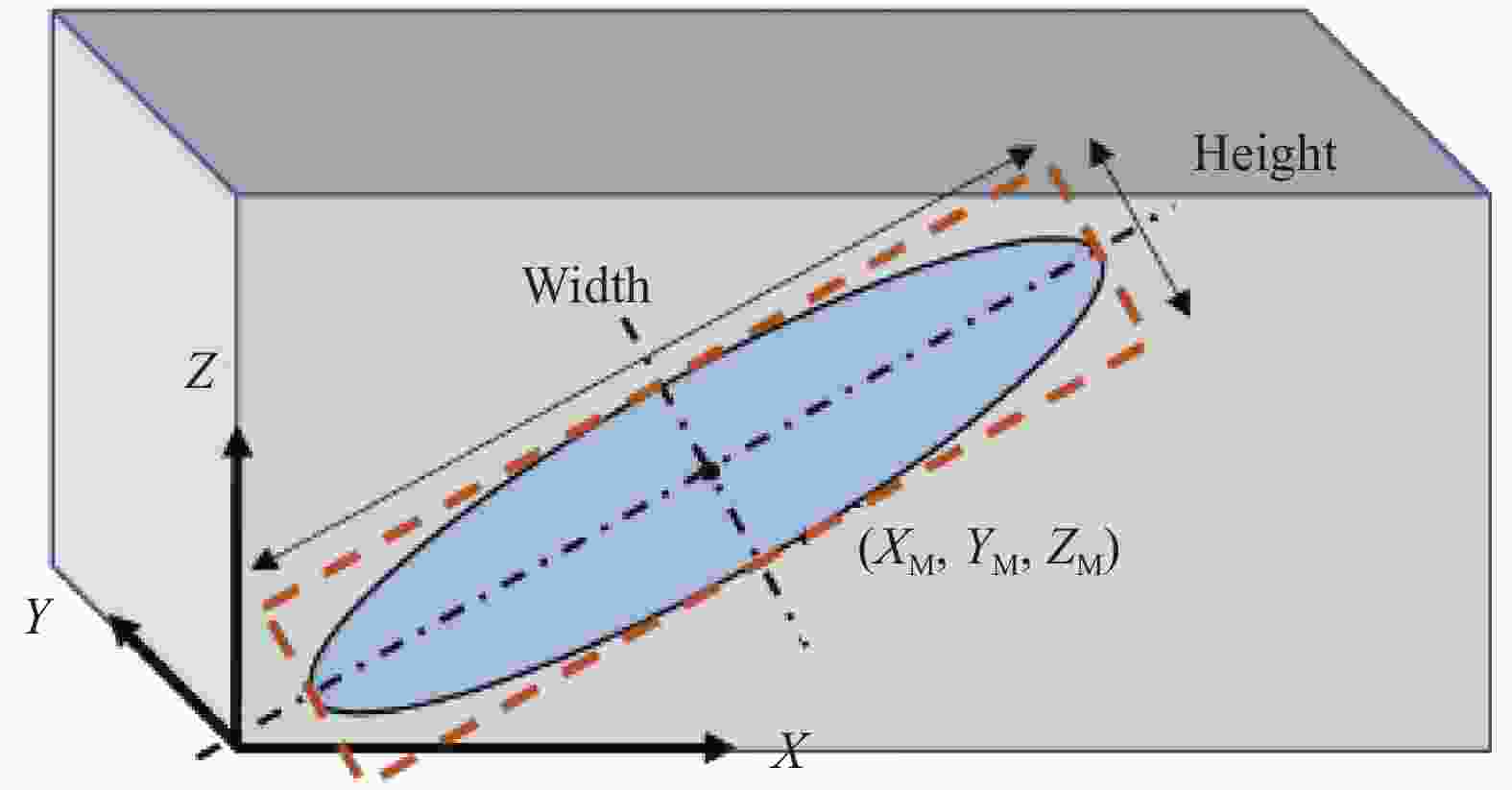
Meso-structure analysis and permeability prediction of satin fabric based on Micro-CT
-
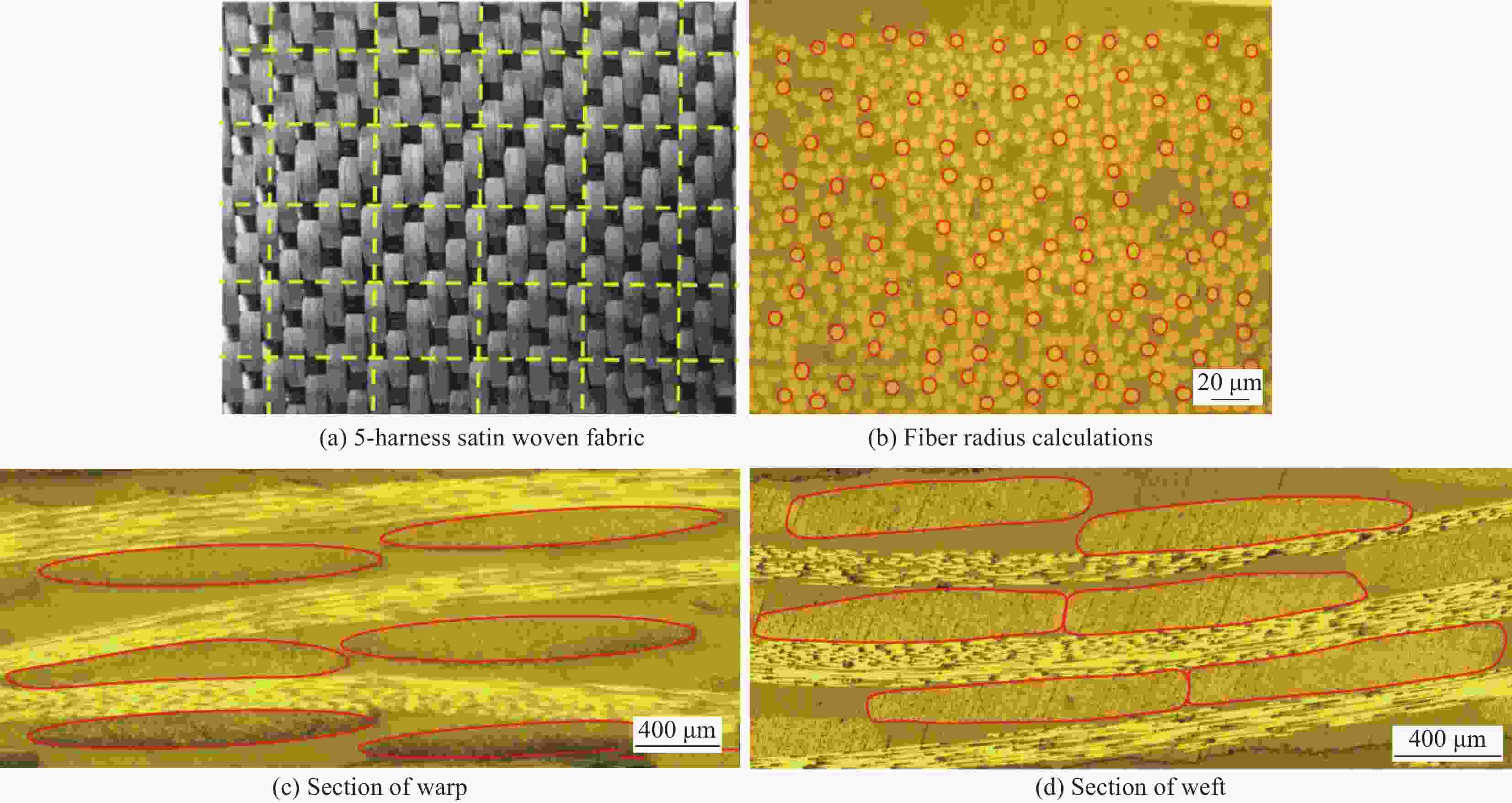
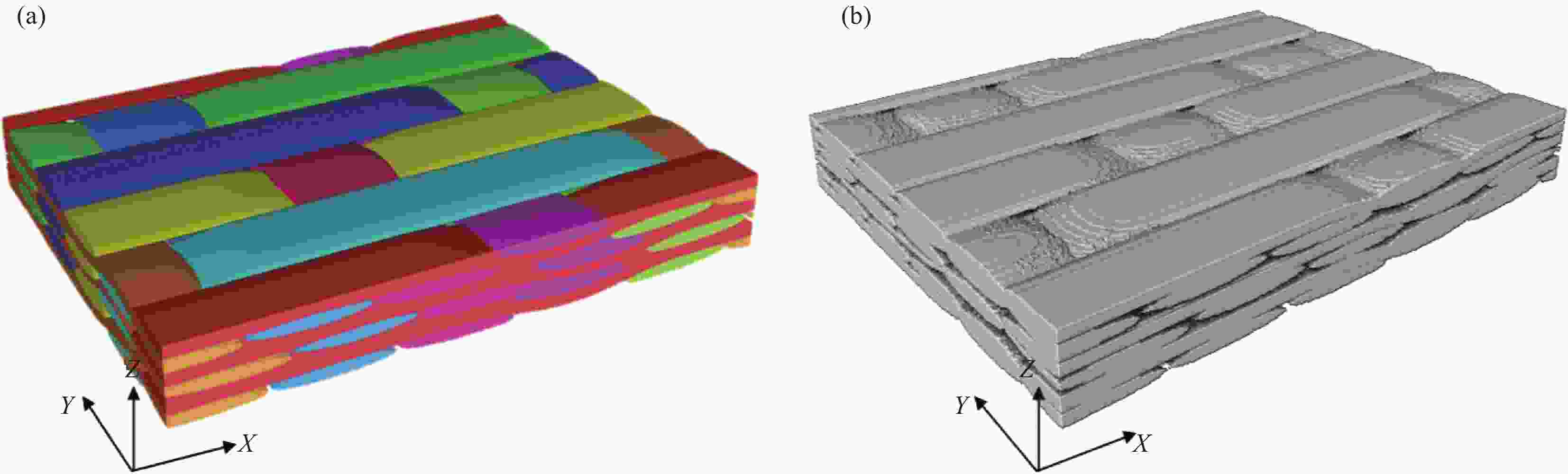
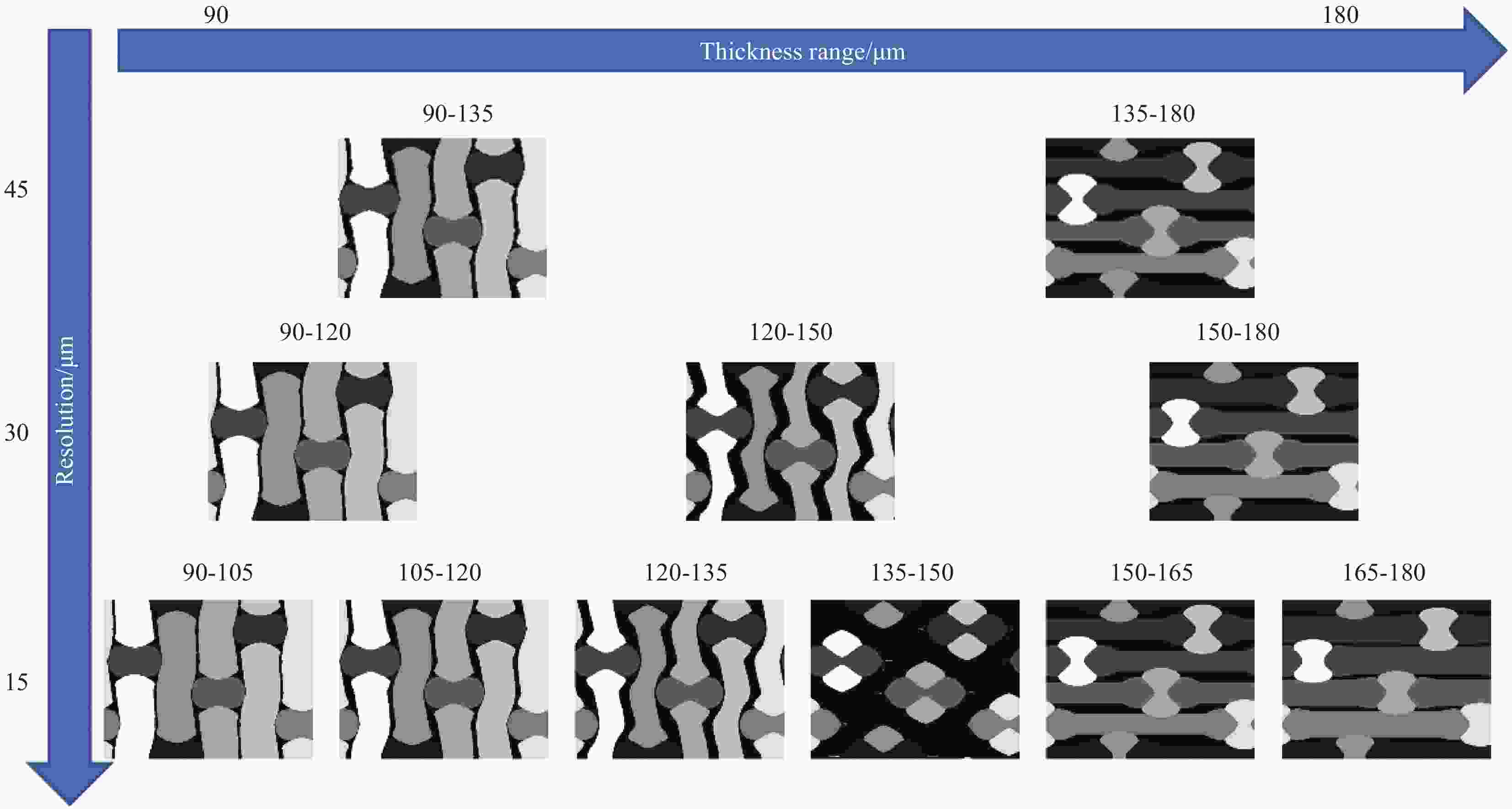
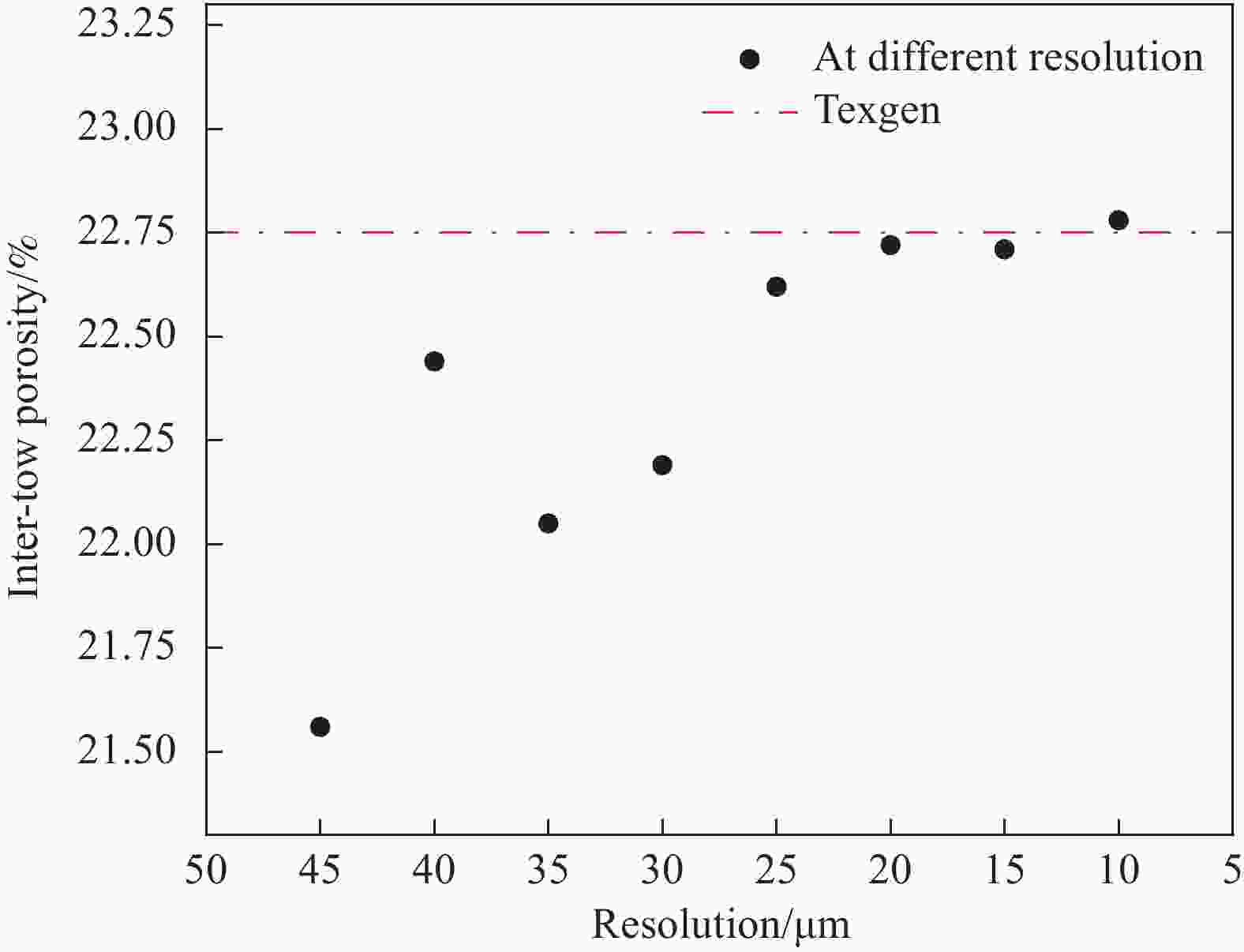
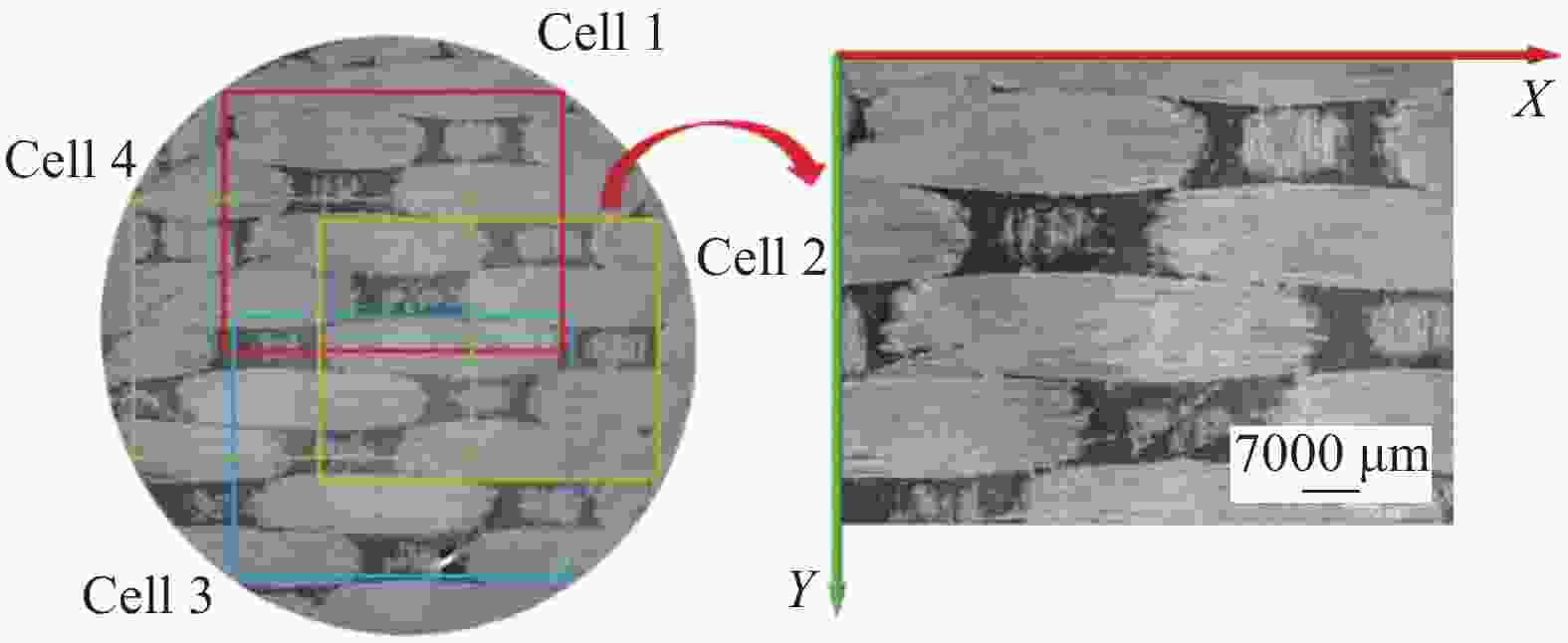
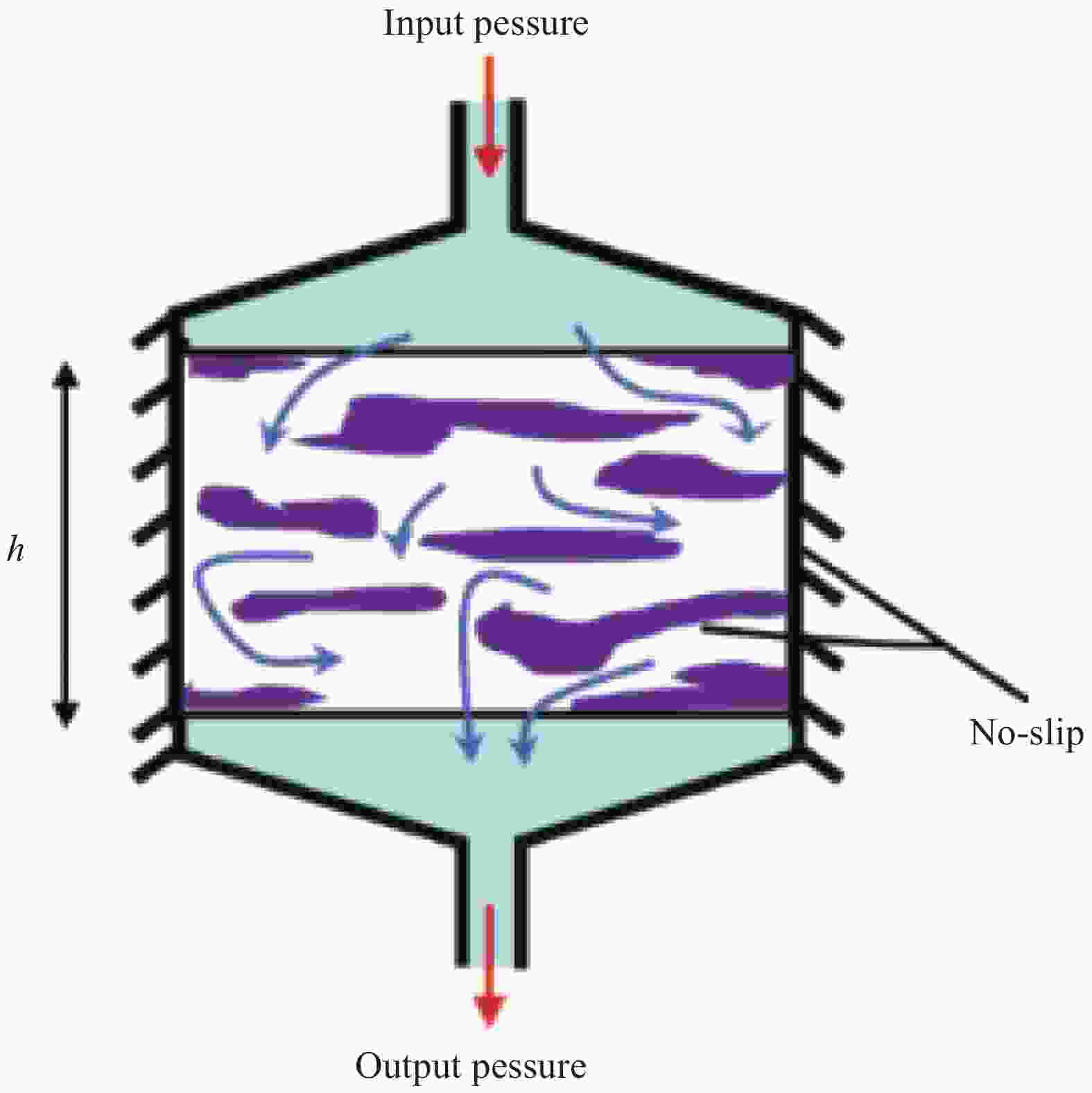
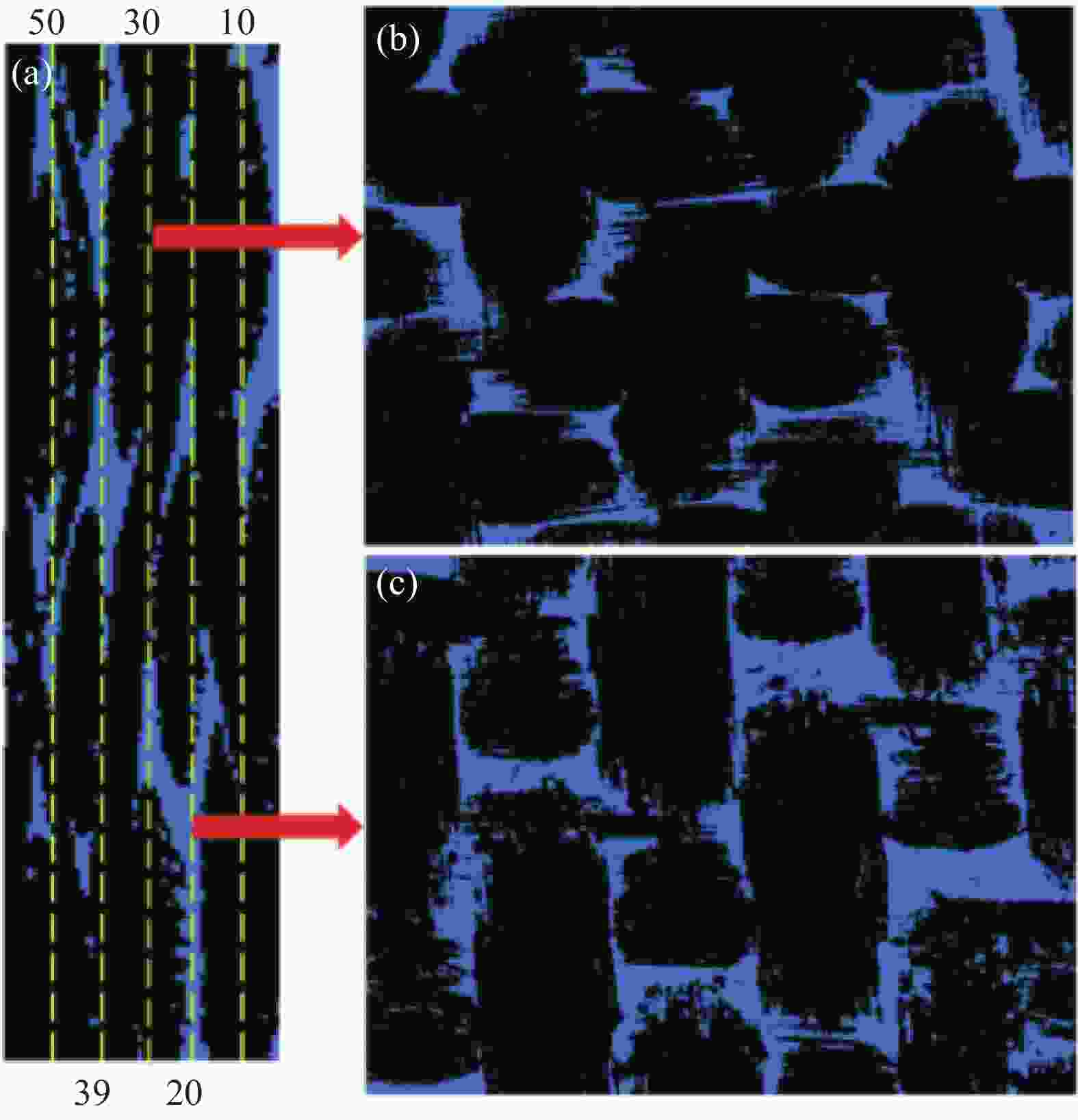
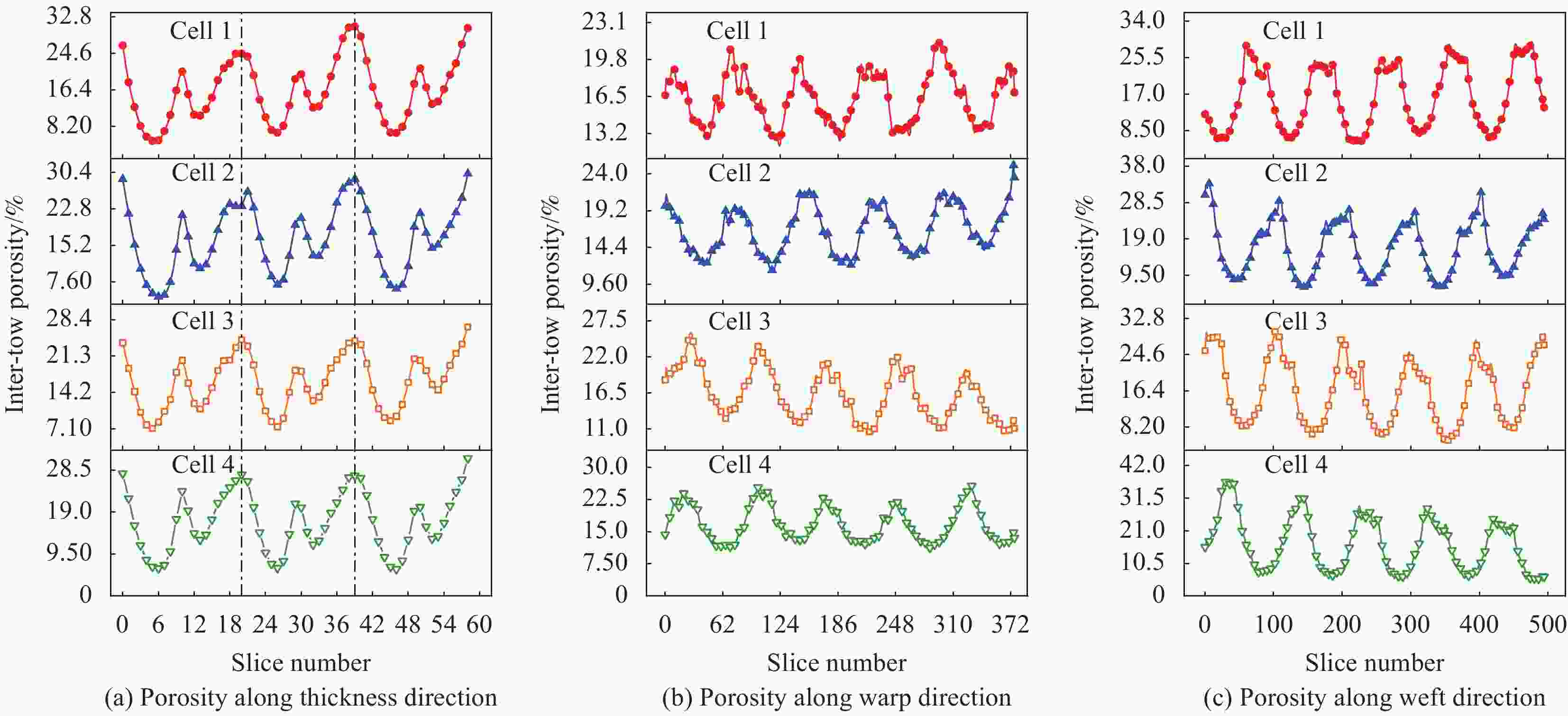
摘要: 建立了确定显微计算机断层扫描技术(Micro-CT)扫描最合适分辨率的方法,并基于CT图像分析了3K五枚缎纹织物的结构,预测了渗透率。首先,将织物理想单胞模型转换为不同分辨率二维切片,考察分辨率对单胞结构、渗透率表征的影响,提出了确定Micro-CT扫描最合适分辨率的方法;其次,采用确定的分辨率对织物进行Micro-CT扫描,获取织物细观结构;最后,使用CT三维细观结构进行厚度方向渗透率数值预测,研究了织物结构的空间离散性对厚度方向渗透率的影响。结果表明:对于本文所用五枚缎纹织物,采用15 μm分辨率进行Micro-CT扫描最合适;通过Micro-CT可准确获取织物纤维束的路径及截面变化;多层织物的孔隙沿3个主方向均呈现周期性排布,且束间孔隙率均值为16.6%;使用真实CT模型的厚度方向渗透率预测结果与实验值具有良好的吻合性。Abstract: The optimal resolution determination method of micro-computed tomography (Micro-CT) scanning was presented here based on two-dimensional slices at different resolutions for ideal unit cell model, and the meso-structure and permeability of 3K 5-harness satin woven fabric were characterized based on the CT image at the optimal resolution. Firstly, the ideal unit cell model of the fabric was converted into 2D slices at different resolutions and the effects of resolution on the characterization of cell structure and permeability were investigated. Thereafter, the optimal resolution was determined for fabric CT scanning. Then, the CT image of the fabric with the optimal resolution was used for the meso-structure and through-thickness permeability characterizations of the fabric. The results show that the optimal resolution for the CT scanning of 5-harness satin woven fabric is 15 μm. The path and cross-sectional variation of the yarns in the fabric can be obtained by Micro-CT accurately. The inter-tow voids of the multilayer fabric are arranged periodically along the three main directions with an average inter-tow porosity of 16.6%. The through-thickness permeabilities obtained based on Micro-CT are in good agreement with experimental results.
-
Key words:
- satin fabric /
- resolution /
- CT image /
- inter-tow voids /
- numerical simulation /
- permeability
-
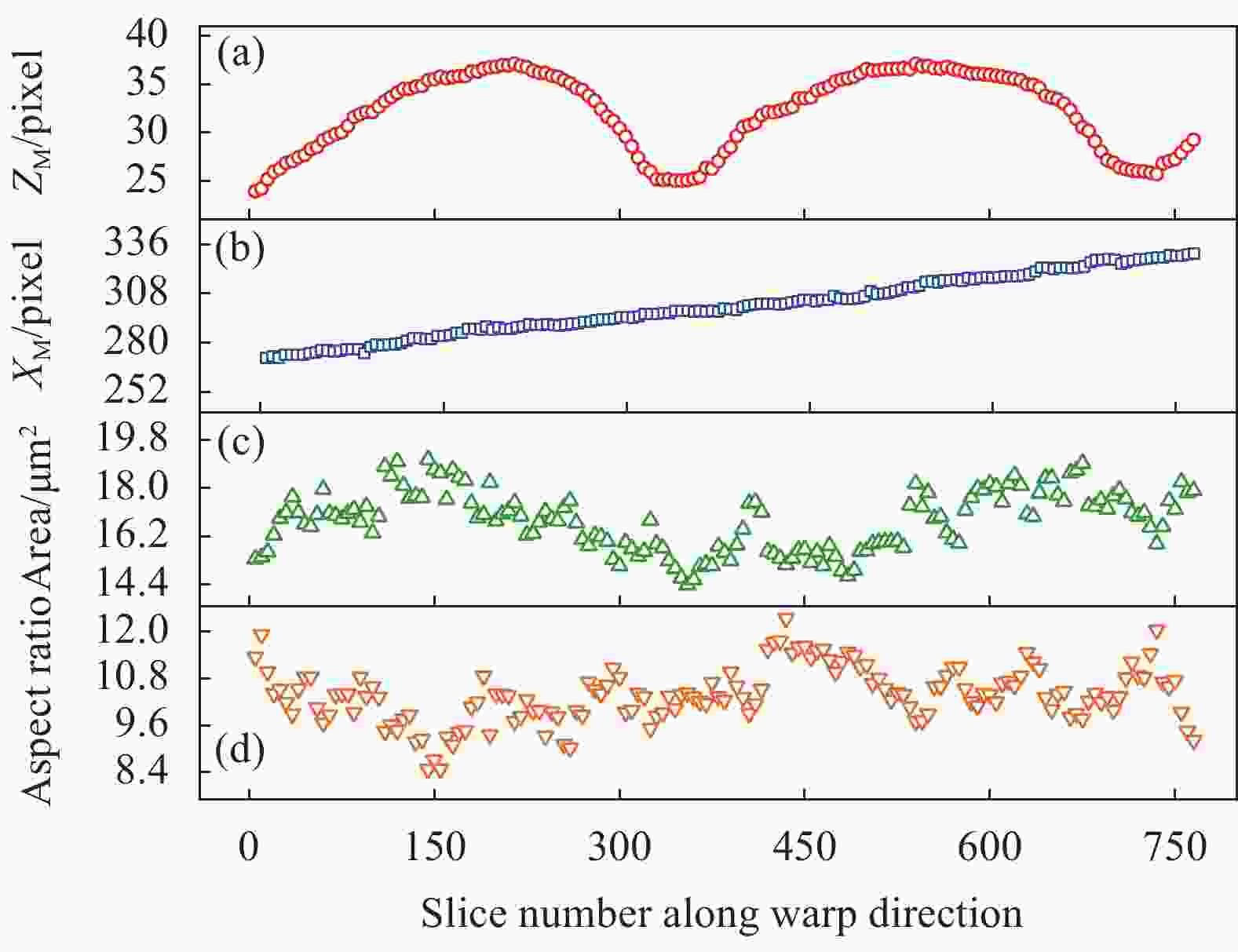
图 14 五枚缎纹织物经向纤维束结构特征:(a) 面内波动参数变化;(b) 面外波动参数变化;(c) 面积变化;(d) 长宽比变化
Figure 14. Structural characteristics of warp yarns of 5-harness satin woven fabric: (a) Variation of in-plane fluctuation parameter; (b) Variation of out-of-plane fluctuation parameter; (c) Changes in area; (d) Changes in aspect ratio
表 1 五枚缎纹织物细观几何参数
Table 1. Geometry parameters of the 5-harness satin woven fabric
Parameter Average/μm Coefficient of variation/% Weft Width 1157±41 2.8 Height 164±13 5.5 Warp Width 1520±31 1.0 Height 144±9 3.7 Fiber diameter 7.0±1.4 7.3 表 2 不同分辨率下五枚缎纹织物厚度方向渗透率计算结果
Table 2. Through-thickness permeability of 5-harness satin woven fabric calculated at different resolutions
Resolution/μm 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 Number of voxels 436020 633650 935220 1464870 2539008 5069200 11010285 39603600 KZ/10−12 m2 2.16 1.48 2.36 1.64 1.71 1.74 1.71 1.73 CPU time/min <10 <10 <10 12 14 26 47 75 Notes: KZ—Permeability of 5-harness satin woven fabric in thickness direction; CPU—Central processing unit. 表 3 实验测得的五枚缎纹织物KZ值
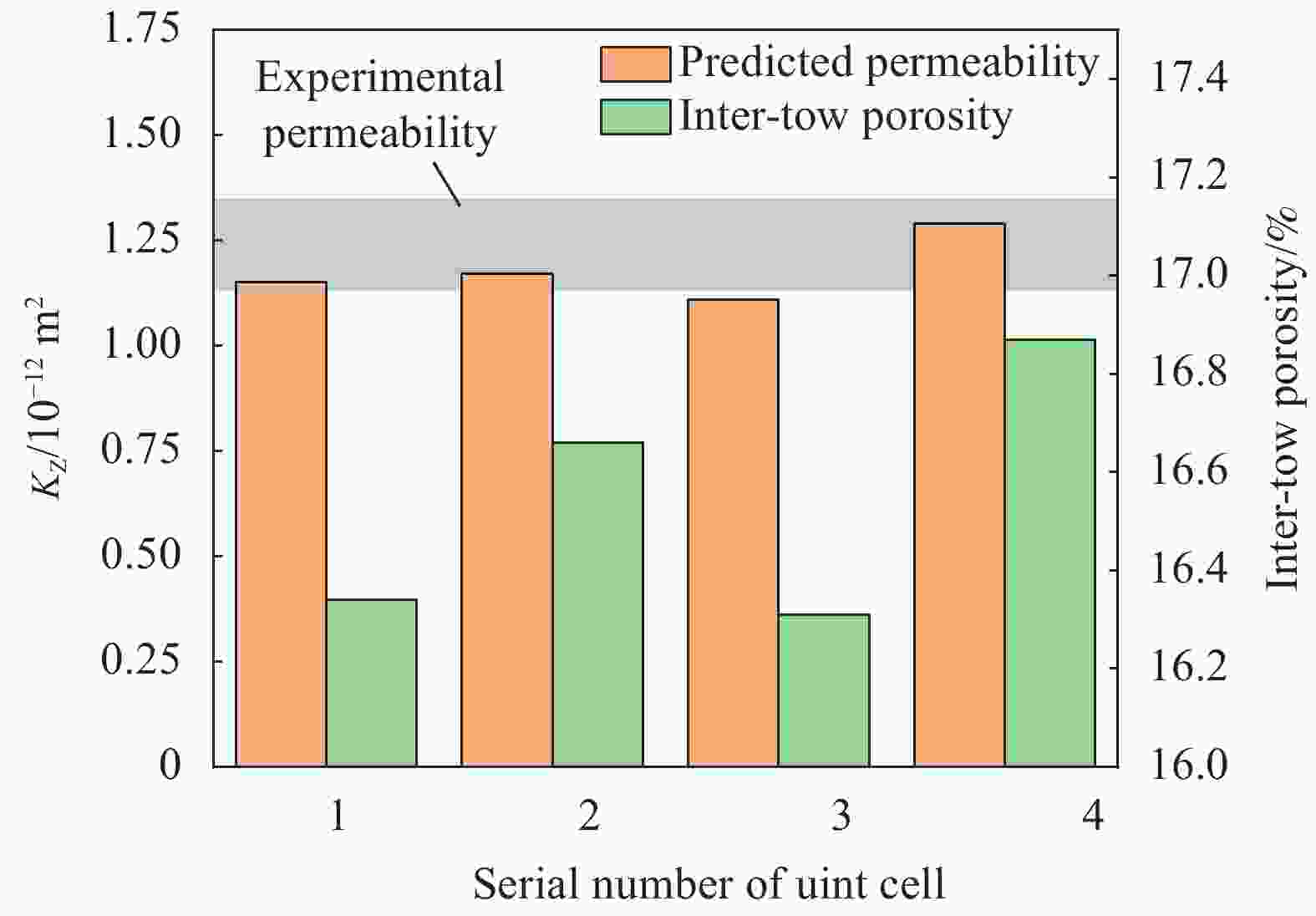
Table 3. KZ values measured by experiment of 5-harness satin woven fabric
Number Permeability/10−12 m2 1 1.35 2 1.32 3 1.28 4 1.17 5 1.13 Average/10−12 m2 1.25 Coefficient of variation/% 7.65 -
[1] KONSTANTOPOULOS S, HUEBER C, ANTONIADIS I, et al. Liquid composite molding reproducibility in real-world production of fiber reinforced polymeric composites: A review of challenges and solutions[J]. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science,2019,5(3):85-99. [2] 杨旭静, 王跃飞, 韦凯, 等. 基于孔隙控制的车身结构树脂传递模塑成型工艺设计[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(5):970-977.YANG Xujing, WANG Yuefei, WEI Kai, et al. Design of resin transfer molding process for vehicle body structure based on porosity control[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(5):970-977(in Chinese). [3] 马彦旭, 王继辉, 倪爱清, 等. 大厚度复合材料曲面典型构件的工艺优化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10):3302-3313.MA Yanxu, WANG Jihui, NI Aiqing, et al. Process optimization of typical composite cambered components with large thickness[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(10):3302-3313(in Chinese). [4] 李嘉禄, 吴晓青, 冯驰. RTM中纤维渗透率预测的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2006, 23(6):1-8. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.06.001LI Jialu, WU Xiaoqing, FENG Chi. Research progress on the permeability prediction of f iber in RTM[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2006,23(6):1-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2006.06.001 [5] 詹明樊, 王继辉, 倪爱清, 等. 基于数字图像技术的纤维织物面内渗透率表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(12):4180-4189.ZHAN Mingfan, WANG Jihui, NI Aiqing, et al. In-plane permeability characterization of fiber fabric based on digital image technology[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(12):4180-4189(in Chinese). [6] 李香林, 王继辉, 倪爱清, 等. 液体模塑成型工艺用纤维织物厚度方向饱和渗透率的预测模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(6):1428-1437.LI Xianglin, WANG Jihui, NI Aiqing, et al. Prediction model of through-thickness saturated permeability of fabric for liquid composite molding[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(6):1428-1437(in Chinese). [7] HUANG W, CAUSSE P, HU H, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation of saturated transverse permeability of 2D woven glass fabrics based on material twins[J]. Polymer Composites,2020,41(4):1341-1355. doi: 10.1002/pc.25458 [8] 张浩, 李书欣, 王继辉, 等. 基于新型测试装置的网孔板层开孔率对纤维厚度方向渗透率的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(5):1175-1183.ZHANG Hao, LI Shuxin, WANG Jihui, et al. Influence of ratio of hole area for mesh plate layer on through-thickness permeability based on a new designed test bench[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(5):1175-1183(in Chinese). [9] VERNET N, RUIZ E, ADVANI S, et al. Experimental determination of the permeability of engineering textiles: Benchmark II[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2014,61:172-184. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.02.010 [10] YONG A, AKTAS A, MAY D, et al. Out-of-plane permeability measurement for reinforcement textiles: A benchmark exercise[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2021,148(1):106480. [11] YANG B, HUANG W, CAUSSE P, et al. On the design of test molds based on unidirectional saturated flows to measure transverse permeability in liquid composite molding[J]. Polymer Composites,2022,43(4):2234-2251. doi: 10.1002/pc.26536 [12] 李永静, 晏石林, 李德权, 等. 液体模塑成型工艺中纤维束横向渗透率的细观数值模拟[J]. 纺织学报, 2015, 36(8):22-27.LI Yongjing, YAN Shilin, LI Dequan, et al. Microscopic numerical simulation of transverse permeability of fiber bundles in liquid composite molding[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2015,36(8):22-27(in Chinese). [13] 倪爱清, 王继辉, 朱以文. 复合材料液体模塑成型工艺中预成型体渗透率张量的数值预测[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(6):50-56. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.06.009NI Aiqing, WANG Jihui, ZHU Yiwen. Numerical prediction of saturated permeability tensor of a woven fabric for use in the fluid simulation of liquid composite molding[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2007,24(6):50-56(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.06.009 [14] CHEN Z R, YE L, LU M. Permeability predictions for woven fabric preforms[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2010,44(13):1569-1586. doi: 10.1177/0021998309355888 [15] ZENG X, ENDRUWEIT A, BROWN L P, et al. Numerical prediction of in-plane permeability for multilayer woven fabrics with manufacture-induced deformation[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,77:266-274. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.03.027 [16] 金天国, 魏雅君, 杨波, 等. 预成型体渗透率预测及其受压缩变形的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(3):840-847.JIN Tianguo, WEI Yajun, YANG Bo, et al. Permeability prediction of preform and influence of compression deformation[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(3):840-847(in Chinese). [17] 张璇, 白国娟, 王星星, 等. 三维织物厚度方向渗透率研究[J]. 中国胶粘剂, 2017, 26(5):21-24.ZHANG Xuan, BAI Guojuan, WANG Xingxing, et al. Study on the thickness-permeability of three-dimensional fabric[J]. China Adhesives,2017,26(5):21-24(in Chinese). [18] YOUSAF Z, POTLURI P, WITHERS P J, et al. Digital element simulation of aligned tows during compaction validated by computed tomography (CT)[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2018,154:78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2017.05.044 [19] ALI M A, UMER R, KHAN K A, et al. In-plane virtual permeability characterization of 3 D woven fabrics using a hybrid experimental and numerical approach[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,173:99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.01.030 [20] STRAUMIT I, HAHN C, WINTERSTEIN E, et al. Computation of permeability of a non-crimp carbon textile reinforcement based on X-ray computed tomography images[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2016,81:289-295. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.11.025 [21] 王法琪 严亚波, 温鑫鑫, 等. Micro-CT分辨率对松质骨微观结构及生物力学测量的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2015, 15(10):1877-1880,1835.WANG Faqi, YAN Yabo, WEN Xinxin, et al. The effect of micro-CT resolution on measuring microstructure and mechanical parameters of human lumbar vertebral trabecular bone[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine,2015,15(10):1877-1880,1835(in Chinese). [22] 耿冲, 杨永飞, 高莹. 不同分辨率岩石CT图像的优化处理方法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(2):1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.02.001GENG Chong, YANG Yongfei, GAO Ying. Optimization of image processing method based on rock CT images of different resolutions[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2014,14(2):1-4(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.02.001 [23] ALI M A, UMER R, KHAN K A. A virtual permeability measurement framework for fiber reinforcements using micro CT generated digital twins[J]. International Journal of Lightweight Materials and Manufacture,2020,3(3):204-216. doi: 10.1016/j.ijlmm.2019.12.002 [24] 王晨晨, 姚军, 杨永飞, 等. 基于CT扫描法构建数字岩心的分辨率选取研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2013, 13(4):1050-1052.WANG Chenchen, YAO Jun, YANG Yongfei, et al. Study of resolution selection for construction of digtal rock with CT scanning method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2013,13(4):1050-1052(in Chinese). [25] RATHORE J S, VIENNE C, QUINSAT Y, et al. Influence of resolution on the X-ray CT-based measurements of metallic AM lattice structures[J]. Welding in the World,2020,64(8):1367-1376. doi: 10.1007/s40194-020-00920-4 [26] BIGGEMANN J, KLLNER D, SCHATZ J, et al. Influence of CT scanning resolution and volume on FEM-simulation of periodic 3D-printed porous ceramics[J]. Materials Letters,2021,303:130529. [27] 杨斌. 复合材料用纤维织物压缩与渗流性能表征方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2018.YANG Bin. Research on compressibility and seepage property characterization methods of preform for FRP[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [28] ZENG X, BROWN L P, ENDRUWEIT A, et al. Geometrical modelling of 3D woven reinforcements for polymer composites: Prediction of fabric permeability and composite mechanical properties[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2014,56(1):150-160. [29] 王浩. 平纹织物复合材料微观结构特征对材料弹性常数的影响研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2016.WANG Hao. Effects of microstructure characteristics on elastic properties of plain-weave composites[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [30] RAJAB M A, GEORGE L E. Stamps extraction using local adaptive k-means and ISODATA algorithms[J]. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,2021,21(1):137-145. doi: 10.11591/ijeecs.v21.i1.pp137-145 [31] TAHIR M W, HALLSTR M S, KERMO M. Effect of dual scale porosity on the overall permeability of fibrous structures[J]. Composites Science & Technology,2014,103:56-62. -





 下载:
下载: