Effect of oxidation heat treatment temperature on microstructure and microwave absorption properties of porous nickel foam
-
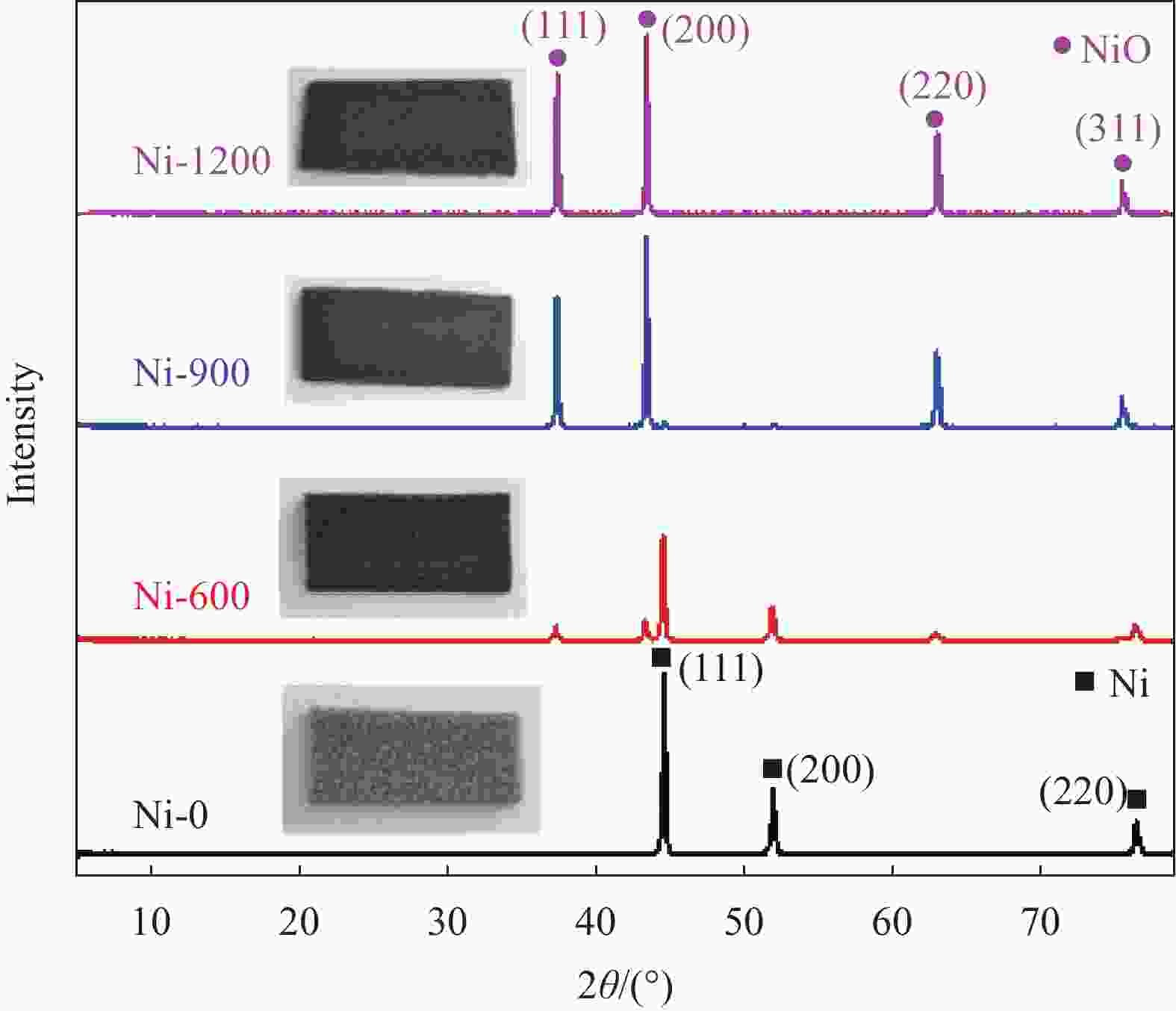
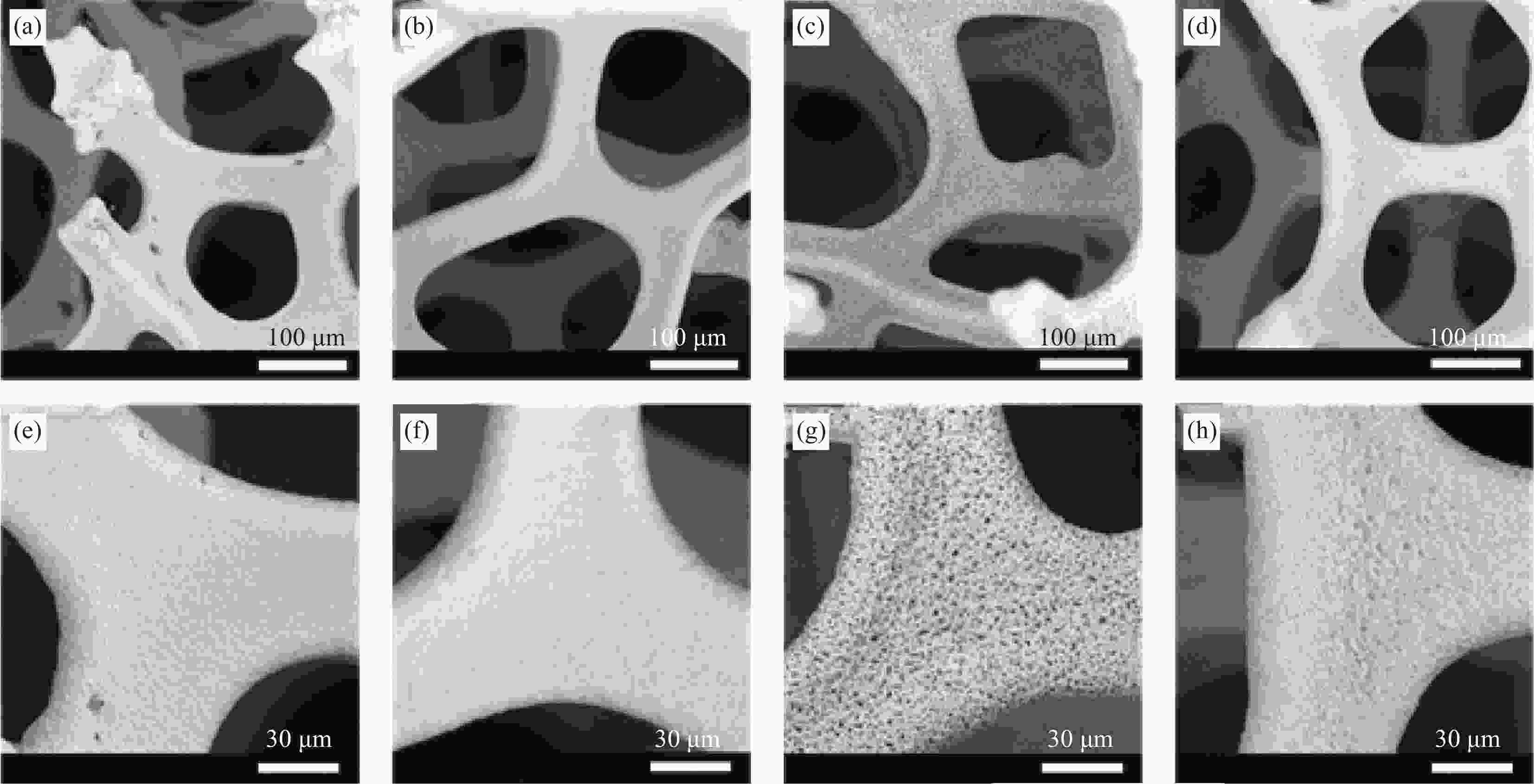
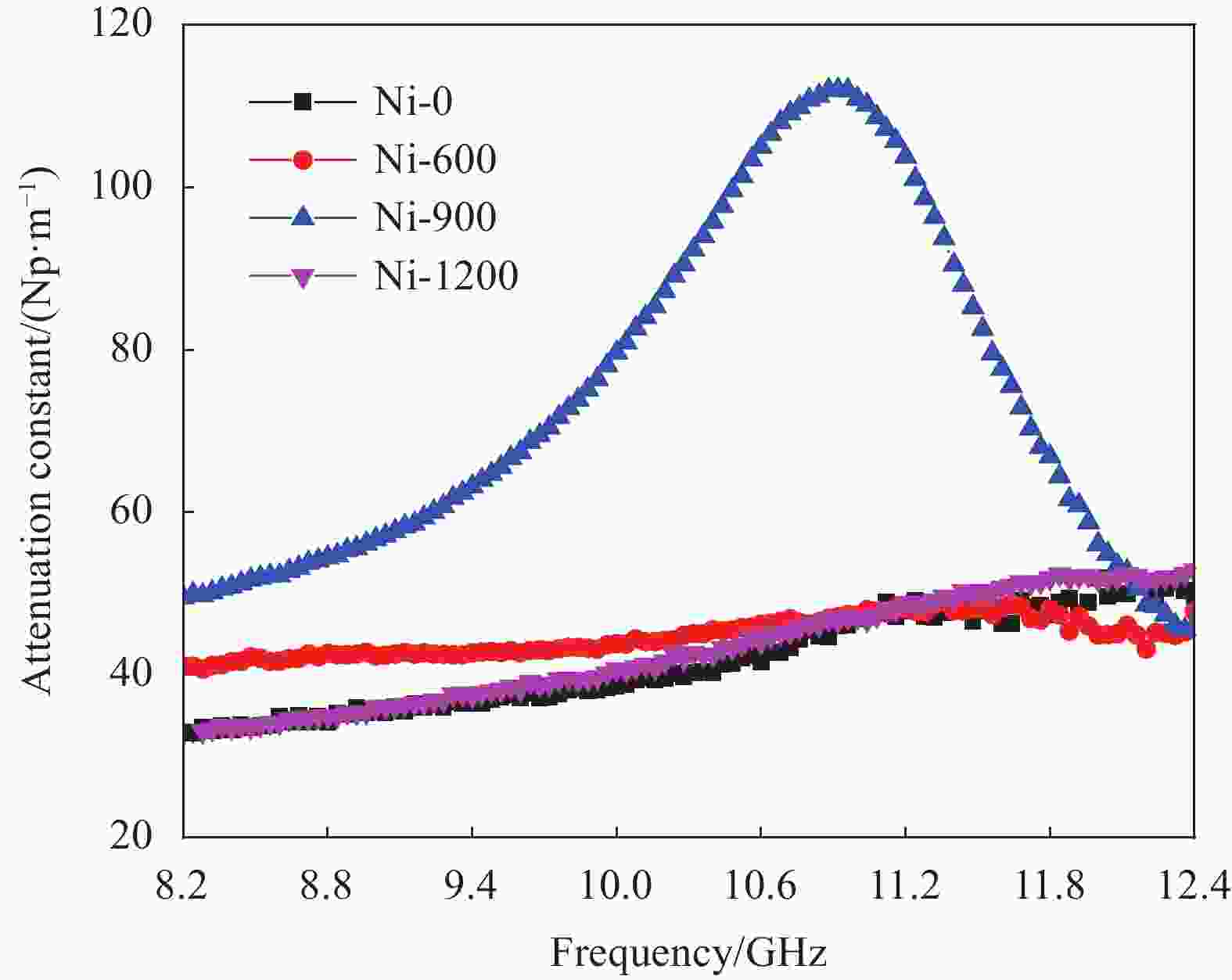
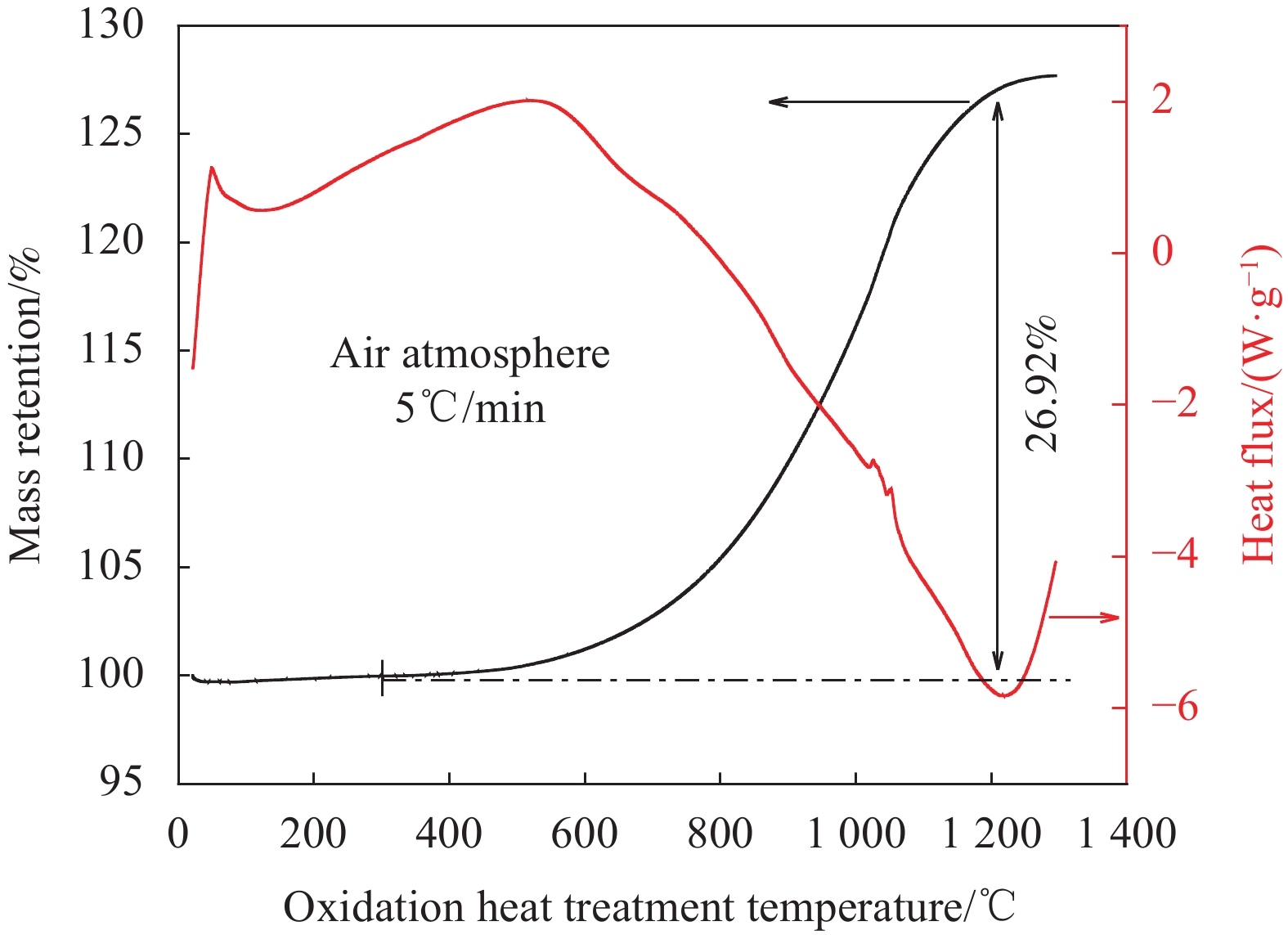
摘要: 为了探究多孔镍泡沫在电磁污染环境应用的可能性,根据多孔镍泡沫在空气下的热重曲线图,采用不同氧化热处理温度对其进行高温处理,借助TG-DSC、XRD、SEM、矢量网络分析仪研究氧化热处理温度对多孔镍泡沫的微观结构和电磁波吸收性能的影响关系。结果表明,当氧化热处理温度超过600℃时,多孔镍泡沫骨架表面产生明显变化,当氧化热处理为900℃时,表面形成大量孔洞,而当氧化热处理温度到达1200℃时,表面呈熔融状。通过物相分析表明,随着氧化热处理温度升高,多孔镍泡沫骨架表面生成氧化镍。对X波段的电磁吸波性能进行测试可以发现,经900℃氧化热处理得到的多孔镍泡沫具有最优异的微波吸收性能,并在10.88 GHz处反射损耗到达最小值−19.66 dB,表明一定的氧化热处理可以有效改善多孔镍泡沫的吸波性能。Abstract: According to the thermogravimetric curve diagram of porous nickel foam in air, different oxidation heat treatment temperatures were employed for high temperature treatment, and the effect of the oxidation heat treatment temperature on the microstructure and electromagnetic microwaves of porous nickel foam was studied by TG-DSC, XRD, SEM, and vector network analyzer to explore the possibility of the application of porous nickel foam in electromagnetic pollution environment. The results show that when the oxidation heat treatment temperature exceeds 600℃, the surface of the porous nickel foam skeleton has obvious changes. When the oxidation heat treatment is 900℃, the surface forms a flaky structure, and when the oxidation heat treatment temperature reaches 1200℃, the surface becomes molten. The phase analysis indicates that with the increase of the oxidation heat treatment, the nickel oxide is formed on the surface of the porous nickel foam network. The electromagnetic absorption performances in the X-band are tested, and the porous nickel foam obtained by the oxidation heat treatment at 900℃ owns the most excellent microwave absorption performance, the reflection loss of which reaches the minimum value of −19.66 dB at 10.88 GHz, indicating that a certain oxidation heat treatment could effectively improve the microwave absorbing properties of the porous nickel foam.
-
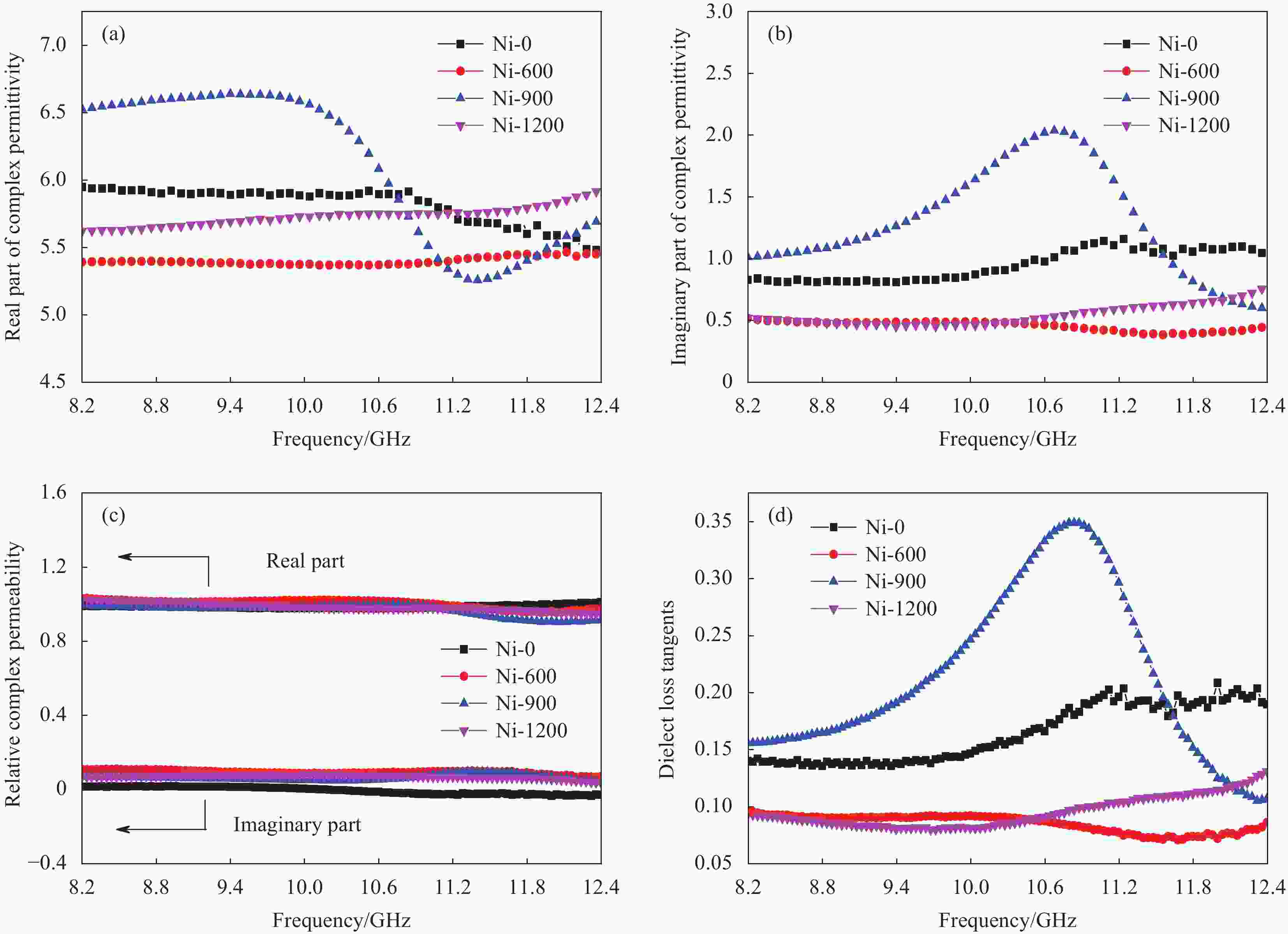
图 4 氧化热处理后多孔镍泡沫的电磁参数分析:(a)相对复介电常数实部;(b)相对复介电常数虚部;(c)相对复磁导率;(d)介电损耗因子
Figure 4. Electromagnetic parameter analysis of porous nickel foam after oxidation heat treatment: (a) Real part of the relative complex permittivity; (b) Imaginary part of the relative complex permittivity; (c) Relative complex permeability; (d) Dielectric dissipation factor
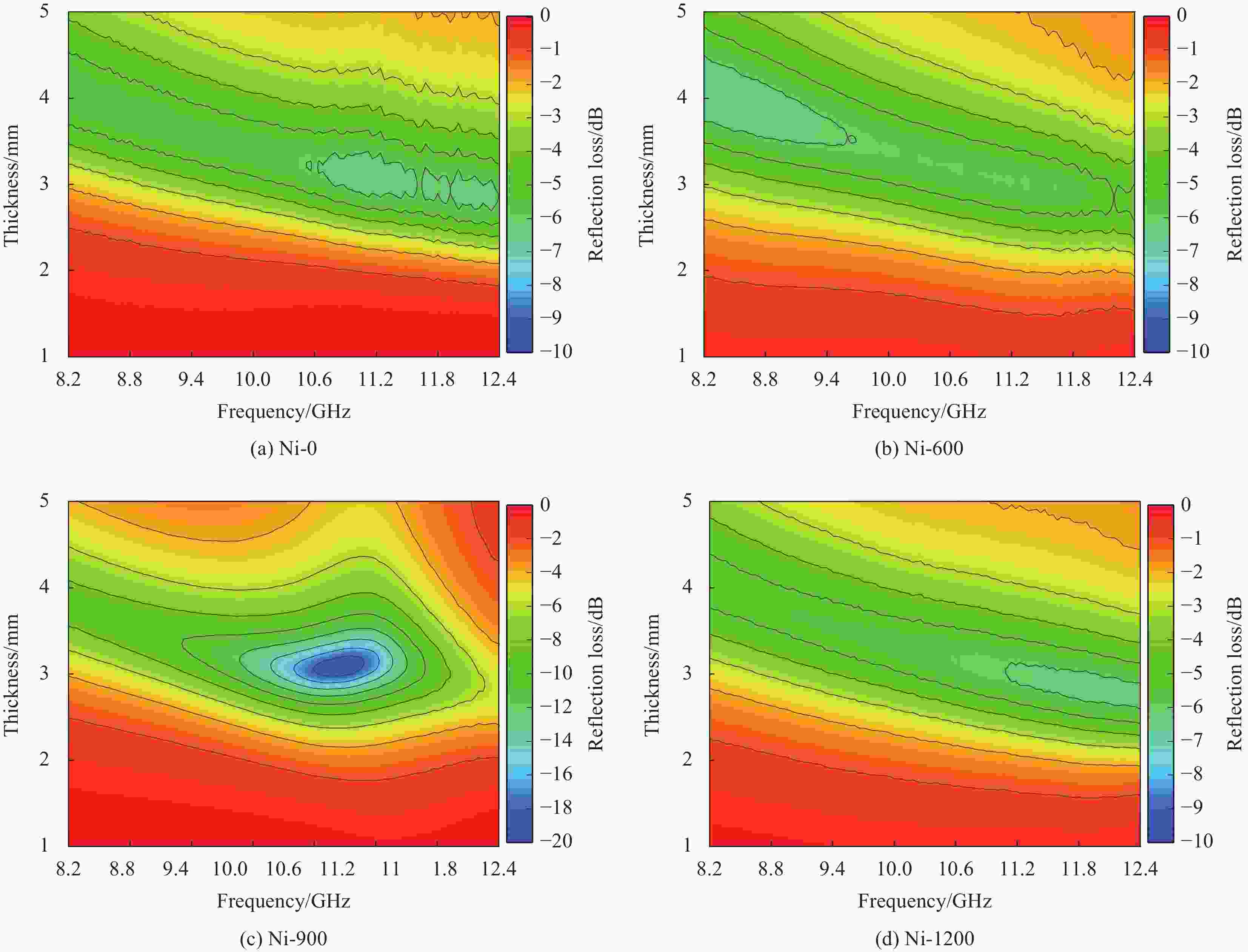
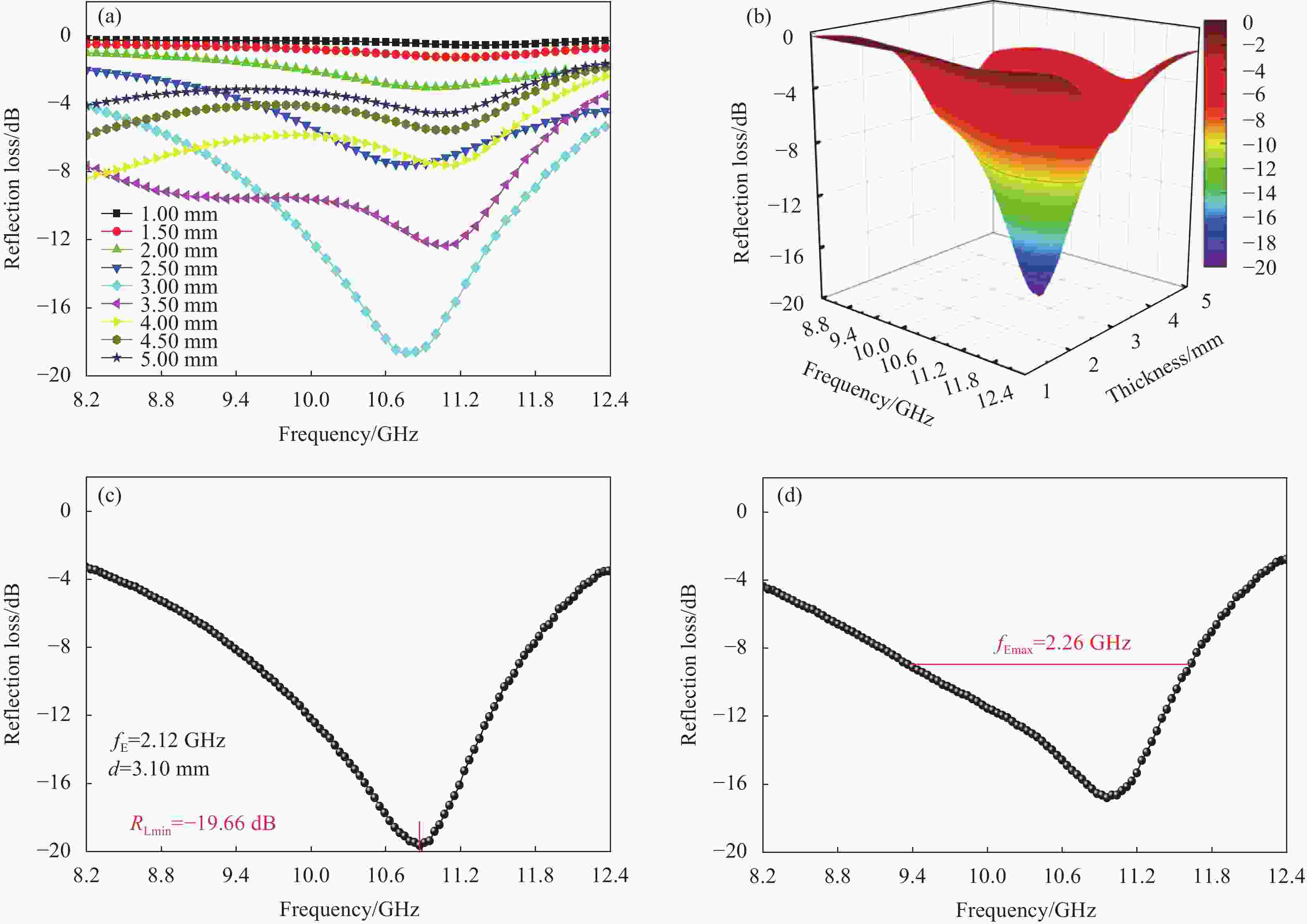
图 6 经900℃氧化热处理后多孔镍泡沫在不同匹配厚度和电磁波频率下的反射损耗图:(a) 二维平面图;(b) 三维曲面图;(c) 反射损耗最小;(d) 有效吸收频带最宽
Figure 6. Reflection loss maps of porous nickel foam after 900℃ oxidation heat treatment at various matching thickness and electromagnetic frequency:(a) Two-dimensional plan; (b) Three-dimensional surface diagram; (c) Minimum reflection loss; (d) Widest effective absorption band
fE—Effective absorption band; d—Matching thickness; fEmax—Widest effective absorption band; RLmin—Minimum reflection loss
-
[1] 李德仁. 镍基吸波材料微波吸收性能研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019.LI Deren. Study on the microwave absorption properties of nickel-based absorbing materials[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019(in Chinese). [2] 胡涛. 屏蔽效能可控结构功能一体化碳纤维复合材料设计及性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.HU Tao. Design and property research of structure and function integration carbon fiber composite with controllable shielding effectiveness[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [3] 牛芳旭. 碳化硅及其复合材料的制备与电磁波吸收性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019.NIU Fangxu. Preparation and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of silicon carbide and its composite[D]. Ji′nan: Shandong University, 2019(in Chinese). [4] SHAHZAD F, ALHABEB M, HATTER C B, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes)[J]. Science,2016,353(6304):1137-1140. doi: 10.1126/science.aag2421 [5] 曹敏, 邓雨希, 徐康, 等. 新型碳基磁性复合吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(12):3004-3016.CAO Min, DENG Yuxi, XU Kang, et al. Research progress of new carbon based magnetic composite electromagnetic wave absorbing materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(12):3004-3016(in Chinese). [6] 黄庭远. 硫化钴基复合纳米材料的制备及微波吸收性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2017.HUANG Tingyuan. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of cobalt sulfide-based composite nanomaterials[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017(in Chinese). [7] 杨振楠, 刘芳, 李朝龙, 等. 核壳结构电磁波吸收材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(7):7061-7070.YANG Zhennan, LIU Fang, LI Chaolong, et al. Research progress of electromagnetic wave absorbing materials with core-shell structure[J]. Materials Reports,2020,34(7):7061-7070(in Chinese). [8] QUAN B, GU W, SHENG J, et al. From intrinsic dielectric loss to geometry patterns: Dual-principles strategy for ultrabroad band microwave absorption[J]. Nano Research,2020,14(5):1495-1501. [9] YAN J, HUANG Y, CHEN C, et al. The 3D CoNi alloy particles embedded N-doped porous carbon foam for high-performance microwave absorber[J]. Carbon,2019,152:545-555. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.06.064 [10] ZHANG X, JI G, LIU W, et al. Thermal conversion of an Fe3O4@metal-organic framework: A new method for an efficient Fe-Co/nanoporous carbon microwave absorbing material[J]. Nanoscale,2015,7(30):12932-12942. doi: 10.1039/C5NR03176A [11] ZHOU J, SHU X, WANG Z, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of polyhedral FeCo alloys with enhanced electromagnetic absorption performances[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,794:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.217 [12] 王敏. 镍锌铁氧体及其复合材料的制备与吸波性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2015.WANG Min. Preparation and microwave absorption performance of nickel zinc ferrite and its composites[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015(in Chinese). [13] CHENG Y, ZHAO H, YANG Z, et al. An unusual route to grow carbon shell on Fe3O4 microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,762:463-472. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.261 [14] YE X, CHEN Z, LI M, et al. Hollow SiC foam with a double interconnected network for superior microwave absorption ability[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,817:153276. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153276 [15] 刘晓菲. 高温结构吸波型SiCf/Si3N4复材优化设计基础[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2017.LIU Xiaofei. Design and optimization of high temperature SiC fibre reinforced Si3N4 ceramic matrix composites with wave-absorbing and structure properties[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2017(in Chinese). [16] HE N, HE Z, LIU L, et al. Ni2+ guided phase/structure evolution and ultra-wide bandwidth microwave absorption of CoxNi1-x alloy hollow microspheres[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122743. [17] LIU M, CHEN Y, WEI H, et al. Finely modulating the morphology and composition of CuxNi1−x for enhanced microwave absorption capability[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2020, 55(27): 12953-12968. [18] YIN H, JIANG L, LIU P, et al. Remarkably enhanced water splitting activity of nickel foam due to simple immersion in a ferric nitrate solution[J]. Nano Research,2018,11(8):3959-3971. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1886-7 [19] JIA L, WEI X, LV L, et al. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapa-tite on nickel foam and further modification with conduc-tive polyaniline for non-enzymatic glucose sensing[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2018,280:315-322. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.05.130 [20] GAO Y, CHEN S, CAO D, et al. Electrochemical capaci-tance of Co3O4 nanowire arrays supported on nickel foam[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2010,195(6):1757-1760. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.09.048 [21] LIU M, YANG X, SHAO W, et al. EDA-steered in situ staged reduction-etching synthesis of hollow CuxNi1-x/Ni core-shell composites with broad bands and strong microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 855: 157326. [22] GU W, QUAN B, LIANG X, et al. Composition and structure design of Co3O4 nanowires network by nickel foam with effective electromagnetic performance in C and X band[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2019,7(5):5543-5552. [23] 李哲. 泡沫金属系材料的吸波增强改性及其在降解废水中的应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2019.LI Zhe. Study on microwave enhancement modification of wastewater foamed metal and its application in treatment[D]. Ji′nan: Shandong University, 2019(in Chinese). [24] 陈国力, 宋坤, 赵楠, 等. 泡沫镍复合材料的制备与表征[J]. 高师理科学刊, 2020, 40(4): 69-71.CHEN Guoli, SONG Kun, ZHAO Nan, et al. Preparation and characterization of nickel foam composites[J]. Journal of Science of Teachers' College and University, 2020, 40(4): 69-71(in Chinese). [25] 刘程成, 王玉锋, 郭攀, 等. 碳球氧化镍复合材料的制备及其超级电容器性能研究[J]. 山东化工, 2020, 49(23):6-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2020.23.003LIU Chengcheng, WANG Yufeng, GUO Pan, et al. Preparation of carbon sphere/nickel oxide composite and its supercapacitor performance[J]. Shangdong Chemical Industry,2020,49(23):6-8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2020.23.003 [26] WU C, CHEN Z, WANG M, et al. Confining tiny MoO2 clusters into reduced graphene oxide for highly efficient low frequency microwave absorption[J]. Small, 2020, 16(30): 2001686. [27] 卢明明, 刘甲, 宫元勋, 等. 不同形貌羰基铁的复合对电磁特性及吸波性能的影响[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(2):95-99, 123.LU Mingming, LIU Jia, GONG Yuanxun, et al. Electromagnetic characteristics and microwave absorbing properties of carbonyl iron composite with different morphologies[J]. Surface Technology,2020,49(2):95-99, 123(in Chinese). [28] 丁冬海, 白冰, 肖国庆, 等. 燃烧合成碳化硼粉体及其介电吸波性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(3):343-350.DING Donghai, BAI Bing, XIAO Guoqing, et al. Dielectric and electromagnetic absorbing properties of B4C powders fabricated by combustion synthesis[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,48(3):343-350(in Chinese). [29] YAN J, HUANG Y, WEI C, et al. Covalently bonded polyani-line/graphene composites as high-performance electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption materials[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,99:121-128. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.04.016 [30] 罗玉亮, 王磊, 陈宗椅, 等. 氧化热处理优化NdFeCo磁粉的吸波性能[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2019, 38(9):49-54.LUO Yuliang, WANG Lei, CHEN Zongyi, et al. Optimization of absorbing properties of NdFeCo magnetic powder by oxidation heat treatment[J]. Electronic Components & Materials,2019,38(9):49-54(in Chinese). [31] 赵婉瑜. 聚合物先驱体陶瓷气凝胶的吸波性能调控及机理研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2018.ZHAO Wanyu. Study on the electromagnetic wave absorption property manipulation of polymer-derived ceramic aerogels and relative mechanisms[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2018. [32] 耿浩然, 赵鹏飞, 梅俊飞, 等. 二硫化钼/多壁碳纳米管/天然橡胶复合材料制备及吸波性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2019, 50(12):216-221.GENG Haoran, ZHAO Pengfei, MEI Junfei, et al. Preparation and absorbing properties of molybdenum disulfide/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/natural rubber compo-sites[J]. Jorunal of Functional Materials,2019,50(12):216-221(in Chinese). [33] LIANG X, QUAN B, CHEN J, et al. Strong electric wave response derived from the hybrid of lotus roots-like compo-sites with tunable permittivity[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):1-13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x [34] LIANG X, QUAN B, SUN Y, et al. Multiple interfaces structure derived from metal-organic frameworks for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Particle and Particle Systems Characterization,2017,34(5):1700006. doi: 10.1002/ppsc.201700006 [35] ZHAO B, SHAO G, FAN B, et al. Facile preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of core-shell composite spheres composited of Ni cores and TiO2 shells[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2015,17(14):8802-8810. doi: 10.1039/C4CP05632A [36] LIU X, OU Z, GENG D, et al. Enhanced natural resonance and attenuation properties in super paramagnetic graphite-coated FeNi3 nanocapsules[J]. Journal of Physics D—Applied Physics,2009,42(15):155004. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/42/15/155004 [37] TONG G, HU Q, WU W, et al. Submicrometer-sized NiO octahedra: Facile one-pot solid synthesis, formation mecha-nism, and chemical conversion into Ni octahedra with excellent microwave-absorbing properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(34): 17494. [38] LI Y, WU T, JIN K, et al. Controllable synthesis and enhanced microwave absorbing properties of Fe3O4/NiFe2O4/Ni heterostructure porous rods[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 387: 190-201. [39] CHENG Y, LI Y, JI G, et al. Magnetic and electromagnetic properties of Fe3O4/Fe composites prepared by a simple one-step ball-milling[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2017,708:587-593. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.03.060 -





 下载:
下载: