Influence of nano-SiO2 dispersion on the direct current dielectric properties of SiO2/LDPE nanocomposite
-
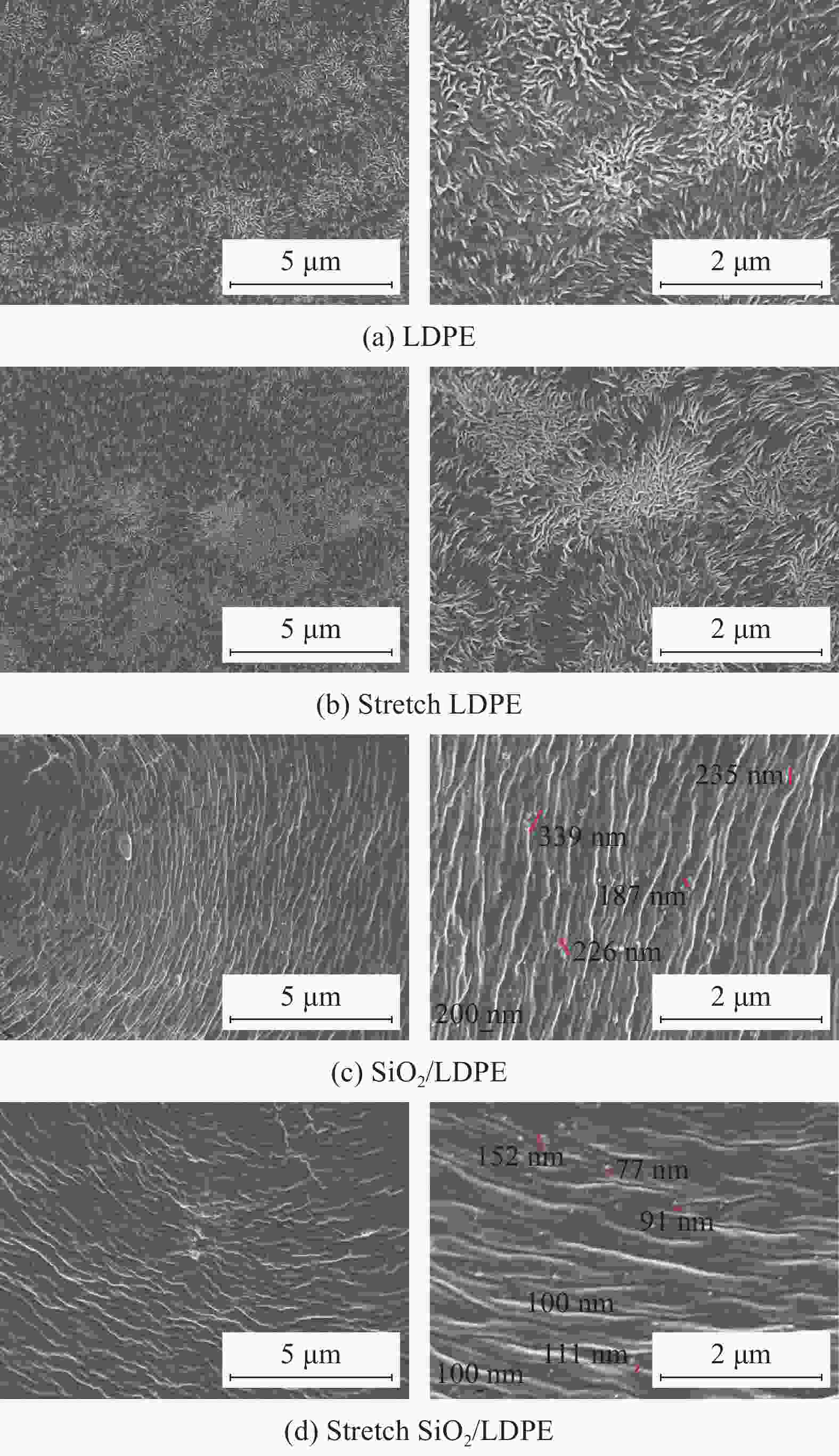
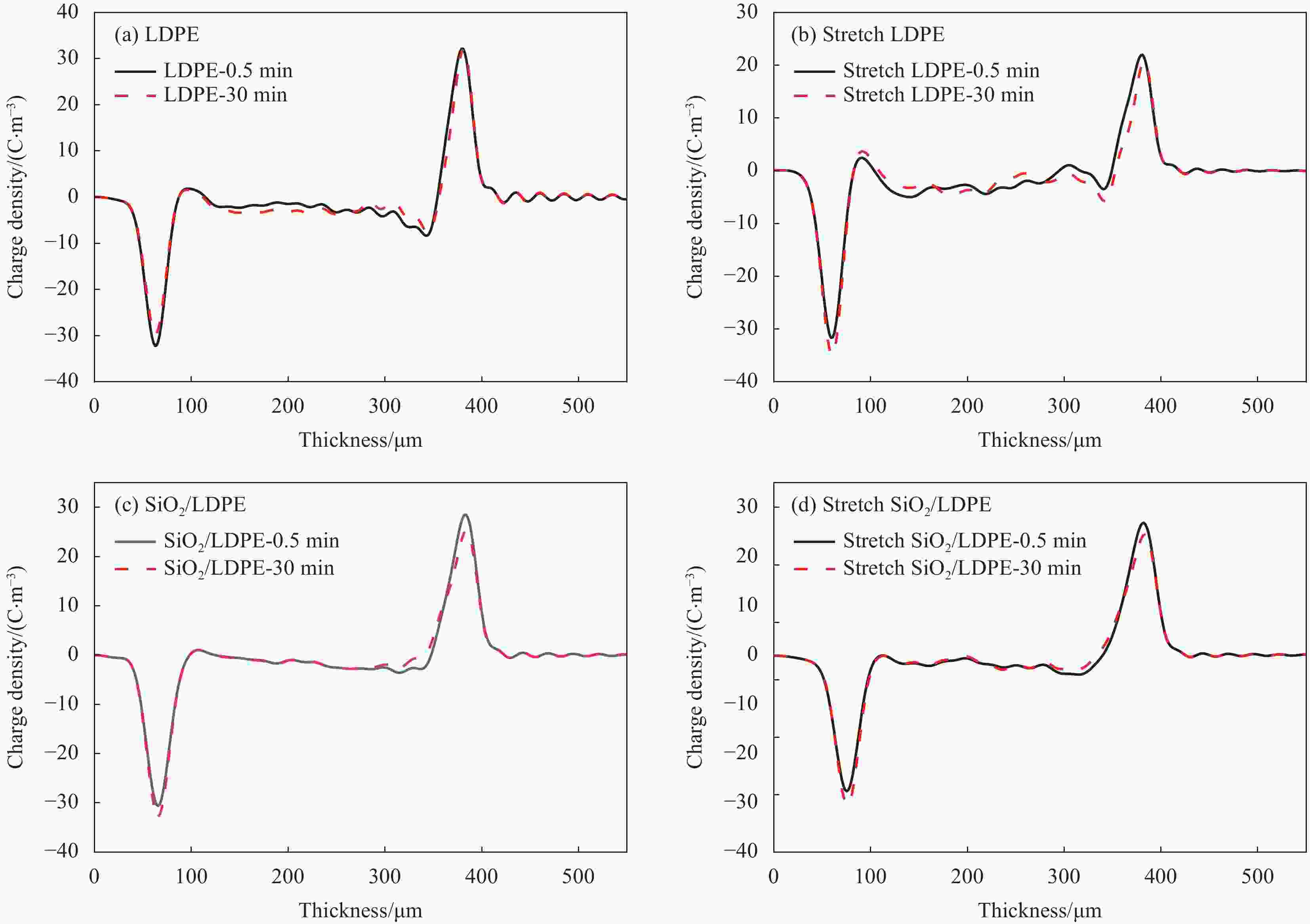
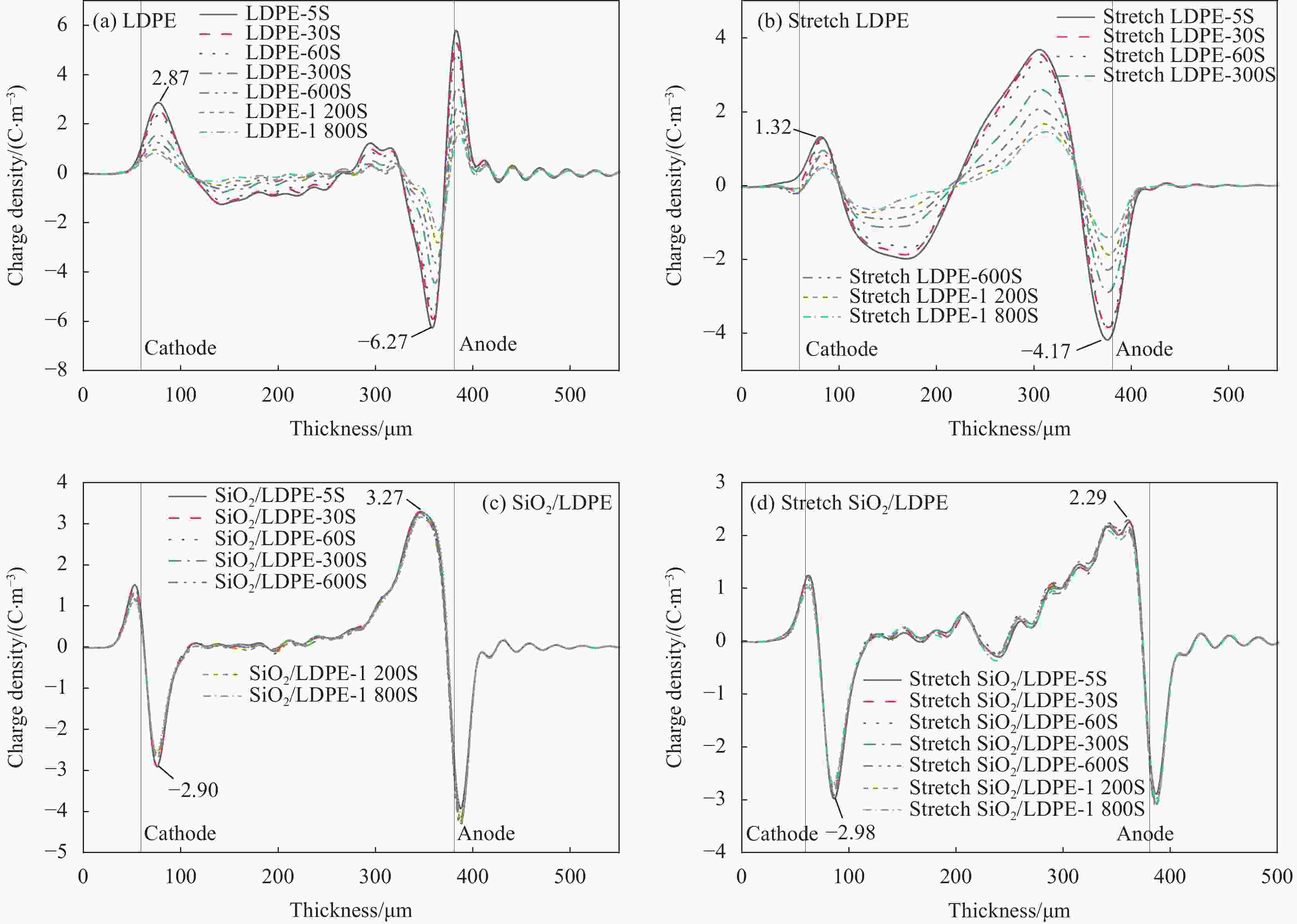
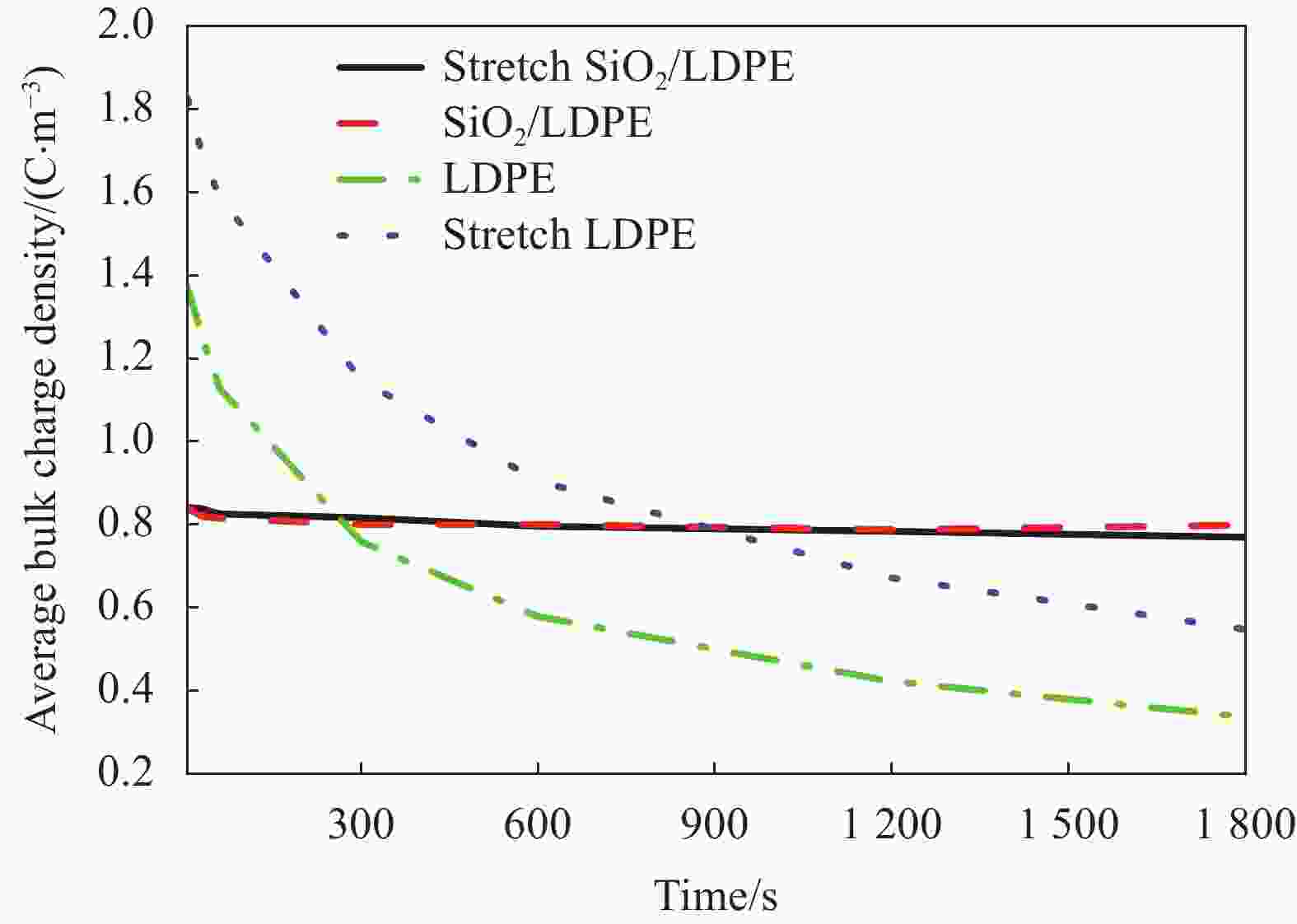
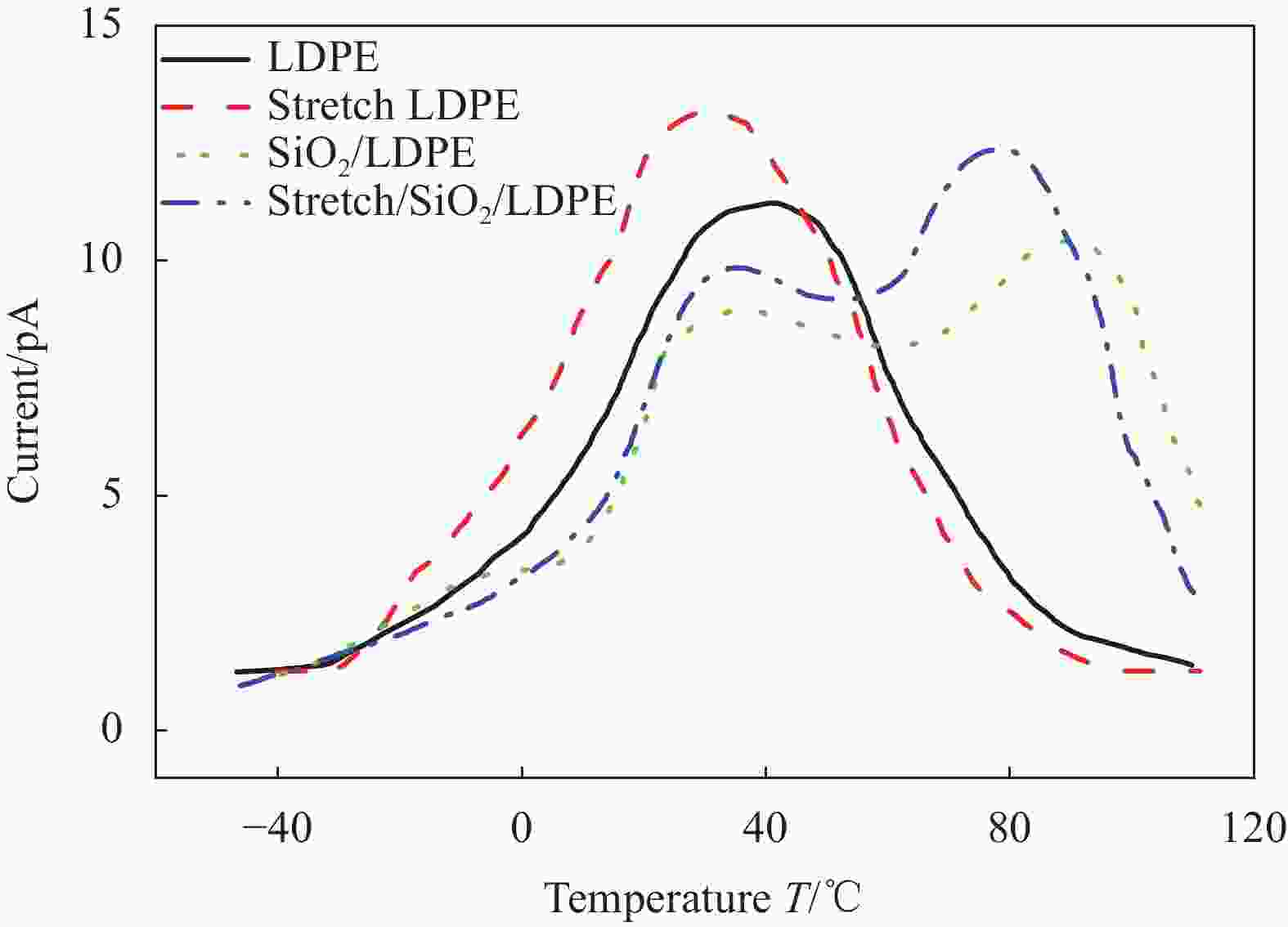
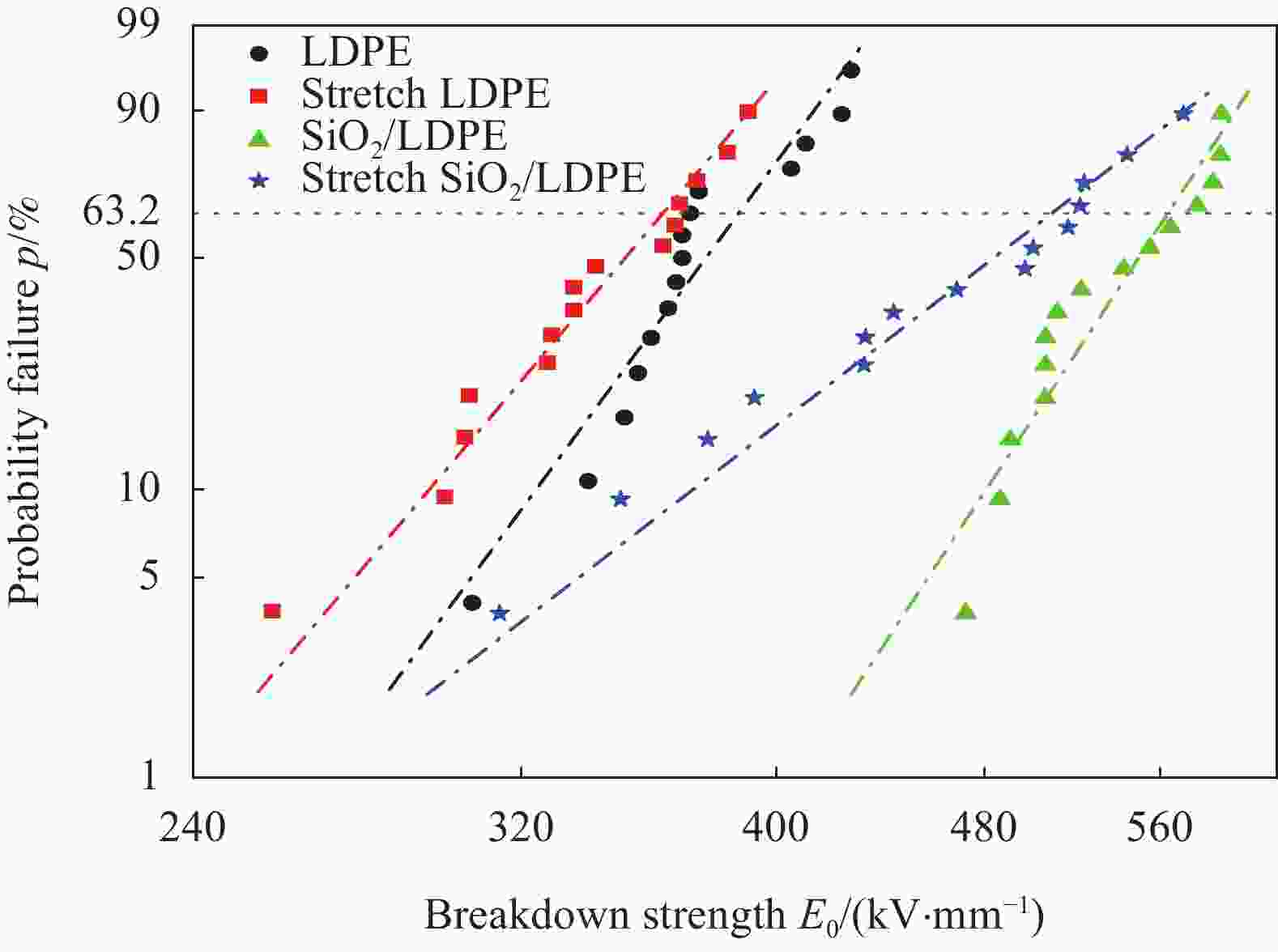
摘要: SiO2/低密度聚乙烯(LDPE)复合材料的介电性能与纳米SiO2在LDPE基体中的分散性密切相关。为研究室温下拉伸处理对纳米SiO2颗粒在LDPE基体中分散性的作用机制,本文选取7 nm粒径的疏水型纳米SiO2与LDPE熔融共混制备SiO2/LDPE纳米复合材料。将制备好的纳米复合材料经过三次拉伸处理,利用SEM、DSC表征纳米粒子的分散性及复合材料的结晶度,利用热刺激电流法(TSC)测试分析复合材料的陷阱能级和陷阱密度。通过对纳米复合材料的空间电荷,电导电流,直流击穿强度进行实验测试,研究了拉伸对纳米粒子分散性的影响及其所导致的直流介电性能的改变。结果表明室温下拉伸有助于纳米粒子的分散,使纳米SiO2粒子的团聚尺寸从200 nm左右缩减到100 nm左右;但拉伸会破坏LDPE的结晶结构,劣化其性能;通过掺杂纳米SiO2引入深陷阱能级可以改善LDPE的直流介电性能。经过拉伸的SiO2/LDPE的空间电荷积累得到抑制,电导电流的机制发生改变。通过对电导电流的数据进行拟合处理,发现拉伸后的SiO2/LDPE的电导以离子跳跃电导为主,其跳跃距离减少到1.98 nm左右。SiO2/LDPE相比LDPE直流击穿强度提高约43%,室温拉伸处理后SiO2/LDPE击穿强度降低的主要原因是拉伸过程导致的LDPE基体结构缺陷。Abstract: The dielectric properties of SiO2/low-density polyethylene (LDPE) composites are closely related to the dispersion of nano-SiO2 in LDPE matrix. In order to study the mechanism of tensile treatment on the dispersion of nano-silica particles in the LDPE matrix at room temperature, a hydrophobic nano-SiO2 with a particle size of 7 nm was selected to be fused and blended with LDPE to prepare SiO2/LDPE nanocomposites. The prepared nanocomposites were stretched three times, and the dispersion of nanoparticles and the crystallinity of the composites were characterized by SEM and DSC, the trap energy levels and trap densities of the composites were analyzed by thermally stimulated galvanometry (TSC). The effects of stretching on the dispersion of nanoparticles and the resulting changes in direct current dielectric properties were investigated by experimentally testing the space charge, electrical conductivity, and direct current breakdown strength of the nanocomposites. The results show that stretching at room temperature helps the dispersion of nanoparticles and reduce the agglomeration size of nano-SiO2 particles from about 200 nm to about 100 nm. However, stretching will destroy the crystal structure of LDPE and deteriorate its properties; The DC dielectric properties of LDPE can be improved by introducing deep trap levels by doping nano-SiO2.The space charge accumulation of the stretched SiO2/LDPE is suppressed, and the mechanism of conducting current is changed. By fitting the conductance current data, it is found that the conductance of the stretched SiO2/LDPE is dominated by ion hopping conductance, and its hopping distance is reduced to about 1.98 nm. Compared with LDPE, the DC breakdown field strength of SiO2/LDPE is improved by about 43%, The main reason for the decrease of the breakdown strength of SiO2/LDPE after stretching at room temperature is the structural defects of the LDPE matrix caused by the stretching process.
-
Key words:
- SiO2/LDPE /
- room temperature stretching /
- dispersion /
- space charge /
- conductance /
- breakdown strength
-
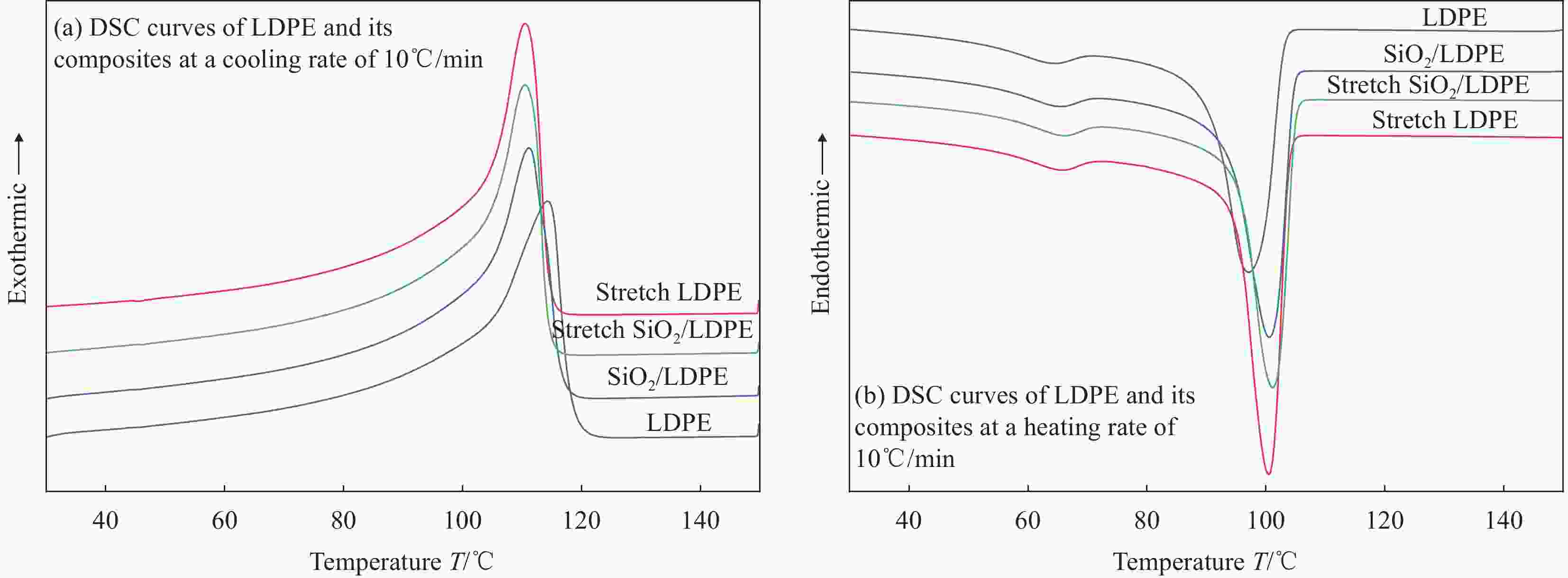
表 1 LDPE及其复合材料的DSC数据
Table 1. DSC data of LDPE and its composites
Sample Tc/℃ Tm/℃ ΔHm/(J∙g−1) Wc/% LDPE 114.3 92.17 116.53 37.19 Stretch LDPE 110.5 95.5 116.38 39.64 SiO2/LDPE 111.2 95.5 111.86 38.53 Stretch SiO2/LDPE 110.5 96.17 113..05 38.94 Notes: Tc and Tm—Crystallization peak temperature and melting peak temperature; ΔHm and Wc —Enthalpy of fusion and crystallinity of each sample. 表 2 各试样的电导斜率和过渡阈值电场
Table 2. Conductivity slope and transition threshold electric field of each sample
Sample β E/(kV·mm−1) jΩ jt EΩ−t LDPE 0.53 4.45 9.52 Stretch LDPE 0.18 4.24 5.74 SiO2/LDPE 0.22 2.57 21.11 Stretch SiO2/LDPE 1.05 − − Notes: β and E—Slope and electric field strength; jΩ,jt and EΩ−t—Slope of the conductance current density curve and the threshold EΩ−t of the transition electric field. 表 3 各试样的特征击穿场强和形状参数
Table 3. Characteristic breakdown field strength and shape parameters of each sample
Sample E0/(kV·mm−1) γ LDPE 387.1 12.67 Stretch LDPE 354.7 11.72 SiO2/LDPE 554.4 15.05 Stretch SiO2/LDPE 491.0 7.634 Note: E0 and γ—Characteristic breakdown field strength and shape parameters, respectively -
[1] TEYSSEDRRE G, LAURENT C. Advances in high-field insulating polymeric materials over the past 50 years[J]. IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine,2013,29:26-36. [2] 何金良, 党斌, 周垚, 等. 挤压型高压直流电缆研究进展及关键技术述评[J]. 高电压技术, 2015, 41(5):1417-1429.HE Jinliang, DANG Bin, ZHOU Yao, et al. Review of research progress and key technologies of extruded HVDC cables[J]. High Voltage Engineering,2015,41(5):1417-1429(in Chinese). [3] 马人凤, 朱永华, 吴建东, 等. 超高压直流电缆的国产化研究进展[J]. 绝缘材料, 2016, 49(11):1-8.MA Renfeng, ZHU Yonghua, WU Jiandong, et al. Research progress in localization of ultra-high voltage DC cables[J]. Insulation Mateials,2016,49(11):1-8(in Chinese). [4] 程羽佳, 张晓虹, 郭宁, 等. 纳米ZnO/低密度聚乙烯复合材料的介电特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(7):1351-1360.CHENG Yujia, ZHANG Xiaohong, GUO Ning, et al. Dielectric properties of nano-ZnO/low density polyethylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(7):1351-1360(in Chinese). [5] 巫运辉, 查俊伟, 王思蛟, 等. 多层介孔纳米MgO/低密度聚乙烯复合材料的制备及其绝缘性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(3):503-509.WU Yunhui, CHA Junwei, WANG Sijiao, et al. Preparation and insulation properties of multilayer mesoporous nano-MgO/low density polyethylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(3):503-509(in Chinese). [6] 杨佳明, 赵洪, 郑昌佶, 等. 纳米MgO/LDPE及SiO2/LDPE复合介质潮气吸附机制及其对直流电导特性的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7):1832-1840.YANG Jiaming, ZHAO Hong, ZHENG Changji, et al. Moisture adsorption mechanis of nano-MgO/LDPE and SiO2/LDPE composite media and its effect on direct current conductivity characteristics[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(7):1832-1840(in Chinese). [7] 张晓虹, 石泽祥, 李琳, 等. 蒙脱土-SiO2/低密度聚乙烯复合材料结晶行为及电树枝化特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11):3034-3043.ZHANG Xiaohong, SHI Zexiang, LI Lin, et al. Crystallization behavior and electrical dendronization characteristics of montmorillonite-SiO2/low-density polyethylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(11):3034-3043(in Chinese). [8] LIU J, WANG Y Y, ZHANG Z X, et al. Investigation of the electrical properties of LDPE/SiO2 nanocomposites under tensile condition[C]//Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomenon. Worth TX: CEIDP, 2017: 489-492. [9] YANG J M, XIE S H, ZHAO H, et al. Space chargeformation related to the structural relaxation of SiO2/LDPE nanocomposite[C]//International Symposium on Electrical Insulating Materials.Toyohashi: ISEIM, 2017: 625-628. [10] CHEN J, YIN Y, LI Z, et al. The effect of nano-SiOx partical on high field conduction in low-density polyethylene (LDPE)[C]//IEEE 9 th International Conference on the Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials. Harbin: ICPADM, 2009: 638-642. [11] 石泽祥. MMT/SiO2/LDPE微纳米复合电介质结构形态与电学性能的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2019.SHI Zexiang. Research on the morphology and electrical properties of MMT/SiO2/LDPE micro-nano composite dielectrics[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [12] 兰莉, 吴建东, 纪哲强, 等. 纳米SiO2/低密度聚乙烯复合介质的击穿特性[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(13):138-143.LAN Li, WU Jiandong, JI Zheqiang, et al. The breakdown characteristics of nano-SiO2/lowdensity polyethylene composite medium[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2012,32(13):138-143(in Chinese). [13] TAKADA T, HAYASE Y, TANAAKA Y, et al. Space charge trapping in electrical potential well causedby permanent and induced dipoles[C]//2007 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena. Victoria BC Canada, CEIDP, 2007, 417-420. [14] 王威望, 李盛涛, 刘文凤. 聚合物纳米复合电介质的击穿性能[J]. 电工技术学报, 2017, 32(16):25-36.WANG Weiwang, LI Shengtao, LIU Wenfeng. Breakdown properties of polymer nanocomposite dielectrics[J]. Transactions of the China Electrotechnical Society,2017,32(16):25-36(in Chinese). [15] 高俊国, 赵贺, 李霞, 等. 纳米SiO2/低密度聚乙烯复合材料的陷阱特性与电击穿机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(4):801-810.GAO Junguo, ZHAO He, LI Xia, et al. Trap characteristics and electrical breakdown mechanism of nano-SiO2/low density polyethylene composites[J]. Acta Materialae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(4):801-810(in Chinese). [16] 田付强, 杨春, 何丽娟, 等. 聚合物/无机纳米复合电介质介电性能及其机理最新研究进展[J]. 电工技术学报, 2011, 26(3): 1-12.TIAN Fuqiang, YANG Chun, HE Lijuan, et al. The latest research progress in the dielectric properties and mechanism of polymer/inorganic nanocomposite dielectrics[J]. Transactions of the China Electrotechnial Society, 2011, 26(3) : 1-12(in Chinese). [17] SMITH R C, LIANG C, LANDRY M, et al. The mechanisms leading to the useful electrical properties of polymer nano-dielectrics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2008,15(1):187-196. doi: 10.1109/T-DEI.2008.4446750 [18] 杨佳明, 赵洪, 郑昌佶, 等. 纳米粒子分散性对SiO2/LDPE纳米复合介质直流介电性能的影响[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(19):5087-5094.YANG Jiaming, ZHAO Hong, ZHENG Changji, et al. The effect of nanoparticle dispersion on the direct current dielectric properties of SiO2/LDPE nanocomposite media[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE,2015,35(19):5087-5094(in Chinese). [19] 吴振升, 叶青, 周远翔, 等. 表面修饰纳米SiO2/XLPE的电导电流和空间电荷特性[J]. 高电压技术, 2014, 40(10): 3268-3275.WU Zhensheng, YE Qing, ZHOU Yuanxiang, et al. Electrical conductivity and space charge characteristics of surface-modified nanoSiO2/XLPE[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2014, 40(10): 3268-3275(in Chinese). [20] 吴强, 杨佳明, 赵洪, 等. 深度混炼对纳米SiO2/低密度聚乙烯复合材料分散性与直流电性能影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11):3008-301.WU Qiang, YANG Jiaming, ZHAO Hong, et al. Effects of deep mixing on the dispersion and direct current properties of nano-SiO2/low density polyethylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(11):3008-301(in Chinese). [21] 迟晓红, 俞利, 郑杰, 等. 蒙脱土/聚丙烯复合材料结晶形态及耐电树枝化特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(1): 76-84.CHI Xiaohong, YU Li, ZHENG Jie, et al. Crystal morphology and electrical dendronization characteristics of montmorillonite/polypropylene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2015, 32(1): 76-84(in Chinesse). [22] 梁基照. 应用DSC测量HDPE熔体的热性能参数(Ⅰ. 熔融热焓与结晶度)[J]. 塑料通讯, 1994(3):23-25, 22.LIANG Jizhao. Using DSC to measure the thermal perfor-mance parameters of HDPE melt (Ⅰ. Melting enthalpy and crystallinity)[J]. Plastic Communications,1994(3):23-25, 22(in Chinese). [23] MONTANARI G C, FABIANI D. Evaluation of dc insulation performance based on space-charge measurements and accelerated life tests[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2000,7(3):322-328. doi: 10.1109/94.848908 [24] BEYER J, MORSHUIS P H F, SMIT J J. Conduction current measurements on polycarbonates subjected toelectrical and thermal stress[C]//2000 Annual Report Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena. Victoria BC: CEIDP, 2000: 617-621. [25] MONTANARI G C, FABIANI D, DISSADO L A. A new conduction phenomenon observed in polyethylene and epoxy resin: Ultra-fast solitonconduction[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics,2011,49(16):1173-1182. doi: 10.1002/polb.22296 [26] CAO Y, IRWIN P C, YOUNSI K. The future of nanodielectrics in the electrical power industry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2004,11(5):797-807. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2004.1349785 [27] 兰莉. 纳米颗粒表面处理对复合介质介电性能的影响[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2012.LAN Li. The effect of nanoparticle surface treatment on the dielectric properties of composite media[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012(in Chinese). [28] WANG W W, MIN D M, LI S T. Understanding the conduction and breakdown properties of polyethylene nanodielectrics: Effect of deep traps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2016,23(1):564-572. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2015.004823 [29] 高俊国. 聚乙烯/纳米蒙脱土复合物的空间电荷特性与介电性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2013.GAO Junguo. Space charge characteristics and dielectric properties of polyethylene/nano-montmorillonite compo-sites[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2013(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: