile stress-strain properties: GB/T 528—2009[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2009(in Chinese). [21] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 电缆和光缆绝缘和护套材料通用实验方法: GB/T 2951—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Common test methods for insulating and sheathing materials of electric and optical cables: GB/T 2951—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese). [22] 郭红霞. 电线电缆材料[M]. 北京: 力学工业出版社 , 2012.GUO Hongxia. Wire and cable materials[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2012(in Chinese). [23] PLANES E, CHAZEAU L, VIGIER G, et al. Influence of fillres on mechanical properties of ATH filled EPDM during ageing by gamma irradiation[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2010,95(6):1029-1038. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.03.008 [24] DELPRAT P, DUTEURTRE X, et al. Photooxidation of unstabilized and HALS-stabilized polyphasic ethylene-propylene polymers[J]. Porymer Degradation and Stability,1995,50(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/0141-3910(95)00061-P [25] MARCO R, IVAN P, LUIGI T, et al. Thermal and ablation properties of EPDM based heat shielding materials modified with density reducer fillers[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,112:71-80. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.05.031 [26] 刘标, 党智敏, 张冬丽, 等. 绝缘电缆用LDPE/EPDM复合材料力学性能及电性能研究[J]. 绝缘材料, 2019, 52(9):36-41.LIU Biao, DANG Zhimin, ZHANG Dongli, et al. Mechanical and electrical properties of LDPE/EPDM for insulated cable[J]. Insulating Materials,2019,52(9):36-41(in Chinese). [27] GIUSEPPE A, GUIDO R, MICHELE V. Theories and simulations of polymer-based nanocomposites: From chain statistics to reinforcement[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2008,33:683-731. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.02.003 [28] 刘丰, 郑秋红, 李小红, 等. 可分散性纳米二氧化硅增强硅橡胶[J]. 复合材料学报, 2006, 23(6):57-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.06.009LIU Feng, ZHENG Qiuhong, LI Xiaohong, et al. Silicone rubber reinforced by a dispersible nano-silica[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2006,23(6):57-63(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.06.009 [29] 张扬. 二氧化钛/聚氨酯紫外光屏蔽涂层的制备[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2009.ZHANG Yang. The preparation of titania/polyurethane UV blocking coatings[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2019(in Chinese). [30] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡热空气加速老化和耐热试验: GB/T 3512—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic—Accelerated aging and heat resistance test—Air-over method: GB/T 3251—2014[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2014(in Chinese). [31] 王猛. 微纳米SiO2/LDPE复合电介质空间电荷与直流电性能的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2021.WANG Meng. Study on space charge characteristics and DC electrical properties of SiO2/LDPE micro-nanocompo-sites[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [32] WANG Y, QIN D Y, XU Z Q, et al. The effect of loading ratios and electric field on charge dynamics in silica-based polyethylene nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,2018,51(39):395302. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aad7e8 [33] WANG W, MIN D, LI S. Understanding the conduction and breakdown properties of polyethylene nanodielectrics: Effect of deep traps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2016,23(1):564-572. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2015.004823 [34] 熊雨琪. 纳米SiO2填充硅橡胶的微观分散性表征及其补强机理研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2021.XIONG Yuqi. Characterization of micro dispersion and reinforcement mechanism of nano-SiO2 filled silicone rubber[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [35] TAGHAVIMEHR M, FAMILI M H N, SHIRSAVAR M A. Effect of nanoparticle network formation on electromagnetic properties and cell morphology of microcellular polymer nanocomposite foams[J]. Polymer Testing,2020,86:106469. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106469 -






 下载:
下载: