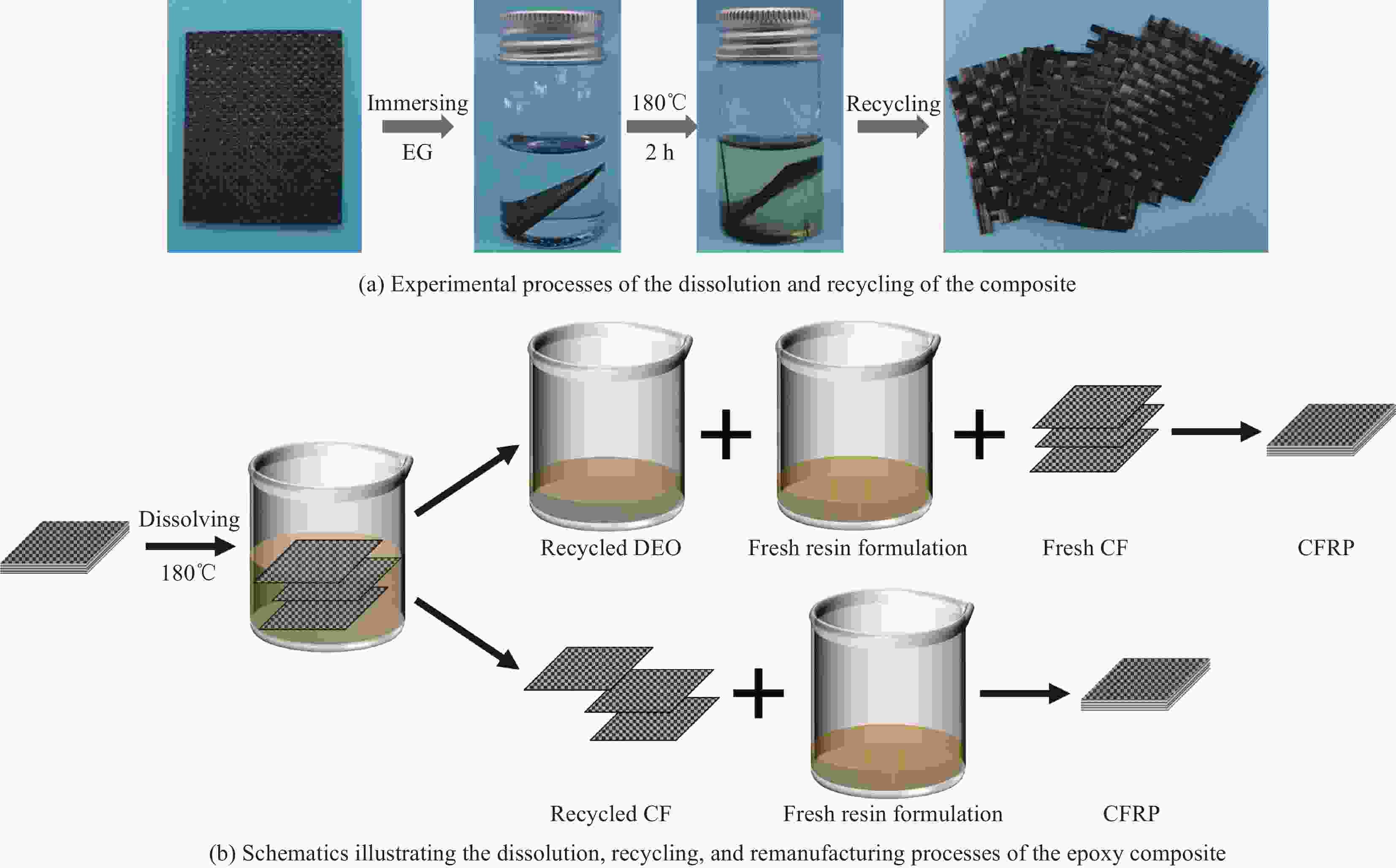
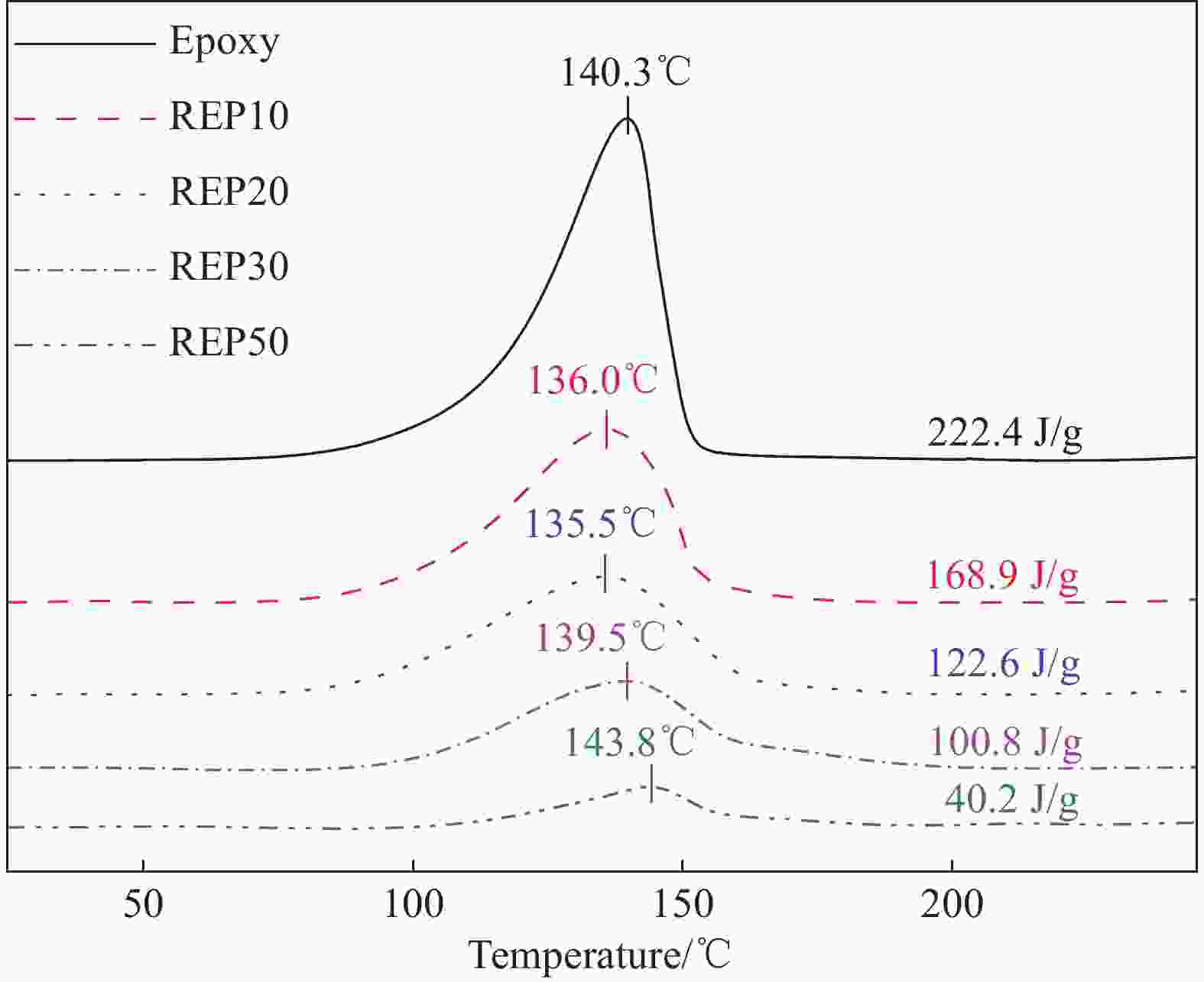
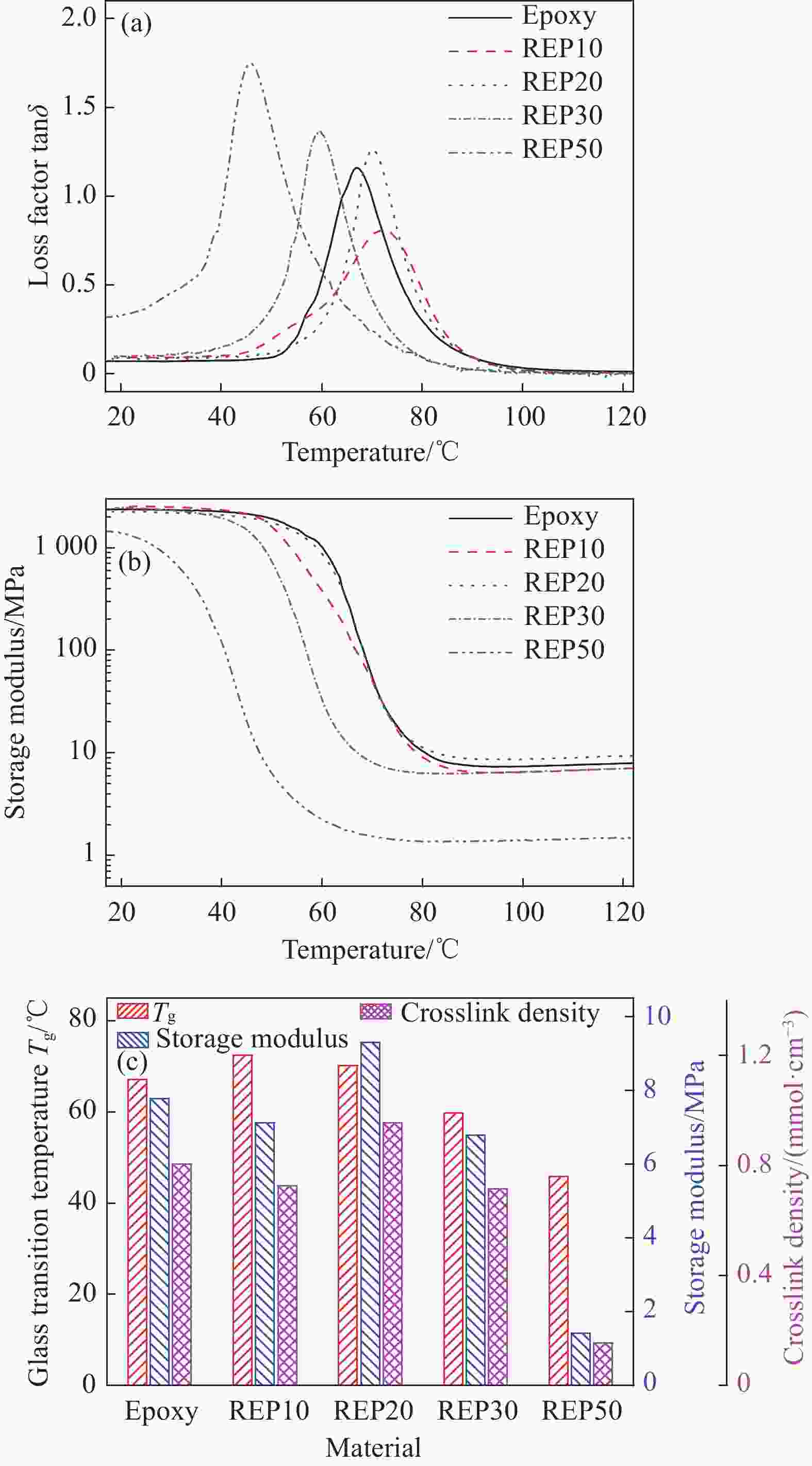
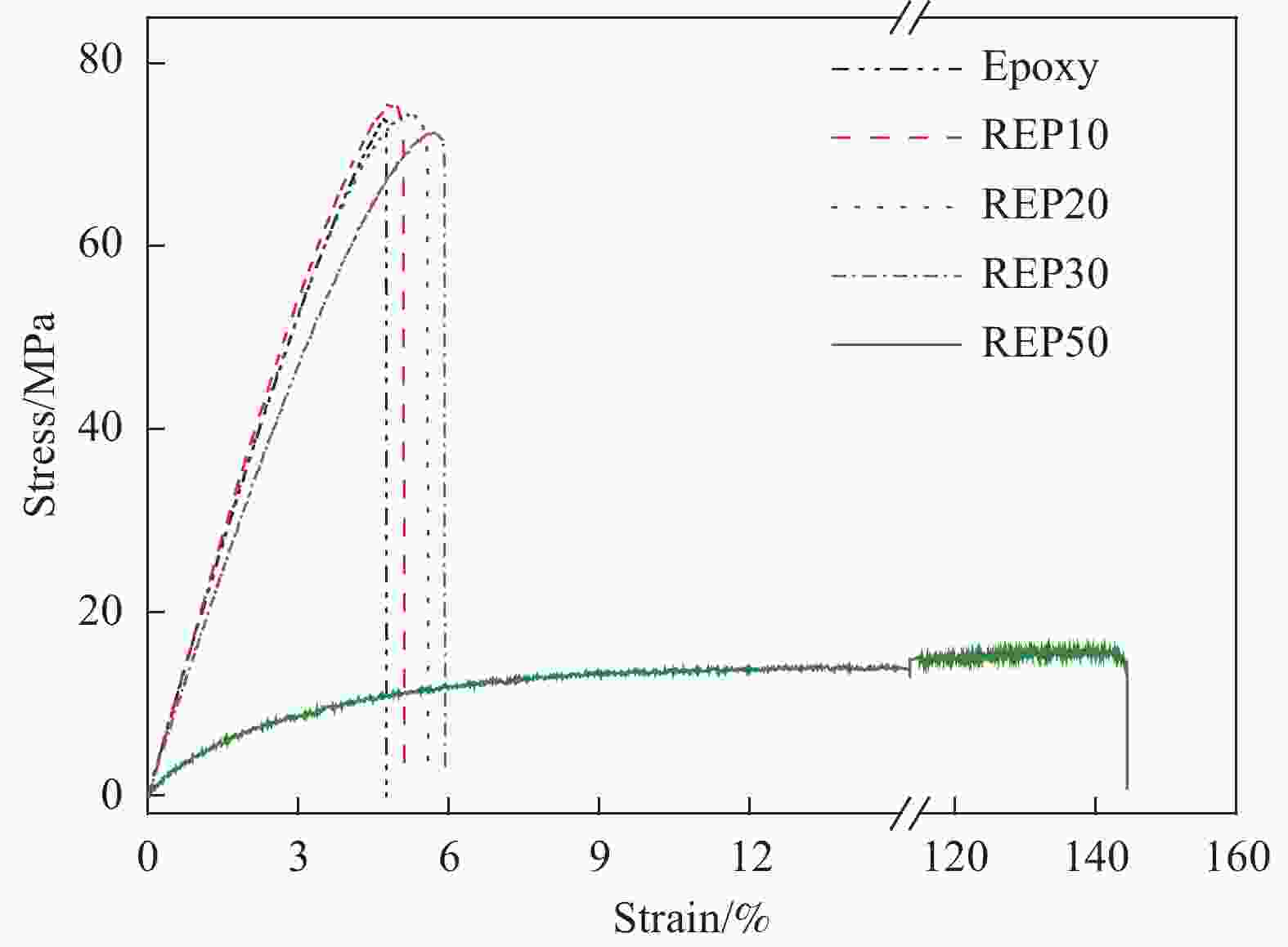
Closed-loop recycling and re-manufacturing of engineering epoxy and its composites
-
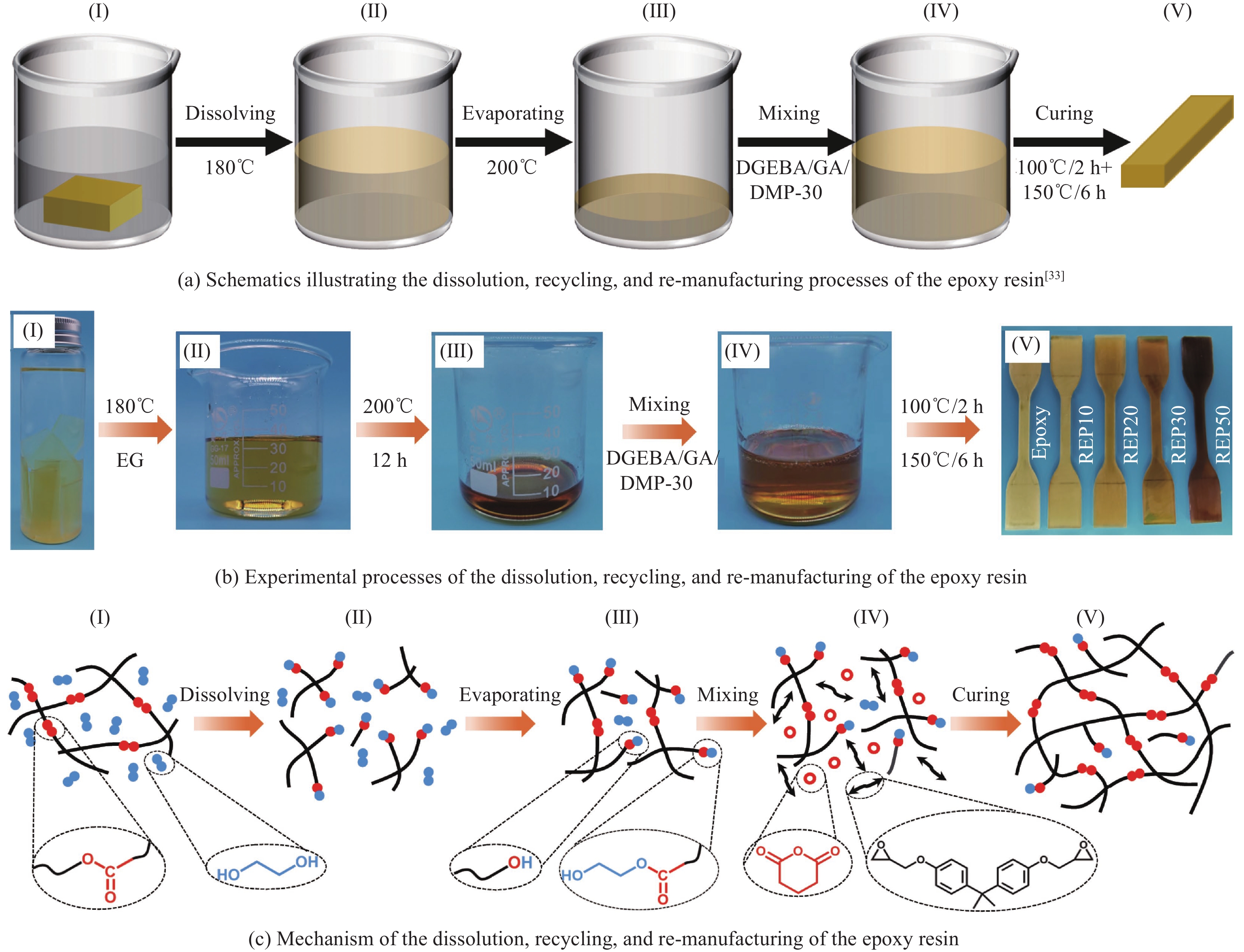
摘要: 环氧树脂基碳纤维增强复合材料因其优异的力学、热学性能已广泛应用于航天航空等领域。环氧树脂由三维共价交联网络组成,难以被降解。工业中通常需高温(300~800℃)、高压(3~27 MPa)等严苛环境或有毒催化剂来破坏树脂基体,以回收复合材料废弃物中昂贵的碳纤维,这一过程往往会造成纤维性能的严重损失。本文利用环氧树脂与醇溶剂之间的动态键交换反应,将工业中常用的高性能环氧树脂降解为低聚物,降解条件温和(200℃、0 MPa),且无需额外催化剂。通过树脂降解,回收得到结构完整的碳纤维织物,其强度保持在94%以上,可继续用于制备复合材料。将低聚物作为反应物制备新的环氧树脂,称为再制造环氧树脂。当再制造环氧树脂中低聚物的含量为20wt%时,其强度与原环氧树脂相当,而断裂伸长率提高了20%。用再制造环氧树脂制备碳纤维复合材料,其强度与原环氧基复合材料相当,同时断裂伸长率提高了50%。本文实现了工业用环氧树脂及其复合材料从制造到回收到再制造过程,即闭环回收再制造。同时,本文新提出了一种绿色、简单、有效的环氧树脂增韧方法。Abstract: High-performance carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites have become important materials for aircraft manufacturing due to their excellent mechanical and thermal properties. The three-dimensional crosslinked network of epoxy matrix is insoluble, making degrading and recycling challenging. In engineering, to reclaim the expensive carbon fiber from composite wastes, harsh conditions such as high temperature (300-800℃), high pressure (3-27 MPa), and trenchant catalyst are usually demanded to destroy the epoxy matrix. However, the properties of carbon fibers are deteriorated simultaneously. In this work, high-performance epoxy resin was decomposed into oligomers via the bond exchange reactions between the epoxy and alcohol solvent. The epoxy resin was dissolved in the alcohol solvent at mild condition (200℃, 0 MPa). Meanwhile, the woven structure of the recycled fabric remains intact, and its tensile strength is 94% of the fresh fabric. Thereby, the recycled fabrics can be used to prepare new composites. Furthermore, the decomposed epoxy oligomer (DEO) is used as a reactant to prepare new epoxy resin. When the DEO content is 20wt%, the elongation at break of the new resin is significantly improved by 20%, while its strength is similar to the original epoxy resin. For the same DEO content, the elongation at break of re-manufactured epoxy composites increased by 50%, compared to the fresh one. To sum up, we develop a closed-loop recycling and re-manufacturing method for an epoxy resin and its composite, and a novel method for the toughening of epoxy resin that is eco-friendly, easy and efficient.
-
Key words:
- epoxy /
- composite /
- bond exchange reaction /
- recycling and re-manufacturing /
- toughening
-
表 1 再制造环氧树脂及其复合材料的命名
Table 1. Naming of re-manufactured epoxy resins and composites
Material DEO content/wt% Epoxy 0 REP10 10 REP20 20 REP30 30 REP50 50 CFs/epoxy 0 CFs/REP10 10 CFs/REP20 20 CFs/REP30 30 CFs/REP50 50 Notes: REP—Re-manufactured epoxy resins; CFs—Carbon fiber; DEO—Decomposed epoxy oligomer. 表 2 再制造环氧树脂的单轴拉伸力学性能
Table 2. Uniaxial tensile mechanical properties of re-manufactured epoxy resins
Material DEO/wt% Tensile strength/MPa Elastic modulus/MPa Elongation at break/% Epoxy 0 74.7±1.4 1875.7±31.5 4.8±0.1 REP10 10 76.4±3.6 1935.1±34.0 5.5±0.2 REP20 20 74.3±1.2 1876.8±35.1 5.7±0.2 REP30 30 72.7±2.1 1756.9±48.7 5.9±0.1 REP50 50 17.2±1.7 429.5±9.2 130.4±19.9 表 3 再制造环氧树脂的热失重分析结果
Table 3. TGA results of re-manufactured epoxy resins
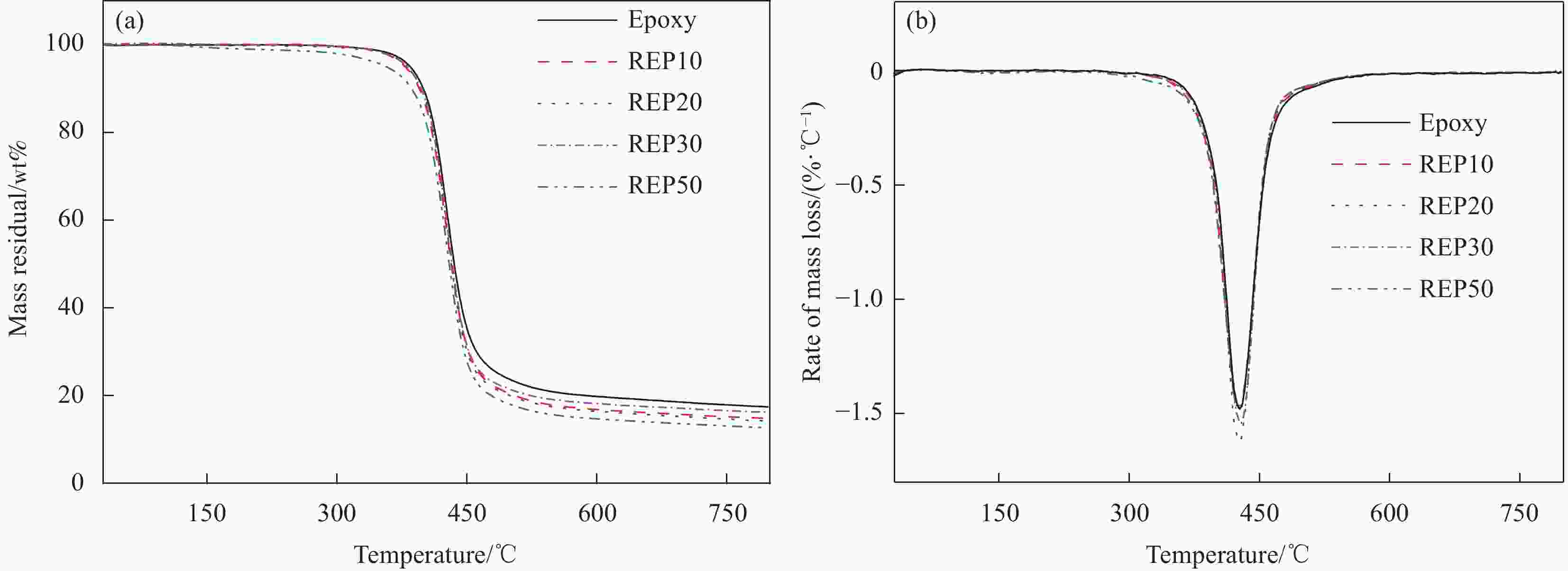
Material DEO/wt% T5%/°C T10%/°C Tmax/°C Epoxy 0 384 399 427 REP10 10 379 396 426 REP20 20 381 397 427 REP30 30 381 397 427 REP50 50 357 387 426 Notes: T5%—Temperature at 5wt% mass loss; T10%—Temperature at 10wt% mass loss; Tmax—Temperature corresponding to the maximum mass lose rate. 表 4 回收环氧基复合材料的单轴拉伸力学性能
Table 4. Uniaxial tensile mechanical properties of re-manufactured epoxy composites
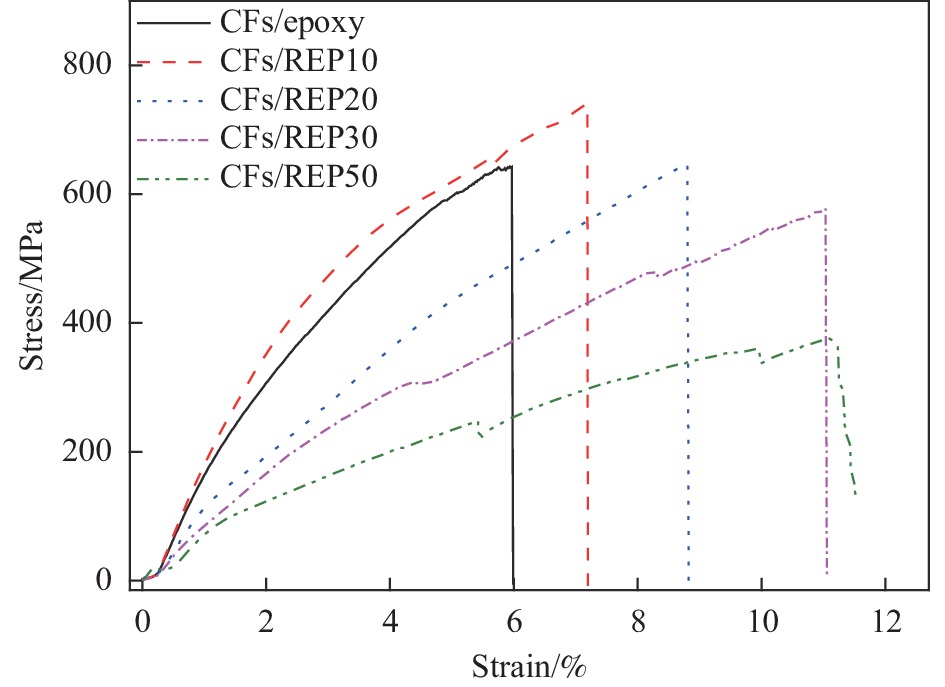
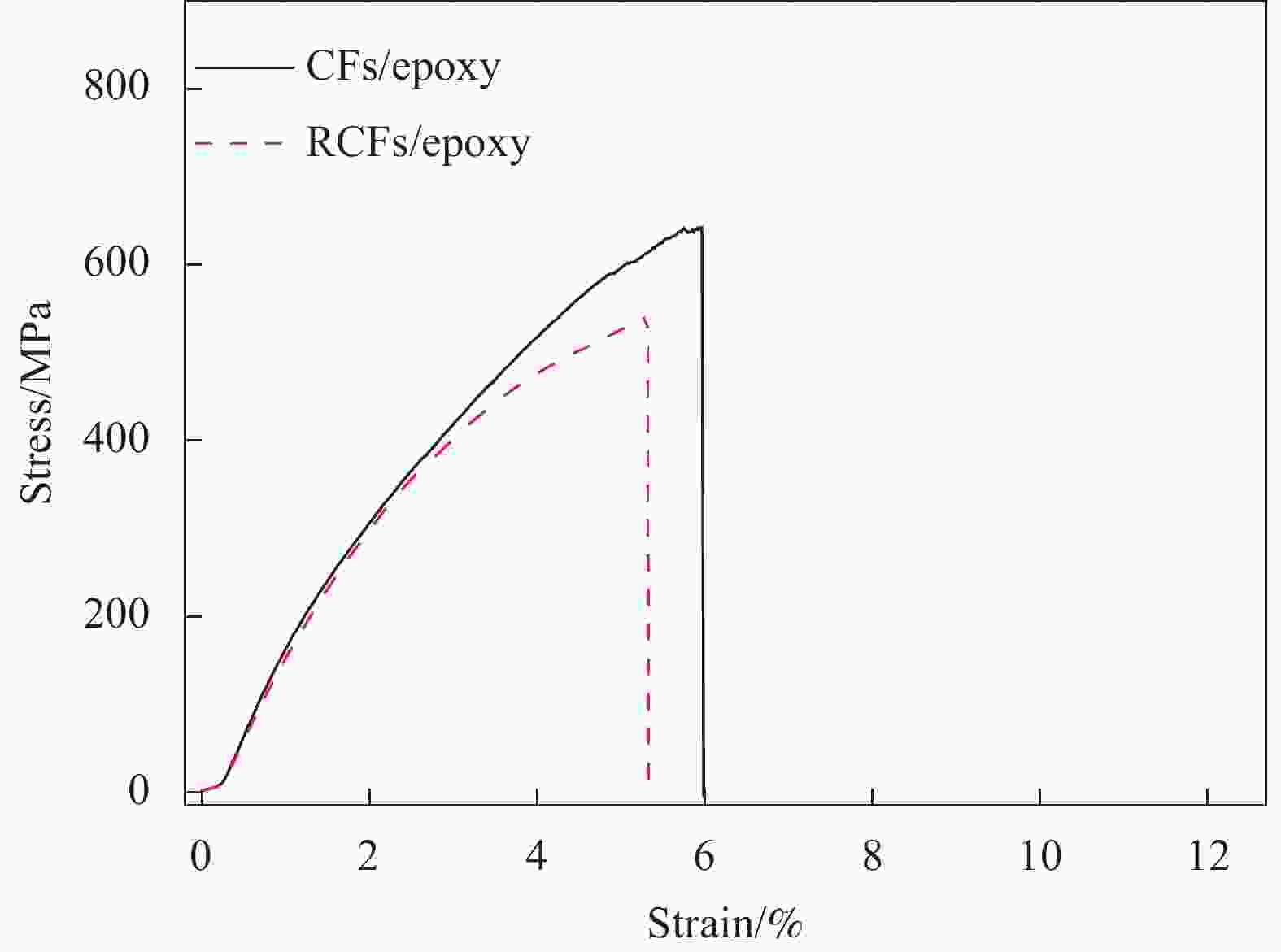
Material DEO/wt% Tensile strength/MPa Elastic modulus/GPa Elongation at break/% CFs/epoxy 0 647.9±9.8 20.5±1.6 6.5±0.8 CFs/REP10 10 737.5±17.8 21.9±2.4 7.6±0.6 CFs/REP20 20 651.9±9.3 18.2±3.7 7.7±2.3 CFs/REP30 30 572.6±38.9 15.0±2.5 8.2±2.6 CFs/REP50 50 402.2±38.9 11.9±1.4 11.0±0.8 -
[1] MARIA M. Advanced composite materials of the future in aerospace industry[J]. Incas Bulletin,2013,5(3):139-150. doi: 10.13111/2066-8201.2013.5.3.14 [2] 邢丽英, 包建文, 礼嵩明, 等. 先进树脂基复合材料发展现状和面临的挑战[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(7):1327-1338. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160323.003XING Liying, BAO Jianwen, LI Songming, et al. Development status and facing challenge of advanced polymer matrix composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(7):1327-1338(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160323.003 [3] 顾轶卓, 李敏, 李艳霞, 等. 飞行器结构用复合材料制造技术与工艺理论进展[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(8):2773-2797.GU Yizhuo, LI Min, LI Yanxia, et al. Progress on manufacturing technology and process theory of aircraft composite structure[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2015,36(8):2773-2797(in Chinese). [4] NAVARRO C A, GIFFIN C R, ZHANG B, et al. A structural chemistry look at composites recycling[J]. Materials Horizons,2020 (10):2479-2486. [5] 汪东, 李丽英, 柯红军, 等. 高性能可回收环氧树脂及其复合材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 高分子学报, 2020, 51(3):303-310. doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2019.19167WANG Dong, LI Liying, KE Hongjun, et al. Preparation and properties of recyclable high-performance epoxy resins and composites[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica,2020,51(3):303-310(in Chinese). doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2019.19167 [6] LI P, MA S, WANG B, et al. Degradable benzyl cyclic acetal epoxy monomers with low viscosity: Synthesis, structure-property relationships, application in recyclable carbon fiber composite[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2022,219:109243. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.109243 [7] DORIGATO A. Recycling of thermosetting composites for wind blade application[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engi-neering Polymer Research,2021,4(2):116-132. doi: 10.1016/j.aiepr.2021.02.002 [8] PEGORETTI A. Recycling concepts for short-fiber-reinforced and particle-filled thermoplastic composites: A review[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research,2021,4(2):93-104. doi: 10.1016/j.aiepr.2021.03.004 [9] SHI X, LUO C, LU H, et al. Primary recycling of anhydride-cured engineering epoxy using alcohol solvent[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science,2019,59(s2):E111-E119. doi: 10.1002/pen.24997 [10] SELVAN R T, RAJA P V, MANGAL P, et al. Recycling technology of epoxy glass fiber and epoxy carbon fiber compo-sites used in aerospace vehicles[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2021, 55(23): 3281-3292. [11] YANG Y, BOOM R, IRION B, et al. Recycling of composite materials[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification,2012,51(1):53-68. [12] 胡侨乐, 端玉芳, 刘志, 等. 碳纤维增强聚合物基复合材料回收再利用现状[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):64-76. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210615.003HU Qiaole, DUAN Yufang, LIU Zhi, et al. Current status of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites recycling and re-manufacturing[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):64-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210615.003 [13] NAQVI S R, PRABHAKARAET H M, BRAMER E A, et al. A critical review on recycling of end-of-life carbon fibre/glass fibre reinforced composites waste using pyrolysis towards a circular economy[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling,2018,136:118-129. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.04.013 [14] CHENG H, HUANG H, JIE Z, et al. Degradation of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer using supercritical fluids[J]. Fibers & Polymers,2017,18(4):795-805. [15] HENRY L, SCHNELLER A, DOERFLER J, et al. Semi-continuous flow recycling method for carbon fibre reinforced thermoset polymers by near- and supercritical solvolysis[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2016,133:264-274. [16] XU P, LI J, DING J. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre/epoxy composites in a mixed solution of peroxide hydrogen and N, N-dimethylformamide[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2013,82:54-59. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.04.002 [17] DANG W, KUBOUCHI M, YAMAMOTO S, et al. An approach to chemical recycling of epoxy resin cured with amine using nitric acid[J]. Polymer,2002,43(10):2953-2958. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00100-3 [18] LIU T, MENG Z, GUO X, et al. Mild chemical recycling of aerospace fiber/epoxy composite wastes and utilization of the decomposed resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2017,139:20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2017.03.017 [19] ADLER S E, GÜTTLER B E, BENDLER L, et al. Evaluation of recycled carbon fibre/epoxy composites: Thermal degradation behaviour of pyrolysed and virgin carbon fibres using thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research,2021,4(2):82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.aiepr.2021.03.003 [20] LUZURAGA A, MARTIN R, MARKAIDE N, et al. Epoxy resin with exchangeable disulfide crosslinks to obtain reprocessable, repairable and recyclable fiber-reinforced thermoset composites[J]. Materials Horizons,2016,3(3):241-247. doi: 10.1039/C6MH00029K [21] KUMAR S, KRISHNA N S. Recycling of carbon fiber with epoxy composites by chemical recycling for future perspective: A review[J]. Chemical Papers,2020,74(11):3785-3807. doi: 10.1007/s11696-020-01198-y [22] YANG Y, XU Y, JI Y, et al. Functional epoxy vitrimers and composites[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2020,120:100710. [23] YU K, SHI Q, MARTIN L, et al. Carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composite with near 100% recyclability[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2016,26(33):6098-6106. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201602056 [24] KUANG X, SHI Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Dissolution of epoxy thermosets via mild alcoholysis: The mechanism and kinetics study[J]. RSC Advances,2018,8(3):1493-1502. doi: 10.1039/C7RA12787A [25] 施前, 齐航, 王铁军. 热固性树脂基复合材料的变革性制造方法研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2019, 49(10): 1121-1132.SHI Qian, QI Hang, WANG Tiejun. Advances in the novel fabrication methods for thermoset composites[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2019, 49(10): 1121-1132(in Chinese). [26] 高亮, 霍红宇, 周典瑞, 等. 基于动态共价化学树脂及复合材料的研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(11):68-75. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.001138GAO Liang, HUO Hongyu, ZHOU Dianrui, et al. Research progress in resin based on dynamic covalent chemistry and its composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2020,48(11):68-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.001138 [27] 吴坤红, 顾雪萍, 冯连芳, 等. 基于动态共价键制备可重复加工交联聚合物[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2020, 34(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2020.01.001WU Kunhong, GU Xueping, FENG Lianfang, et al. Preparation of reprocessacle cross-linked polymers via dynamic covalent bonds[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities,2020,34(1):1-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9015.2020.01.001 [28] LIU T, ZHAO B, ZHANG J. Recent development of repairable, malleable and recyclable thermosetting polymers through dynamic transesterification[J]. Polymer,2020,194:122392. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2020.122392 [29] DELAHAVE M, WINNE J M, PREZ F. Internal catalysis in covalent adaptable networks: Phthalate monoester transesterification as a versatile dynamic cross-linking chemistry[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2019,141(38):15277-15287. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b07269 [30] HAO C, LIU T, ZHANG S, et al. Triethanolamine-mediated covalent adaptable epoxy network: Excellent mechanical properties, fast repairing, and easy recycling[J]. Macromolecules, 2020, 53(8): 3110-3118. [31] LI Y, LIU T, ZHANG S, et al. Catalyst-free vitrimer elastomer based on dimer acid: Robust mechanical performance, adaptivity and hydrothermal recyclability[J]. Green Chemistry, 2020, 22(3): 870-881. [32] 陈子豪, 阮英波, 杨杰. 环氧树脂增韧方法及机理研究进展[J]. 热固性树脂, 2022, 37(1): 64-69.CHEN Zihao, RUAN Yingbo, YANG Jie. Research progress on toughening methods and mechanism of epoxy resin[J]. Thermosetting Resin, 2022, 37(1): 64-69(in Chinese). [33] ZHAO W, AN L, WANG S. Recyclable high-performance epoxy-Anhydride resins with DMP-30 as the catalyst of transesterification reactions[J]. Polymers,2021,13(2):296. doi: 10.3390/polym13020296 [34] ASTM. Standard test method for tensile properties of plastics: D638-14[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2014. [35] 陈平, 王德中. 环氧树脂及其应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004.CHEN Ping, WANG Dezhong. Epoxy resin and its applications[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004(in Chinese). [36] 罗金树, 李鹏, 蔡宏洋, 等. 超支化聚酯增韧环氧体系固化动力学[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2008(5):16-21.LUO Jinshu, LI Peng, CAI Hongyang, et al. Cure kinetics of epoxy resin system toughened by hyperbranched polymers[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics/Composites,2008(5):16-21(in Chinese). [37] KUANG X, ZHOU Y, SHI Q, et al. Recycling of epoxy thermoset and composites via good solvent assisted and small molecules participated exchange reactions[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,8(3):1493-1502. -





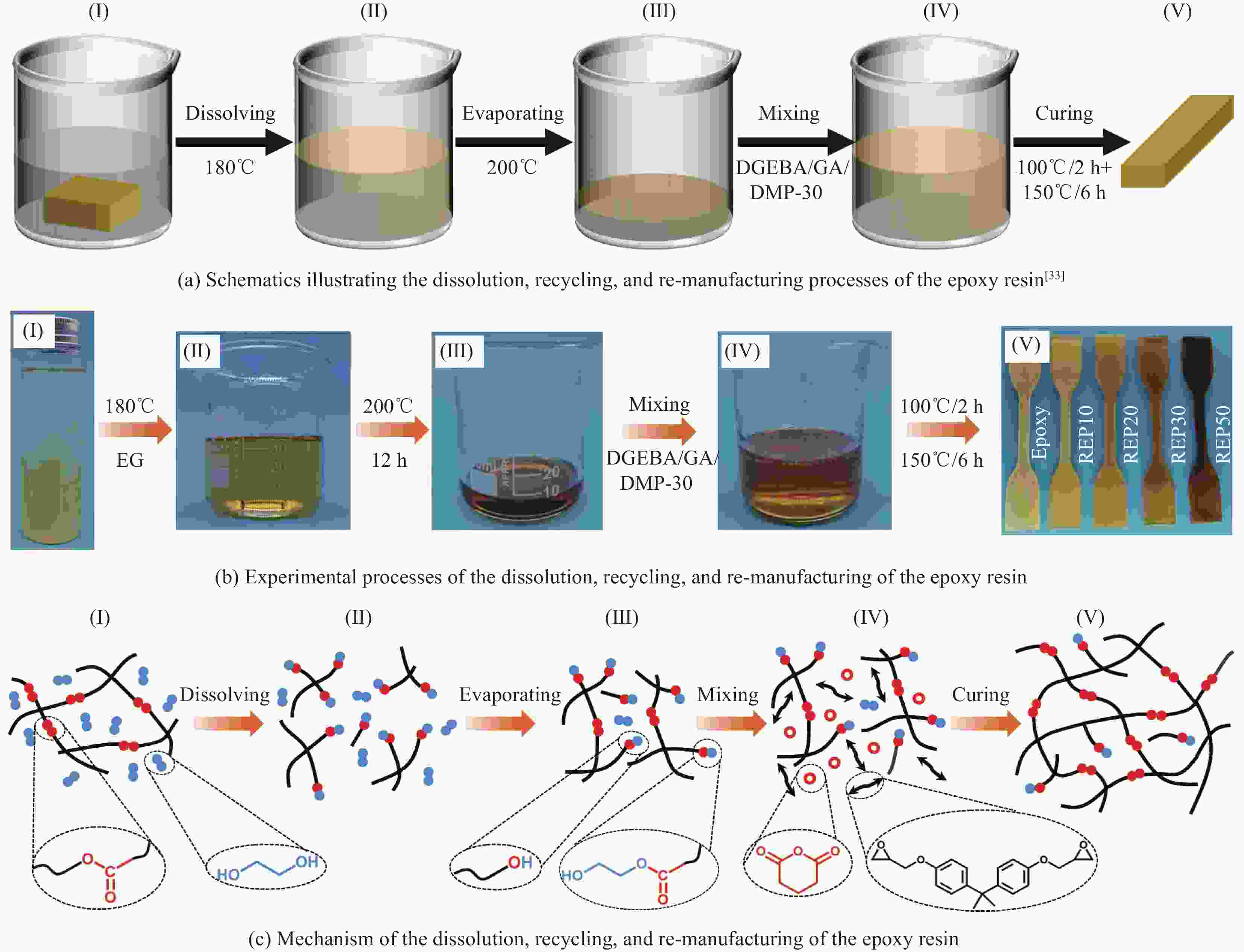
 下载:
下载: