Calculation of normal section bearing capacity of high-strength rebars reinforced high ductility fiber reinforced concrete members
-
摘要: 高延性混凝土(High ductile fiber-reinforced concrete,HDC)具有良好的变形能力,用其替代普通混凝土,与高强钢筋结合形成构件,可使高强钢筋的强度利用率有效提高。本文基于我国《混凝土结构设计规范》(GB/T 50010—2010)中钢筋混凝土构件正截面承载力计算方法,对高强钢筋混凝土构件和高强钢筋HDC构件的正截面承载力进行分析,推导了相对界限受压区高度、最大与最小配筋率、受压区高度取值范围和轴压比限值等系数,研究了不同强度等级的钢筋、混凝土和HDC对各计算系数的影响,给出高强钢筋HDC构件正截面承载力计算方法,其计算结果与试验结果误差的平均值在12.5%以内。Abstract: High ductile fiber-reinforced concrete (HDC) is characterized by its excellent deformation ability. The utilization ratio of high-strength steel bars (HSS) can be effectively increased when HSS is applied in reinforced HDC members. Based on the analytical model for the flexural capacity of reinforced concrete members in code GB/T 50010—2010, the flexural capacities of the HSS reinforced concrete members and HSS reinforced HDC members were derived, respectively. Besides, some key parameters such as the relative depth of compression zone for balanced failure, maximum and minimum reinforcement ratios, the range of compression zone height and the limitation of the axial load ratio of the HSS reinforced HDC members were derived, respectively. The effect of strength grade of the steel bars, strength grade of concrete and HDC on each parameter aforementioned were investigated, respectively. A calculation method for the bearing capacity of the HSS reinforced HDC members was proposed, and the average error between the calculated results and the experimental results is less than 12.5%.
-
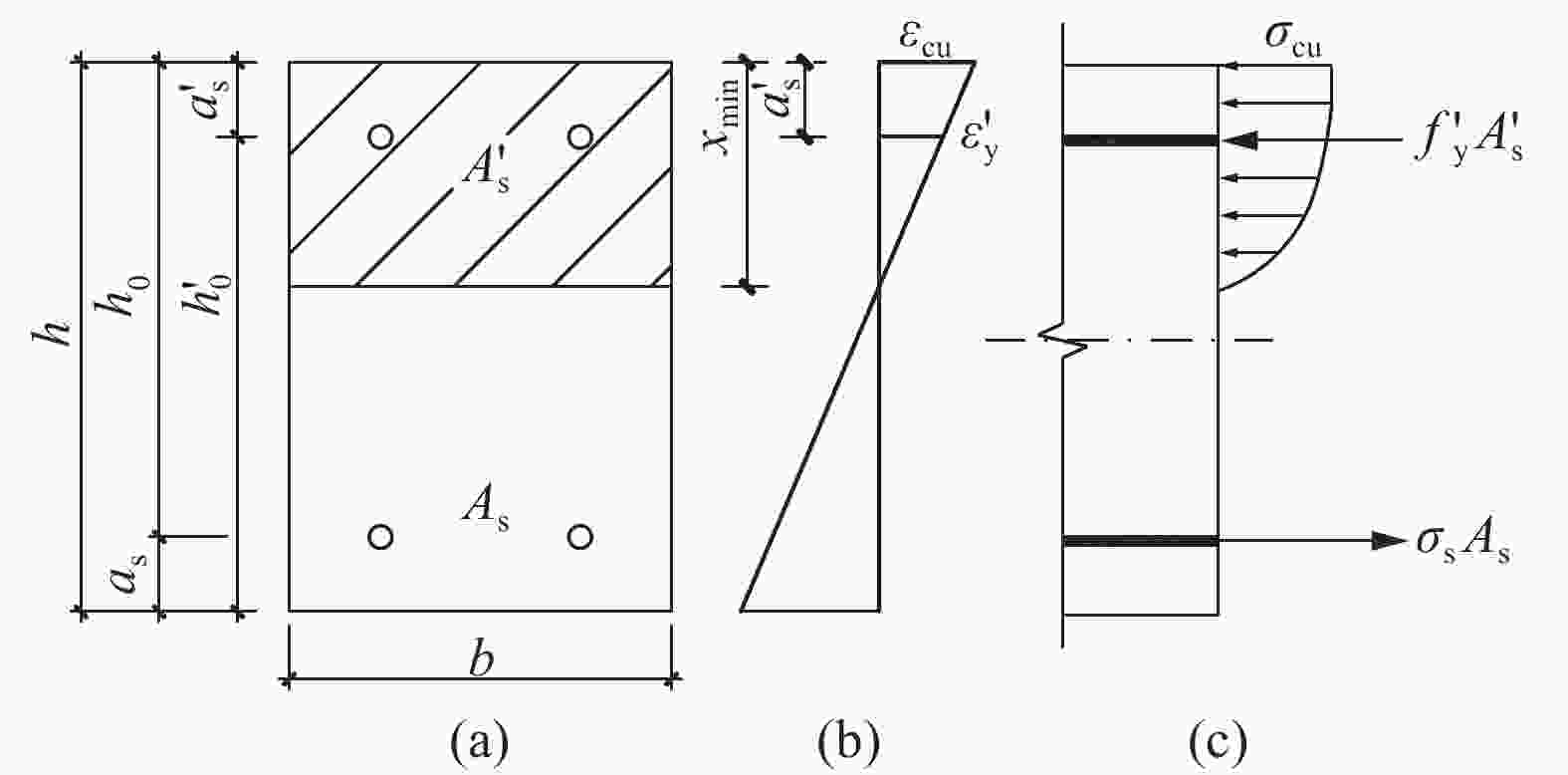
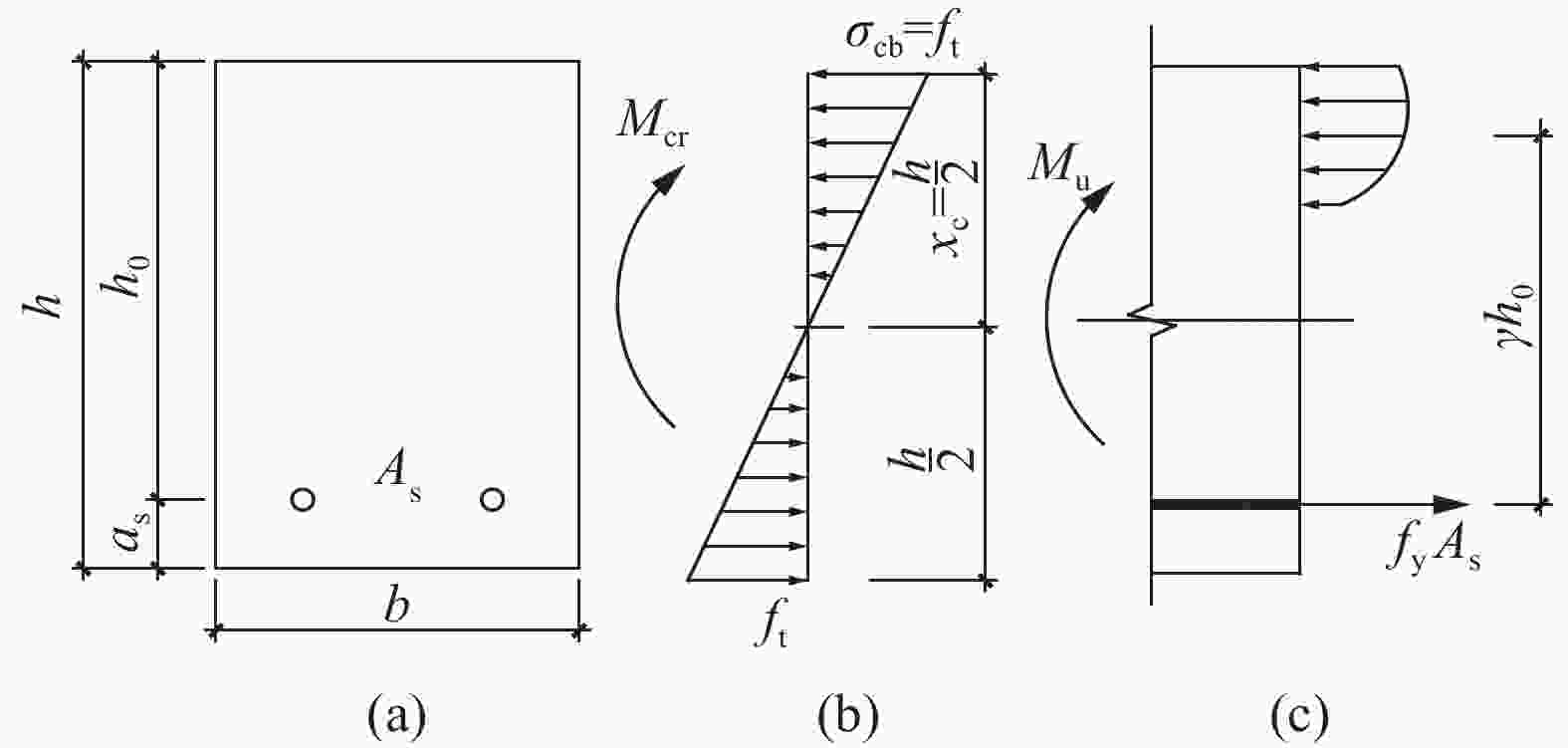
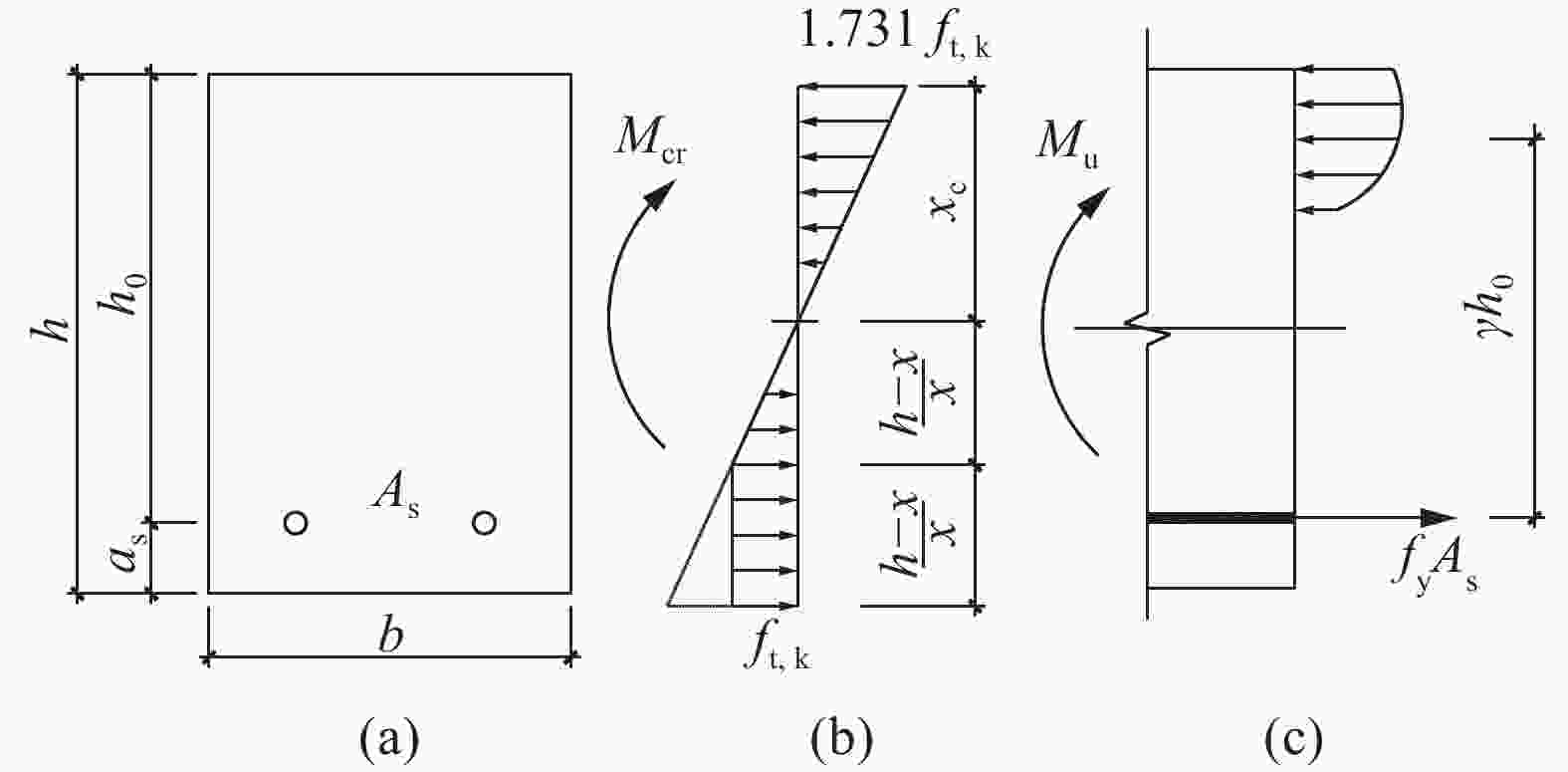
图 1 RC梁正截面应力-应变:(a) 截面;(b) 素混凝土开裂状态截面应力;(c) 少筋梁极限状态应力
Figure 1. Stress and strain distinction of section of RC beam: (a) Section; (b) Stress distribution on the cross-section of plain concrete member in cracked state; (c) Stress distribution of few-reinforced beams at ultimate state
h—Cross section height; h0—Section effective height; b—Section width; as—Distance from resultant force point of tensile reinforcement to edge of tensile zone; As—Section area of tension reinforcement; ft,k—Standard value of concrete tensile strength; xc—Actual height of compression zone; γh0—Section moment arm of tensile reinforcement in limit state; Mcr—Cracking moment of plain concrete; Mu—Ultimate bending moment; fy—Yield strength of the steel bar
图 2 受压区高度为最小值时对应正截面应变-应力分布:(a) 截面;(b) 截面应变;(c) 截面应力
Figure 2. Strain and stress calculation diagram of the corresponding normal section when the compression zone height is the minimum: (a) Section; (b) Strain distribution of section; (c) Stress distribution of section
A' s—Section area of compression reinforcement; a' s—Distance from resultant force point of compression reinforcement to edge of compression zone; xmin—Minimum height of compression zone; h' 0—Distance from the resultant point of the longitudinally pressurized rebar to the far side of the cross-section; ε' y—Rebar yield strain
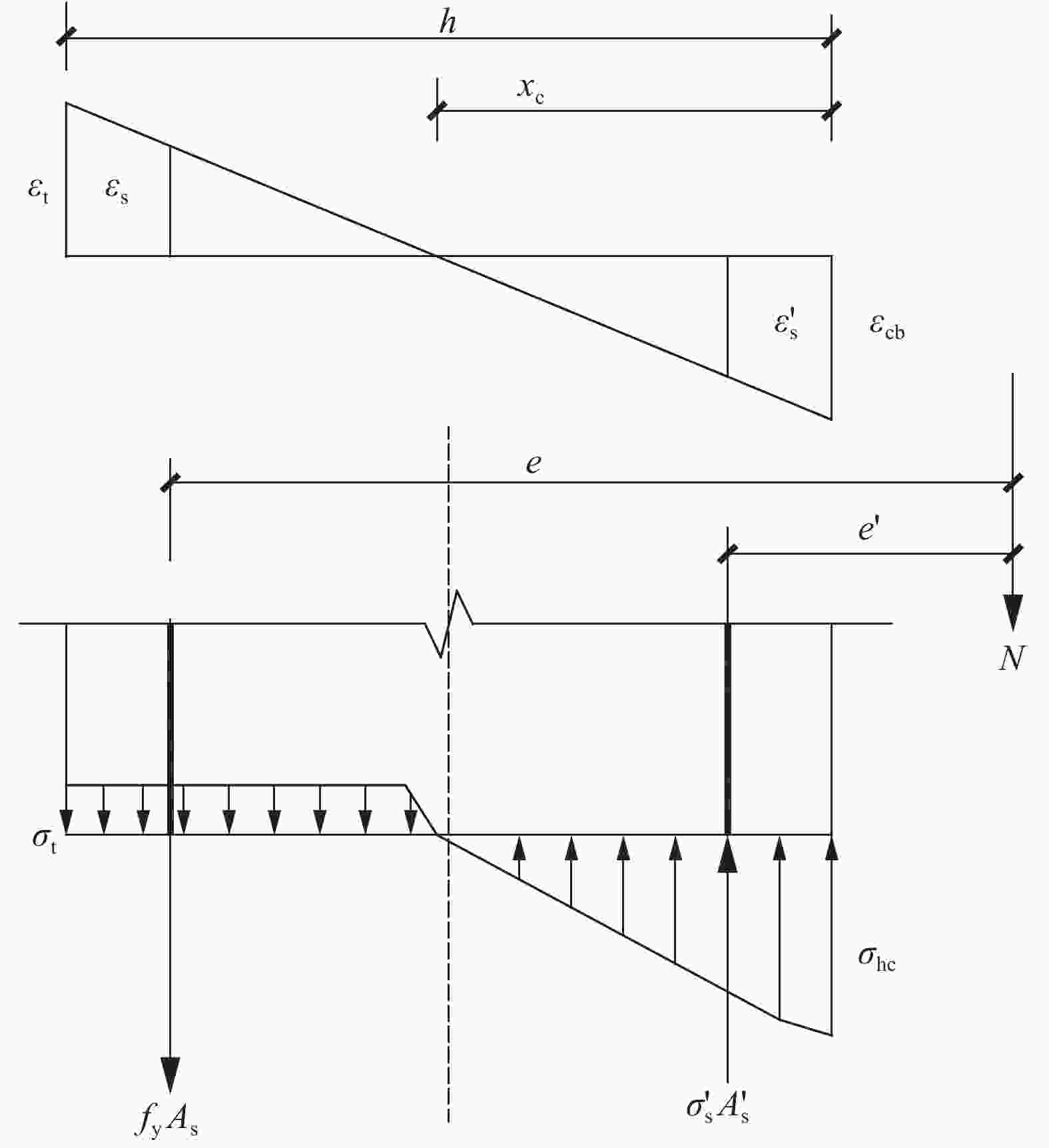
图 3 大偏心受压柱应力-应变分布
Figure 3. Stress and strain distribution of column under large eccentricity compression
εcb—Compressive strain value at the edge of compression zone; εt—Tensile strain value at the edge of the tensile zone; εs—Tension strain of reinforcement in tension zone; εs'—Compressive strain of reinforcement in compression zone; $ e $—Point of application of axial force to the resultant point of longitudinal tension reinforcement; $ e' $—Point of application of axial force to the resultant point of longitudinal compression reinforcement; N—Axial pressure design value; σt—Tensile stress value at the edge of the tensile zone
表 1 钢筋的力学性能
Table 1. Properties of reinforcing bars
Strength grade of reinforcement HRB400 HRB500 HRB600 Grade690 Grade830 Standard yield strength value fy,k/MPa 400 500 600 690 830 Ultimate strength fst,k/MPa 540 630 730 1030 1030 Design value of yield strength fy/MPa 360 435 520 600 720 表 2 不同强度等级钢筋对应的相对界限受压区高度
${\xi _{\text{b}}}$ 和设计轴压比限值${n_{\text{d}}}$ Table 2. Height of compressive region at the balanced point
${\xi _{\text{b}}}$ and the limitation of axial load ratio${n_{\text{d}}}$ corresponding to different strength grade of reinforcementStrength grade of reinforcement ≤C50 C60 C70 C80 HRB400 0.518(0.906) 0.499(0.856) 0.481(0.808) 0.463(0.761) HRB500 0.482(0.844) 0.464(0.796) 0.447(0.750) 0.429(0.706) HRB600 0.447(0.783) 0.430(0.738) 0.413(0.694) 0.396(0.652) Grade690 0.318(0.733) 0.304(0.690) 0.291(0.649) 0.278(0.609) Grade830 0.297(0.670) 0.284(0.630) 0.271(0.591) 0.258(0.553) Note: nd of steel bars and concrete at different strength grades are shown in parentheses. 表 3 不同强度等级钢筋对应的钢筋混凝土受弯构件最大配筋率
${\rho _{\max }}$ Table 3. Maximum reinforcement rate ρmax of reinforced concrete flexural members corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcement
% Strength grade
of reinforcementConcrete C20 C25 C30 C35 C40 C45 C50 C55 C60 C65 C70 C75 C80 HRB400 1.37 1.72 2.06 2.40 2.75 3.04 3.32 3.54 3.74 3.92 4.07 4.21 4.33 HRB500 1.06 1.32 1.59 1.85 2.12 2.34 2.56 2.73 2.88 3.01 3.13 3.24 3.33 HRB600 0.95 1.19 1.43 1.66 1.90 2.11 2.30 2.45 2.59 2.71 2.82 2.92 3.00 Grade690 0.58 0.73 0.88 1.02 1.17 1.29 1.41 1.50 1.58 1.65 1.71 1.76 1.80 Grade830 0.39 0.49 0.59 0.69 0.79 0.87 0.95 1.01 1.06 1.11 1.15 1.18 1.21 表 4 不同强度等级钢筋对应的最小配筋率
${\rho _{\min }}$ Table 4. Minimum reinforcement rate ρmin of RC flexural members corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcement
% Strength grade of reinforcement Concrete C20 C25 C30 C35 C40 C45 C50 C55 C60 C65 C70 C75 C80 HRB400 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.20 0.21 0.22 0.24 0.24 0.25 0.26 0.27 0.27 0.28 HRB500 0.11 0.13 0.15 0.16 0.18 0.19 0.20 0.20 0.21 0.22 0.22 0.23 0.23 HRB600 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.17 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.19 0.19 Grade690 0.08 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.15 0.16 0.16 0.16 0.17 Grade830 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.11 0.11 0.12 0.12 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.14 0.14 表 5 不同强度等级钢筋对应等效受压区高度最小值
$ {\beta _1}{x_{\min }} $ Table 5. Minimum of the height of equivalent rectangular stress blocks
$ {\beta _1}{x_{\min }} $ corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcementStrength grade of reinforcement Concrete ≤C50 C55 C60 C65 C70 C75 C80 HRB400 1.76${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.79${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.83${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.91${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.95${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.00${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.00${a'_{\text{s}}}$ HRB500 2.35${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.42${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.50${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.58${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.68${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.79${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.91${a'_{\text{s}}}$ HRB600 3.77${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 4.00${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 4.27${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 4.58${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 4.96${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 5.42${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 6.00${a'_{\text{s}}}$ Grade690 8.80${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 10.40${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 12.80${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 16.80${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 24.80${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 48.80${a'_{\text{s}}}$ ∞ Grade830 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ Note: ${a'_{\text{s}}}$—Distance from resultant force point of compression reinforcement to edge of compression zone. 表 6 不同强度等级钢筋对应双筋截面适筋梁的相对受压区高度
$ \xi $ 取值范围Table 6. Ranges of relative height
$\xi $ of compression zone of doubly reinforced section beams corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcementStrength grade of reinforcement Concrete ≤C50 C55 C60 C65 C70 C75 C80 HRB400 [0.18,0.52] [0.18,0.51] [0.18,0.50] [0.18,0.49] [0.18,0.48] [0.18,0.47] [0.19,0.46] HRB500 [0.23,0.48] [0.24,0.47] [0.24,0.46] [0.24,0.46] [0.25,0.45] [0.26,0.44] [0.27,0.43] HRB600 [0.38,0.45] [0.40,0.44] — — — — — Grade690 — — — — — — — Grade830 — — — — — — — Note: “—”in the table indicates that the minimum height of the pressure area is greater than the maximum. 表 7 高延性混凝土(HDC)本构模型参数
Table 7. Parameters of the constitutive model of high ductile concrete (HDC)
$ {\varepsilon _{{\text{t0}}}} $/10−4 $ {\varepsilon _{{\text{tu}}}} $/10−3 $ {\varepsilon _{{\text{h0}}}} $/10−3 $ {\varepsilon _{{\text{hu}}}} $/10−3 $ {f_{{\text{tu}}}} $/MPa $ {f_{{\text{cu}}}} $/MPa $ {f_{\text{c}}} $/MPa $ {f_{{\text{h0}}}} $/MPa 2.43 9.00 4.30 5.50 4.88 67.07 51.94 37.1 Notes: εt0—Cracking tensile strain of HDC; εtu—Ultimate tensile strain of HDC; εh0—Strain at peak stress of HDC; εhu—Ultimate compressive strain of HDC; ftu—Ultimate tensile strength of HDC; fcu—Standard value of cube compressive strength of HDC; fc—Standard value of axial compressive strength of HDC; fh0—Axial compressive strength design value of HDC. 表 8 HDC等效矩形应力图形系数
Table 8. Equivalent rectangular stress blocks parameters of HDC
$ {\varepsilon _{{\text{cb}}}} $/10−3 $ {\alpha _{\text{c}}} $ ${\beta _{\text{c}}}$ $ {\varepsilon _{{\text{tb}}}} $/10−3 $ {\alpha _{\text{t}}} $ $ {\beta _{\text{t}}} $ 2.00 0.518 0.686 0.24 0.750 0.667 3.00 0.710 0.702 2.00 0.998 0.941 4.00 0.845 0.723 4.00 0.999 0.970 5.00 0.902 0.758 6.00 0.999 0.980 5.50 0.887 0.786 9.00 1.000 0.987 Notes: $ {\alpha _{\text{c}}} $, ${\beta _{\text{c}}}$—Compressive equivalent rectangular stress blocks parameters of HDC; $ {\alpha _{\text{t}}} $, ${\beta _{\text{t}}}$—Tensile equivalent rectangular stress blocks parameters of HDC; εcb—Compressive strain value at the edge of compression zone of HDC; εtb—Tensile strain value at the edge of the tensile zone of HDC. 表 9 HDC柱承载力试验值和计算值[24]
Table 9. Test results and calculation results of bearing capacity of HDC columns[24]
Column specimen number Nt/kN Nc/kN Nt/Nc HDC1 2780 2566 1.08 HDC2 2368 2039 1.16 HDC3 1791 1642 1.09 HDC4 1317 1276 1.03 HDC5 992 971 1.02 HDC6 721 711 1.01 Notes: Nt—Test results of HDC columns; Nc—Calculation results of HDC columns. 表 10 高强钢筋HDC (HRHDC)梁抗弯承载力试验值和计算值
Table 10. Test results and calculation results of bending capacity of high-strength steel rebars reinforced HDC (HRHDC) beams
Beam specimen number Mt/(kN·m) Mc/(kN·m) Mt/Mc HRECC1[22] 7.66 7.00 1.09 HRECC2[22] 10.87 9.57 1.14 HRECC3[22] 11.03 11.01 1.00 RECC1[22] 5.55 5.51 1.01 HSS-ECC-0.53-M[23] 35.32 27.45 1.29 HSS-ECC-0.96-M[23] 48.48 38.19 1.27 HSS-ECC-1.48-M[23] 70.52 55.65 1.27 NSS-ECC-0.96-M[23] 27.32 24.25 1.13 NSS-ECC-2.10-M[23] 53.96 46.01 1.17 RU2 
5.57 5.79 0.96 RU3 
8.19 9.61 0.85 RU3 
9.02 11.32 0.80 Group A B2[30] 44.90 44.65 1.01 Group A B3[30] 50.10 47.71 1.05 Group A B4[30] 41.30 45.80 0.90 Group A B5[30] 46.50 50.21 0.93 Notes: Mt—Test results of ultimate bending moment; Mc—Calculation results of ultimate bending moment; HRECC—HSS-reinforced ECC; RU—Steel reinforced UHP-ECC; 0.53—Reinforcing ratios; NSS—Normal strength steel. 表 11 不同强度等级钢筋对应的HDC构件的相对界限受压区高度ξb和设计轴压比限值nd
Table 11. Height of compressive region at the balanced point ξb and the limitation of axial load ratio nd of HDC members corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcement
Strength grade of reinforcement Height of compressive region at the balanced point ξb Limitation of axial load ratio nd C60 C70 HDC C60 C70 HDC HRB400 0.499 0.481 0.595 0.856 0.808 0.927 HRB500 0.464 0.447 0.566 0.796 0.750 0.882 HRB600 0.430 0.413 0.536 0.738 0.694 0.835 Grade690 0.304 0.291 0.414 0.690 0.649 0.796 Grade830 0.284 0.271 0.391 0.630 0.591 0.744 表 12 不同强度等级钢筋对应的RC受弯构件最大配筋率
Table 12. Maximum reinforcement rate of RC flexural members corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcement
% Strength grade
of reinforcementC60 C70 HDC HRB400 3.74 4.07 5.46 HRB500 2.88 3.13 4.30 HRB600 2.59 2.82 3.78 Grade690 1.58 1.71 2.63 Grade830 1.06 1.15 1.80 表 13 不同强度等级钢筋对应的RC受弯构件最小配筋率
Table 13. Minimum reinforcement rate of RC flexural members corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcement
% Strength grade
of reinforcementC60 C70 HDC HRB400 0.25 0.27 0.35 HRB500 0.21 0.22 0.29 HRB600 0.18 0.18 0.24 Grade690 0.15 0.16 0.21 Grade830 0.13 0.13 0.18 表 14 不同强度等级钢筋对应等效受压区高度最小值
$ {\beta _1}{x_{\min }} $ Table 14. Minimum
$ {\beta _1}{x_{\min }} $ of the height of equivalent rectangular stress blocks corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcementStrength grade of reinforcement C60 C70 HDC HRB400 1.83${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.95${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.19${a'_{\text{s}}}$ HRB500 2.50${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 2.68${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.32${a'_{\text{s}}}$ HRB600 4.27${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 4.96${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.52${a'_{\text{s}}}$ Grade690 12.80${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 24.80${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 1.76${a'_{\text{s}}}$ Grade830 ∞ ∞ 2.32${a'_{\text{s}}}$ 表 15 不同强度等级钢筋对应双筋截面适筋梁的相对受压区高度
$ \xi $ 取值范围Table 15. Ranges of relative height
$ \xi $ of compression zone of doubly reinforced section beam corresponding to different strength grades of reinforcementStrength grade of reinforcement C60 C70 HDC HRB400 [0.18,0.50] [0.18,0.48] [0.12,0.60] HRB500 [0.24,0.46] [0.25,0.45] [0.13,0.57] HRB600 — — [0.15,0.54] Grade690 — — [0.17,0.41] Grade830 — — [0.23,0.39] Note: “—”in the table indicates that the minimum height of the pressure area is greater than the maximum. 表 16 高强钢筋的强度利用率
Table 16. Strength utilization ratio of high-strength steel rebars
Strength grade of reinforcement C70 HDC HDC/C70 HRB500 0.6217 0.8795 1.415 HRB600 0.5179 0.6530 1.261 -
[1] American Concrete Institute. Guide for the use of ASTM A1035/A1035 M type CS grade 100 (690) steel bars for structural concrete: 6 R-19[S]. Farmington Hills: American Concrete Institute, 2019. [2] ALDABAGH S, ALAM M S. High-strength steel reinforcement (ASTM A1035/A1035 M Grade 690): State-of-the-art review[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering,2020,146(8):03120003. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0002720 [3] MAST R F, DAWOOD M, RIZKALLA S H, et al. Flexural strength design of concrete beams reinforced with high-strength steel bars[J]. ACI Structural Journal,2008,113(2):325-336. [4] SHAHROZ B M, REIS J M, WELLS E L, et al. Flexural members with high-strength reinforcement: Behavior and code implications[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering,2014,19(5):04014003. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000571 [5] RAUTENBERG J M, PUJOL S, TAVALLALI H, et al. Reconsidering the use of high-strength reinforcement in concrete columns[J]. Engineering Structures,2012,37:135-142. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2011.12.036 [6] ALAVI-DEHKORDI S, DAVOOD M. Behavior of concrete columns reinforced with high-strength steel rebars under eccentric loading[J]. Materials and Structures, 2018, 51(6): 145. [7] 卓卫东, 黄璐, 陈阵, 等. 500 MPa级钢筋自密实混凝土偏压短柱受力性能试验及有限元模拟分析[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(9):197-206. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.11.0797ZHUO Weidong, HUANG Lu, CHEN Zhen, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis on mechanical behavior of eccentrically loaded self-compacting concrete short columns with 500 MPa steel bars[J]. Engineering Mecha-nics,2018,35(9):197-206(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.11.0797 [8] 王静, 王命平, 耿树江. HRBF500钢筋混凝土柱的受压试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2011, 28(10):152-157.WANG Jing, WANG Mingping, GENG Shujiang. The experimental research on reinforced concrete column by HRBF500 bars[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2011,28(10):152-157(in Chinese). [9] 张建伟, 夏冬瑞, 乔崎云, 等. HRB600级钢筋高强混凝土柱的轴心受压性能[J]. 工业建筑, 2017, 47(11):77-83. doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz201711016ZHANG Jianwei, XIA Dongrui, QIAO Qiyun, et al. Research on compression performance of high strength concrete columns with HRB600 steel bars[J]. Industrial Construction,2017,47(11):77-83(in Chinese). doi: 10.13204/j.gyjz201711016 [10] 张建伟, 夏冬瑞, 乔崎云, 等. HRB600级钢筋高强混凝土柱偏心受压性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2019, 40(4):74-80. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2019.04.008ZHANG Jianwei, XIA Dongrui, QIAO Qiyun, et al. Experimental study on eccentric compression performance of high-strength concrete columns with HRB600 steel bars[J]. Journal of Building Structures,2019,40(4):74-80(in Chinese). doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2019.04.008 [11] HOU Y, CAO S, NI X, et al. Research on concrete columns reinforced with new developed high-strength steel under eccentric loading[J]. Materials,2019,12(13):2139. doi: 10.3390/ma12132139 [12] SHIN H O, YOON Y S, COOK W D, et al. Axial load response of ultra-high-strength concrete columns and high-strength reinforcement[J]. ACI Structural Journal,2016,113(2):325-336. [13] LI V C. Engineered cementitious composites (ECC): Bendable concrete for sustainable and resilient infrastructure[M]. Germany: Springer, 2019: 4-9. [14] LI V C, WANG S, WU C. Tensile strain-hardening behavior of polyvinyl alcohol engineered cementitious composite (PVA-ECC)[J]. ACI Materials Journal-American Concrete Institute,2001,98(6):483-492. [15] LI V C. On engineered cementitious composites (ECC): A review of the material and its applications[J]. Advance Concrete Technology,2003,1(3):215-230. doi: 10.3151/jact.1.215 [16] LI V C. Engineered cementitious composites-tailored composites through micromechanical modeling[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 1998, 1(3): 1-38. [17] LI V C, LEUNG C K Y. Steady-state and multiple cracking of short random fiber composites[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics,1992,118(11):2246-2264. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1992)118:11(2246 [18] 邓明科, 潘姣姣, 秦萌, 等. 高延性混凝土单轴受压本构模型研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 48(6):826-831. doi: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2016.06.009DENG Mingke, PAN Jiaojiao, QIN Meng, et al. Research on the constitutive relation of high ductile fiber reinforced concrete under uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,48(6):826-831(in Chinese). doi: 10.15986/j.1006-7930.2016.06.009 [19] 邓明科, 刘海勃, 秦萌, 等. 高延性纤维混凝土抗压韧性试验研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 47(5):660-665.DENG Mingke, LIU Haibo, QIN Meng, et al. Experimental research on compressive toughness of the high ductile fiber reinforced concrete[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition),2015,47(5):660-665(in Chinese). [20] 徐世烺, 李贺东. 超高韧性水泥基复合材料直接拉伸试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2009, 42(9):32-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2009.09.005XU Shilang, LI Hedong. Uniaxial tensile experiments of ultra-high toughness cementitious composite[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering,2009,42(9):32-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2009.09.005 [21] 寇佳亮, 邓明科, 梁兴文. 延性纤维增强混凝土单轴拉伸性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2013, 43(1):59-64.KOU Jialiang, DENG Mingke, LIANG Xingwen. Experimental study of uniaxial tensile properties of ductile fiber reinforced concrete[J]. Building Structure,2013,43(1):59-64(in Chinese). [22] 薛会青, 邓宗才. HRECC梁弯曲性能的试验研究与理论分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2013, 46(4):10-17.XUE Huiqing, DENG Zongcai. Experimental and theoretical studies on bending performance of HRECC beams[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2013,46(4):10-17(in Chinese). [23] SHAO Y, BILLINGTON S L. Flexural performance of steel-reinforced engineered cementitious composites with different reinforcing ratios and steel types[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,231:117159. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117159 [24] 邓明科, 李睿喆, 张阳玺, 等. 高延性混凝土偏心受压柱正截面受力性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2019, 36(11):62-71.DENG Mingke, LI Ruizhe, ZHANG Yangxi, et al. Experimental study on mechanical behavior of high ductile concrete members under eccentric compression[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2019,36(11):62-71(in Chinese). [25] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构设计规范: GB/T 50010—2010[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2010.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for design of concrete structures: GB/T 50010—2010[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2010(in Chinese). [26] 李小龙, 郭正洪, 戎咏华, 等. 基于屈服平台理论开发的600 MPa级高强塑性螺纹钢的研究[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50(4):439-446.LI Xiaolong, GUO Zhenghong, DI Yonghua, et al. 600 MPa grade rebar with high ductility development based on theory of yield plateau[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica,2014,50(4):439-446(in Chinese). [27] 邓明科, 张阳玺, 陈尚城. 高延性混凝土加固框架柱抗震性能试验研究及其轴压比限值分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2019, 52(2):22-31, 65.DENG Mingke, ZHANG Yangxi, CHEN Shangcheng. Experimental research of the seismic performance of frame columns strengthened with high ductile concrete jacket and analysis of the limitation of axial load ratio[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2019,52(2):22-31, 65(in Chinese). [28] 邓明科, 李睿喆, 张阳玺. HDC与RPC加固RC柱轴心受压性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(9):74-83.DENG Mingke, LI Ruizhe, ZHANG Yangxi. Experimental investigation on axial compression behavior of RC columns strengthened with HDC and RPC jackets[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2020,37(9):74-83(in Chinese). [29] DING Y, YU K Q, YU J, et al. Structural behaviors of ultra-high performance engineered cementitious composites (UHP-ECC) beams subjected to bending-experimental study[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 177: 102-115. [30] SHANOUR A S, SAID M, ARAFA A I, et al. Flexural performance of concrete beams containing engineered cementitious composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,180:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.05.238 [31] 邓明科, 张辉, 梁兴文, 等. 高延性纤维混凝土短柱抗震性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2015, 36(12):62-69. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2015.12.008DENG Mingke, ZHANG Hui, LIANG Xingwen, et al. Experimental study on seismic behavior of high ductile fiber reinforced concrete short column[J]. Journal of Building Structures,2015,36(12):62-69(in Chinese). doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2015.12.008 [32] DENG M, MA F, YE W, et al. Flexural behavior of reinforced concrete beams strengthened by HDC and RPC[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,188:995-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.124 -





 下载:
下载: