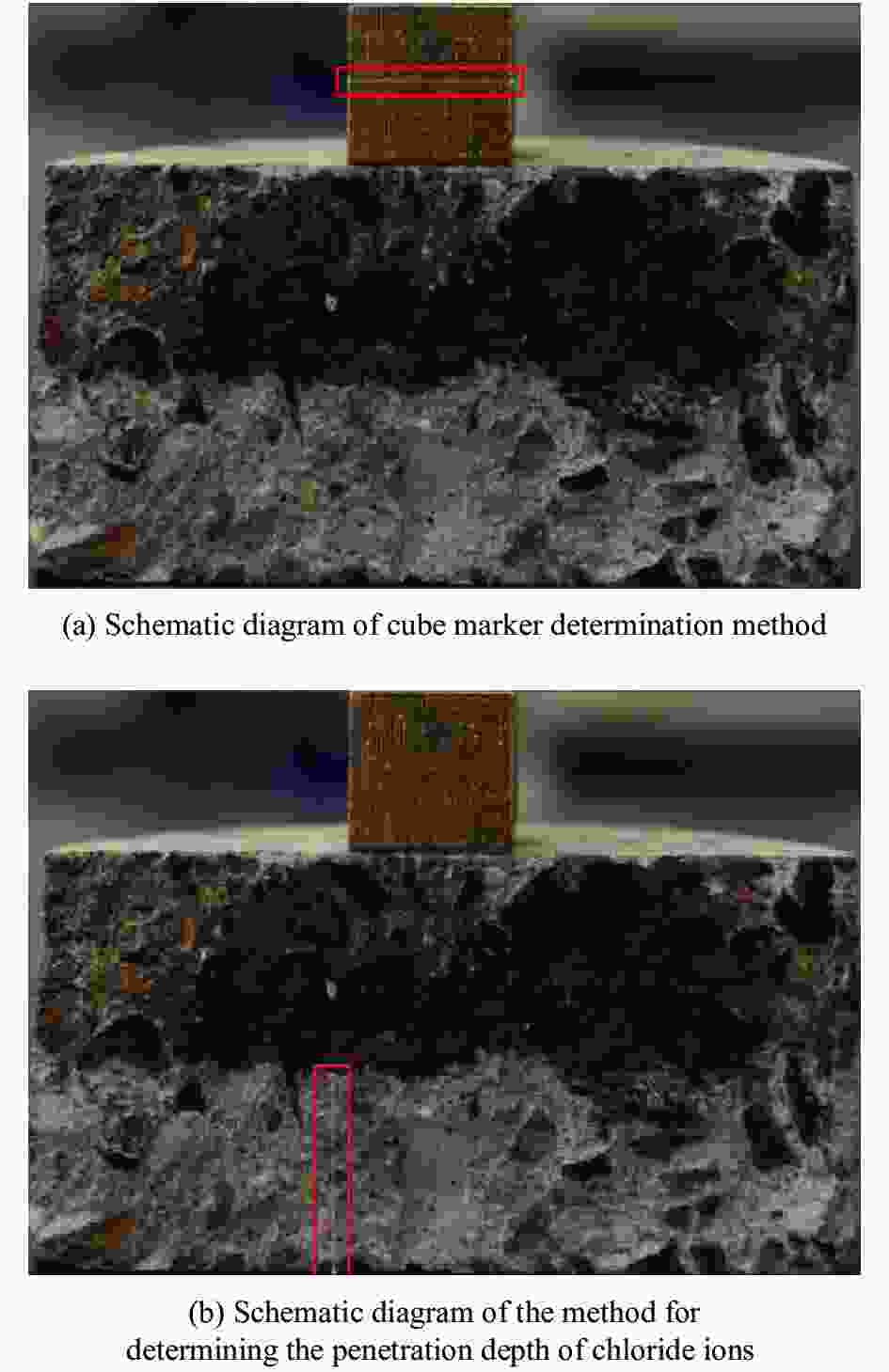
Chloride ion penetration resistance of multi-walled carbon nanotubes reinforced concrete
-
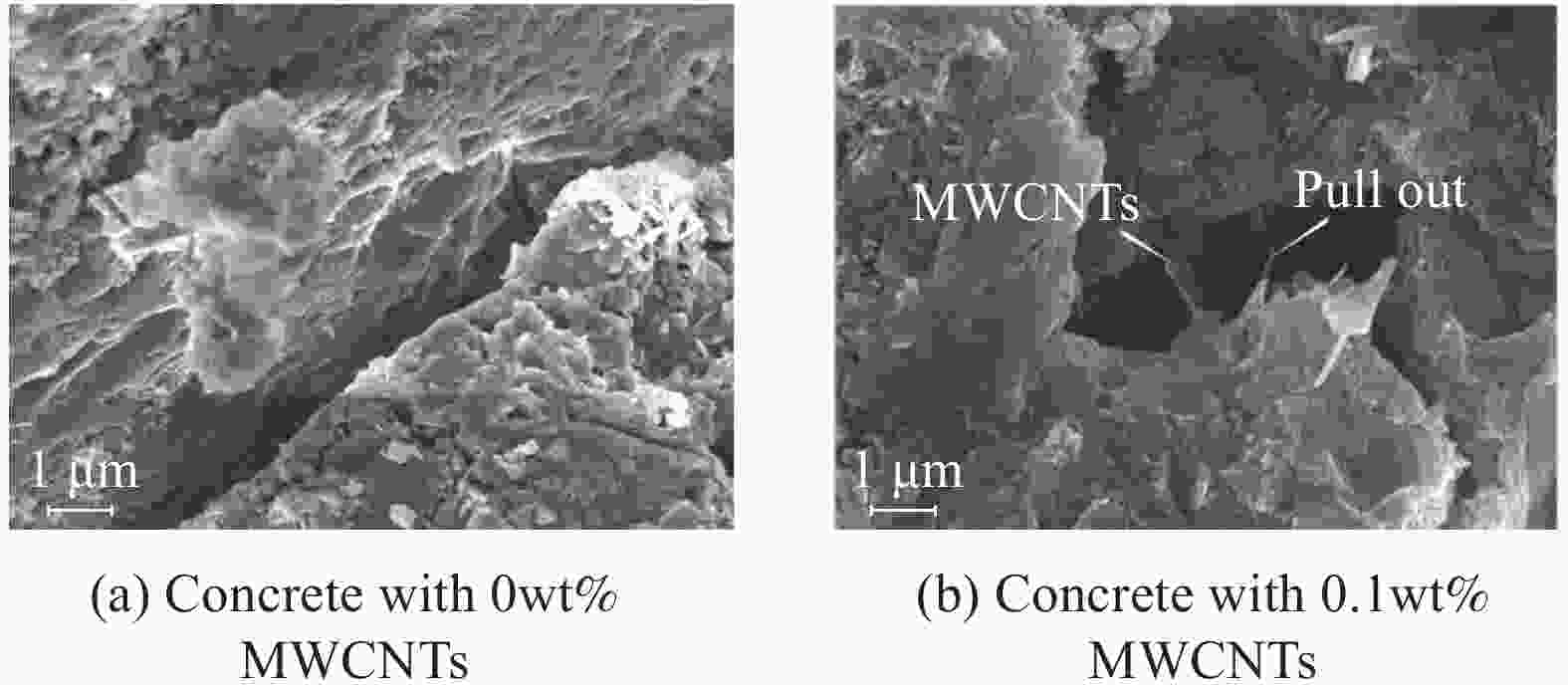
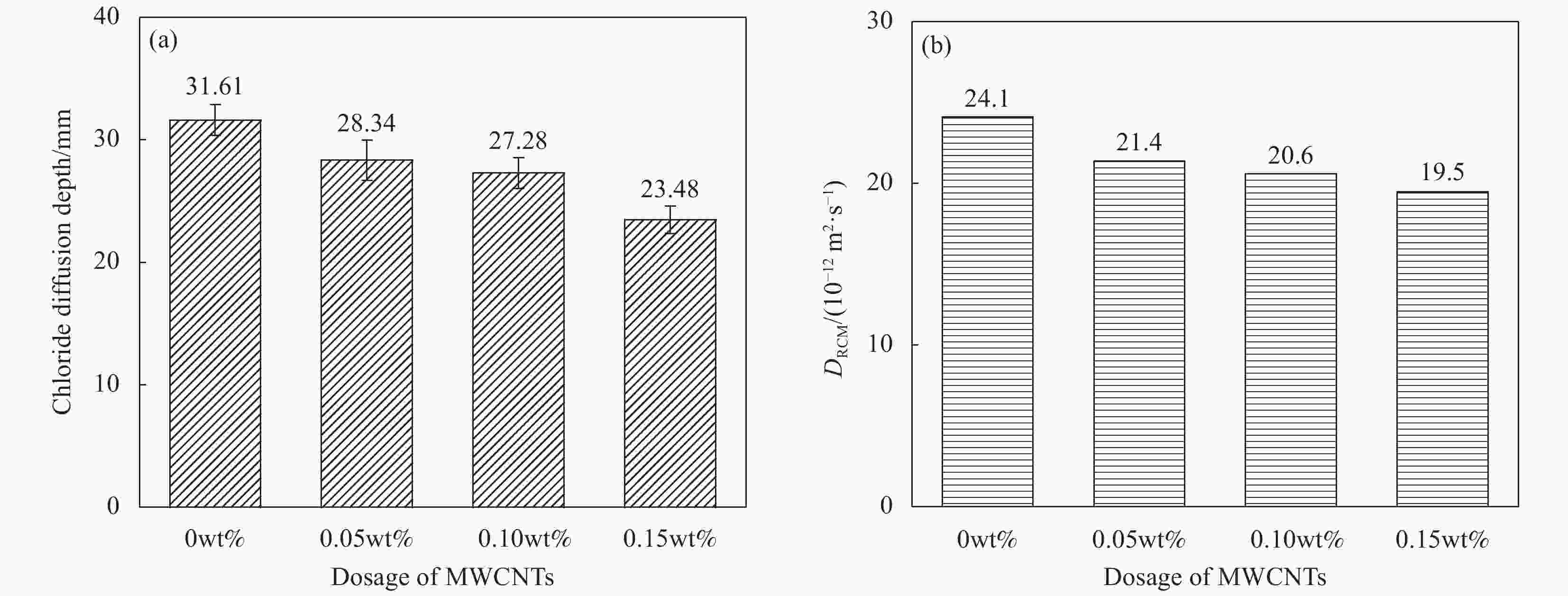
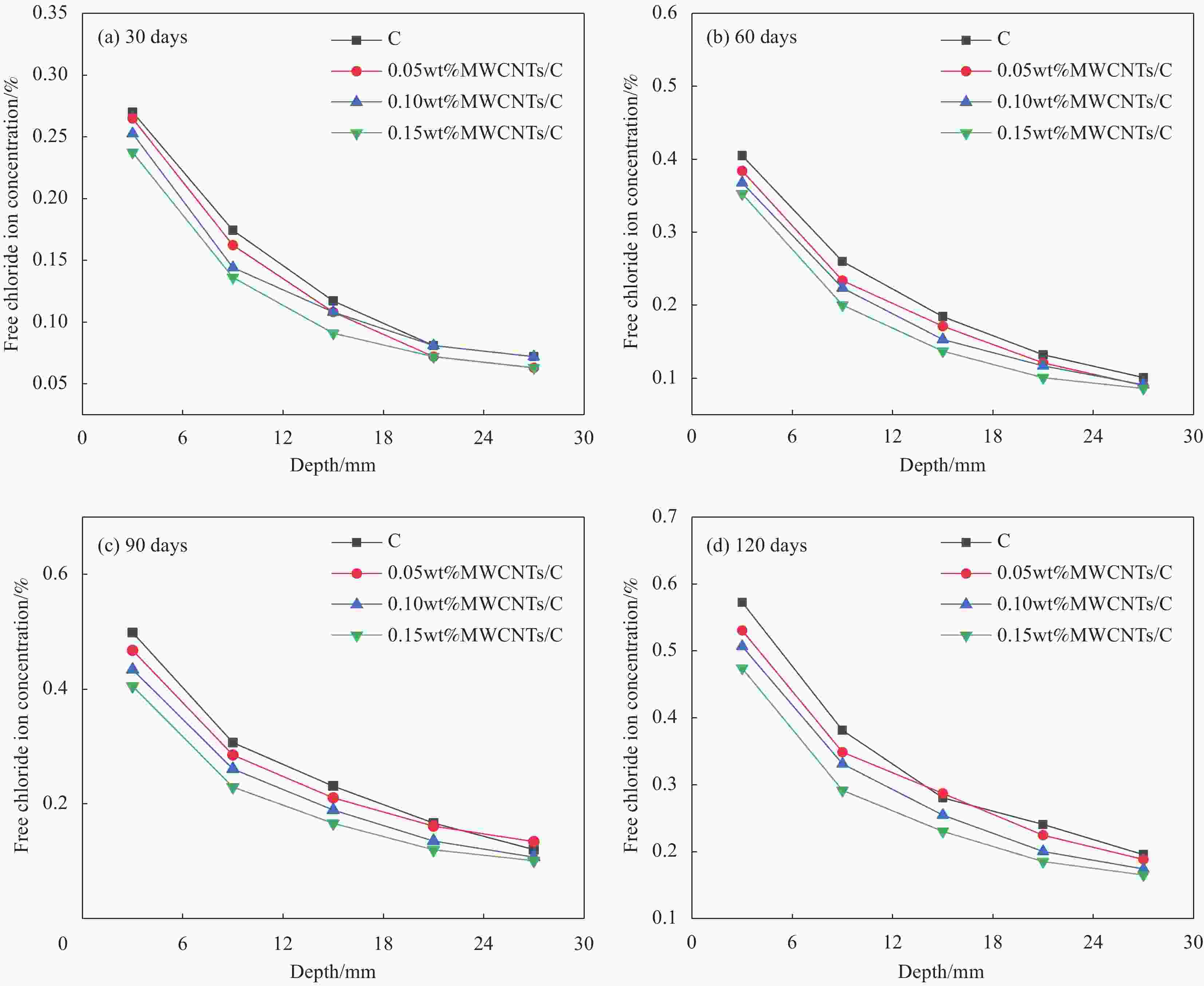
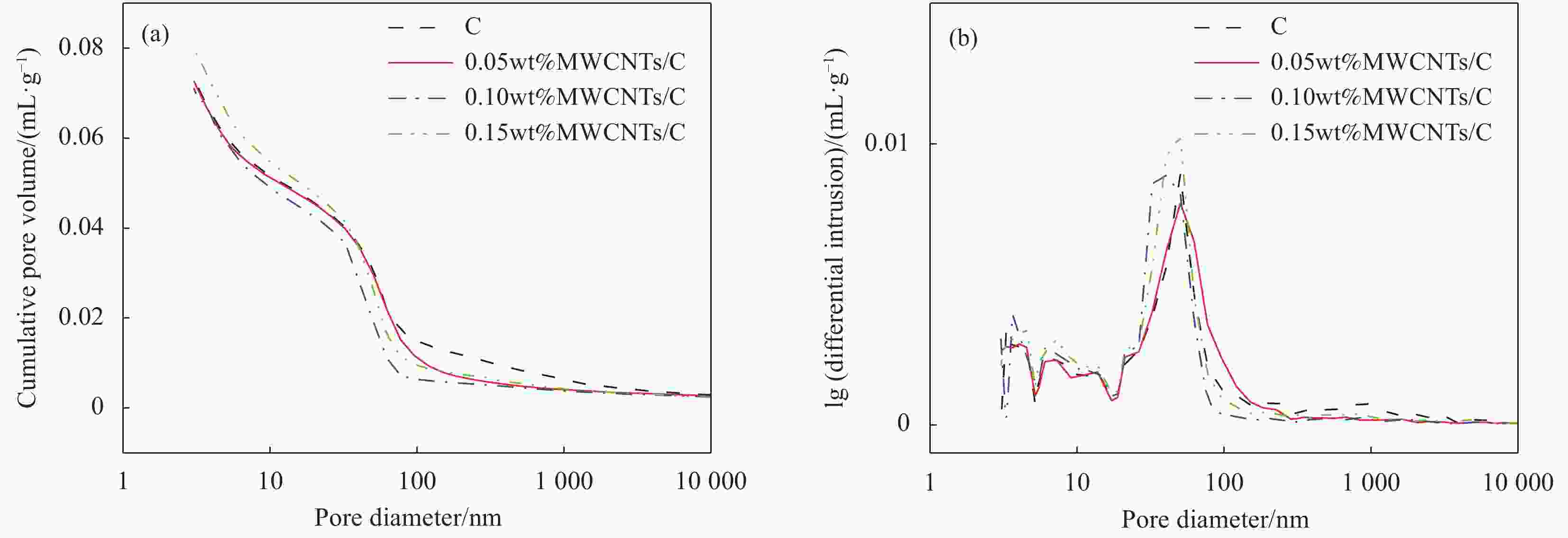
摘要: 采用快速氯离子迁移系数(RCM)法和自然浸泡法对多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)增强混凝土的抗氯离子渗透性能进行研究,测量混凝土试件纵向断面上的氯离子扩散深度,据此计算氯离子扩散系数。试验结果表明:当MWCNTs掺量为0.15wt%时,混凝土28天的氯离子扩散深度、氯离子扩散系数分别降低了25.7%、19.1%;在4种不同侵蚀龄期的自然浸泡下,掺入MWCNTs的混凝土,内部氯离子浓度始终低于对照组。结合两种方法分析得出:混凝土内部各深度的自由氯离子浓度随着MWCNTs掺量的增加而降低,致使氯离子扩散系数随着MWCNTs掺量的增加而变小,MWCNTs的掺入提高了混凝土的抗氯离子渗透性能。此外,通过SEM和压汞(MIP)测试进一步探究MWCNTs对混凝土抗氯离子渗透性能的微观增强机制,分析结果表明,MWCNTs具有一定的桥接和填充效应,这可能使混凝土裂缝扩展受到抑制、孔隙更加细化,从而改善混凝土的微观结构,提高混凝土的抗氯离子渗透性能。Abstract: The rapid chloride migration coefficient (RCM) method and the natural immersion method were used to study the chloride ion penetration resistance of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) reinforced concrete. The chloride ion diffusion depth on the longitudinal section of the concrete specimen was measured, and the chloride ion diffusion coefficient was calculated based on this. The test results show that when the content of MWCNTs is 0.15wt%, the chloride ion diffusion depth and chloride ion diffusion coefficient of concrete at 28 days are reduced by 25.7% and 19.1%, respectively. Under four different erosion ages of natural soaking, mixing in the concrete of MWCNTs, the internal chloride ion concentration is always lower than that of the control group. Combining the analysis of the two methods, it is concluded that the free chloride ion concentration at each depth of the concrete decreases with the increase of the MWCNTs content, so that the chloride diffusion coefficient decreases with the increase of the MWCNTs content, and the incorporation of MWCNTs improves the resistance of concrete to chloride ion penetration. In addition, through SEM and mercury intrusion (MIP) tests, the microscopic enhancement mechanism of MWCNTs on the anti-chloride ion permeability of concrete was further explored. The analysis results show that MWCNTs have a certain bridging and filling effect, which may cause concrete crack propagation to be affected, inhibit and refine the pores, thereby improving the microstructure of concrete and improving the resistance of concrete to chloride ion penetration.
-
表 1 水泥的化学组成
Table 1. Chemcial compositions of cement
wt% Material CaO SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 SO3 MgO Loss Cement 64.47 22.18 4.51 3.15 2.56 1.2 1.36 表 2 多壁碳纳米管(MWCNTs)浆料的参数
Table 2. Parameters of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) aqueous paste
Model Medium Medium content/wt% CNTs model CNTs content/wt% Dispersant Dispersant content/wt% TNWPM-M8 Water 88 TNIM8 10 TNWDIS 2 表 3 MWCNTs的物理特性
Table 3. Physical parameters of MWCNTs
Model Outer diameter/nm Purity/wt% Length/μm Special surface area/(m2·g−1) Tap density/(g·cm−3) TNIM8 30-80 >95 5-10 >60 0.18 表 4 不同MWCNTs掺量混凝土的配合比
Table 4. Mix proportions of concrete with different contents of MWCNTs
Specimen group MWCNTs
/wt%TNWDIS
/wt%Water
/kgCement
/kgSand
/kgAggregate
/kgSlump
/mmC 0.00 0.03 230 437 656 1077 80 0.05wt%MWCNTs/C 0.05 0.03 230 437 656 1077 80 0.10wt%MWCNTs/C 0.10 0.03 230 437 656 1077 80 0.15wt%MWCNTs/C 0.15 0.03 230 437 656 1077 80 表 5 不同MWCNTs掺量混凝土的孔径结构参数
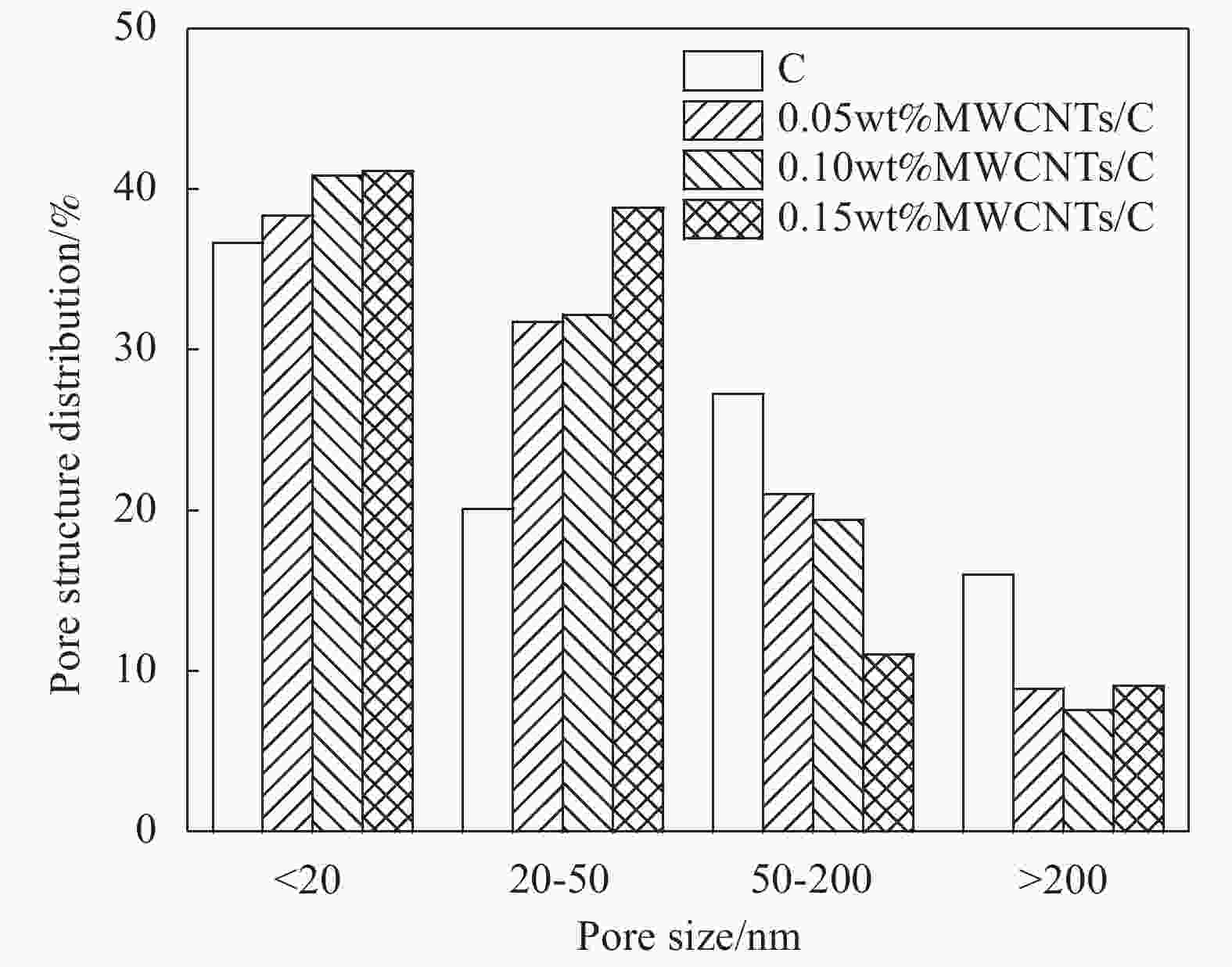
Table 5. Pore structure parameters of concrete with different MWCNTs contents
Specimen group Harmless pore
(<20 nm)/%Less harmful pore
(20-50 nm)/%Harmful pore
(50-200 nm)/%More harmful pore
(>200 nm)/%C 36.67 20.08 27.23 16.01 0.05wt%MWCNTs/C 38.34 31.74 21.01 8.91 0.10wt%MWCNTs/C 40.84 32.18 19.39 7.60 0.15wt%MWCNTs/C 41.10 38.81 11.04 9.06 -
[1] JIN M, JIANG L, LU M, et al. Monitoring chloride ion penetration in concrete structure based on the conductivity of graphene/cement composite[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,136:394-404. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.01.054 [2] HUANG D G, NIU D T, ZHENG H, et al. Study on chloride transport performance of eco-friendly coral aggregate concrete in marine environment[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,258:120272. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120272 [3] 李庚英, 王中坤. 碳纳米管对钢筋混凝土耐氯盐腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(3):103-107.LI Gengying, WANG Zhongkun. Effect of CNTs on the corrosion performance of reinforced concrete[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Nature Science Edition),2018,46(3):103-107(in Chinese). [4] SHI T, GAO Y, CORR D J, et al. FTIR study on early-age hydration of carbon nanotubes-modified cement-based materials[J]. Advances in Cement Research,2019,31(8):353-361. doi: 10.1680/jadcr.16.00167 [5] LAN Y J, SHI T, FU Y Y, et al. Preliminary investigation on silicon carbide whisker-modified cement-based composites[J]. Open Ceramics,2021,6:100107. doi: 10.1016/j.oceram.2021.100107 [6] YE Y X, LIU Y M, SHI T, et al. Effect of nano-magnesium oxide on the expansion performance and hydration process of cement-based materials[J]. Materials,2021,14(13):3766. doi: 10.3390/ma14133766 [7] REN M, SHI T, CORR D J, et al. Mechanical properties of micro-regions in cement-based material based on the peakforce QNM mode of AFM[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Materials Science Edition),2019,34(4):893-899. doi: 10.1007/s11595-019-2134-7 [8] CARRIO A, BOGAS J A, HAWREEN A, et al. Durability of multi-walled carbon nanotube reinforced concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,164:121-133. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.221 [9] WANG T, XU J, MENG B, et al. Experimental study on the effect of carbon nanofiber content on the durability of concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,250:118891. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118891 [10] IIJIMA S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon[J]. Nature,1991,354(6348):56-58. doi: 10.1038/354056a0 [11] ALSHAGHEL A, PARVEEN S, RANA S, et al. Effect of multiscale reinforcement on the mechanical properties and microstructure of microcrystalline cellulose-carbon nanotube reinforced cementitious composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,149:122-134. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.05.024 [12] FENG L, XIE N, ZHONG J. Carbon nanofibers and their composites: A review of synthesizing, properties and applications[J]. Materials,2014,7(5):3919-3945. doi: 10.3390/ma7053919 [13] LIU Q L, SUN W, JIANG H, et al. Effects of carbon nanotubes on mechanical and 2D-3D microstructure properties of cement mortar[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology (Materials Science Edition),2014,29(3):513-517. doi: 10.1007/s11595-014-0950-3 [14] ZHAO Y, LIU Y, SHI T, et al. Study of mechanical properties and early-stage deformation properties of graphene-modified cement-based materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,257:119498. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119498 [15] LI G Y, WANG P M, ZHAO X. Mechanical behavior and microstructure of cement composites incorporating surface-treated multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Carbon,2004,43(6):1239-1245. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.12.017 [16] YAZDANBAKHSH A, GRASLEY Z. The theoretical maximum achievable dispersion of nanoinclusions in cement paste[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2012,42(6):798-804. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2012.03.001 [17] NOCHAIYA T, CHAIPANICH A. Behavior of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the porosity and microstructure of cement-based materials[J]. Applied Surface Science,2010,257(6):1941-1945. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.09.030 [18] KONSTA-GDOUTOS M S, METAXA Z S, SHAH S P. Highly dispersed carbon nanotube reinforced cement based materials[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2010,40(7):1052-1059. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2010.02.015 [19] 刘颐. 碳纳米管对水泥砂浆抗碳化与氯盐侵蚀的试验研究[D]. 深圳: 深圳大学, 2016.LIU Yi. Experimental research on the ability of anti-carbonization and chloride corrosion of cement mortar by CNTs[D]. Shenzhen: Shenzhen University, 2016(in Chinese). [20] WANG B M, LIU S, HAN Y, et al. Preparation and durability of cement-based composites doped with multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Letters,2015,7(5):411-416. doi: 10.1166/nnl.2015.1979 [21] HAN B, YANG Z, SHI X, et al. Transport properties of carbon-nanotube/cement composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance,2013,22(1):184-189. doi: 10.1007/s11665-012-0228-x [22] 赵晋津, 任书霞, 吕臣敬, 等. 碳纳米管对硅酸盐水泥耐腐蚀性的影响研究[J]. 石家庄铁道大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 26(2):88-91.ZHAO Jinjin, REN Shuxia, LV Chenjing, et al. Research on anti-corrosion properties of portland cement doped with carbon nanotubes[J]. Journal of Shijiazhuang Tiedao University (Nature Science Edition),2013,26(2):88-91(in Chinese). [23] ALAFOGIANNI P, DALLA P T, TRAGAZIKIS I K, et al. Rapid chloride permeability test for durability study of carbon nanoreinforced mortar[M]. Bellingham: International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2015. [24] CAMACHO M D C, GALAO O, BAEZA F J, et al. Mechanical properties and durability of CNT cement composites[J]. Materials,2014,7(3):1640-1651. doi: 10.3390/ma7031640 [25] 施韬, 李泽鑫, 李闪闪. 碳纳米管增强水泥基复合材料的自收缩及抗裂性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(6):1528-1535.SHI Tao, LI Zexin, LI Shanshan. Autogenous shrinkage and crack resistance of carbon nanotubes reinforced cement based composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(6):1528-1535(in Chinese). [26] SHI T, LI Z, GUO J, et al. Research progress on CNTs/CNFs-modified cement-based composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,202:290-307. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.01.024 [27] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2009(in Chinese). [28] 杨绿峰, 陈俊武, 赵家琦, 等. 混凝土RCM试验分析的面均法研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(12):22-28.YANG Lufeng, CHEN Junwu, ZHAO Jiaqi, et al. Area average method for RCM test of concrete[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2020,53(12):22-28(in Chinese). [29] 韩学强, 詹树林, 徐强, 等. 干湿循环作用对混凝土抗氯离子渗透侵蚀性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(1):198-204.HAN Xueqiang, ZHAN Shulin, XU Qiang, et al. Effect of dry-wet cycling on resistance of concrete to chloride ion permeation erosion[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(1):198-204(in Chinese). [30] THOMAS M D A, BAMFORTH P B. Modelling chloride diffusion in concrete: Effect of fly ash and slag[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,1999,29(4):487-495. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00192-6 [31] 冯奇, 刘光明, 巴恒静. 颗粒级配对水泥基材料有害孔隙率的影响[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 32(9):1168-1172. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2004.09.011FENG Qi, LIU Guangming, BA Hengjing. Relation of grain grading and deleterious porosity of cement-based materials[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2004,32(9):1168-1172(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-374X.2004.09.011 [32] 刘巧玲. 碳纳米管增强水泥基复合材料多尺度性能及机理研究 [D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2015.LIU Qiaoling. Multi-scale properties and mechanism of carbon nanotubes/cement nanocomposites[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015(in Chinese). [33] LIU Y, SHI T, ZHAO Y J, et al. Autogenous shrinkage and crack resistance of carbon nanotubes reinforced cement-based materials[J]. International Journal of Concrete Structures and Materials,2020,14(1):525-534. [34] 牛荻涛, 何嘉琦, 傅强, 等. 碳纳米管对水泥基材料微观结构及耐久性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(5):705-717.NIU Ditao, HE Jiaqi, FU Qiang, et al. Effect of carbon nanotubes on the microstructure and durability of cement-based materials[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,48(5):705-717(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: