Progress in preparation, properties and applications of MXene fiber
-
摘要: 二维过渡金属碳/氮化物(MXenes)是一种新颖的二维纳米材料,具有优异的电学、力学性能及丰富的表面官能团,在功能材料领域受到了广泛关注,常被作为基元材料构筑宏观复合材料,其中MXene纤维有望成为继石墨烯纤维后另一种结构-功能一体化纤维材料,在多功能织物、传感、能源、电磁屏蔽等领域显示出巨大的应用前景。但目前MXene复合纤维的力学和电学性能与MXene纳米材料本征性能差距较大,主要原因是组装MXene纳米片过程中产生的褶皱、无序结构、界面作用力弱等问题,往往导致MXene纤维内部的孔隙、缺陷存在及纤维外形不规则等。针对MXene纤维研究过程中存在的问题及未来研究方向,本文做了详细综述,首先介绍MXene纤维的制备方法,然后详细阐述MXene复合纤维的力学和电学性能,并讨论提升其性能的策略。同时通过一些实例,综述了MXene复合纤维的应用。最后总结了MXene纤维存在的关键科学问题和挑战,并对MXene纤维的未来发展和前景进行了展望及对未来MXene纤维的研究和应用提供一些帮助。Abstract: 2D transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) are a novel two-dimensional nanomaterial, which attracted extensive attention in the field of functional materials due to outstanding electrical, mechanical properties and abundant surface terminations. Therefore, it often has been used as building block for constructing macroscopic composites, such as MXene fibers, which are expected to be another structure-function integrated fiber after graphene fiber, and have widespread applications prospect in numerous fields, including smart textiles, sensing, energy, electromagnetic shielding, etc. However, the mechanical and electrical properties of MXene composite fibers are far lower than the intrinsic properties of MXene flakes. The main problems are that the existence of defects and voids in the MXene fiber caused by the wrinkling, disorder and weak interface interactions of MXene flakes during assembly, as well as the irregular shape of the fibers. In view of the existing problems as well as the future development direction, this review first introduces the fabrication approaches of MXene fiber. Then, we statement the mechanical and electrical properties of MXene composite fibers in detail, and discuss the strategies for improving the mechanical and electrical properties. Meanwhile, we outline the applications of MXene composite fibers by some instances. Finally, the existing scientific problems and challenges of MXene fiber are summarized, and the upcoming trends in MXene fiber are prospected, and some helpful viewpoint is provided for the research and application of MXene fiber in the future.
-
Key words:
- MXene fiber /
- fabrication /
- mechanical properties /
- electrical conductivity /
- application
-
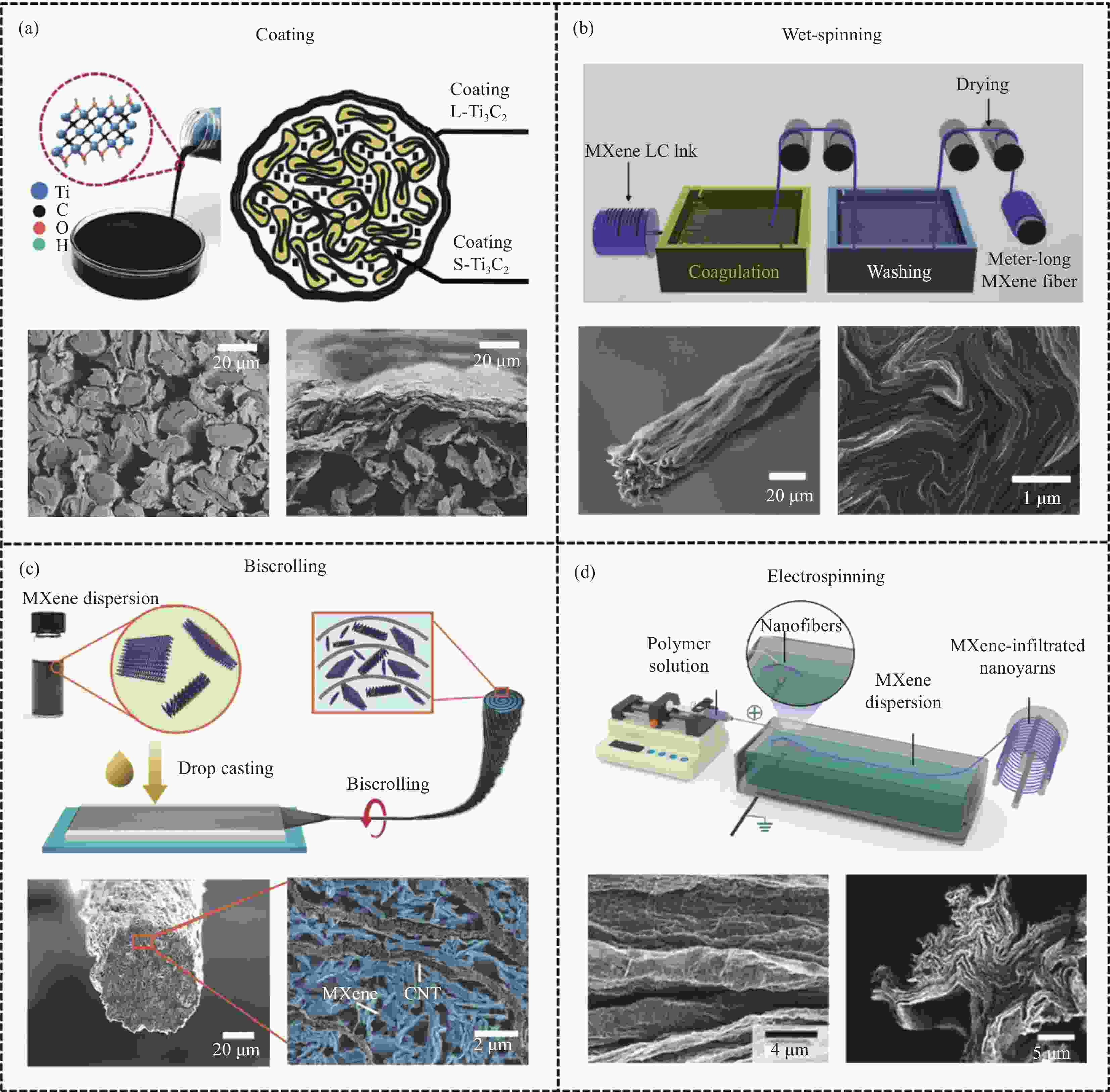
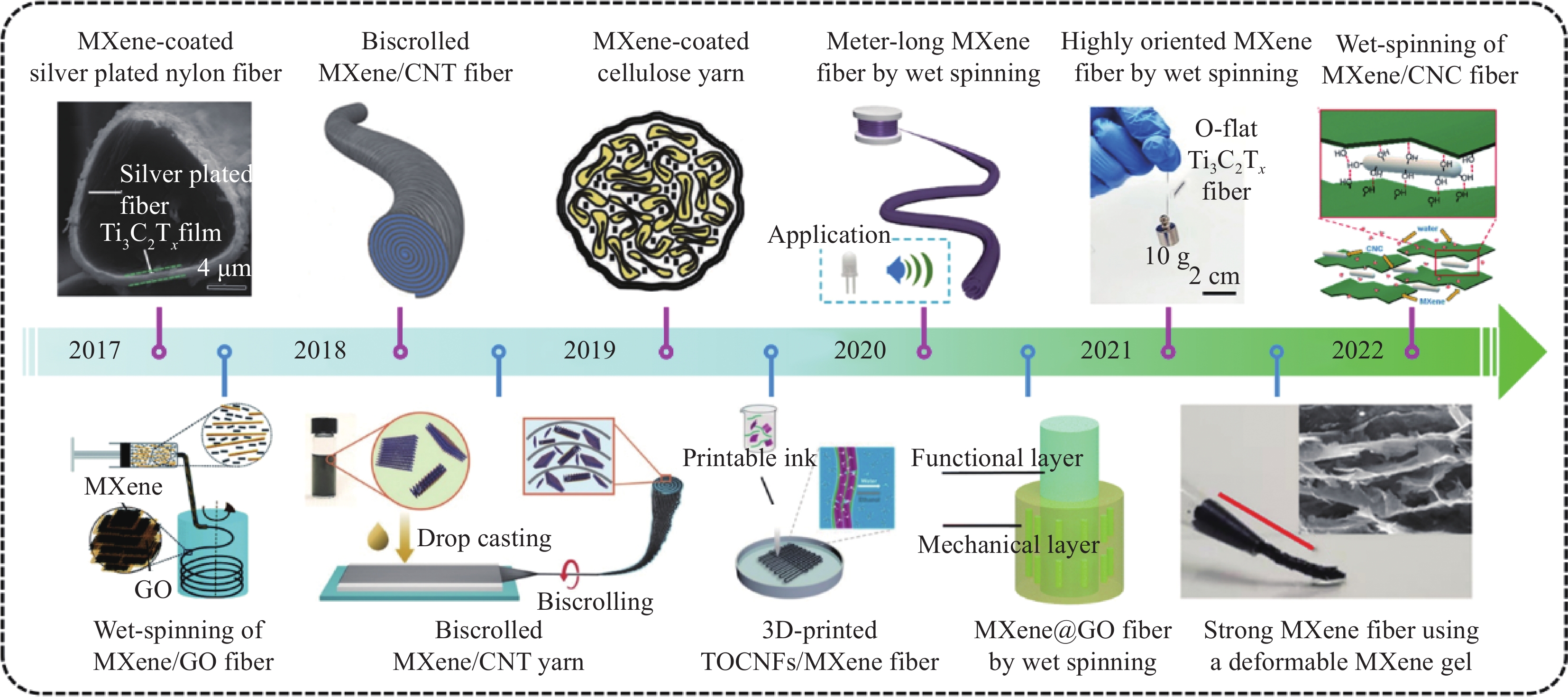
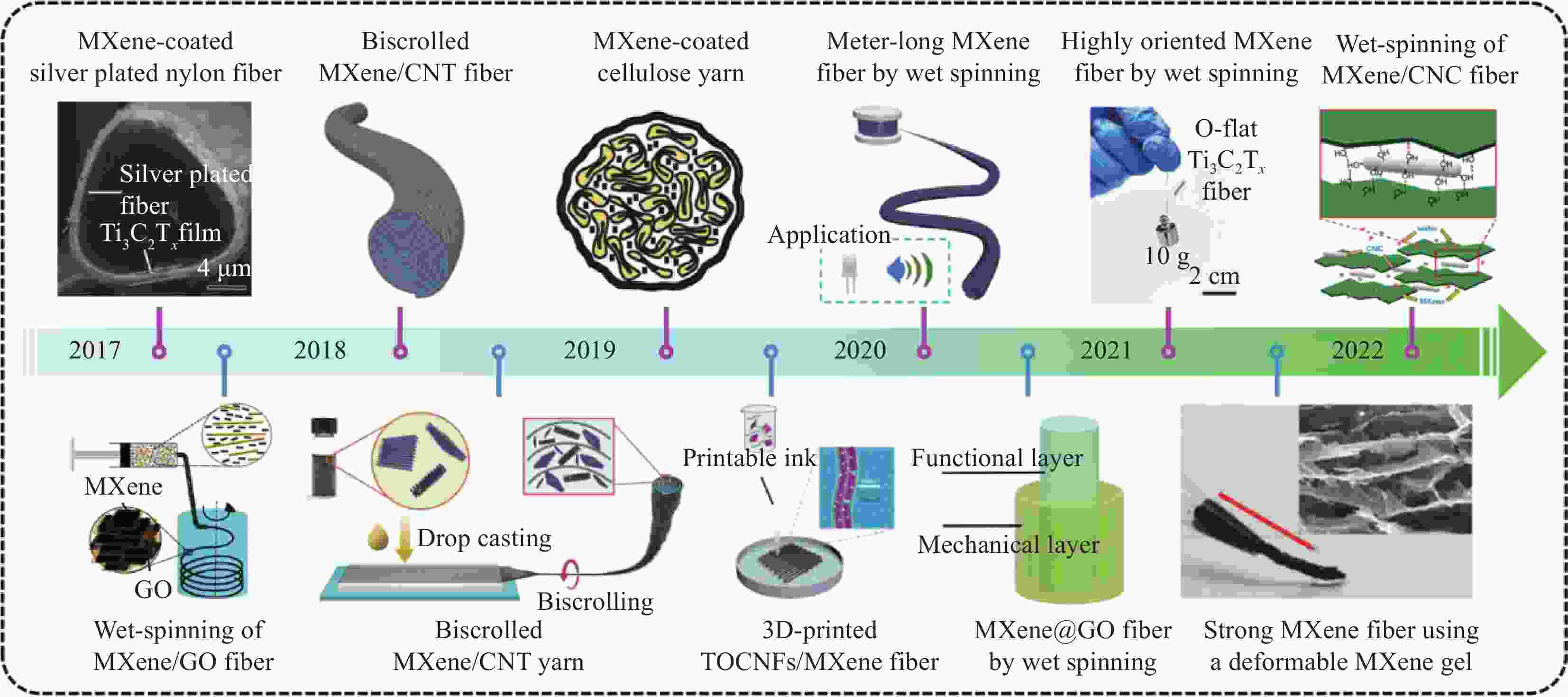
图 1 二维过渡金属碳/氮化物(MXenes)复合纤维的制备研究进展
Figure 1. Research progress in preparation of 2D transition metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) composite fiber
CNT—Carbon nanotube; CNC—Cellulose nanocrystal; GO—Graphene oxide; TOCNFs—2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxylradical-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibril
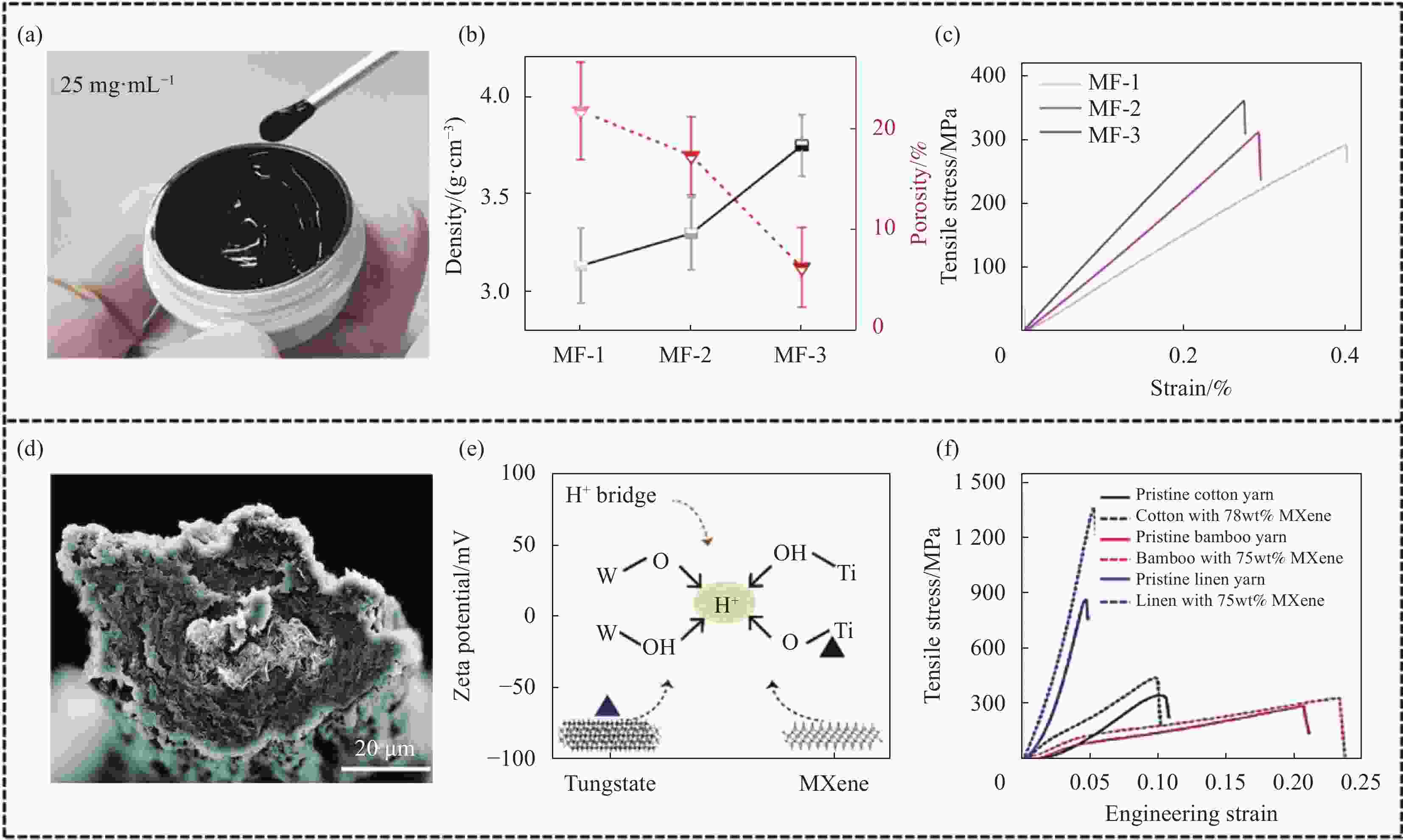
图 3 MXene纤维的力学性能与增强策略:(a) 高浓度MXene液晶油墨的光学图像[30];不同拉伸比制备的MXene纤维的密实度、孔隙率 (b) 和拉伸强度-应变曲线 (c) (MF-1、MF-2和MF-3分别指在拉伸比为1、2、3下制备的MXene纤维)[32]; (d) 具有芯壳结构的MXene@GO纤维的截面SEM图像[28];(e) 带正电的质子和带负电的纳米片之间静电相互作用的示意图[41];(f) 纤维素纱线和MXene包覆的纤维素纱线的拉伸强度-应变曲线[26]
Figure 3. Mechanical properties and strengthening strategy of MXene fibers: (a) Optical image of the concentrated MXene liquid crystal inks[30]; Density, porosity (b) and tensile strength-strain curves (c) of MXene fibers for each draw ratio (MXene fibers obtained through draw ratios of 1, 2 and 3 were denoted as MF-1, MF-2 and MF-3, respectively)[32]; (d) Cross-sectional SEM image of the MXene@GO fiber with core-shell structure[28]; (e) Schematic illustration of the electrostatic interactions between the positive protons and the negatively charged nanosheets[41]; (f) Tensile strength-strain curves of cellulose yarns and MXene-coated cellulose yarns[26]
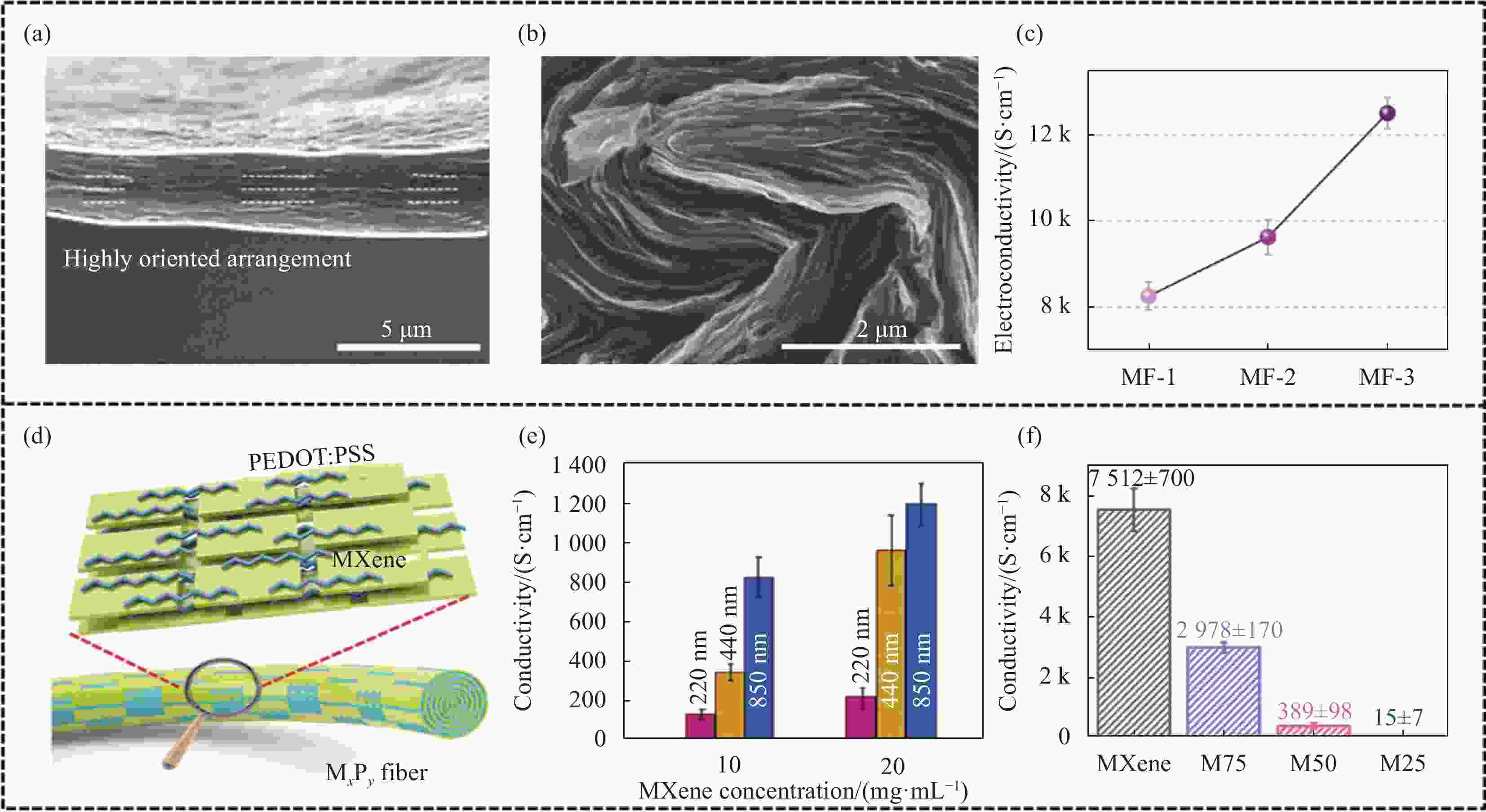
图 4 MXene复合纤维的电导率与提升策略:(a) 高度取向的带状MXene纤维截面SEM图像[31];(b) MF-3纤维的截面SEM图像;(c) 不同拉伸比的MXene纤维的电导率[32];(d) MXene/PEDOT:PSS纤维的界面结构示意图[40];(e) 用不同浓度和尺寸的MXene分散液制备的MXene/尼龙纱线的电导率[37];(f) 不同MXene含量的MXene/CNC纤维的电导率[33]
Figure 4. Electrical conductivity and improving strategy of MXene composite fiber: (a) Cross-sectional SEM image of MXene fiber with flat orientation[31]; (b) Cross-sectional SEM image of MF-3 fiber; (c) Electrical conductivity of MXene fibers for each draw ratio[32]; (d) Schematic diagram of interfacial cross-linking structure of MXene/PEDOT:PSS fiber[40]; (e) Electrical conductivity of MXene/nylon yarns produced by different MXene concentrations and flake sizes[37]; (f) Electrical conductivity of MXene/CNC fibers with different MXene contents[33]
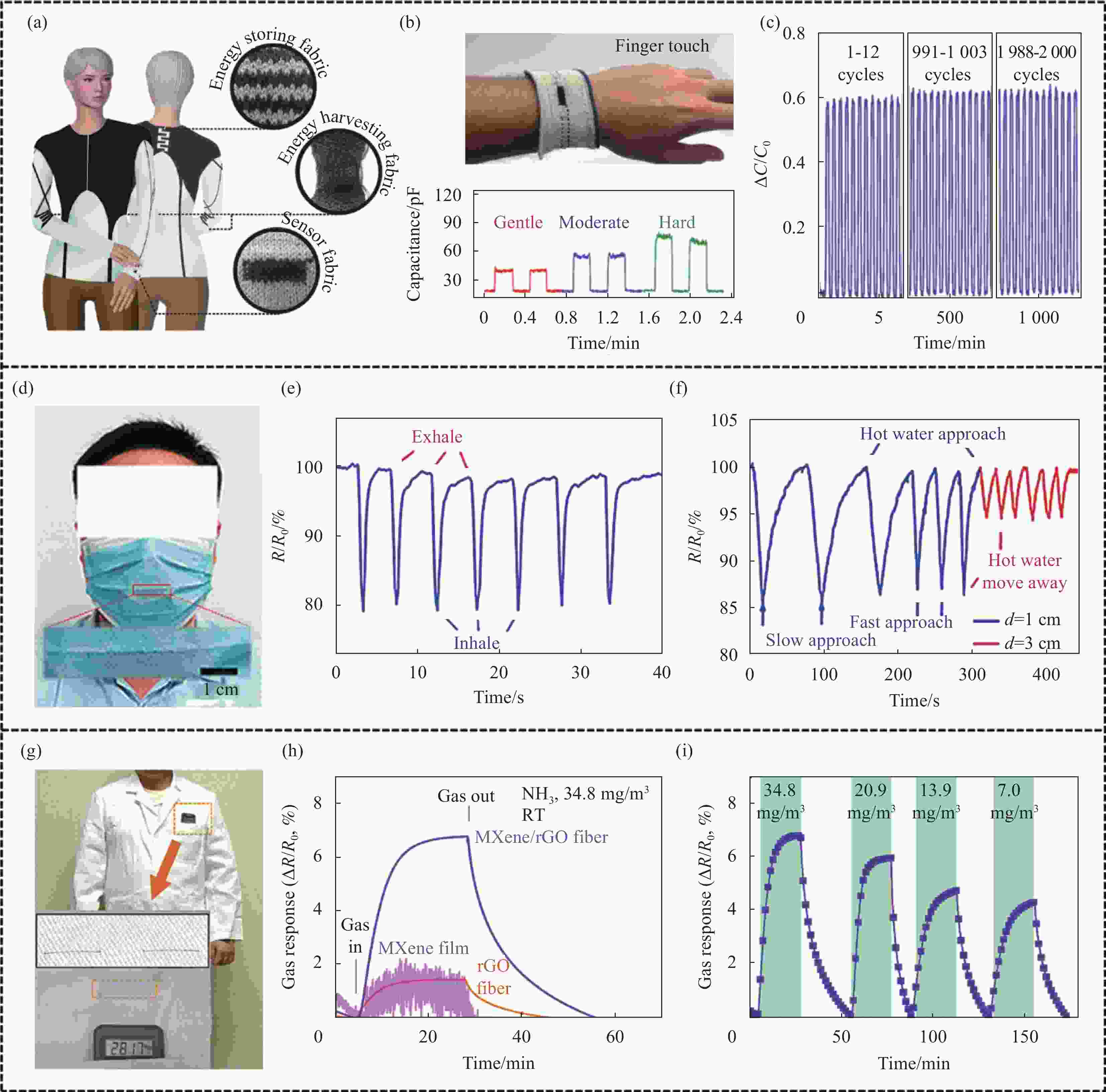
图 5 MXene复合纤维用于多功能织物和传感器:((a)~(c)) MXene包覆的纤维素纱线用于多功能织物:(a) 多功能织物概念图;(b) 针织压力传感器实物图和传感性能;(c) 针织压力传感器在14.1%应变下的相对电容变化的循环稳定性[26];((d)~(f)) Kevlar/MXene纤维用于智能感知口罩和手套:(d) 智能感知口罩实物图;(e) 智能感知口罩在定时呼吸时的电阻-时间曲线;(f) 智能感知手套在不同速度靠近和远离热水的电阻-时间曲线[52];((g)~(i)) MXene/rGO纤维用于气体传感器:(g) 实验服上的气体传感器实物图;(h) 基于MXene薄膜、rGO纤维和MXene/rGO纤维的传感器的电阻响应对比;(i) MXene/rGO纤维传感器在不同NH3浓度下的动态电阻响应[53]
Figure 5. MXene composite fibers for multifunctional fabrics and sensors: ((a)-(c)) MXene-coated cellulose yarns for multifunctional fabrics: (a) Concept illustration of multifunctional fabrics; (b) Digital photo and sensing performance of the knitted pressure sensor; (c) Cyclic stability of relative capacitance change of knitted pressure sensors at 14.1% strain[26]; ((d)-(f)) Kevlar/MXene fiber for smart sensory mask and glove: (d) Photograph of smart sensory mask; (e) Resistance-time curve of smart sensory mask during breathing regularly; (f) Resistance-time curve of smart sensory glove when approaching and removing hot water at different speeds[52]; ((g)-(i)) MXene/rGO fiber for gas sensor: (g) Photograph of gas sensor on the lab coat; (h) Comparison of resistance responses of sensor based on MXene film, rGO fiber and MXene/rGO fiber; (i) Dynamic resistance response of MXene/rGO fiber sensor at different NH3 concentrations[53]
C—Capacitance; C0—Initial capacitance; R—Resistance; R0—Initial resistance; d—Distance; RT—Room temperature
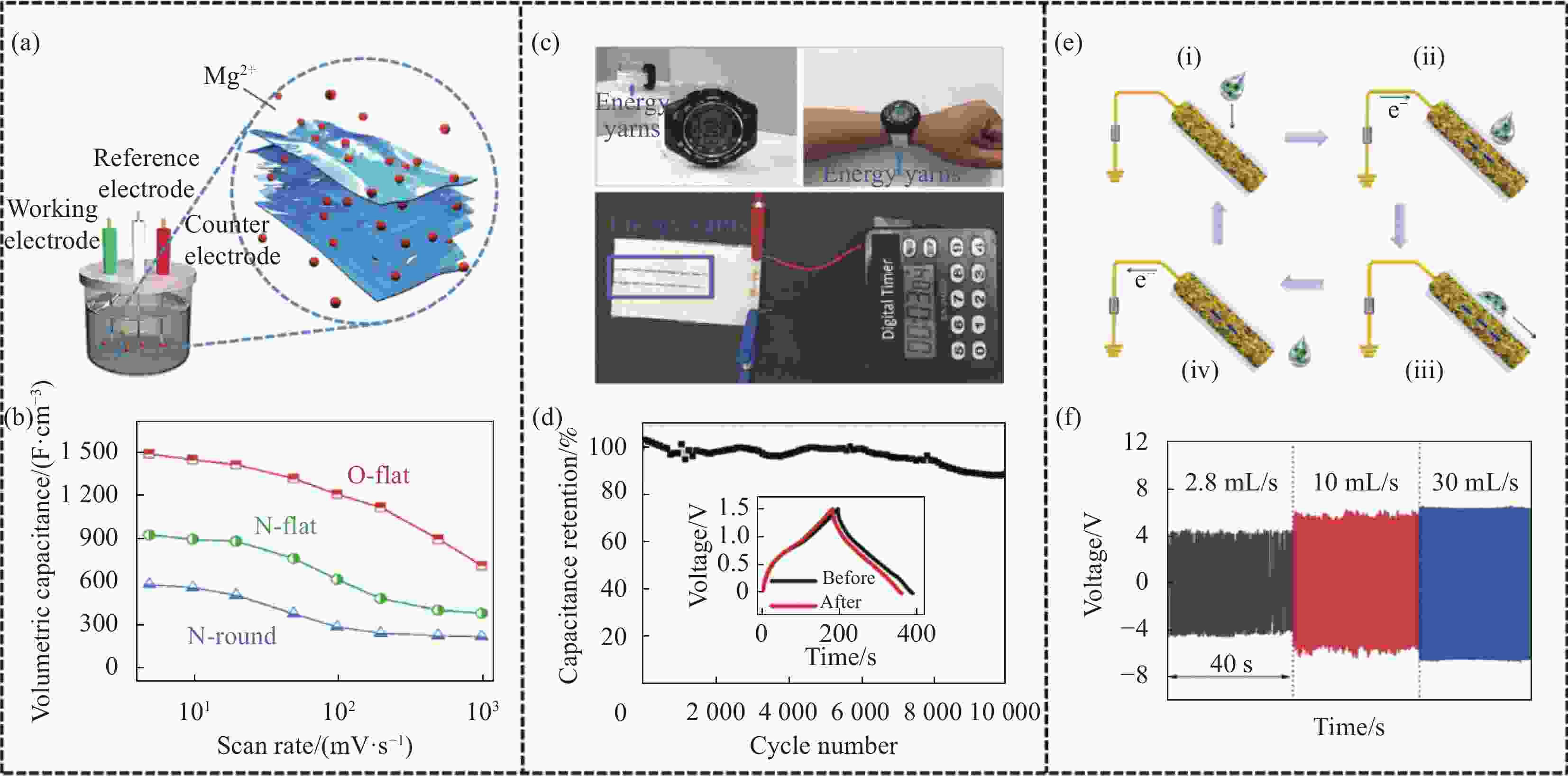
图 6 MXene复合纤维用于能量储存与转化:(a) 测量MXene纤维电容性能的三电极装置示意图[31];(b) 三种MXene纤维在不同扫描速率下的体积电容对比[31];(c) MXene/CNT纱线作为储能纺织给手表和计时器供电[24];(d) 基于MXene/CNT纱线的超级电容器的电容循环稳定性[24];(e) 基于Au纳米颗粒(AuCNS)包覆的MXene/CNT/聚氨酯(PU)(MCP)复合纤维(AuCNS@MCP)纤维的摩擦纳米发电机用于收集水能的机制图[60];(f) 摩擦纳米发电机在不同水流速率下的输出电流[60]
Figure 6. MXene composite fibers for energy storage and transformation: (a) Schematic of the three-electrode setup for measuring the capacitive performance of MXene fiber[31]; (b) Volumetric capacitance comparison of three MXene fibers at different scan rates[31]; (c) MXene/CNT yarn as energy storage textile to power watch and timer[24]; (d) Capacitance retention of the supercapacitors based on MXene/CNT yarn[24]; (e) Schematic illustration of the mechanism of the triboelectric nanogenerators based on Au nanoparticles (AuCNS) coated MXene/CNT/polyurethane(PU) (MCP) composite fibers (AuCNS@MCP) fiber for collecting water energy[60]; (f) Output current of the triboelectric nanogenerators under different water flow rates[60]
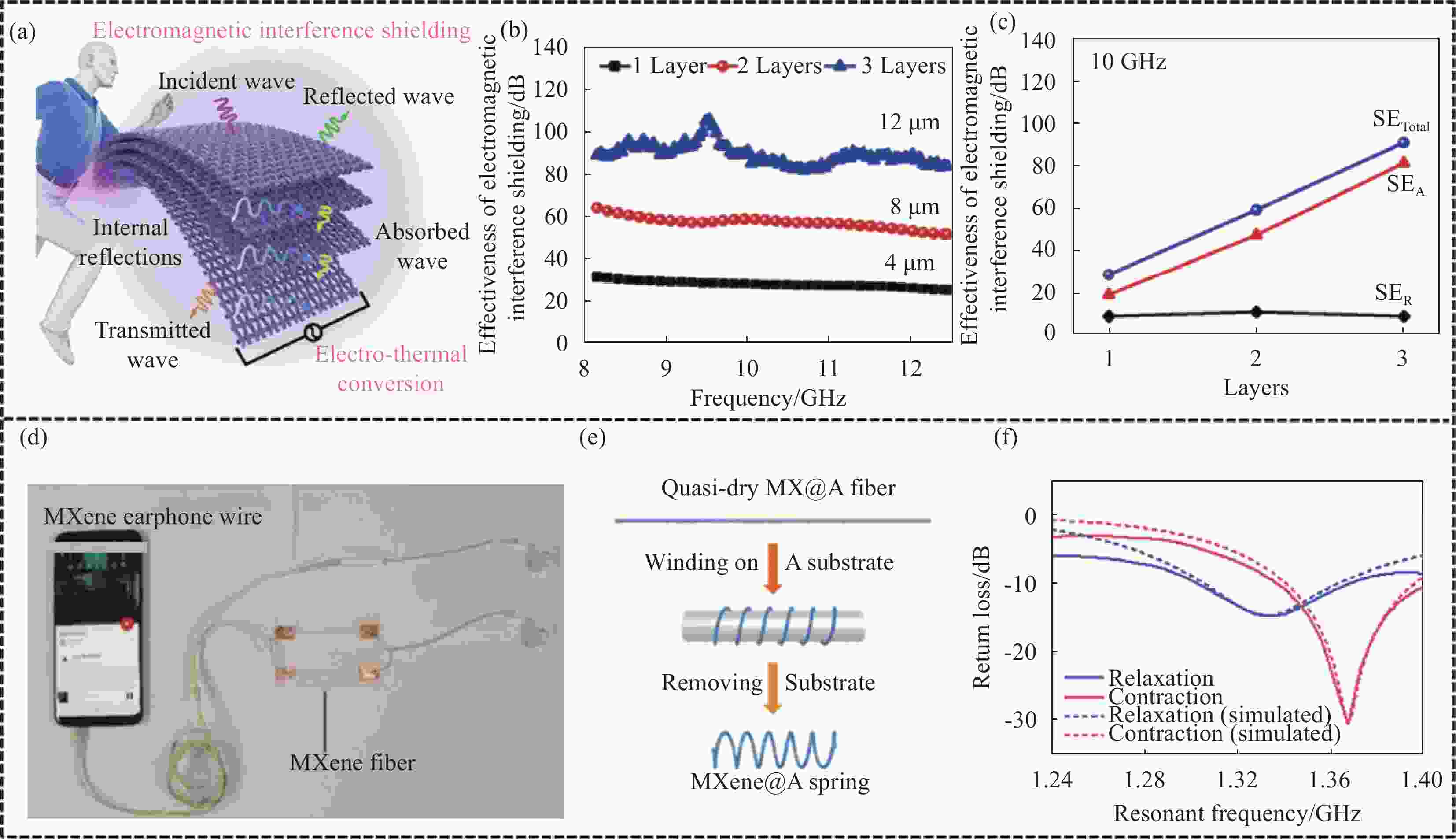
图 7 MXene复合纤维用于电磁干扰(EMI)屏蔽、导线及无线通信:(a) 在可穿戴EMI屏蔽和电热综合应用的概念图[50];不同层数下再生纤维素(RC)@GO/MXene织物的EMI屏蔽效率 (b) 和EMI屏蔽机制对比 (c)[50];(d) MXene纤维用作耳机电线[30];(e) MXene@藻朊酸盐(A)纤维弹簧的制备机制图[61];(f) MXene@A弹簧天线在收缩和松弛状态下的回波损耗频率分布图[61]
Figure 7. MXene composite fibers for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, wire and wireless communications: (a) Concept illustration of integrated applications in wearable EMI shielding and electro-thermal[50]; EMI shielding efficiencies of regenerated cellulose (RC)@GO/MXene textiles under different thickness (b) and comparison of the EMI shielding mechanisms (c)[50]; (d) MXene fiber for earphone wire[30]; (e) Schematic illustration of MXene@alginate (A) springs[61]; (f) Return loss-frequency profiles of the antenna with MXene@A springs under contraction state and relaxation state[61]
SETotal—Total EMI; SEA—EMI absorption; SER—EMI reflection
表 1 MXene纤维的制备方法和性能
Table 1. Summary of the preparation methods and properties of MXene fiber
Composition Preparation method MXene
content/wt%Tensile
strength/MPaFailure
strain/%Young’s
modulus/GPaToughness/
MJ·m−3Conductivity/
S· cm−1Years Ref. MXene fiber Wet spinning 100 40.5 1.7 — ~0.34 7750 2020 [29] MXene fiber Wet spinning 100 63.9 0.22 29.6 0.09 7713 2020 [30] MXene fiber Wet spinning 100 118 1.85 — ~1.09 7200 2021 [31] MXene fiber Wet spinning 100 343.68 0.28 121.97 ~0.48 12503.78 2021 [32] MXene/rGO fiber Wet spinning 88 116.1 1.3 13.3 0.94 72.3 2017 [23] MXene/rGO fiber Wet spinning 90 12.9 3.4 1.2 ~0.22 290 2017 [22] MXene/CNT fiber Biscrolling 90 38.4 4.7 — ~0.90 2.7 2018 [25] MXene/CNT yarn Biscrolling 97.5 26.6 15.1 0.09 ~2.01 26 2018 [24] MXene/TOCNFs fiber 3D printing 50 75.6 3.75 4.7 ~1.42 2.11 2019 [27] MXene/PEDOT:
PSS fiberWet spinning 70 58.1 1.1 7.5 ~0.32 1489.8 2019 [40] MXene-coated cotton yarn Coating 78 468.4 ~0.1 5.0 ~0.23 198.5 2019 [26] MXene@GO fiber Coaxial wet spinning 50 290 1.5 30 ~2.18 24 2020 [28] Tungstate/MXene fiber Wet spinning 10 220 3.9 — ~4.29 — 2020 [41] MXene/nylon nanoyarn Electrospinning 90 29 1.85 3.94 ~0.27 1195 2020 [37] MXene@ANF fiber Coaxial wet spinning — 130 10.8 0.033 ~7.02 25.15 2021 [49] MXene/ANF fiber Wet spinning — 104 7.9 — ~4.11 1025 2021 [42] MXene/CNC
fiberWet spinning 75 62 0.9 1.17 0.37 2978 2022 [33] GO/MXene@RC fiber Coaxial wet spinning 70 92.2 4 9.0 ~3.0 167.5 2022 [50] ANF@MXene Coaxial wet spinning — 502.9 13.1 — 48.1 3000 2022 [51] Notes: rGO—Reduced graphene oxide; PEDOT: PSS—Poly(3,4-ethylene dioxythiophene):poly(styrene sulfonic acid); ANF—Aramid nanofiber; RC—Regenerated cellulose. -
[1] VAHIDMOHAMMADI A V, ROSEN J, GOGOTSI Y. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes)[J]. Science,2021,372(6547):eabf1581. doi: 10.1126/science.abf1581 [2] NOVOSELOV K S, GEIM A K, MOROZOV S V, et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films[J]. Science,2004,306(5696):666-669. doi: 10.1126/science.1102896 [3] WENG Q H, WANG X B, WANG X, et al. Functionalized hexagonal boron nitride nanomaterials: Emerging properties and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews,2016,45(14):3989-4012. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00869G [4] NICOLOSI V, CHHOWALLA M, KANATZIDIS M G, et al. Liquid exfoliation of layered materials[J]. Science,2013,340(6139):1420. [5] NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2[J]. Advanced Materials,2011,23(37):4248-4253. doi: 10.1002/adma.201102306 [6] FREY N C, WANG J, BELLIDO G I V, et al. Prediction of synthesis of 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) and their precursors with positive and unlabeled machine learning[J]. ACS Nano,2019,13(3):3031-3041. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b08014 [7] WEI Y, ZHANG P, SOOMRO R A, et al. Advances in the synthesis of 2D MXenes[J]. Advanced Materials,2021,33(39):2103148. doi: 10.1002/adma.202103148 [8] LIPATOV A, LU H D, ALHABEB M, et al. Elastic properties of 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene monolayers and bilayers[J]. Science Advances,2018,4(6):eaat0491. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aat0491 [9] LIPATOV A, GOAD A, LOES M J, et al. High electrical conductivity and breakdown current density of individual monolayer Ti3C2Tx MXene flakes[J]. Matter,2021,4(4):1413-1427. doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2021.01.021 [10] MENG W X, LIU X J, SONG H Q, et al. Advances and challenges in 2D MXenes: From structures to energy storage and conversions[J]. Nano Today,2021,40:101273. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2021.101273 [11] SHAHZAD F, ALHABEB M, HATTER C B, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes)[J]. Science,2016,353(6304):1137-1140. doi: 10.1126/science.aag2421 [12] 吴梦, 饶磊, 张建峰, 等. MXene及其复合吸波材料的制备与性能研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3):942-955.WU Meng, RAO Lei, ZHANG Jianfeng, et al. Research progress in preparation and performance of MXene and its composite absorbing materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(3):942-955(in Chinese). [13] QIN S, USMAN K A S, HEGH D, et al. Development and applications of MXene-based functional fibers[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(31):36655-36669. [14] LEVITT A, ZHANG J Z, DION G, et al. MXene-based fibers, yarns, and fabrics for wearable energy storage devices[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(47):2000739. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000739 [15] LIU X H, MIAO J L, FAN Q, et al. Recent progress on smart fiber and textile based wearable strain sensors: Materials, fabrications and applications[J]. Advanced Fiber Materials,2022,4(3):361-389. doi: 10.1007/s42765-021-00126-3 [16] 杨开勋, 张吉振, 谭娅, 等. MXene与纤维基材料复合应用研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2):460-466.YANG Kaixun, ZHANG Jizhen, TAN Ya, et al. Research progress of MXene/fibrous material composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(2):460-466(in Chinese). [17] 罗大军, 高进, 田鑫, 等. Ti3C2Tx MXene材料的制备、组装及应用研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2):467-477.LUO Dajun, GAO Jin, TIAN Xin, et al. Research and developing in preparation, assembly and applications of Ti3C2Tx MXene materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(2):467-477(in Chinese). [18] 蹇木强, 张莹莹, 刘忠范. 石墨烯纤维: 制备、性能与应用[J]. 物理化学学报, 2022, 38(2):22-39.JIAN Muqiang, ZHANG Yingying, LIU Zhongfan. Graphene fibers: Preparation, properties, and applications[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2022,38(2):22-39(in Chinese). [19] 胡晓珍, 高超. 石墨烯纤维研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2014, 33(8):458-467. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2014.08.02HU Xiaozhen, GAO Chao. Progress in research of graphene fibers[J]. Materials China,2014,33(8):458-467(in Chinese). doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2014.08.02 [20] 张媛媛, 程群峰. 石墨烯复合纤维材料研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2019, 38(1):49-57. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2019.01.06ZHANG Yuanyuan, CHENG Qunfeng. Progress in research of graphene nanocomposite fibers[J]. Materials China,2019,38(1):49-57(in Chinese). doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.2019.01.06 [21] HU M M, LI Z J, LI G X, et al. All-solid-state flexible fiber-based MXene supercapacitors[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies,2017,2(10):1700143. doi: 10.1002/admt.201700143 [22] YANG Q Y, XU Z, FANG B, et al. MXene/graphene hybrid fibers for high performance flexible supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(42):22113-22119. doi: 10.1039/C7TA07999K [23] SEYEDIN S, YANZA E R S, RAZAL J M. Knittable energy storing fiber with high volumetric performance made from predominantly MXene nanosheets[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(46):24076-24082. doi: 10.1039/C7TA08355F [24] WANG Z Y, QIN S, SEYEDIN S, et al. High-performance biscrolled MXene/carbon nanotube yarn supercapacitors[J]. Small,2018,14(37):1802225. doi: 10.1002/smll.201802225 [25] YU C Y, GONG Y J, CHEN R Y, et al. A solid-state fibriform supercapacitor boosted by host-guest hybridization between the carbon nanotube scaffold and MXene nanosheets[J]. Small,2018,14(29):1801203. doi: 10.1002/smll.201801203 [26] UZUN S, SEYEDIN S, STOLTZFUS A L, et al. Knittable and washable multifunctional MXene-coated cellulose yarns[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2019,29(45):1905015. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201905015 [27] CAO W T, MA C, MAO D S, et al. MXene-reinforced cellulose nanofibril inks for 3D-printed smart fibres and textiles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2019,29(51):1905898. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201905898 [28] CHEN X, JIANG J J, YANG G Y, et al. Bioinspired wood-like coaxial fibers based on MXene@graphene oxide with superior mechanical and electrical properties[J]. Nanoscale,2020,12(41):21325-21333. doi: 10.1039/D0NR04928J [29] ZHANG J Z, UZUN S, SEYEDIN S, et al. Additive-free MXene liquid crystals and fibers[J]. ACS Central Science,2020,6(2):254-265. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.9b01217 [30] EOM W, SHIN H, AMBADE R B, et al. Large-scale wet-spinning of highly electroconductive MXene fibers[J]. Nature Communications,2020,11(1):2825. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16671-1 [31] LI S, FAN Z D, WU G Q, et al. Assembly of nanofluidic MXene fibers with enhanced ionic transport and capacitive charge storage by flake orientation[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(4):7821-7832. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c02271 [32] SHIN H, EOM W, LEE K H, et al. Highly electroconductive and mechanically strong Ti3C2Tx MXene fibers using a deformable MXene gel[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(2):3320-3329. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c10255 [33] USMAN K A S, ZHANG J Z, QIN S, et al. Inducing liquid crystallinity in dilute MXene dispersions for facile processing of multifunctional fibers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2022,10(9):4770-4781. doi: 10.1039/D1TA09547A [34] ZHANG J Z, SEYEDIN S, GU Z J, et al. MXene: A potential candidate for yarn supercapacitors[J]. Nanoscale,2017,9(47):18604-18608. doi: 10.1039/C7NR06619H [35] PARK T H, YU S, KOO M, et al. Shape-adaptable 2 D titanium carbide (MXene) heater[J]. ACS Nano,2019,13(6):6835-6844. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01602 [36] LEVITT A, HEGH D, PHILLIPS P, et al. 3 D knitted energy storage textiles using MXene-coated yarns[J]. Materials Today,2020,34:17-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2020.02.005 [37] LEVITT A, SEYEDIN S, ZHANG J Z, et al. Bath electrospinning of continuous and scalable multifunctional MXene-infiltrated nanoyarns[J]. Small,2020,16(26):2002158. doi: 10.1002/smll.202002158 [38] SEYEDIN S, ZHANG J Z, USMAN K A S, et al. Facile solution processing of stable MXene dispersions towards conductive composite fibers[J]. Global Challenges,2019,3(10):1900037. doi: 10.1002/gch2.201900037 [39] SEYEDIN S, UZUN S, LEVITT A, et al. MXene composite and coaxial fibers with high stretchability and conductivity for wearable strain sensing textiles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(12):1910504. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910504 [40] ZHANG J Z, SEYEDIN S, QIN S, et al. Highly conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene hybrid fibers for flexible and elastic fiber-shaped supercapacitors[J]. Small,2019,15(8):1804732. doi: 10.1002/smll.201804732 [41] WANG Y L, ZHENG Y C, ZHAO J P, et al. Assembling free-standing and aligned tungstate/MXene fiber for flexible lithium and sodium-ion batteries with efficient pseudocapacitive energy storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials,2020,33:82-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2020.06.018 [42] LIU Q, ZHAO A R, HE X X, et al. Full-temperature all-solid-state Ti3C2Tx/aramid fiber supercapacitor with optimal balance of capacitive performance and flexibility[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,31(22):2010944. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202010944 [43] LIMA M D, FANG S L, LEPRÓ X, et al. Biscrolling nanotube sheets and functional guests into yarns[J]. Science,2011,331(6013):51-55. doi: 10.1126/science.1195912 [44] XIONG F Y, CAI Z Y, QU L B, et al. Three-dimensional crumpled reduced graphene oxide/MoS2 nanoflowers: A stable anode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(23):12625-12630. [45] MAYERBERGER E A, URBANEK O, MCDANIEL R M, et al. Preparation and characterization of polymer-Ti3C2Tx (MXene) composite nanofibers produced via electrospinning[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2017,134(37):45295. doi: 10.1002/app.45295 [46] MAYERBERGER E A, STREET R M, MCDANIEL R M, et al. Antibacterial properties of electrospun Ti3C2Tz (MXene)/chitosan nanofibers[J]. RSC Advances,2018,8(62):35386-35394. doi: 10.1039/C8RA06274A [47] SOBOLCIAK P, ALI A, HASSAN M K, et al. 2 D Ti3C2Tx (MXene)-reinforced polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibers with enhanced mechanical and electrical properties[J]. Plos One,2017,12(8):e0183705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183705 [48] LEVITT A S, ALHABEB M, HATTER C B, et al. Electrospun MXene/carbon nanofibers as supercapacitor electrodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2019,7(1):269-277. doi: 10.1039/C8TA09810G [49] WANG L, ZHANG M Y, YANG B, et al. Lightweight, robust, conductive composite fibers based on MXene@aramid nanofibers as sensors for smart fabrics[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(35):41933-41945. [50] LIU L X, CHEN W, ZHANG H B, et al. Tough and electrically conductive Ti3C2Tx MXene based core-shell fibers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding and heating application[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,430(4):133074. [51] LIU L X, CHEN W, ZHANG H B, et al. Super-tough and environmentally stable aramid. Nanofiber@MXene coaxial fibers with outstanding electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2022,14(1):111. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00853-1 [52] CHENG B C, WU P Y. Scalable fabrication of kevlar/Ti3C2Tx MXene intelligent wearable fabrics with multiple sensory capabilities[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(5):8676-8685. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c00749 [53] LEE S H, EOM W, SHIN H, et al. Room-temperature, highly durable Ti3C2Tx MXene/graphene hybrid fibers for NH3 gas sensing[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(9):10434-10442. [54] LI H, DU Z Q. Preparation of a highly sensitive and stretchable strain sensor of MXene/silver nanocomposite-based yarn and wearable applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(49):45930-45938. [55] PU J H, ZHAO X, ZHA X J, et al. Multilayer structured AgNW/WPU-MXene fiber strain sensors with ultrahigh sensitivity and a wide operating range for wearable monitoring and healthcare[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2019,7(26):15913-15923. doi: 10.1039/C9TA04352G [56] ZHANG X S, WANG X F, LEI Z W, et al. Flexible MXene-decorated fabric with interwoven conductive networks for integrated joule heating, electromagnetic interference shielding, and strain sensing performances[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(12):14459-14467. [57] WANG S, DU X S, LUO Y F, et al. Hierarchical design of waterproof, highly sensitive, and wearable sensing electronics based on MXene-reinforced durable cotton fabrics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,408:127363. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127363 [58] LI Y Z, ZHANG X T. Electrically conductive, optically responsive, and highly orientated Ti3C2Tx MXene aerogel fibers[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,32(4):2107767. [59] LUKATSKAYA M R, KOTA S, LIN Z F, et al. Ultra-high-rate pseudocapacitive energy storage in two-dimensional tran-sition metal carbides[J]. Nature Energy,2017,2(8):17105. doi: 10.1038/nenergy.2017.105 [60] LAN L Y, JIANG C M, YAO Y, et al. A stretchable and conductive fiber for multifunctional sensing and energy harvesting[J]. Nano Energy,2021,84:105954. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.105954 [61] FU X M, YANG H T, LI Z P, et al. Cation-induced assembly of conductive MXene fibers for wearable heater, wireless communication, and stem cell differentiation[J/OL]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2021, [2022-08-08]. DOI:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1 c00591. -





 下载:
下载: