Fabrication and thermally conductive properties of functionalized SiC nanowires/liquid crystal epoxy composites
-
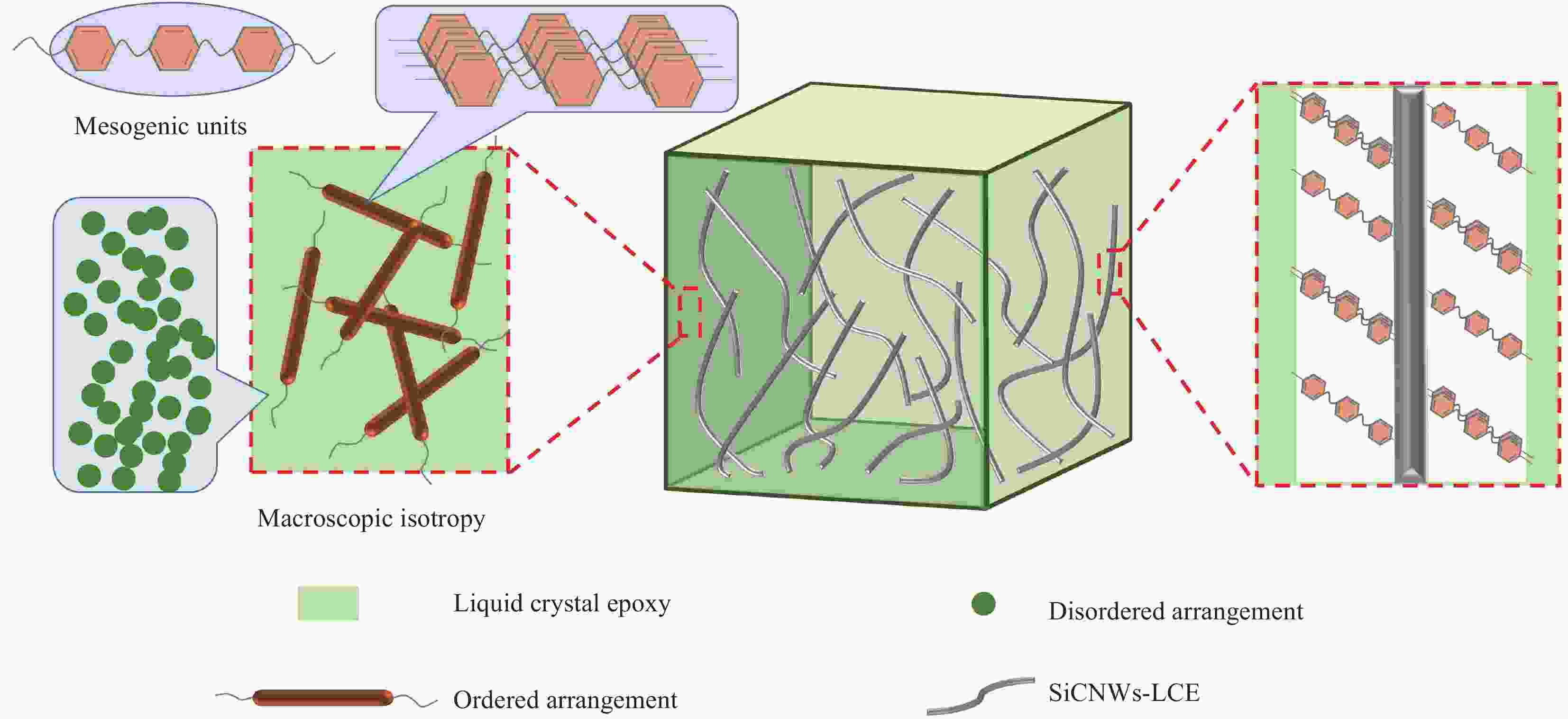
摘要: 高导热聚合物基复合材料在电子设备领域具有重要的应用价值。本论文基于“本征-填充”协同作用,以合成的本征型导热液晶环氧树脂为基体,以液晶环氧功能化改性碳化硅纳米线(SiCNWs-LCE)为高导热填料,采用液相共混法制得低填充且高导热SiCNWs-LCE/液晶环氧复合材料。分析了合成液晶环氧树脂的化学结构和结晶行为,以及功能化改性SiCNWs的微观形貌、化学结构和热稳定性等,深入研究了SiCNWs-LCE含量对SiCNWs-LCE/液晶环氧复合材料导热性能和热稳定性的影响规律。结果表明:采用硅烷偶联剂和液晶环氧功能化改性后的SiCNWs具有良好的分散性;“本征-填充”的协同作用使SiCNWs-LCE/液晶环氧复合材料具有良好的导热性能;复合材料的导热性能随着SiCNWs-LCE含量的增加而提高。与纯的液晶环氧树脂相比较,SiCNWs-LCE/液晶环氧复合材料热导率由0.33 W/(m·K)增加至0.72 W/(m·K),提升了118%。Abstract: Highly thermally-conductive polymer-based composites have important application value in the field of electronic equipment. Based on the “intrinsic-filled” synergistic effect, the liquid crystal epoxy functionalized SiC nanowires (SiCNWs-LCE)/liquid crystal epoxy composites with low filling amount and high thermal conductivity were prepared by the liquid phase blending method, using the synthesized intrinsic thermally-conductive liquid crystal epoxy as matrix and SiCNWs-LCE as highly thermally-conductive fillers. The chemical structures, crystallization behaviors of the liquid crystal epoxy and microstructures, chemical structures and thermal stability of the functionalized SiCNWs were analyzed. The influences of SiCNWs-LCE content on the thermal conductivity and thermal stability of the SiCNWs-LCE/liquid crystal epoxy composites were investigated in detail. The results show that the SiCNWs functionalized by silane coupling agent and liquid crystal epoxy have good dispersibility. The “intrinsic-filled” synergistic effect endows the SiCNWs-LCE/liquid crystal epoxy composite with excellent thermal conduc-tive properties. The thermal conductivity of SiCNWs-LCE/liquid crystal epoxy composites increases with the SiCNWs-LCE content. Compared with the pure liquid crystal epoxy resin, the SiCNWs-LCE/liquid crystal epoxy composites exhibit an increased thermal conductivity from 0.33 W/(m·K) to 0.72 W/(m·K) with an improvement of 118%.
-
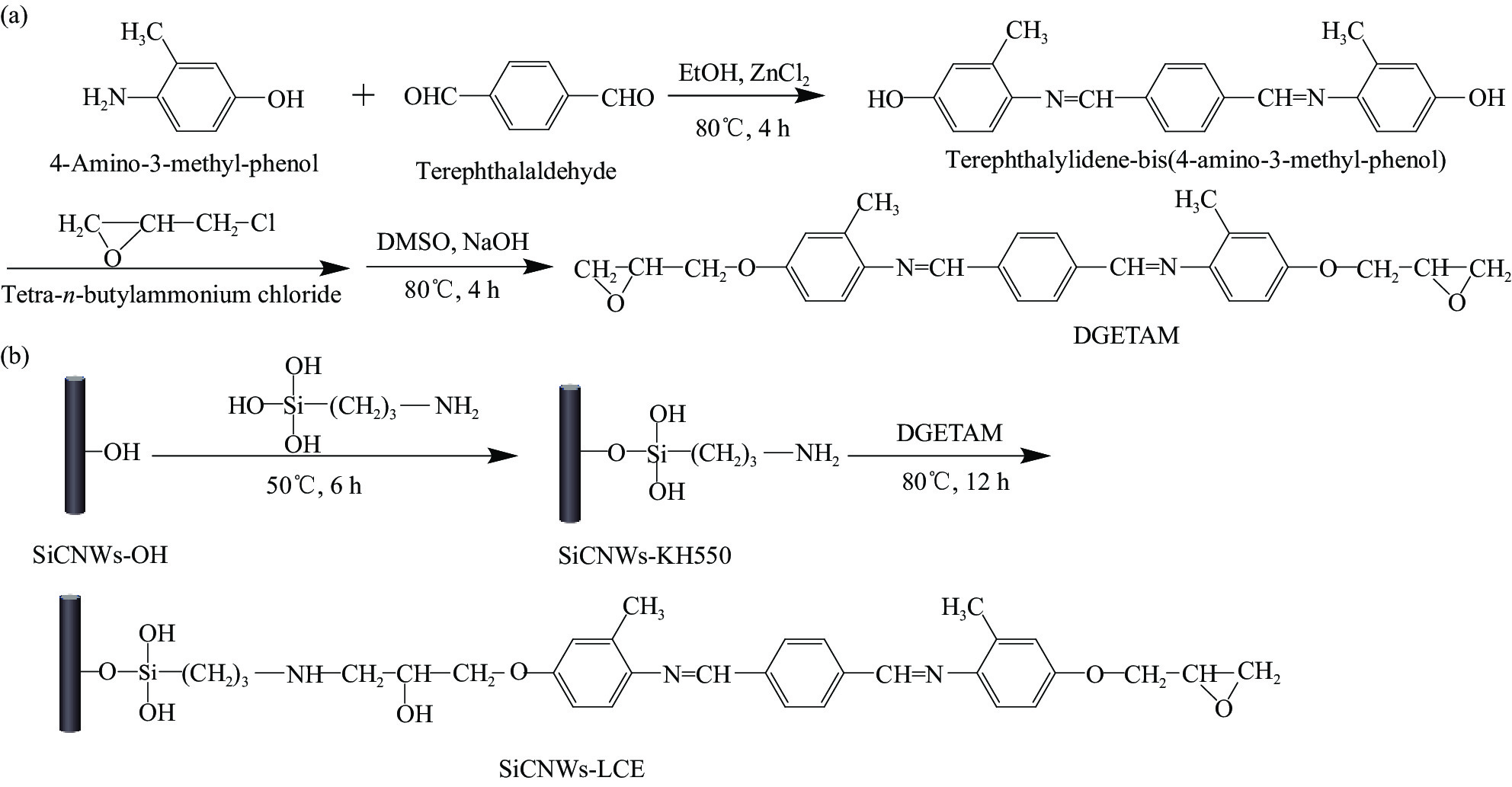
图 1 对苯二亚甲基-二-(4-氨基-3-甲基苯酚)缩水甘油醚(DGETAM) (a)和碳化硅纳米线-液晶环氧树脂(SiCNWs-LCE) (b)的合成机制
Figure 1. Synthetic mechanism of diglycidyl ether of terephthalylidene-bis(4-amino-3-methylphenol) (DGETAM) (a) and liquid crystal epoxy functionalized SiC nanowires (SiCNWs-LCE) (b)
DMSO—Dimethylsulfoxide; KH550—γ-Aminopropyl triethoxysilane; EtOH—Ethyl alcohol
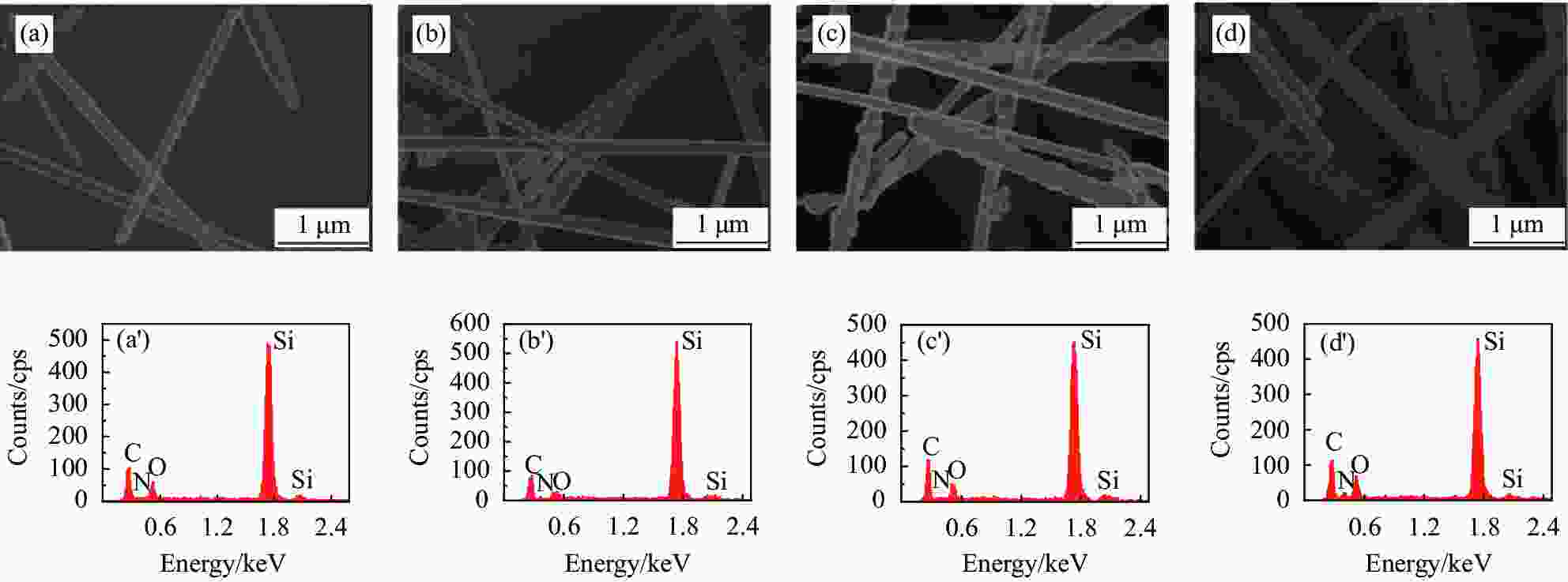
表 1 SiCNWs、SiCNWs-OH、SiCNWs-KH550和SiCNWs-LCE的元素含量
Table 1. Element contents of SiCNWs, SiCNWs-OH, SiCNWs-KH550 and SiCNWs-LCE
Nanomaterials C/at% N/at% O/at% Si/at% SiCNWs 13.01 0.07 1.11 85.81 SiCNWs-OH 29.78 0.18 4.18 65.86 SiCNWs-KH550 34.06 0.64 5.76 59.54 SiCNWs-LCE 34.28 1.04 8.07 57.69 -
[1] MIN P, LIU J, LI X, et al. Thermally conductive phase change composites featuring anisotropic graphene aerogels for real-time and fast-charging solar-thermal energy conversion[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28:1805365. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201805365 [2] 王文, 夏宇. 导热绝缘材料的研究与应用[J]. 绝缘材料, 2012, 45(1):19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9239.2012.01.006WANG W, XIA Y. Research on heat conductive insulating material and its application[J]. Insulating Materials,2012,45(1):19-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9239.2012.01.006 [3] HONG H J, KWAN S M, LEE D S, et al. Highly flexible and stretchable thermally conductive composite film by polyurethane supported 3D networks of boron nitride[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,152:94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.09.020 [4] SHAO L, SHI L, LI X, et al. Synergistic effect of BN and graphene nanosheets in 3D framework on the enhancement of thermal conductive properties of polymeric composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2016,135:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.09.013 [5] SONG J, CHEN C, ZHANG Y. High thermal conductivity and stretchability of layer-by-layer assembled silicone rubber/graphene nanosheets multilayered films[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,105:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.11.001 [6] BAI H, XUE C, LYU J L, et al. Thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of flake graphite/copper composite with a boron carbide-boron nano-layer on graphite surface[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,106:42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.11.019 [7] LIU P, LI X, MIN P, et al. 3D Lamellar-structured graphene aerogels for thermal interface composites with high through-plane thermal conductivity and fracture toughness[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2021,13(2):13-27. [8] 魏世洋, 郑智博, 余桥溪, 等. 具有rGO三维导热网络结构聚酰亚胺复合薄膜的制备及性能[J]. 高分子学报, 2019, 50(4):402-409. doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2018.18253WEI S Y, ZHENG Z B, YU Q X, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity of PI films by strengthening three-dimensional rGO network template[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica,2019,50(4):402-409(in Chinese). doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2018.18253 [9] 钟洨, 孟旭东, 张睿涵, 等. 改性纳米BN/甲基乙烯基硅橡胶导热复合材料的制备[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(11):2644-2650.ZHONG X, MENG X D, ZHANG R H, et al. Preparation of functionalized nano-BN/methyl vinyl silicone rubber thermal conductivity composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(11):2644-2650(in Chinese). [10] WU Y, YE K, LIU Z, et al. Cotton candy-templated fabrication of three-dimensional ceramic pathway within polymer composite for enhanced thermal conductivity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11:44700-44707. [11] YAN Q, DAI W, GAO J, et al. Ultrahigh-aspect-ratio boron nitride nanosheets leading to superhigh in-plane thermal conductivity of foldable heat spreader[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15:6489-6498. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09229 [12] 李果, 欧阳婷, 蒋朝, 等. 碳纤维-纳米石墨片网络体导热增强石蜡相变储能复合材料的制备及表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(5):1130-1137.LI G, OUYANG T, JIANG Z, et al. Preparation and characterization of paraffin phase change composites reinforced by carbon fiber-graphite nanoplatelets network[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(5):1130-1137(in Chinese). [13] GUO Y, RUAN K, GU J. Controllable thermal conductivity in composites by constructing thermal conduction networks[J]. Materials Today Physics,2021,20:100449. doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2021.100449 [14] LIN Y, HUANG X, CHEN J, et al. Epoxy thermoset resins with high pristine thermal conductivity[J]. High Voltage,2017,2:139-146. doi: 10.1049/hve.2017.0120 [15] 闫蓉, 张玲, 李春忠. 泡沫骨架构筑3D-BN/环氧树脂复合材料的制备和研究[J]. 高分子学报, 2019, 50(11):1202-1210. doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2019.19064YAN R, ZHANG L, LI C Z. Study on the construction of 3D-BN network in epoxy resin by introducing foam skeleton[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica,2019,50(11):1202-1210(in Chinese). doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2019.19064 [16] YANG X, ZHU J, YANG D, et al. High-efficiency improvement of thermal conductivities for epoxy composites from synthesized liquid crystal epoxy followed by doping BN fillers[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,185:107784. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107784 [17] DENG Y, LI J, NIAN H. Polyethylene glycol-enwrapped silicon carbide nanowires network/expanded vermiculite composite phase change materials: Form-stabilization, thermal energy storage behavior and thermal conductivity enhancement[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2018,174:283-291. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2017.09.013 [18] MERCAN K, NUMANOGLU H M, AKGÖZ B, et al. Higher-order continuum theories for buckling response of silicon carbide nanowires (SiCNWs) on elastic matrix[J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics,2017,87:1797-1814. doi: 10.1007/s00419-017-1288-z [19] WU R, ZHOU K, YUE C Y, et al. Recent progress in synthesis, properties and potential applications of SiC nanomaterials[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2015,72:1-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.01.003 [20] CHEN J, JIANG M, LIN W, et al. Scalable fabrication of novel SiC nanowire nonwoven fabric[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2017,53:3289-3295. [21] HAN Y, SHI X, WANG S, et al. Nest-like hetero-structured BNNS@SiCNWs fillers and significant improvement on thermal conductivities of epoxy composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2021,210:108666. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108666 [22] YAO Y, ZHU X, ZENG X, et al. Vertically aligned and interconnected SiC nanowire networks leading to significantly enhanced thermal conductivity of polymer composites[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10:9669-9678. [23] HARADA M, OCHI M, TOBITA M, et al. Thermomechanical properties of liquid-crystalline epoxy networks arranged by a magnetic field[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, Part B: Polymer Physics,2004,42:758-765. doi: 10.1002/polb.10740 [24] TAGUCHI T, TSUBAKIYAMA R, MIYAJIMA K, et al. Effect of surface treatment on photoluminescence of silicon carbide nanotubes[J]. Applied Surface Science,2017,403:308-313. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.176 [25] WILLIAMS E H, SCHREIFELS J A, RAO M V, et al. Selective streptavidin bioconjugation on silicon and silicon carbide nanowires for biosensor applications[J]. Journal of Materials Research,2012,28:68-77. -






 下载:
下载: