Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles/polyvinyl alcohol composite and its antibacterial activity against six aquatic pathogens
-
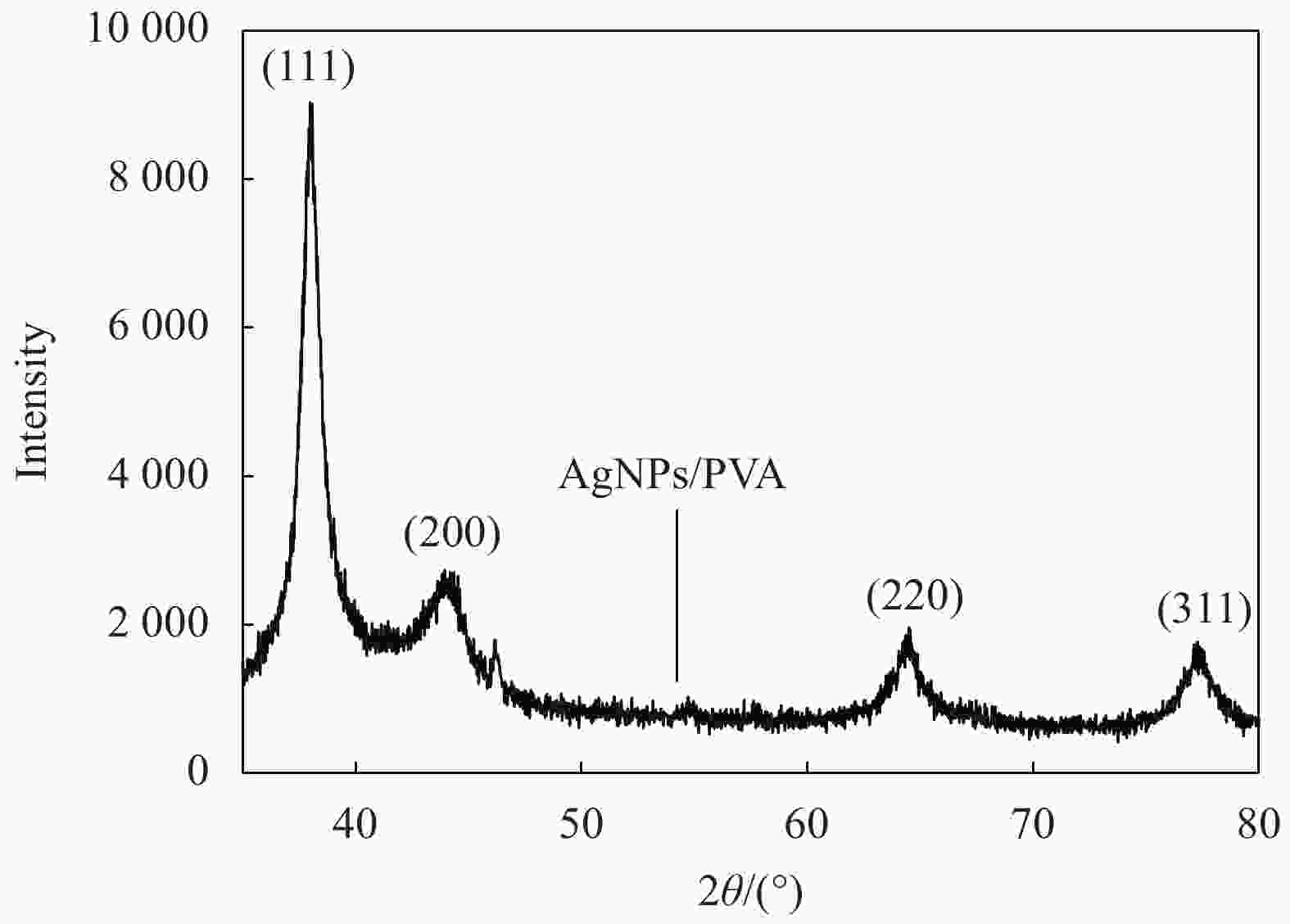
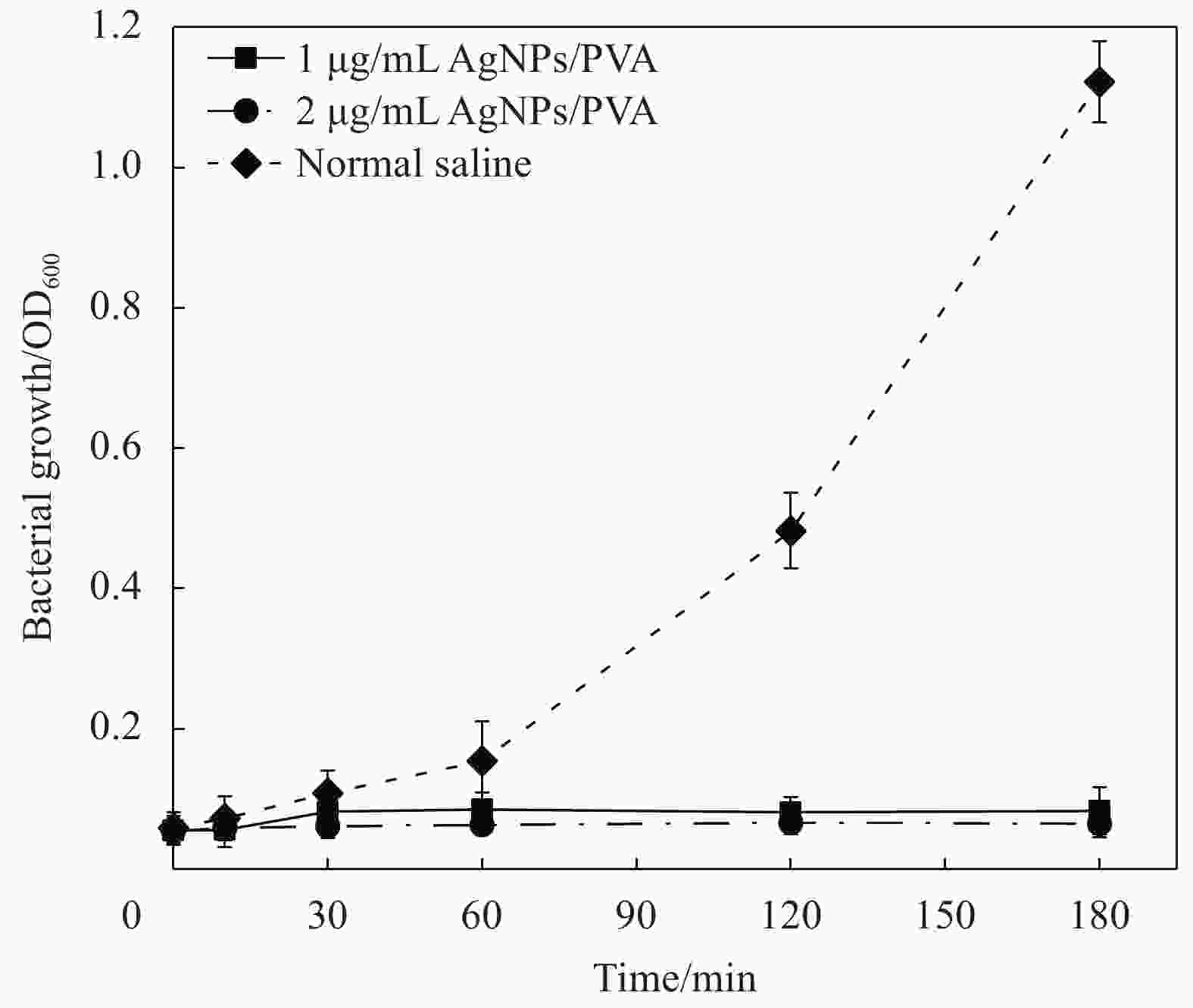
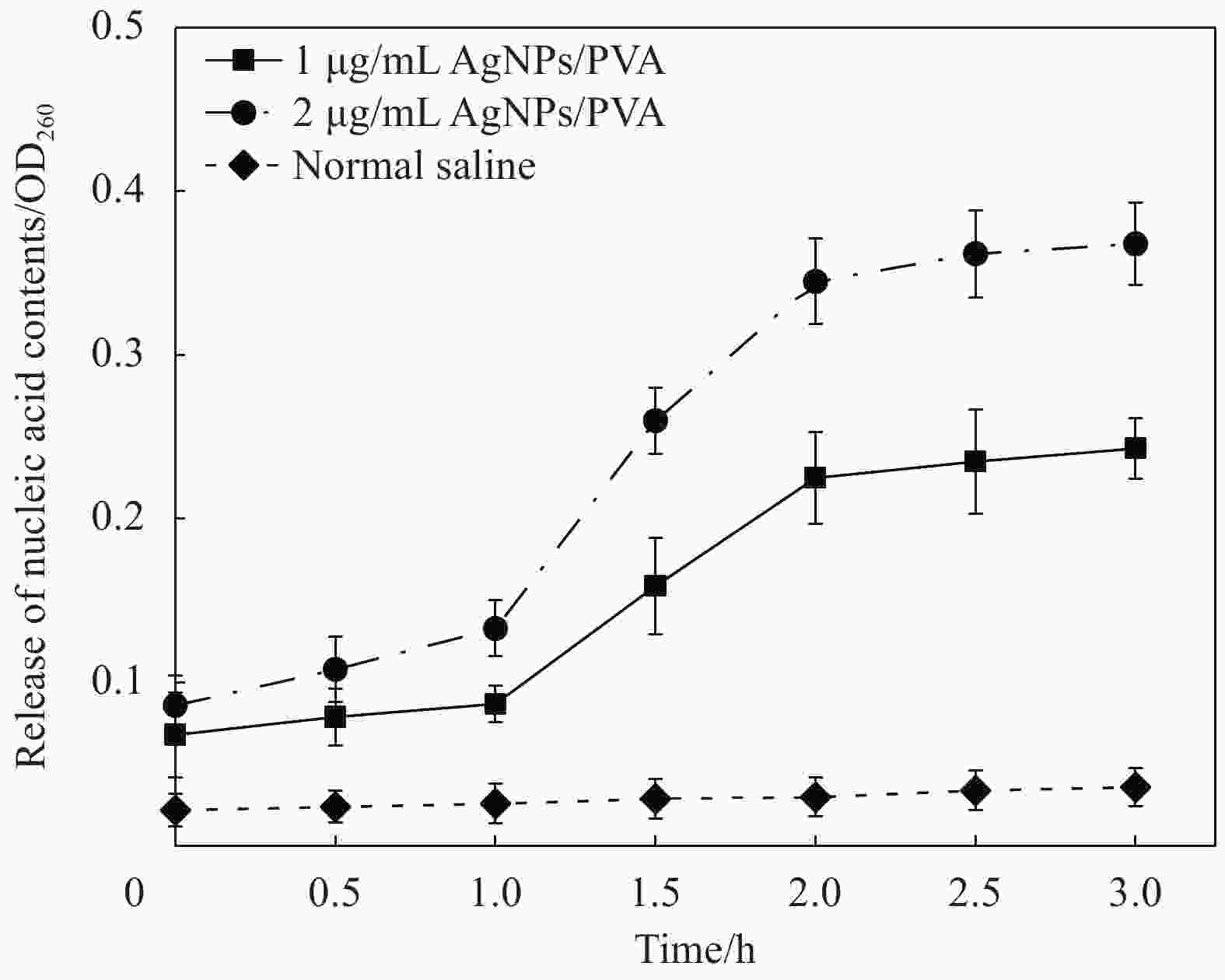
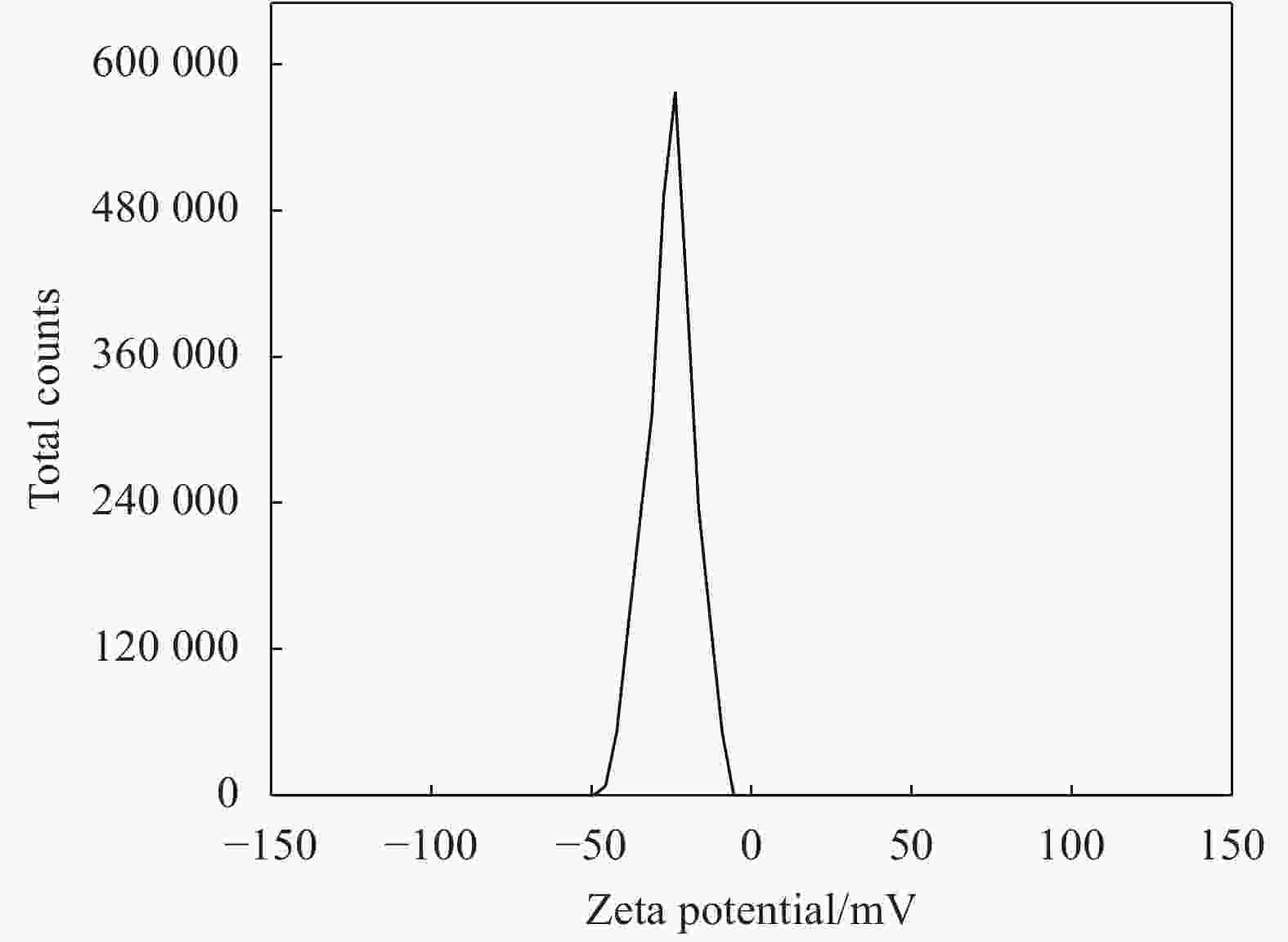
摘要: 纳米银作为一种新型抑菌剂有望成为传统抑菌剂的替代品,制备稳定、高效、环保的新型纳米银抑菌产品成为当今的研究热点。本研究以葡萄籽提取液为还原剂和稳定剂,聚乙烯醇(PVA)为载体,采用一步法“绿色”生物合成出一种纳米银/聚乙烯醇复合物(AgNPs/PVA)。通过紫外-可见(UV-Vis)吸收光谱、透射电镜(TEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)等手段对合成产物进行了表征。结果表明银离子被葡萄籽提取物成功还原成纳米银并附着在PVA的表面,纳米银颗粒均匀,呈现单分散状态,粒径较小,平均粒径为14 nm左右。AgNPs/PVA对鳗弧菌、溶藻弧菌、副溶血弧菌、哈维氏弧菌、灿烂弧菌及点状气单胞菌等6种典型的水产病原菌均有显著的抑菌效果。以溶藻弧菌为指示菌,AgNPs/PVA的最小抑菌浓度(MIC)为1.1 μg/mL,最小杀菌浓度(MBC)为2.2 μg/mL。AgNPs/PVA的Zeta电位为−24.1 mV,表明纳米银颗粒间有很强的排斥力,为其稳定分散提供保障,后续实验证明制备的AgNPs/PVA具有良好的稳定性和热稳定性。以上研究结果表明,AgNPs/PVA复合材料在水产养殖病害防治中具有广阔的应用前景。Abstract: As a new generation of antibacterial agent, silver nanoparticles are expected to be a substitute for traditional antibacterial agents in the future. Developing a new stable, efficient and eco-friendly nano-silver antibacterial agent has become the hot spot of current research. In this study, the grape seeds extract was used as an reducing and stabilizing agent, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was used as the carrier, the silver nanoparticles/polyvinyl alcohol (AgNPs/PVA) composites were prepared by a facile, green, “one-pot” biological method. The asprepared AgNPs/PVA composites were characterized by UV absorption spectroscopy (UV-Vis), transmission electron transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and X ray diffraction (XRD). The results indicate that the silver ions are successfully reduced by the grade seeds extract and the produced AgNPs are decorated on the surface of PVA. The AgNPs are uniform and monodisperse, the particle size is small with mean diameter about 14 nm. The AgNPs/PVA composites show superior antibacterial effects against six tipical aquatic pathogens, such as Vibrio splendidus, V. harveyi, V. anguillarum, V. alginolyticus, V. parahaemolyticus and Aeromonas punctata. They have a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 1.1 μg/mL and a minimum inhibitory concentration (MBC) of 2.2 μg/mL against V. alginolyticus. The Zeta potential of AgNPs/PVA is found to be −24.1 mV, indicating that the strong repulsion between the nanoparticles, which provide guarantee for stable dispersion. The subsequent experiments prove that the prepared AgNPs/PVA has good stability and thermostability. The above research results indicate that AgNPs/PVA composites have a great application prospect in the control of aquaculture diseases.
-
Key words:
- silver nanoparticles /
- grape seeds /
- polyvinyl alcohol /
- biosynthesis /
- antibacterial activity /
- stability
1) 共同作者:魏亚楠和马新冉为共同第一作者,对本文具有同等贡献 -
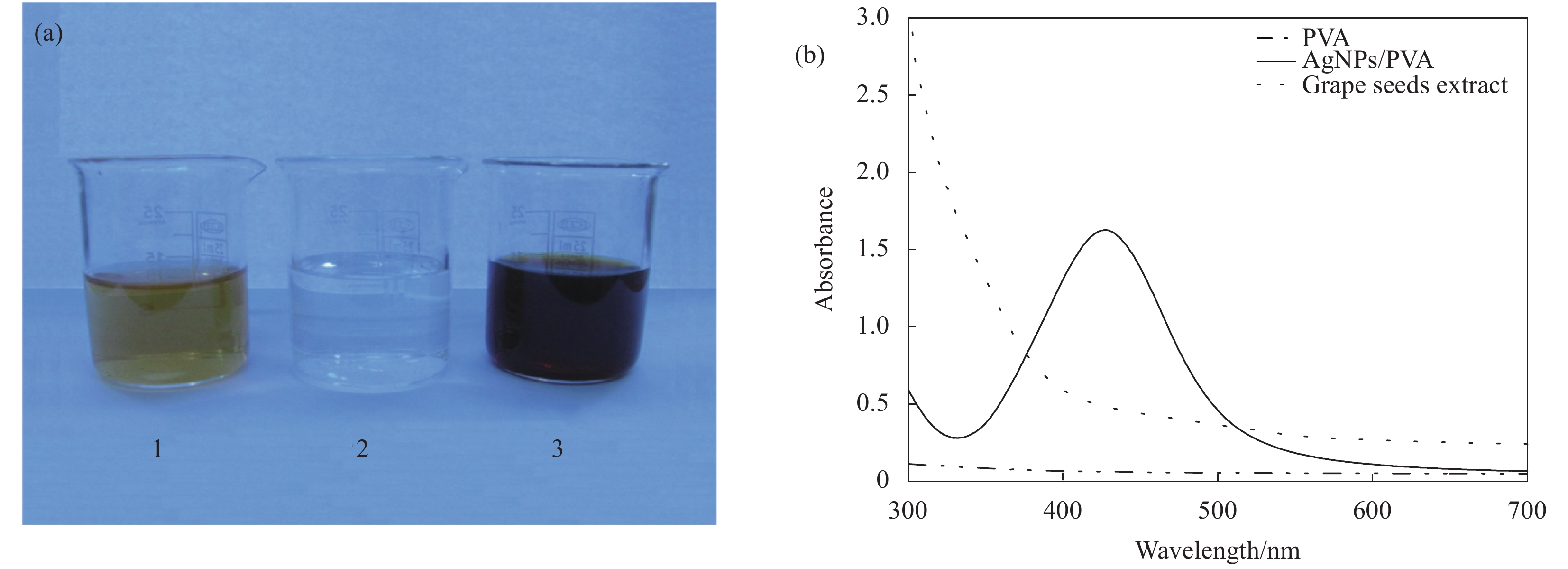
图 1 (a)葡萄籽提取液、聚乙烯醇(PVA)和纳米银/聚乙烯醇复合物 (AgNPs/PVA)的照片;(b)葡萄籽提取液、PVA和AgNPs/PVA的紫外吸收光谱
1—Grape seeds extract; 2—PVA; 3—AgNPs/PVA
Figure 1. (a) Photograph of aqueous suspension of grape seeds extract, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and silver nanoparticles/polyvinyl alcohol (AgNPs/PVA) composites;(b) UV-Vis absorption spectra of grape seeds extract, PVA and AgNPs/PVA
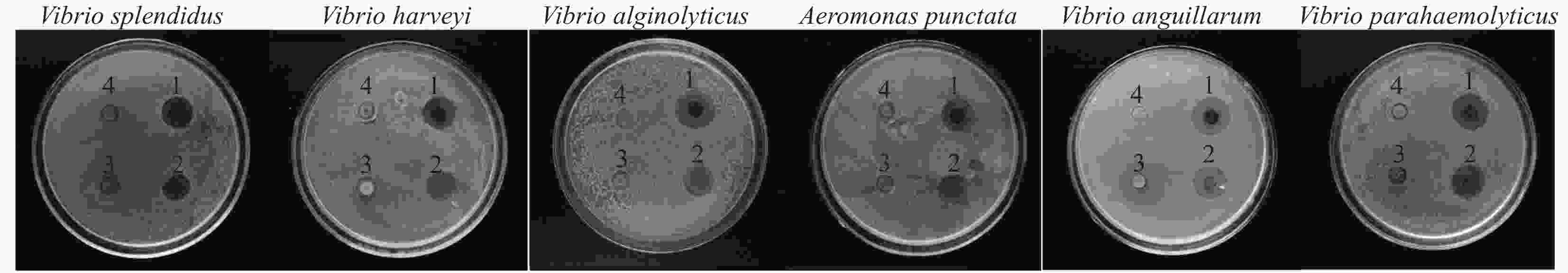
表 1 AgNPs/PVA对6种水产致病菌的抑菌圈直径的统计结果(n=3)
Table 1. Statistics of the inhibition zones of 6 aquatic pathogenic bacteria of AgNPs/PVA (n=3)
Aquatic pathogens Inhibition zone/mm AgNPs/PVA AgNPs Grape seeds extract Normal saline V.splendidus 17.7±0.3 15.9±0.7 0 0 V. harveyi 17.6±0.2 16.2±0.2 0 0 V. anguillarum 20.3±0.4 17.2±0.3 0 0 V. alginolyticus 21.5±0.6 16.0±0.2 0 0 V. parahaemolyticus 19.3±0.1 17.1±0.4 0 0 A. Punctata 17.4±0.4 16.4±0.4 0 0 表 2 AgNPs/PVA复合物对溶藻弧菌最小抑菌浓度和最小杀菌浓度的测定
Table 2. MIC and MBC tests of AgNPs/PVA composites against V. alginolyticus
Label Concentration of
AgNPs/PVA/(μg·mL−1)24 h 48 h 1 137.5 − − 2 68.8 − − 3 34.4 − − 4 17.2 − − 5 8.6 − − 6 4.3 − − 7 2.2 − − 8 1.1 − + 9 0.6 + + 10 0.3 + + Negative control − − Positive control + + 表 3 葡萄籽生物合成AgNPs单体对溶藻弧菌最小抑菌浓度和最小杀菌浓度的测定
Table 3. MIC and MBC tests of AgNPs against V. alginolyticus
Label Concentration of
AgNPs/(μg·mL−1)24 h 48 h 1 65.5 − − 2 32.8 − − 3 16.4 − − 4 8.2 − − 5 4.1 − − 6 2.0 − − 7 1.0 − + 8 0.5 + + 9 0.2 + + 10 0.1 + + Negative control − − Positive control + + -
[1] ZHU F. A review on the application of herbal medicines in the disease control of aquatic animals[J]. Aquaculture,2020,526:735422. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735422 [2] 胡梁及, 朱盛山, 彭亮, 等. 水产养殖中药物滥用的危害及问题分析[J]. 水产学杂志, 2015, 28(2):47-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2015.02.011HU Liangji, ZHU Shengshan, PENG Liang, et al. The harm and problem analysis of drug abuse in aquaculture[J]. Chinese Journal of Fisheries,2015,28(2):47-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3832.2015.02.011 [3] DANKOVICH T A, GRAY D G. Bactericidal paper impregnated with silver nanoparticles for point-of-use water treatment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2011,45(5):1992-1998. [4] WEI Y, WANG L R, ZHAO J, et al. Recyclable, non-leaching antimicrobial magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters,2019,30(12):2047-2050. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.06.010 [5] WANG A Z, LANGER R, FAROKHZAD O C. Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs[J]. Annual Review of Medicine,2012,63(1):185-198. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-040210-162544 [6] AYEKPAM B D, DINESH S M, NARAYAN C T, et al. Novel synthesis and characterization of CuO nanomaterials: Biological applications[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters,2014,25(12):1615-1619. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2014.07.014 [7] KHANNA P K, SINGH N, CHARAN S, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Ag/PVA nanocomposite by chemical reduction method[J]. Materials Chemistry & Physics,2005,93(1):117-121. [8] PANACEK A, KVITEK L, PRUCEK R, et a1. Silver colloid nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2006,110(33):16248-16253. doi: 10.1021/jp063826h [9] CHALOUPKA K, MALAM Y, SEIFALIAN A M. Nanosilver as a new generation of nanoproduct in biomedical applications[J]. Trends Biotechnol,2010,28(11):580-588. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2010.07.006 [10] 于嘉伦, 徐丹, 任丹, 等. 橘皮还原法和硼氢化钠还原法制备的纳米银的结构和性能比较[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(20):3489-3495. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.20.001YU Jialun, XU Dan, REN Dan, et al. Conparisons in the structures and properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized by amakusa peels and sodium borhydride[J]. Materials Reports,2018,32(20):3489-3495(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.20.001 [11] SHEKHAR A, SOUMYO M, SUPARNA M. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5-100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy[J]. RSC Advances,2014(4):3974-3983. [12] BEYENE H D, WERKNEH A A, BEZABH H K, et al. Synthesis paradigm and applications of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), a review[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies,2017(13):18-23. [13] RAVICHANDARAN V, VASANTHI S, SHALINI S, et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Atrocarpus altilis leaf extract and the study of their antimicrobial and antioxidant activity[J]. Materials Letters,2016,180:264-267. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2016.05.172 [14] SUN Q, CAI X, LI J W, et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using tea leaf extract and evaluation of their stability and antibacterial activity[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2014,444(4):226-231. [15] 罗应, 李彦青, 李永川, 等. 基于柠檬提取液的银纳米颗粒绿色制备工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技, 2018, 39(12):194-199.LUO Ying, LI Yanqing, LI Yongchuan, et al. Optimization of preparation technology for silver nanoparticles using lemon juice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(12):194-199(in Chinese). [16] 姜宇, 李福艳, 刘冲冲, 等. 山楂提取物生物合成纳米银对四种常见水产病原菌的抑制作用[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(1):253-260.JIANG Yu, LI Fuyan, LIU Chongchong, et al. Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using hawthorn fruit extract and their antibacterial activity against four common aquatic pathogens[J]. Ceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,2016,47(1):253-260(in Chinese). [17] 刘冲冲, 王磊, 徐慧, 等. 姜提取物生物合成纳米银抑菌活性的研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2017, 36(6):590-597. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2017.06.005LIU Chongchong, WANG Lei, XU Hui, et al. Antibacterial study of silver nanoparticles biosynthesized with ginger extract[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2017,36(6):590-597(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2017.06.005 [18] SUBRAMANIAN M, ALIKUNHI N M, KANDASAMY K. In vitro synthesis of silver nanoparticles by marine yeasts from coastal mangrove sediment[J]. Advanced Science Letters,2010,3(4):428-433. doi: 10.1166/asl.2010.1168 [19] BAGCHI D, BAGCHI M, STOHS S J, et al. Free radicals and grape seed proanthocyanidin extract: importance in human health and disease prevention[J]. Toxicology,2000,148(2-3):187-197. doi: 10.1016/S0300-483X(00)00210-9 [20] 司华艳, 毛晨憬, 谢雅萌, 等. PVP辅助制备单分散纳米银颗粒研究[J]. 石家庄学院学报, 2017, 19(3):5-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1972.2017.03.001SI Huayan, MAO Chenjing, XIE Yameng, et al. Preparation of monodisperse superfine silver powder[J]. Journal of Shijiazhuan University,2017,19(3):5-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1972.2017.03.001 [21] ZHANG T, SONG Y J, ZHANG X Y, et al. Synthesis of silver nanostructures by multistep method[J]. Sensors,2014,14(4):5860-5889. doi: 10.3390/s140405860 [22] LI K, MA C Y, JIAN T C, et al. Making good use of the byproducts of cultivation: green synthesis and antibacterial effects of silver nanoparticles using the leaf extract of blueberry. Journal of Food Science and Technology-MYSORE. 2017, 54(11): 3569-3576. [23] CHEN C Z, COOPER S L. Interactions between dendrimer biocides and bacterial membranes[J]. Biomaterials,2002,23(16):3359-3368. doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(02)00036-4 [24] 吴姗姗. 不同Zeta电位的水合TGD吸附Pb(Ⅱ)和Cd(Ⅱ)的行为和机理研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019.WU Shanshan. Behavior and mechanism of Pb(II) and Cd(II) adsorption by hydrous TGD with different Zeta potentials[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019 (in Chinese). [25] SADEGHI B, GHOLAMHOSEINPOOR F. A study on the stability and green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ziziphora tenuior (Zt) extract at room temperature[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2015,134(1):310-315. [26] DARROUDI M, AHMAD M B, MASHREGHI M. Gelatinous silver colloid nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization, and their antibacterial activity[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials,2014,16(1):182-187. [27] 殷海荣, 武丽华, 陈福. 机械力化学合成纳米晶体的研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2005, 33(9):36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2005.09.010YIN Hairong, WU Lihua, CHEN Fu. Study on mechanochemistry synthesis for nano-crystalline[J]. New Chemical Materials,2005,33(9):36-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2005.09.010 [28] SOTIRIOU G A, PRATSINIS S E. Antibacterial activity of nanosilver ions and particles[J]. Environmental Science & Technology. 2010, 44(14): 5649-5654. [29] 张曼莹, 刘姿铔, 邬艳君. 生物纳米银稳定性及抗菌性能研究[J]. 现代化工, 2018, 38(10):109-113.ZHANG Manying, LIU Ziya, WU Yanjun. Study on stability and antibacterial property of biogenic silver nanoparticles[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2018,38(10):109-113(in Chinese). [30] MOSTAFA M, RAMADAN H E, ElAMIR M A. Sorption and desorption studies of radioiodine onto silver chloride via batch equilibration with its aqueous media[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity,2015,150(12):9-19. [31] GAHLAWAT G, SHIKHA S, CHADDHA BS, et al. Microbial glycolipoprotein-capped silver nanoparticles as emerging antibacterial agents against cholera [J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2016, 15(1): 25. [32] FENG Q L, WU J, CHEN G Q, et al. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus[J] Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2000, 52(4): 662-668. [33] LI W R, XIR X B, SHI Q S, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2010,85(4):1115-1122. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2159-5 [34] SHEN S X, ZHANG T H, YUAN Y, et al. Effects of cinnamaldehyde on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureusmembrane[J]. Food Control,2015(47):196-202. [35] 徐光年, 金俊成. 一种绿色合成稳定单分散纳米银溶胶的新方法[J]. 化工新型材料, 2013, 41(10):39-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2013.10.013XU Guangnian, JIN Juncheng. A new method for green synthesis of stable monodisperse nano-silver sol[J]. New Chemical Materials,2013,41(10):39-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3536.2013.10.013 [36] 刘鹏威, 郭彤, 魏华. 纳米载铜蒙脱石体外对三种水产病原菌及两种肠道有益菌杀菌作用[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2009, 18(5):520-526.LIU Pengwei, GUO Tong, WEI Hua. Bacteriaidal effects of copper-bearing nano-montmorillonite on three aquatic pathogenic bacteria and two intestinal available bacteria in vitro[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University,2009,18(5):520-526(in Chinese). [37] ROMBAUT N, SAVOIRE R, THOMASSET B, et al. Grape seed oil extraction: Interest of supercritical fluid extraction and gas-assisted mechanical extraction for enhancing polyphenol co-extraction in oil[J]. Comptes rendus chimie,2014,17(3):284-292. doi: 10.1016/j.crci.2013.11.014 [38] XU H, WANG L, SU H Y, et al. Making good use of food wastes: green synthesis of highly stabilized silver nanoparticles from grape seed extract and their antimicrobial activity[J]. Food Biophysics. 2015, 10(1): 12-18. -






 下载:
下载: